目录
- 1.背景
- 2.算法原理
- 2.1算法思想
- 2.2算法过程
- 3.结果展示
- 4.参考文献
1.背景
2020年, Alsattar等人受到秃鹰猎食自然行为启发,提出了秃鹰搜索算法(Bald Eagle Search,BES)。
2.算法原理
2.1算法思想
BES主要分为三个阶段选择搜索空间、搜索空间猎物和俯冲捕获猎物。

2.2算法过程
选择搜索空间:
秃鹰个体在飞行中的位置代表 1个可行解,在选择搜索空间阶段,秃鹰会挑选猎物聚集数量最多的区域当做搜索空间,该阶段的秃鹰行为由如下方程描述:
P
i
,
n
e
w
(
t
)
=
P
b
e
s
t
(
t
)
+
α
×
r
×
(
P
m
e
a
n
(
t
)
−
P
i
(
t
)
)
(1)
P_{i,\mathrm{new}}(t)=P_{\mathrm{best}}(t)+\alpha\times r\times(P_{\mathrm{mean}}(t)-P_{i}(t))\tag{1}
Pi,new(t)=Pbest(t)+α×r×(Pmean(t)−Pi(t))(1)
其中,Pi,new(t)表示第 i 只秃鹰的更新位置;Pbest(t)表示秃鹰最佳搜索位置;Pmean(t)表示秃鹰之前搜索结束后所有秃鹰个体的平均分布位置,Pi(t)表示第 i只秃鹰的搜索位置,称作领导者;t是当前迭代次数,参数 α∈[1.5,2]是控制秃鹰搜索位置的参数,参数 α 设置为 2;r 是取值范围在 0~1之间的随机数。
搜索空间猎物:
秃鹰个体在完成选择目标搜索空间后,会在该搜索空间中对猎物进行“螺旋式”搜索,并向不同的方向飞行移动以加速搜索进程。该阶段的秃鹰行为如下方程描述:
P
i
,
n
e
w
(
t
)
=
P
i
(
t
)
+
x
(
i
)
×
(
P
i
(
t
)
−
P
m
e
a
n
(
t
)
)
+
y
(
i
)
×
(
P
i
(
t
)
−
P
i
+
1
(
t
)
)
x
(
i
)
=
x
r
(
i
)
max
(
∣
x
r
∣
)
,
y
(
i
)
=
y
r
(
i
)
max
(
∣
y
r
∣
)
x
r
(
i
)
=
r
(
i
)
×
sin
(
θ
(
i
)
)
,
y
r
(
i
)
=
r
(
i
)
×
cos
(
θ
(
i
)
)
θ
(
i
)
=
a
×
π
×
r
a
n
d
,
r
(
i
)
=
θ
(
i
)
+
R
×
r
a
n
d
(2)
\begin{aligned} &P_{i,\mathrm{new}}(t)=P_{i}(t)+x(i)\times(P_{i}(t)-P_{\mathrm{mean}}(t))+y(i)\times \left(P_{i}(t)-P_{i+1}(t)\right) \\ &x(i)=\frac{x_{r}(i)}{\operatorname*{max}(\left|x_{r}\right|)},y(i)=\frac{y_{r}(i)}{\operatorname*{max}(\left|y_{r}\right|)} \\ &x_{_r}(i)=r(i)\times\sin(\theta(i)),y_{_r}(i)=r(i)\times\cos(\theta(i)) \\ &\theta(i)=a\times\pi\times\mathrm{rand},r(i)=\theta(i)+R\times\mathrm{rand} \end{aligned} \tag{2}
Pi,new(t)=Pi(t)+x(i)×(Pi(t)−Pmean(t))+y(i)×(Pi(t)−Pi+1(t))x(i)=max(∣xr∣)xr(i),y(i)=max(∣yr∣)yr(i)xr(i)=r(i)×sin(θ(i)),yr(i)=r(i)×cos(θ(i))θ(i)=a×π×rand,r(i)=θ(i)+R×rand(2)
