图论练习题目
- 拓扑排序
- 深度优先搜索方法
- 广度优先搜索方法
- 无向无权图
- 无向有权图
- 有向无权图 利用广度优先搜索算法
- 有向有权图 带排序的广度优先算法/dijkstra
- 最小生成树
- prims算法
- Kruskal's Algorithm
- 最小割 min-cut
- 二分图 Bipartite Graph 队列
- 例题1 所有可能的路径
- 例题2 岛屿数量
- 例题3 岛屿最大面积
- 例题4 飞地的数量
- 例题5 被围绕的区域
- 例题6 太平洋大西洋水流问题
- 例题7 钥匙和房间
- 例题8 寻找图中是否存在路径
- 例题9 冗余连接
- 例题10 课程表 拓扑排序
- 例题11 单词接龙
- 例题12 最小高度树
- 例题13 省份数量
dfs采用的是栈,bfs采用的是队列。
sorted(L.items(),key=lambda x:(x[0],x[1],x[2],x[3]))
拓扑排序
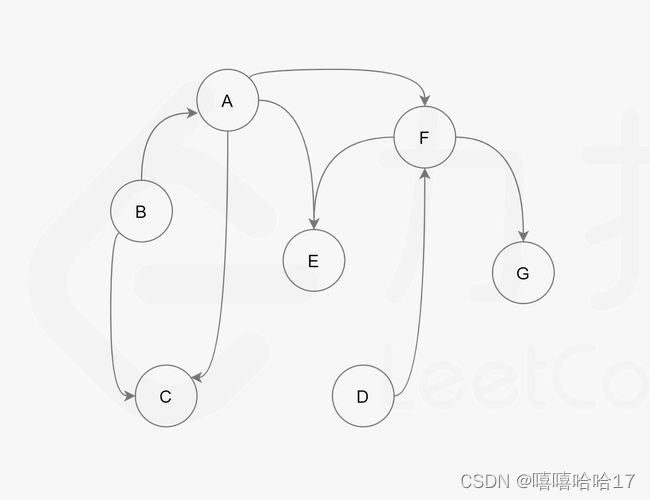
深度优先搜索方法
import collections
graph = {
'A':['F','E','C'],
'B':['A','C'],
'C':[],
'D':['F'],
'E':[],
'F':['E','G'],
'G':['F']
}
n=len(graph)
visted={key:0 for key in graph.keys()}
ans=[]
def dfs(u):
if visted[u]==2:
return
visted[u]=1
for v in graph[u]:
if visted[v]==0:
dfs(v)
visted[u]=2
ans.append(u)
for key in graph.keys():
dfs(key)
print(ans)
