文章目录
- 1.基本介绍
- 2.正则底层实现
- 1.matcher.find()完成的任务
- 2.matcher.group(0)分析
- 1.源代码
- 2.解释(不分组)
- 3.解释(分组)
- 3.总结
- 3.正则表达式语法
- 1.基本介绍
- 2.元字符的转义符号
- 1.基本介绍
- 2.代码实例
- 3.字符匹配符
- 1.基本介绍
- 2.字符匹配案例一
- 3.字符匹配案例二
- 4.选择匹配符
- 1.基本介绍
- 2.代码实例
- 5.正则限定符
- 1.基本介绍
- 2.代码实例
- 6.正则定位符
- 1.基本介绍
- 2.代码实例
- 7.捕获分组
- 1.基本介绍
- 2.代码实例
- 8.非捕获分组
- 1.基本介绍
- 2.代码实例
- 9.非贪婪匹配
- 代码实例
- 4.正则应用实例
- 1.题目
- 代码
- 2.验证复杂URL
- 3.注意事项
- 5.正则表达式三个常用类
- 1.Pattern类
- 整体匹配
- 代码实例
- 2.Matcher类
- 代码实例
- 6.反向引用
- 1.基本介绍
- 2.反向引用案例
- 案例一
- 代码实例
- 案例二——结巴去重
- 代码实例
- 7.String类型使用正则表达式替换
- 题目一(replaceAll)
- 题目二(matches)
- 题目三(split)
- 按照#、-、~或者数字来分割
- 8.本章练习
- 练习一
- 练习二
- 练习三
- 9.正则表达式大全
1.基本介绍

2.正则底层实现
1.matcher.find()完成的任务
- 根据特定的规则,找到满足要求的字符串
- 找到后将索引放到mather对象的属性int[] groups;
- 字符串的第一个字符的索引放到groups[0],最后一个字符的索引加一放到groups[1]
2.matcher.group(0)分析
1.源代码
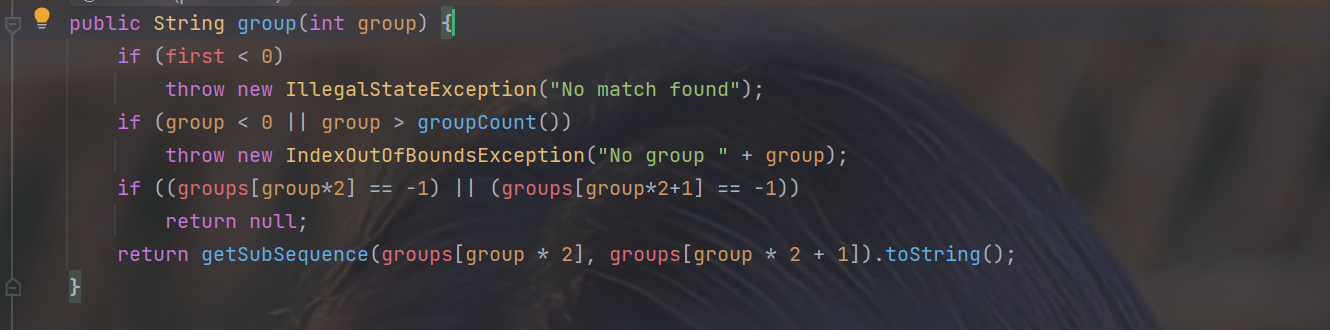
2.解释(不分组)
- 前面的都是做的验证,直接看最后一句话
- 传进的参数是0,所以返回的是
groups[0 * 2]到groups[0 * 2 + 1]也就是截取索引为groups[0]和groups[1]的内容并转换成String类型 - 总结一下,group[0]就是返回截取到的整个字符串
3.解释(分组)
String regStr = "(\\d\\d)(\\d\\d)";- 上面的这种情况就是分组的情况
- 此时groups数组记录的情况看下图
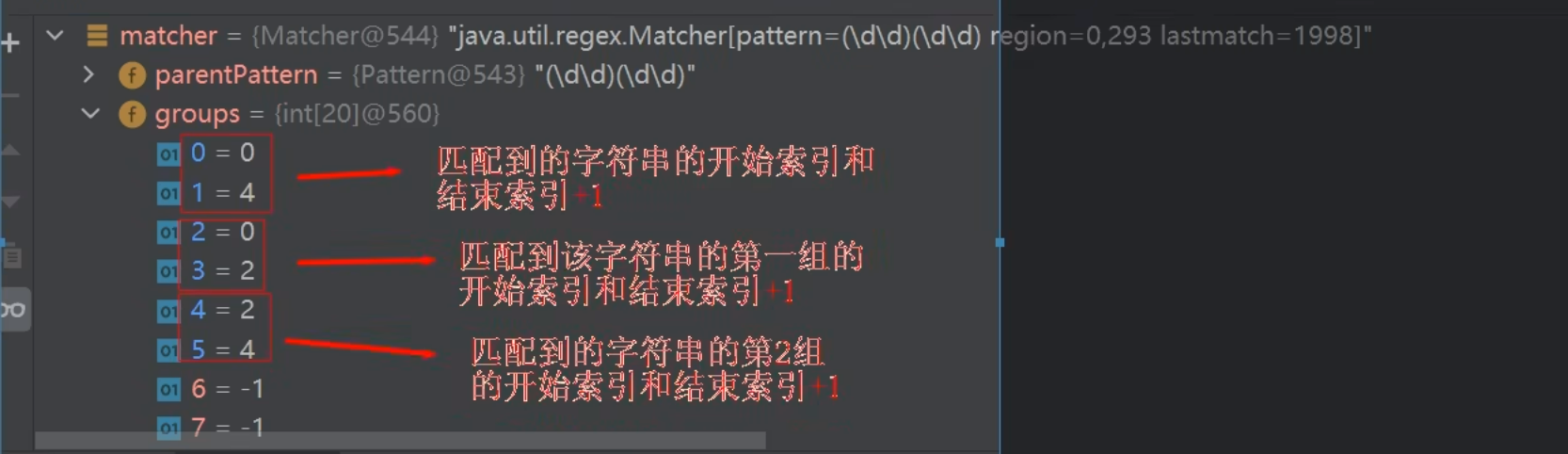
- 总结一下,在分组的情况下,group[x]对应groups[y]的下标
- x = 0 : y = 0, 1
- x = 1 : y = 2, 3
- x = 2 : y = 4, 5
- 以此类推
3.总结
- matcher.find()就是查找匹配到的字符串
- group(0)就是返回整个查找到的字符串,group(1)、(2)…就是返回第一组、第二组…匹配的字符串
3.正则表达式语法
1.基本介绍

2.元字符的转义符号