其中,x(i)与 y(i)表示极坐标中秃鹰的位置,取值范围均为(-1,1);θ(i)与 r(i)分别表示螺旋方程的极角与极径;a∈[5,10]与 R∈(0.5,2)表示控制秃鹰螺旋飞行轨迹的参数。
俯冲捕获猎物:
秃鹰在搜索空间锁定目标猎物后,从最佳位置快速飞行至目标猎物位置,与此同时所有的秃鹰个体也会朝着最佳位置飞行移动。该阶段的秃鹰行为由如下方程描述:
P
i
,
n
e
w
(
t
)
=
r
a
n
d
×
P
b
e
s
t
(
t
)
+
x
1
(
i
)
×
(
P
i
(
t
)
−
c
1
×
P
m
e
a
n
(
t
)
)
+
y
1
(
i
)
×
(
P
i
(
t
)
−
c
2
×
P
b
e
s
t
(
t
)
)
x
1
(
i
)
=
x
r
(
i
)
max
(
∣
x
r
∣
)
,
y
1
(
i
)
=
y
r
(
i
)
max
(
∣
y
r
∣
)
x
r
(
i
)
=
r
(
i
)
×
sinh
(
θ
(
i
)
)
,
y
r
(
i
)
=
r
(
i
)
×
cosh
(
θ
(
i
)
)
θ
(
i
)
=
a
×
π
×
r
a
n
d
,
r
(
i
)
=
θ
(
i
)
(3)
\begin{aligned} &&&P_{i,new}(t)=\mathrm{rand}\times P_{\mathrm{best}}(t)+x_{1}\left(i\right)\times\left(P_{i}(t)-c_{1}\times P_{\mathrm{mean}}(t)\right)+ y_{1}\left(i\right)\times\left(P_{i}(t)-c_{2}\times P_{\mathrm{best}}(t)\right) &&&& \\ &&&x_{1}\left(i\right)=\frac{x_{r}\left(i\right)}{\operatorname*{max}(\left|x_{r}\right|)},y_{1}\left(i\right)=\frac{y_{r}\left(i\right)}{\operatorname*{max}(\left|y_{r}\right|)}&& \\ &&&x_{r}(i)=r(i)\times\sinh\left(\theta(i)\right),y_{r}(i)=r(i)\times\cosh\left(\theta(i)\right)&& \\ &&&\theta(i)=a\times\pi\times\mathrm{rand},r(i)=\theta(i)&& \end{aligned}\tag{3}
Pi,new(t)=rand×Pbest(t)+x1(i)×(Pi(t)−c1×Pmean(t))+y1(i)×(Pi(t)−c2×Pbest(t))x1(i)=max(∣xr∣)xr(i),y1(i)=max(∣yr∣)yr(i)xr(i)=r(i)×sinh(θ(i)),yr(i)=r(i)×cosh(θ(i))θ(i)=a×π×rand,r(i)=θ(i)(3)
伪代码:

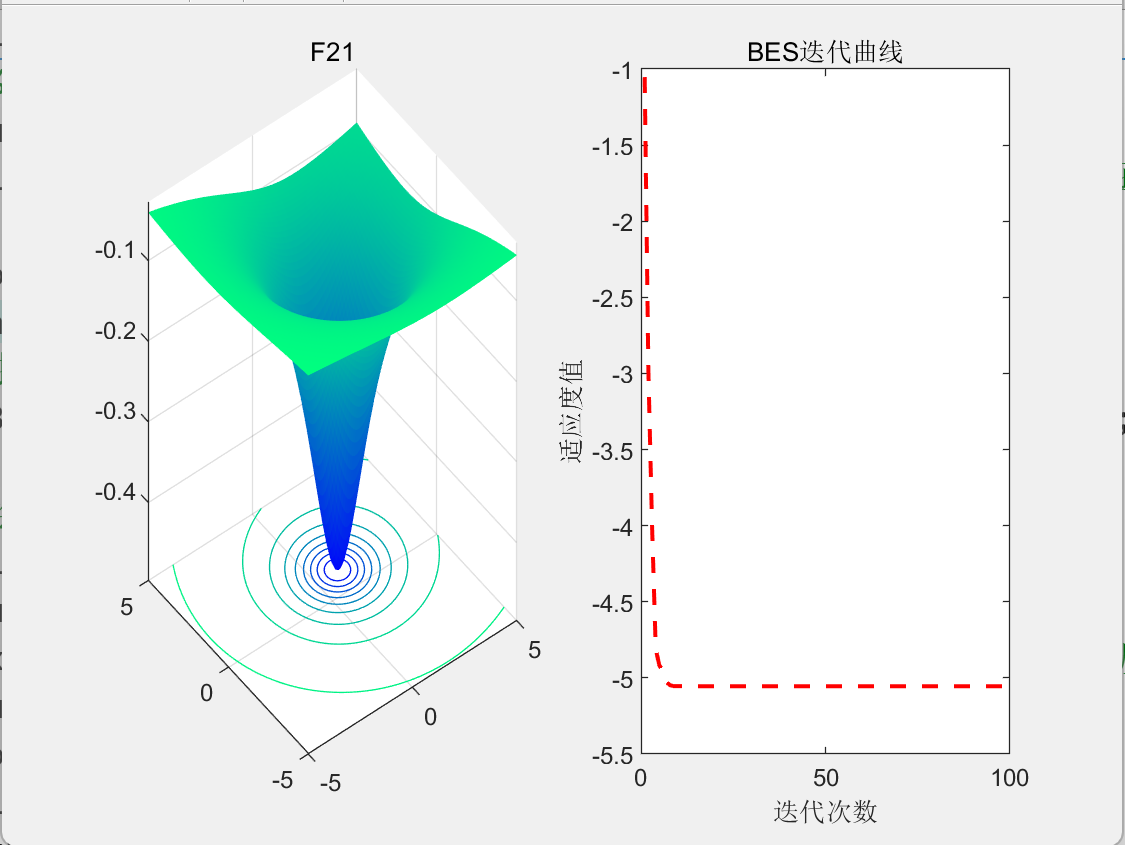
3.结果展示
4.参考文献
[1] Alsattar H A, Zaidan A A, Zaidan B B. Novel meta-heuristic bald eagle search optimisation algorithm[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2020, 53: 2237-2264.