# ['E', 'G', 'F', 'C', 'A', 'B', 'D']
广度优先搜索方法
import collections
graph = {
'A':['F','E','C'],
'B':['A','C'],
'C':[],
'D':['F'],
'E':[],
'F':['E','G'],
'G':['F']
}
n=len(graph)
visted={key:0 for key in graph.keys()}
queue=[]
ans=[]
def bfs(u):
if visted[u]:return
queue.append(u)
visted[u]=1
while queue:
node=queue.pop(0)
ans.append(node)
for v in graph[node]:
if visted[v]==0:
visted[v]=1
queue.append(v)
for key in graph.keys():
bfs(key)
# bfs('A')
# print(ans,visted)
# bfs('B')
# print(ans,visted)
# ['E', 'G', 'F', 'C', 'A', 'B', 'D']
print(ans)
# ['A', 'F', 'E', 'C', 'G', 'B', 'D']
无向无权图
graph={
1:[2,5],
2:[1,3,4],
3:[2],
4:[2],
5:[1,6],
6:[5,7],
7:[6]
}
n=len(graph)+1
# visted=[0]*n
visted=[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,0]
def dfs(u):
ans=1
visted[u]=1
for v in graph[u]:
if visted[v]==0:
vh=dfs(v)
# print(u,v,vh)
ans=max(ans,vh+1)
return ans
dfs(2) #5
无向有权图
有向无权图 利用广度优先搜索算法
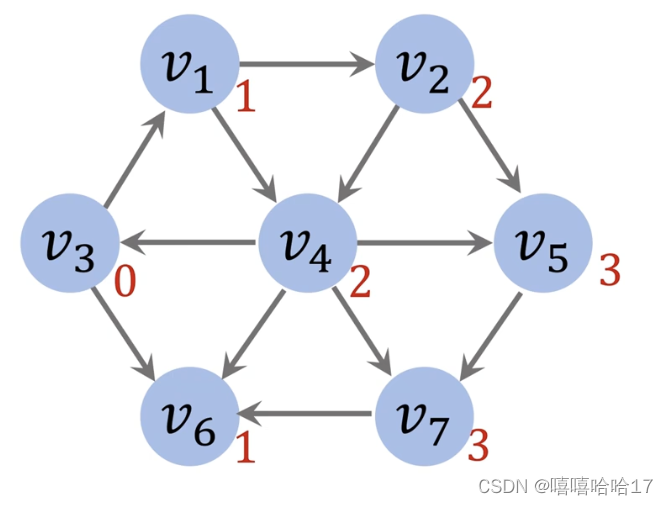
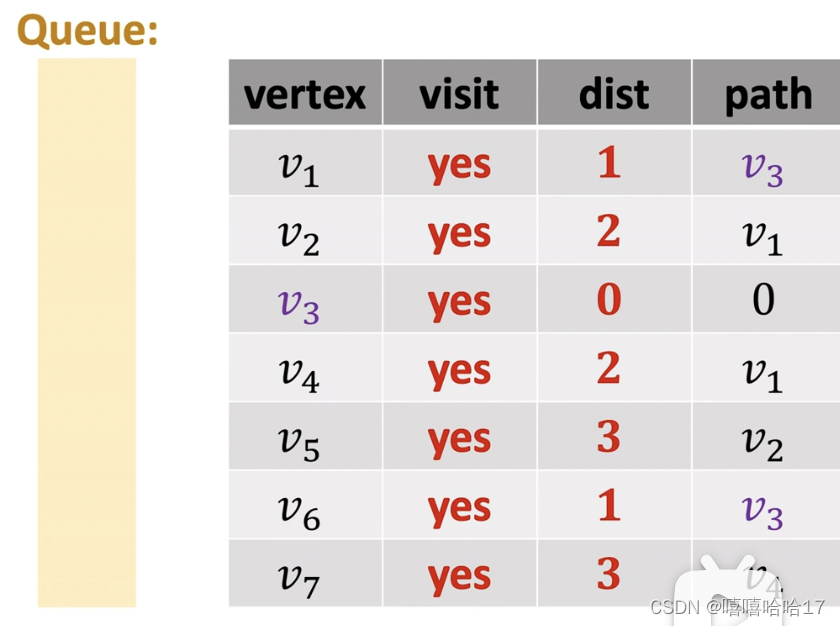
graph={
1:[2,4],
2:[4,5],
3:[1,6],
4:[3,5,6,7],
5:[7],
6:[],
7:[6],
}
def shortest(root,graph):
n=len(graph)+1
path=[0]*n
visit=[0]*n
dist=[float('inf')]*n
queue=[root]
visit[root]=1
dist[root]=0
while queue:
ver=queue.pop()
for nex in graph[ver]:
if visit[nex]==0:
path[nex]=ver
visit[nex]=1
dist[nex]=dist[ver]+1
queue.append(nex)
print(dist,path,visit)
shortest(3,graph)
有向有权图 带排序的广度优先算法/dijkstra
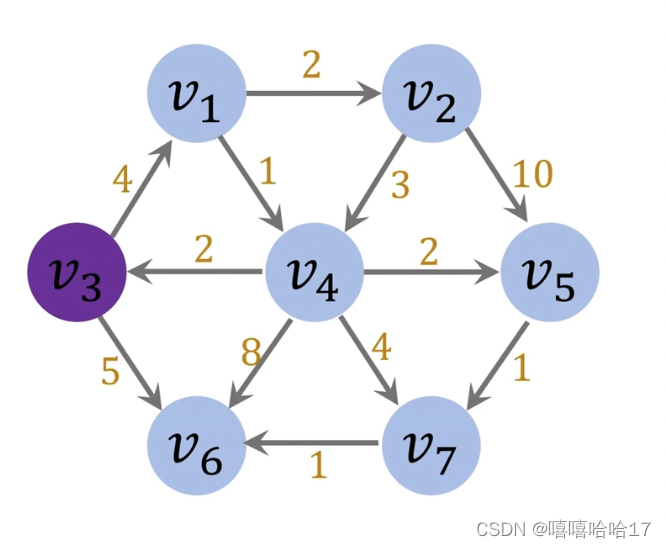
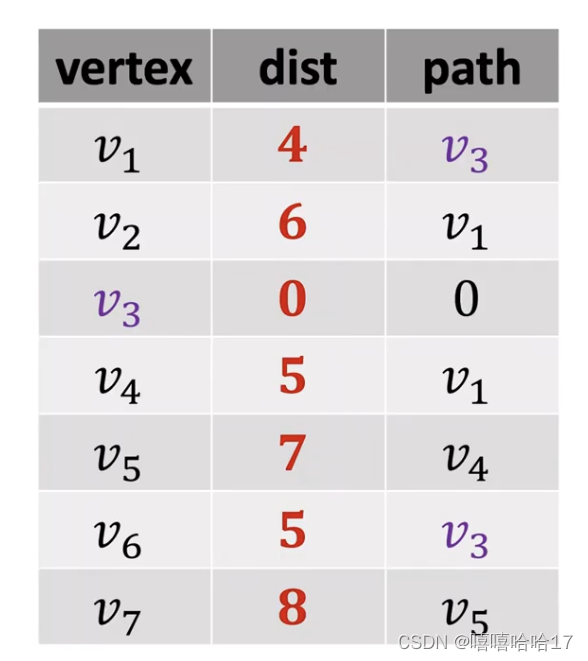
import heapq
graph1={
1:[(2,2),(1,4)],
2:[(3,4),(10,5)],
3:[(4,1),(5,6)],
4:[(2,3),(2,5),(8,6),(4,7)],
5:[(1,7)],
6:[],
7:[(1,6)],
}
def shortest2(root,graph):
n=len(graph)+1
path=[0]*n