1.基本介绍

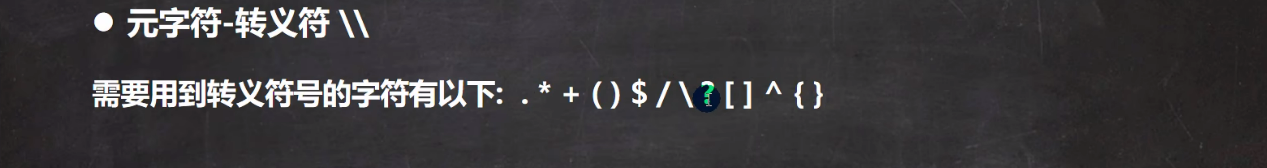
2.代码实例
package regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RegExp02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//内容
String content = "abc$(abc(123(";
//要匹配的样式
String regStr = "\\("; //转义符\\
//1.传入匹配的样式,创建模式对象
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr);
//2.传入要匹配的内容,创建匹配器对象
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content);
//3.开始匹配
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("匹配到:" + matcher.group(0));
}
}
}
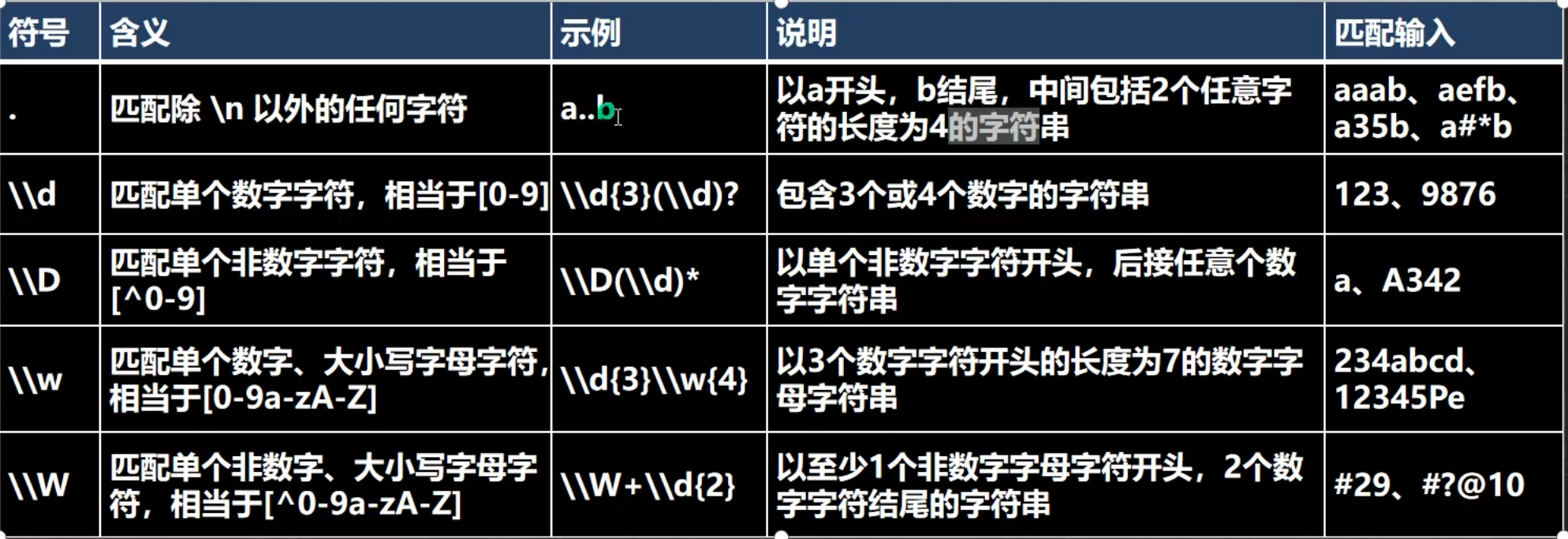
3.字符匹配符
1.基本介绍
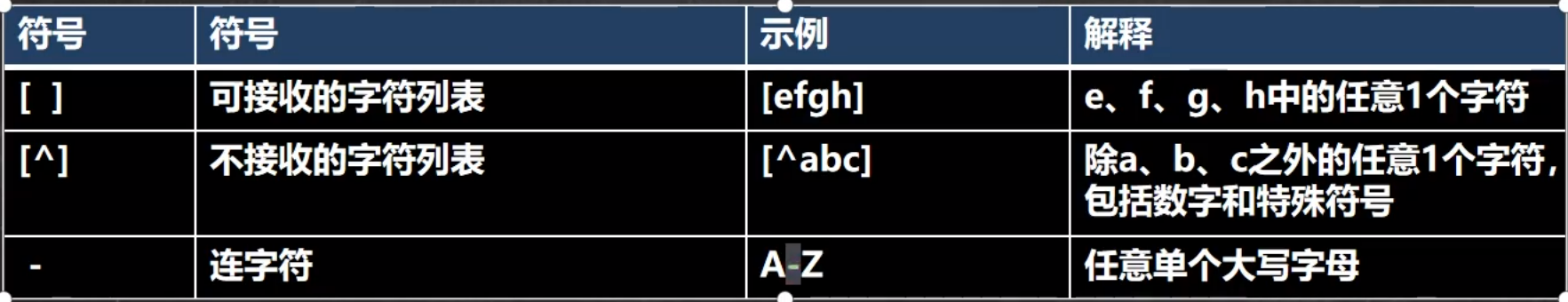
2.字符匹配案例一


package regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RegExp03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "a11c8aBC";
// String regStr = "[a-z]"; //a到z
// String regStr = "[A-Z]"; //A到Z
// String regStr = "(?i)abc"; //匹配abc字符串不区分大小写
// String regStr = "a((?i)bc)"; //匹配bc不区分大小写
// String regStr = "abc";
String regStr = "[^a-z]{2}"; //匹配非a到z的两个字符
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr); //模式对象
// Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr, Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE); //匹配时不区分大小写
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("找到:" + matcher.group(0));
}
}
}
3.字符匹配案例二

package regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RegExp04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "asdg";
String regStr = "[abcd]"; //abcd任意一个字符
String regStr1 = "[^abcd]"; //除了abcd
String regStr2 = "[\\d]"; //任意数字
String regStr3 = "[\\D]"; //任意非数字
String regStr4 = "[\\w]"; //任意数字字母,下划线
String regStr5 = "[\\W]"; //非数字字母,下划线
String regStr6 = "[\\s]"; //匹配任意空白字符,空格制表符等
String regStr7 = "[\\S]"; //匹配任意非空白字符
String regStr8 = "[.]"; //匹配除了\n以外的任何字符,如果要匹配.则需要加\\
//模式对象
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr);
//匹配对象
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content);
//开始匹配
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("匹配到:" + matcher.group(0));
}
}
}
4.选择匹配符
1.基本介绍

2.代码实例
package regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RegExp05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "hanshunping 韩顺平";
String regStr = "han|韩"; //匹配到han或韩
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("匹配到:" + matcher.group(0));
}
}
}
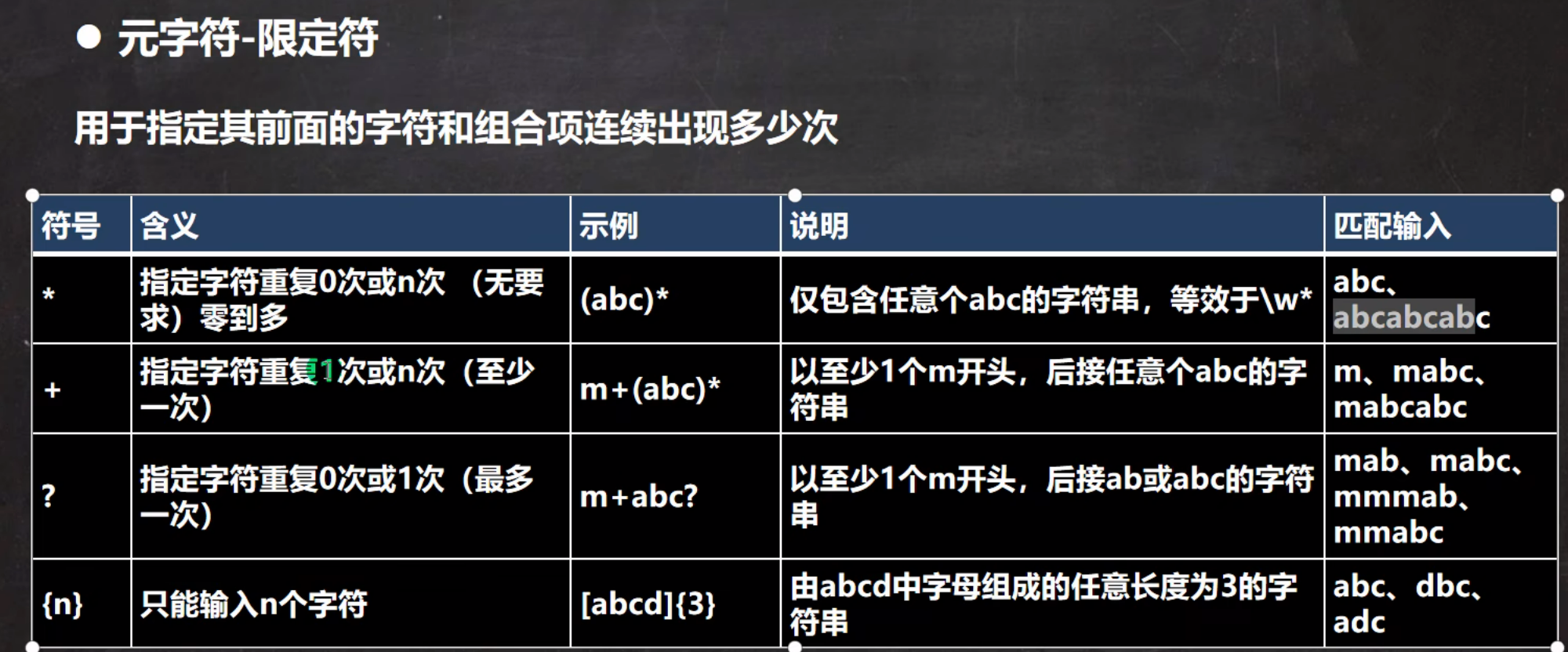
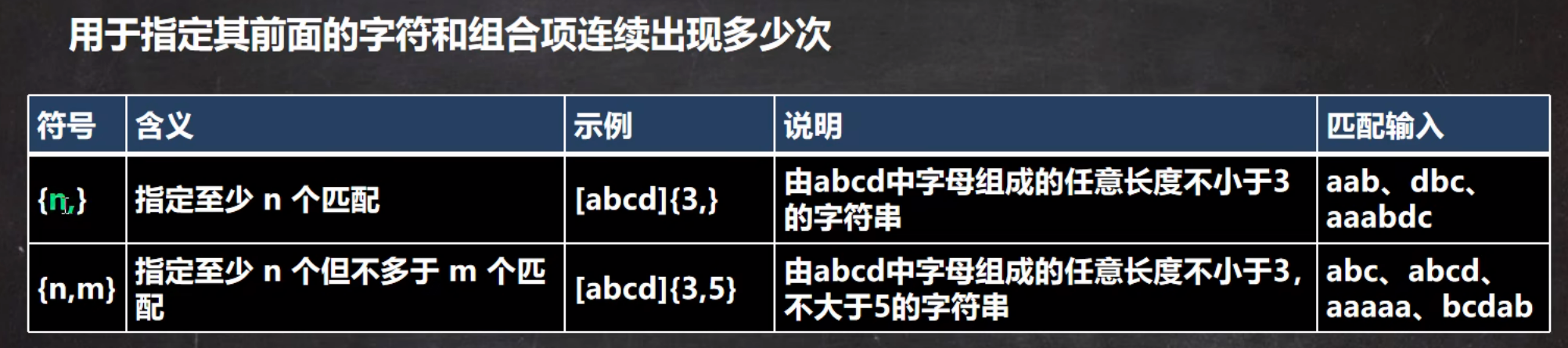
5.正则限定符
1.基本介绍
2.代码实例
package regexp;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RegExp06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "aaaaaaa11111";
String regStr = "a{3}"; //匹配三个a
String regStr1 = "1{4}"; //匹配四个1
String regStr2 = "(\\d){2}"; //匹配两个数字
String regStr3 = "a{3, 4}"; //匹配三到四个a
//java默认贪婪匹配,默认匹配多的