visit=[0]*n
dist=[float('inf')]*n
dist[root]=0
queue=[(0,root)]
heapq.heapify(queue)
while queue:
dis,ver=heapq.heappop(queue)
visit[ver]=1
for nex in graph[ver]:
if visit[nex[1]]==0:
heapq.heappush(queue,nex)
if dist[ver]+nex[0]<dist[nex[1]]:
dist[nex[1]]=dist[ver]+nex[0]
path[nex[1]]=ver
print(dist,path,visit)
shortest2(3,graph1)
#[inf, 4, 6, 0, 5, 7, 5, 8] [0, 3, 1, 0, 1, 4, 3, 5] [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
最小生成树
prims算法
树是连通 无向 无环图。n个结点一定有n-1条边。
一个普通的生成树
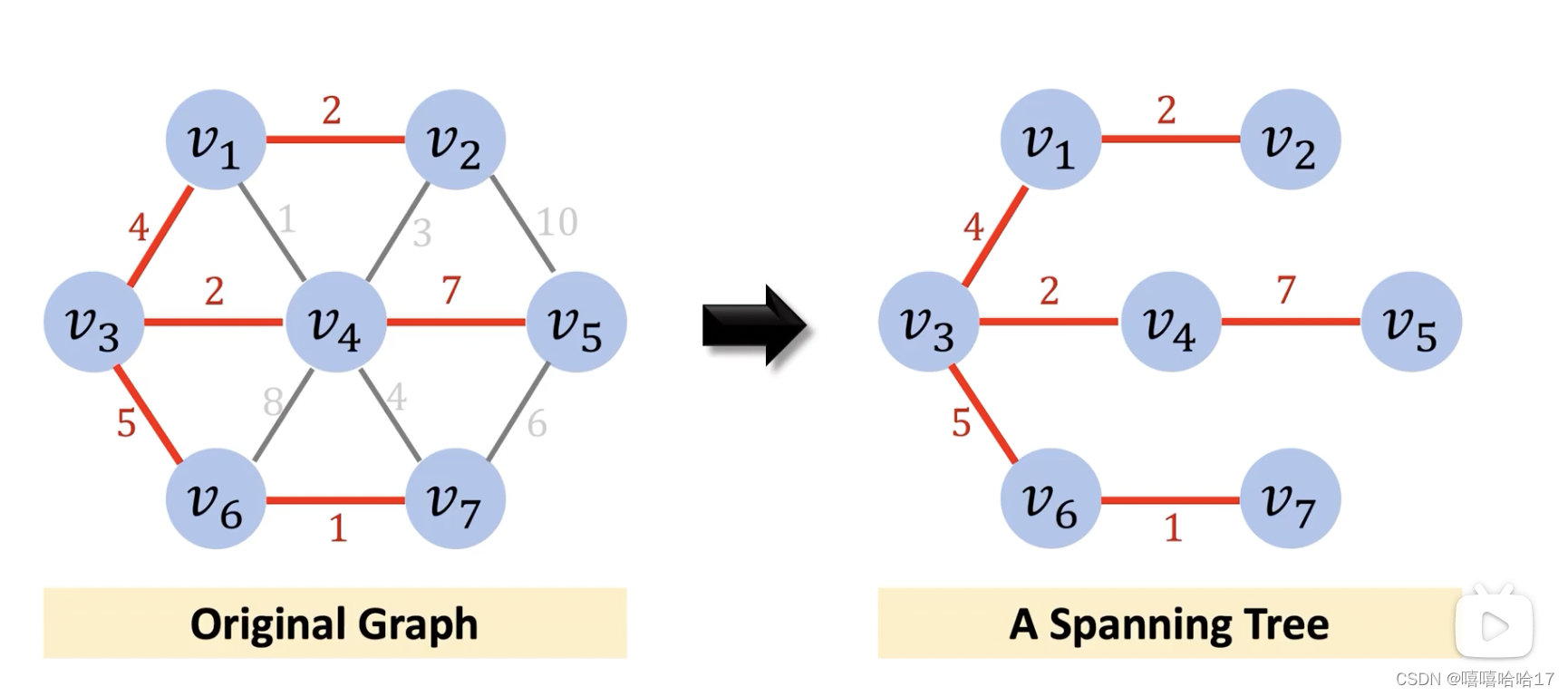
最小生成树
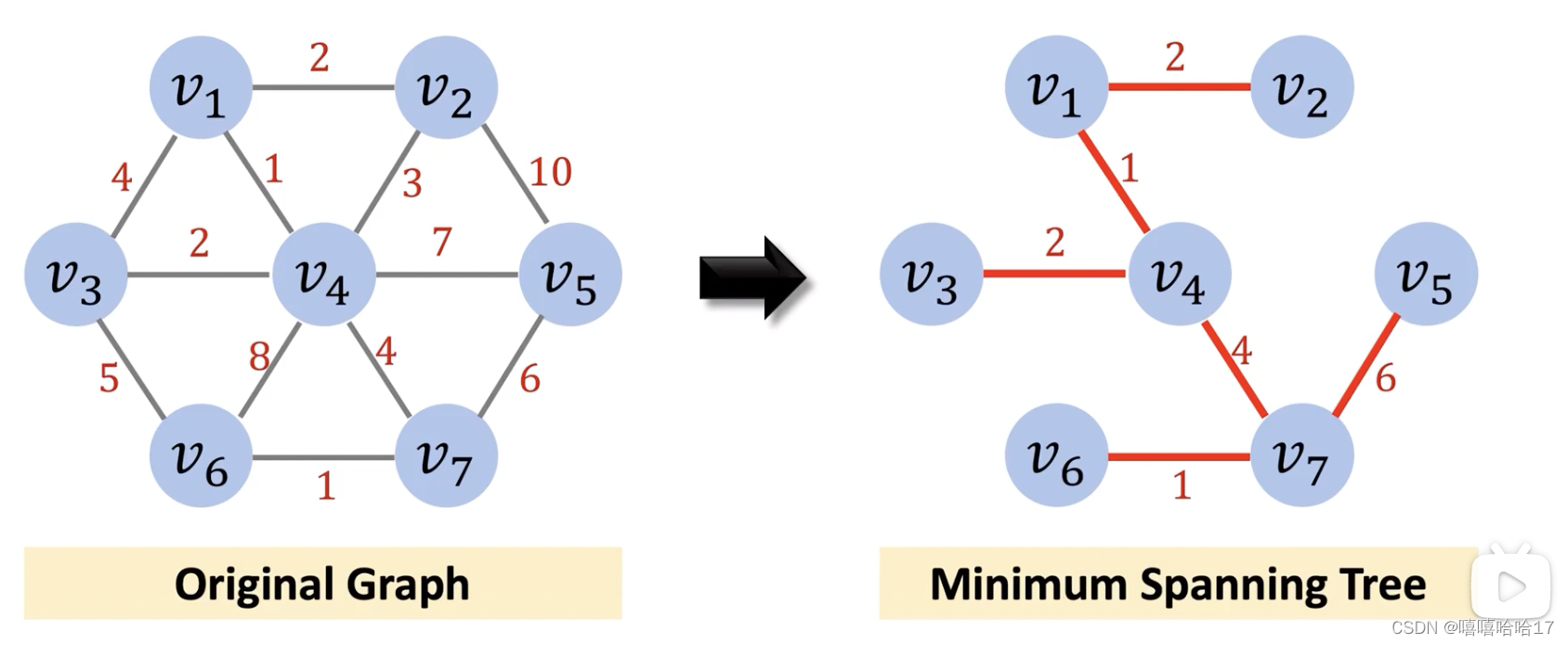
Kruskal’s Algorithm
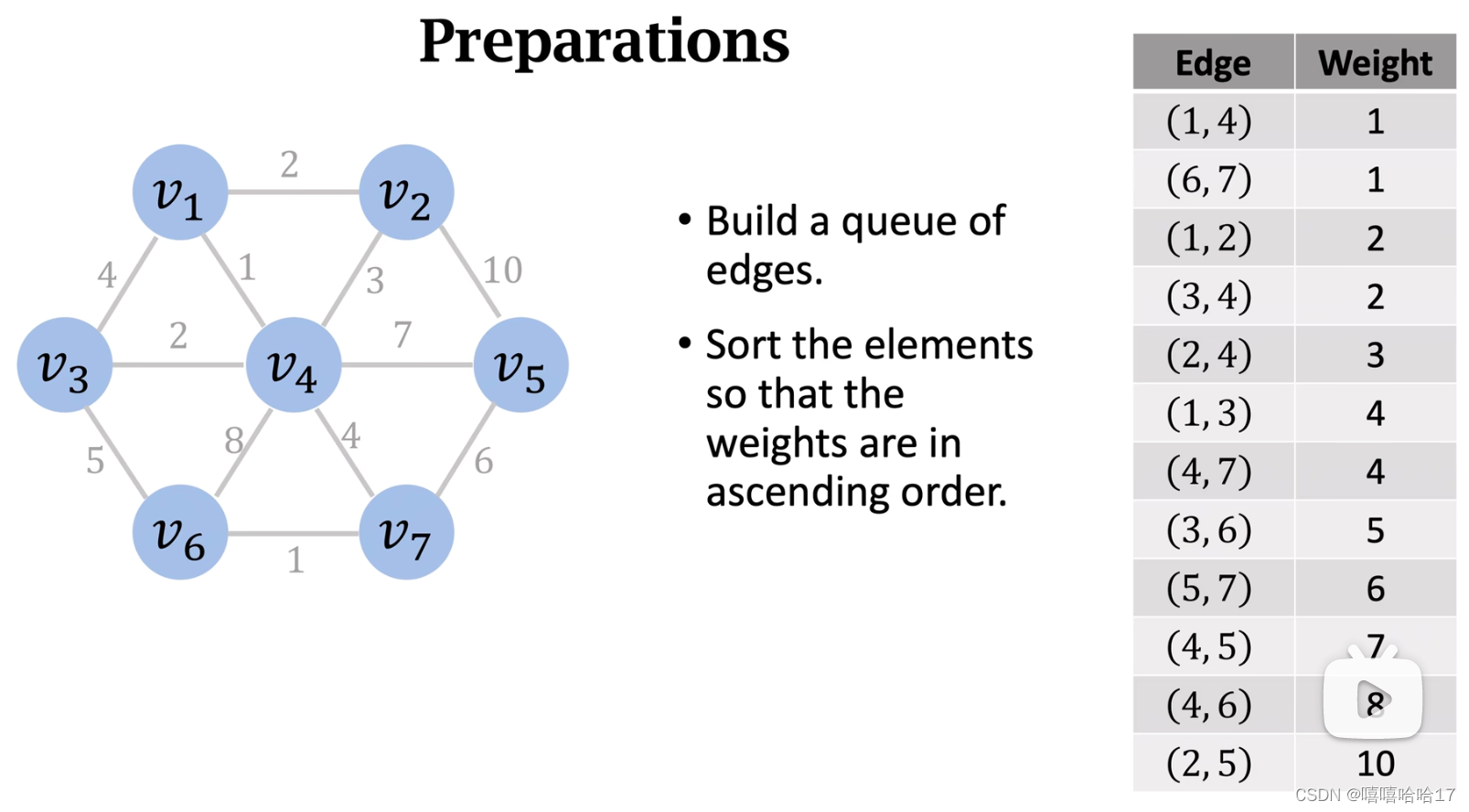
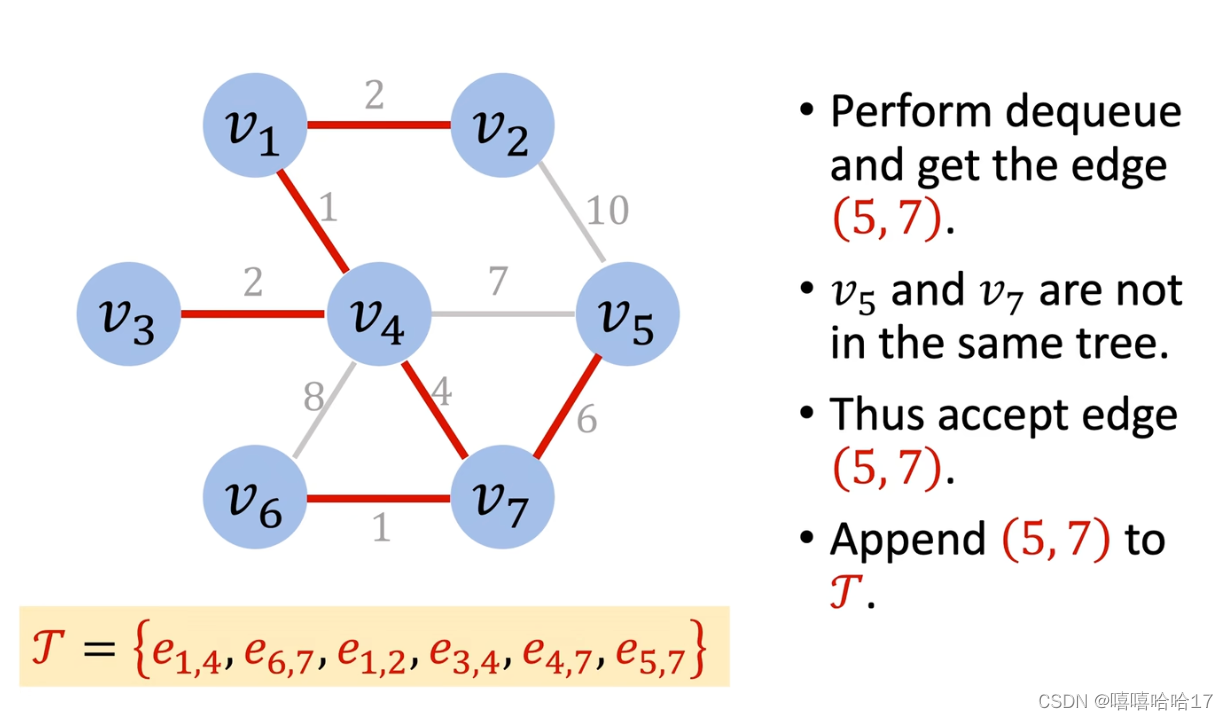
graph=[
[3,1,4],[3,4,2],[3,6,5],[1,4,1],[4,6,8],[1,2,2],[6,7,1],[2,4,3],[4,7,4],[2,5,10],[5,7,6],[4,5,7]
]
def kruskal(graph,n):
find=[i for i in range(n+1)]