String regStr4 = "1{4, 5}"; //匹配四到五个1
String regStr5 = "\\d{2, 5}"; //匹配二到五个数字
String regStr6 = "1+"; //匹配一个或多个1
String regStr7 = "a*"; //匹配任意个a
String regStr8 = "1?"; //匹配0个或一个1
}
}
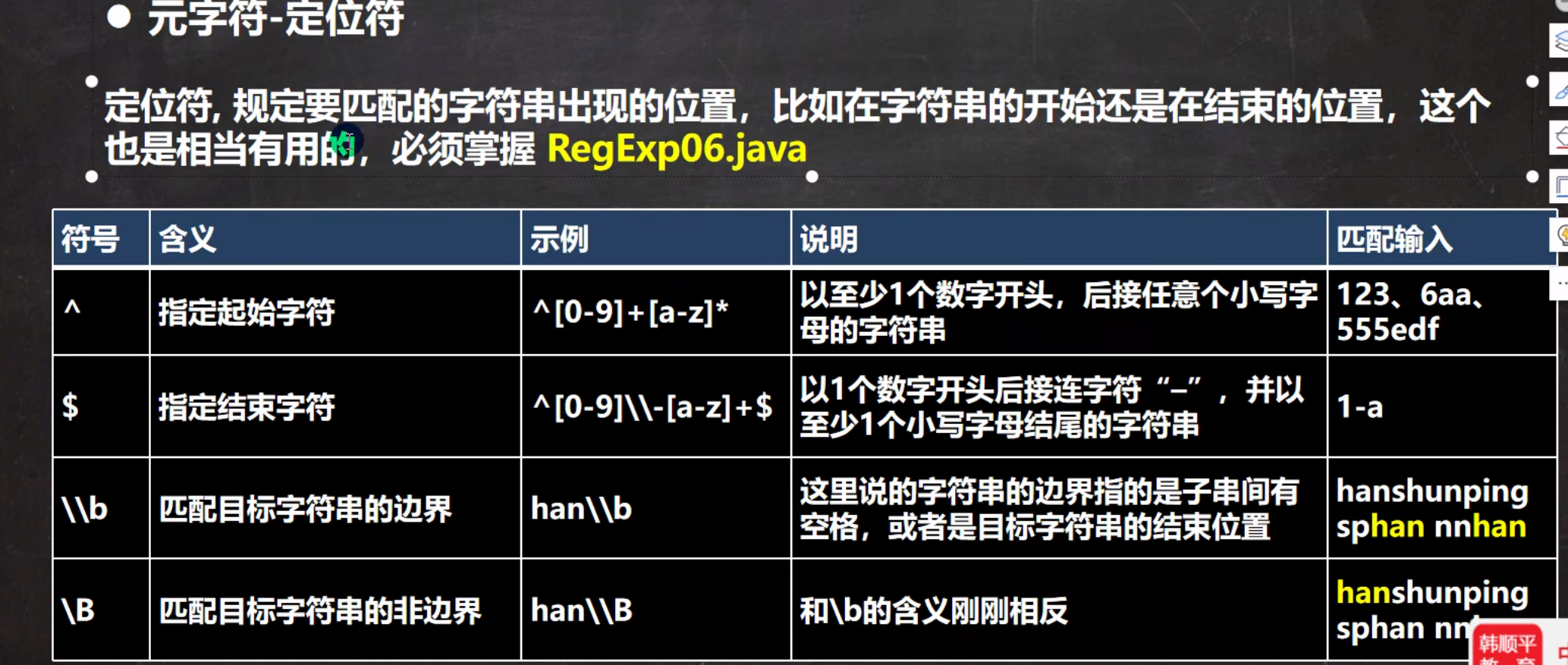
6.正则定位符
1.基本介绍
2.代码实例
package regexp;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RegExp07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "^[0-9]+[a-z]*"; //至少一个数字开头,任意个小写字母结尾
String str2 = "^[0-9]\\-[a-z]+$"; //以一个数字开头后接一个“-”以至少一个小写字母结尾
String str3 = "han\\b"; //匹配han的后边界,即han后面没东西,或者是空格
String str5 = "han\\B"; //匹配han的前边界,即han前面没东西,或者是空格
}
}
7.捕获分组
1.基本介绍
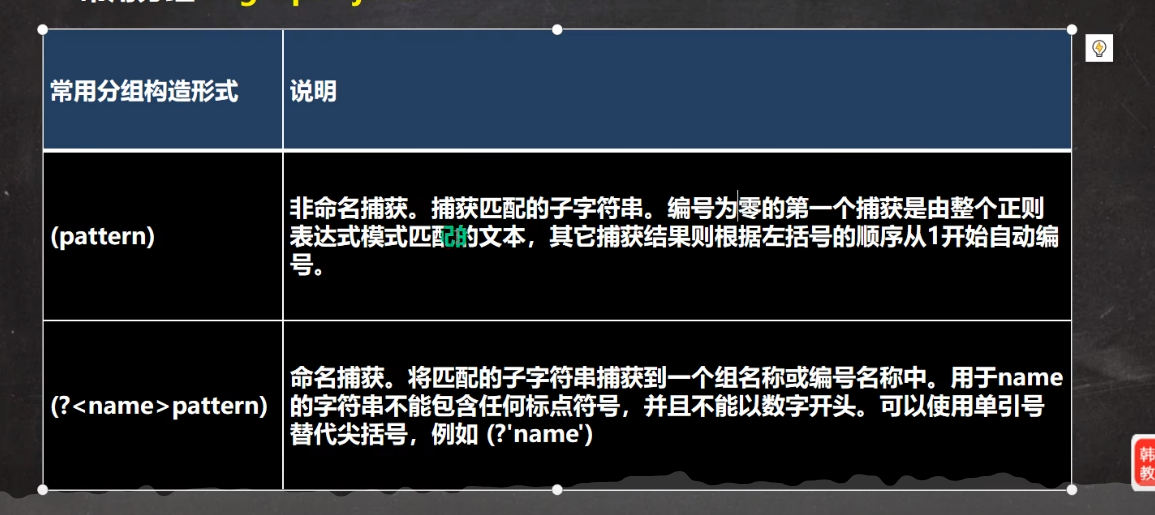
2.代码实例
package regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RegExp08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "hanshunping s7789 nn1189han";
String regStr = "(\\d\\d)(\\d\\d)"; //非命名分组
String regStr1 = "(?<g1>\\d\\d)(?<g2>\\d\\d)"; //非命名分组
//模式对象
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr1);
//匹配对象
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
// System.out.println(matcher.group(1)); //分组一
// System.out.println(matcher.group(2)); //分组二
//命名分组,可以使用编号或者名字
System.out.println(matcher.group("g1")); //分组一
System.out.println(matcher.group("g2")); //分组二
}
}
}
8.非捕获分组
1.基本介绍
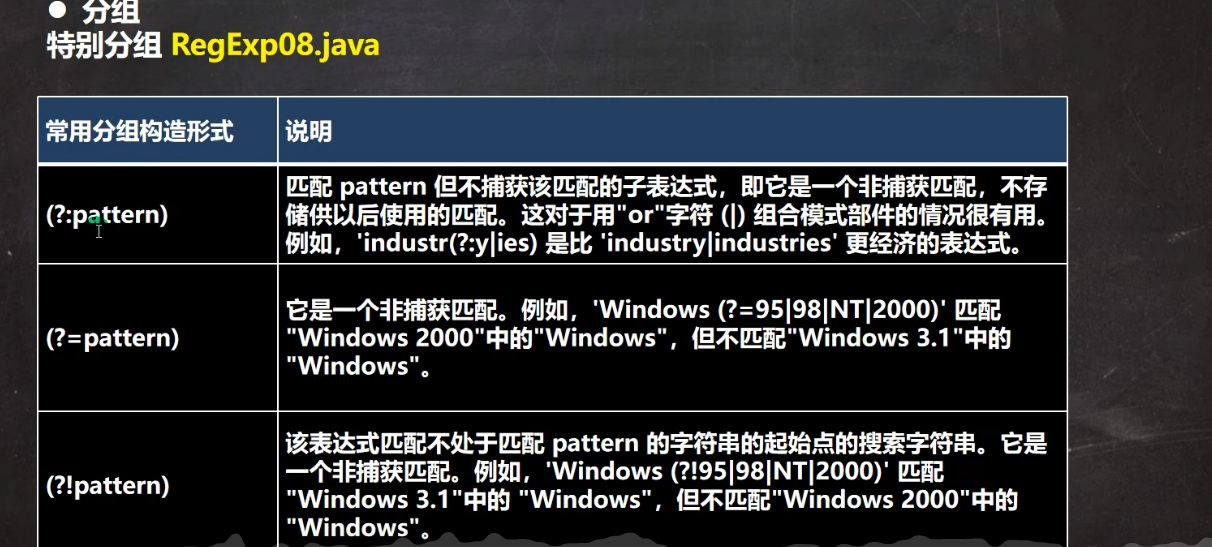
2.代码实例
package regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
* 非捕获分组
*/
public class RegExp09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "hello韩顺平教育 jack韩顺平老师 韩顺平同学hello";
// String regStr = "韩顺平(?:教育|老师|同学)"; //匹配韩顺平教育韩顺平老师韩顺平同学
// String regStr = "韩顺平(?=教育|老师|同学)"; //匹配韩顺平后面有教育|老师|同学的韩顺平,也就是三个
String regStr = "韩顺平(?!教育|老师)"; //匹配韩顺平后面没有教育|老师的韩顺平,也就是只有一个
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println(matcher.group(0));
}
}
}
9.非贪婪匹配
代码实例
package regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RegExp10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "hello111111";
String regStr ="\\d+?";//在限定符后面加?表示非贪婪匹配,这里每次就匹配一个1
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println(matcher.group(0));
}
}
}
4.正则应用实例
1.题目

代码
package regexp;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RegExercise {
//汉字
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content1 = "史蒂夫";
String regStr1 = "^[\u3091-\uffe5]+$"; //匹配至少一个汉字,并规定了开头结尾为空
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr1);
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content1);
if (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("匹配成功");
}
else {
System.out.println("匹配失败");
}
}
//邮政编码 1-9开头的一个六位数
@Test
public void find1() {
String content1 = "123458";
String regStr1 = "^[1-9]\\d{5}$"; //匹配1-9开头的一个六位数
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr1);
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content1);
if (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("匹配成功");
}
else {
System.out.println("匹配失败");
}
}
//qq号码 1-9开头的一个(5位到10位数)
@Test
public void find2() {
String content1 = "1721469477";
String regStr1 = "^[1-9]\\d{4,9}$"; //匹配1-9开头的一个六位数
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr1);
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content1);
if (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("匹配成功");
}
else {
System.out.println("匹配失败");
}
}
//手机号码 13,14,15,18开头的11位数
@Test
public void find3() {
String content1 = "13604959178";
String regStr1 = "^1(?:3|4|5|8)\\d{9}$"; //匹配1-9开头的一个六位数
String regStr2 = "^1(3|4|5|8)\\d{9}$"; //匹配1-9开头的一个六位数
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr2);
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content1);
if (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("匹配成功");
}
else {
System.out.println("匹配失败");
}
}
}
2.验证复杂URL
package regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RegUrl {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// String content = "https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fh411y7R8?p=894&vd_source=6ca8808c5ff14bd32a1acd1b4774a821";
String content = "https://www.bilibili.com";
String regStr = "^((http|https)://)([\\w-]+\\.)+[\\w-]+(\\/[\\w-?=&%.#]*)?$";
//注意:在[.]指的是真的.
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content);
if (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("匹配成功");
}
else {
System.out.println("匹配失败");
}
}
}
3.注意事项
在使用常规方法验证的时候一定要加定位符^和$
5.正则表达式三个常用类
1.Pattern类
整体匹配
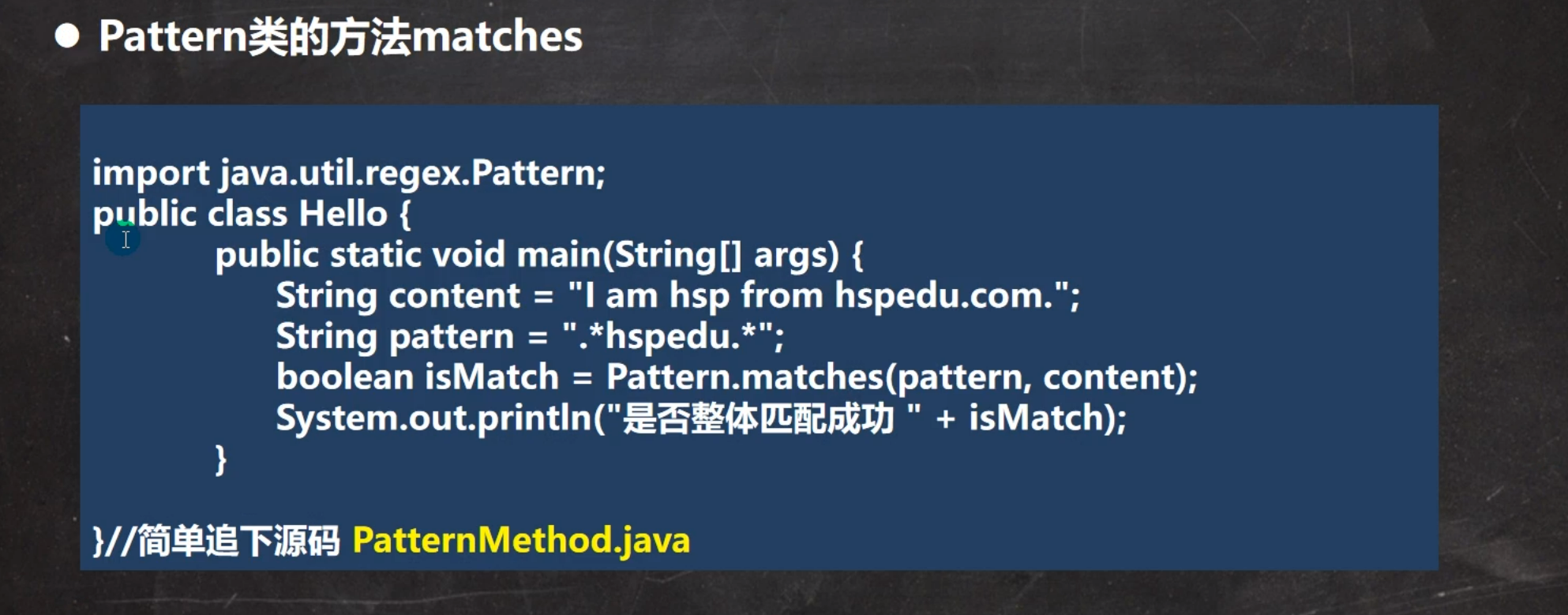
代码实例
package regexp;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RegExp11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//整体匹配,不需要添加定位符,直接匹配整体
String content = "我是孙先生12321";
String pattern = ".{5}\\d{5}";
boolean matches = Pattern.matches(pattern, content);
System.out.println(matches);
}
}
2.Matcher类
代码实例
package regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RegExp12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "hello edu jack hello tom hspedu hspedu";
String regStr = "hspedu";
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("==================");
//分别返回每次匹配到的起始索引和结束索引加一
System.out.println(matcher.start());
System.out.println(matcher.end());
}
//整体匹配方法
System.out.println(matcher.matches());
//把所有的hspedu替换成韩顺平教育,不是真的替换,因为String是不可变类型的,只能返回另一个String类型的对象
String s = matcher.replaceAll("韩顺平教育");
System.out.println(s);
}
}
6.反向引用
1.基本介绍

2.反向引用案例
案例一

代码实例
package regexp;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RegExp13 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "1221 jack 5225 jack33 yyy xxx";
String regStr = "(\\d)(\\d)\\2\\1"; //每次匹配过后数字都会被记录下来,在后面就可以引用
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println(matcher.group(0));
}
}
//整体匹配检索编号 12321-333999111这样的号码
@Test
public void find1() {
String content = "12321-333999111";
String regStr = "\\d{5}-(\\d)\\1{2}(\\d)\\2{2}(\\d)\\3{2}";
//获取模式对象
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr);
//获取匹配器
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content);
//整体匹配
System.out.println(matcher.matches());
}
}
案例二——结巴去重

代码实例
package regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RegExp14 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "我...我我要....学学学学。。。编程java";
String regStr = "(.)\\1+"; //匹配所有重复的字符
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr); //获取模式
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(content); //获取匹配器
//在外部反向引用使用$,去重
String s = matcher.replaceAll("$1");
System.out.println(s);
}
}
7.String类型使用正则表达式替换
题目一(replaceAll)
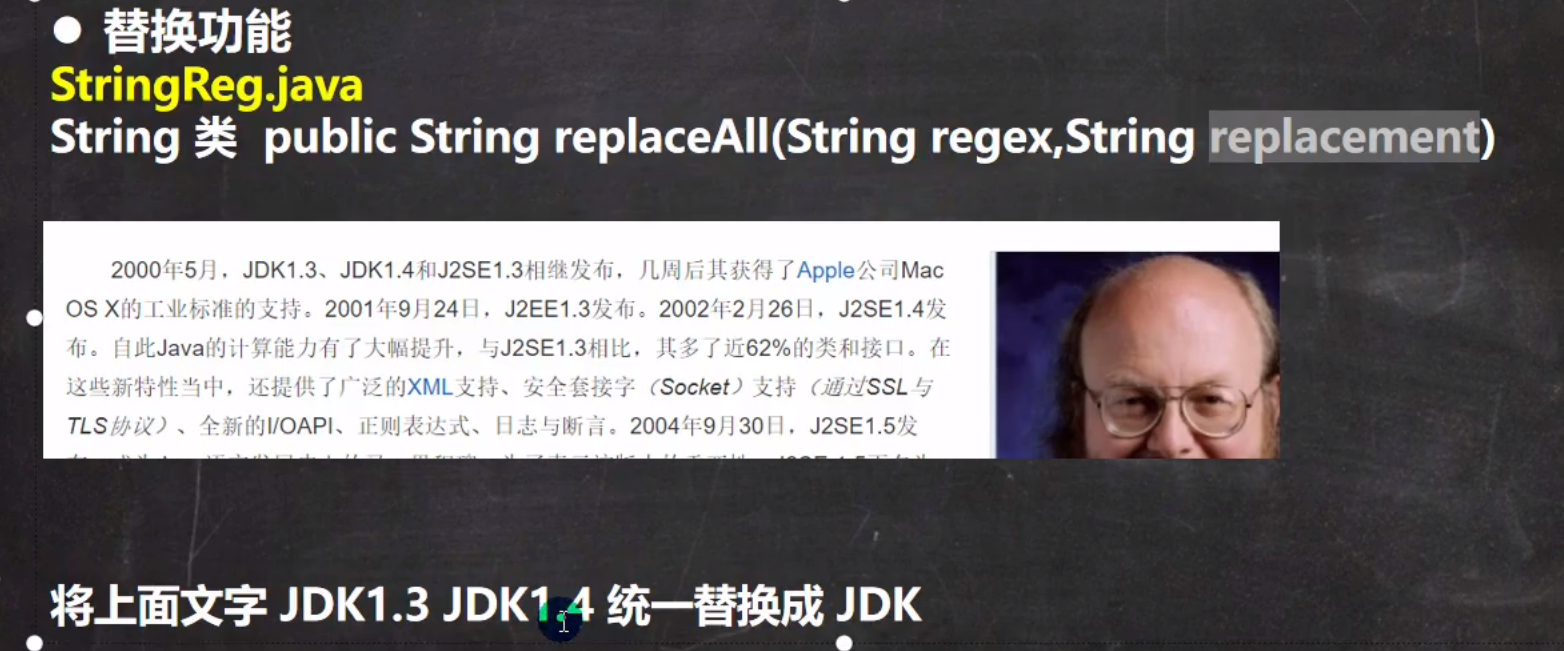
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "2000年5月,JDK1.3、JDK1.4和J2SE1.3相继发布,几周后其获得了Apple公司Mac OS X的工业标准的支持。2001年9月24日,J2EE1.3发布。2002年2月26日,J2SE1.4发布。自此Java的计算能力有了大幅提升,与J2SE1.3相比,其多了近62%的类和接口。在这些新特性当中,还提供了广泛的XML支持、安全套接字(Socket)支持(通过SSL与TLS协议)、全新的I/OAPI、正则表达式、日志与断言。2004年9月30日,J2SE1.5发布,成为Java语言发展史上的又一里程碑。为了表示该版本的重要性,J2SE 1.5更名为Java SE 5.0(内部版本号1.5.0),代号为“Tiger”,Tiger包含了从1996年发布1.0版本以来的最重大的更新,其中包括泛型支持、基本类型的自动装箱、改进的循环、枚举类型、格式化I/O及可变参数。";
//使用正则表达式将jdk1.3和1.4替换成jdk
String s = content.replaceAll("JDK1\\.3|JDK1\\.4", "JDK");
System.out.println(s);
}
题目二(matches)
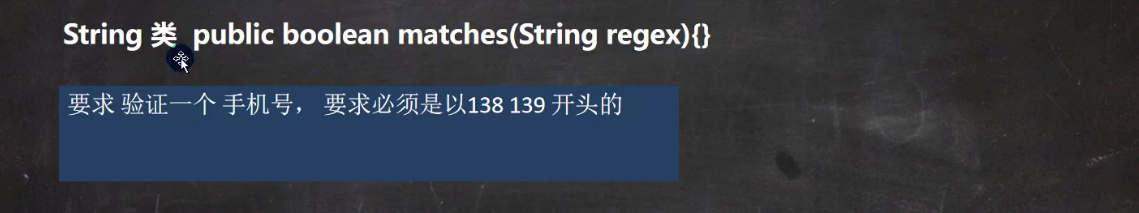
public static void main(String[] args) {
//验证这个手机号是否是138,139开头的
String content = "13888889999";
boolean matches = content.matches("^(138|139)\\d{8}");
System.out.println(matches);
}
题目三(split)
按照#、-、~或者数字来分割
package regexp;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Regexp15 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "hello#abc-jack12smith~北京";
//按照指定符号分割
String[] split = content.split("[#\\-~]");
for (String s : split) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
8.本章练习
练习一

package regexp;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class HomeWork01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "1-721469477@qq.com";
String regStr = "[\\w-]+@([a-zA-Z]+\\.)+[a-zA-Z]+";
//整体匹配
boolean matches = Pattern.matches(regStr, content);
System.out.println(matches);
}
}
练习二

package regexp;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class HomeWork02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content1 = "1223";
String content2 = "-1223";
String content3 = "12.23";
String content4 = "+1223";
String content5 = "0.89";
//匹配整数或小数
String regStr = "[-+]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?";
boolean matches = content5.matches(regStr);
System.out.println(matches);
}
}
练习三

package regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author 孙显圣
* @version 1.0
*/
public class HomeWorrk03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "http://www.sohu.com:8080/abc/dfs/df/index.htm";
//分组解析
String regStr = "^([a-zA-Z]+)://([a-zA-Z.]+):(\\d+)[/\\w-]*/([a-zA-Z.]+)$";
Pattern compile = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = compile.matcher(url);
if (matcher.matches()) {
System.out.println("协议:" + matcher.group(1));
System.out.println("域名:" + matcher.group(2));
System.out.println("端口:" + matcher.group(3));
System.out.println("文件:" + matcher.group(4));
}
else {
System.out.println("匹配失败");
}
}
}
9.正则表达式大全
java正则表达式大全(参考).zip










![[AutoSar]BSW_Com020 Handle_ID,Global_PDU,Local_PDU的联系](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/c04895863f1249cabf1ab04dcf48d825.png)