graph.sort(key=lambda x:x[2])
def parent(x):
if find[x]==x:
return x
else:
return find[x]
ans=[]
while len(ans)<n-1:
x,y,w = graph.pop(0)
if parent(x)!=parent(y):
ans.append([x,y,w])
find[x]=y
return ans
kruskal(graph,7)
# [[1, 4, 1], [6, 7, 1], [3, 4, 2], [1, 2, 2], [2, 4, 3], [3, 1, 4]]
最小割 min-cut
二分图 Bipartite Graph 队列
例题1 所有可能的路径
https://leetcode.cn/problems/all-paths-from-source-to-target/description/
class Solution:
def allPathsSourceTarget(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
path = [0]
ans=[]
def dfs(graph,index):
if index==len(graph)-1:
ans.append(path[:])
return
for node in graph[index]:
path.append(node)
dfs(graph,node)
path.pop()
dfs(graph,0)
return ans
class Solution:
def allPathsSourceTarget(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
from collections import deque
ans=[]
q=deque([[0],])
while q:
path = q.popleft()
if path[-1]==len(graph)-1:
ans.append(path)
continue
for v in graph[path[-1]]:
q.append(path+[v])
return ans
例题2 岛屿数量
https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-islands/description/
class Solution:
def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
n=len(grid)
m=len(grid[0])
ans=0
def wipe(x,y):
dir=[
lambda x,y:[x+1,y],#下
lambda x,y:[x-1,y],#上
lambda x,y:[x,y+1],#右
lambda x,y:[x,y-1],#左
]
stack=[(x,y)]
while stack:
x,y=stack.pop()
grid[x][y]='0'
for i in range(4):
nxt_x,nxt_y=dir[i](x,y)
if nxt_x>=0 and nxt_x <n and nxt_y<m and nxt_y>=0:
if grid[nxt_x][nxt_y]=='1':
stack.append((nxt_x,nxt_y))
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if grid[i][j]=='1':
ans+=1
wipe(i,j)
return ans
例题3 岛屿最大面积
https://leetcode.cn/problems/max-area-of-island/
class Solution:
def maxAreaOfIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n=len(grid)
m=len(grid[0])
ans=0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if grid[i][j]==1:
grid[i][j]=0
tmp=1
stack=[(i,j)]
dir=[
lambda x,y:[x+1,y],
lambda x,y:[x-1,y],
lambda x,y:[x,y+1],
lambda x,y:[x,y-1],
]
while stack:
x,y=stack.pop()
grid[x][y]=0
for k in range(4):
nx,ny = dir[k](x,y)
if nx>=0 and nx<n and ny>=0 and ny<m and grid[nx][ny]==1:
tmp+=1
grid[nx][ny]=0
stack.append((nx,ny))
ans = max(ans,tmp)
return ans
例题4 飞地的数量
https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-enclaves/
class Solution:
def numEnclaves(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n=len(grid)
m=len(grid[0])
ans=0
def dfs(x,y):
for dx,dy in (0,1),(1,0),(-1,0),(0,-1):
nx = x+dx
ny =y+dy
if 0<= nx <n and 0<= ny <m and grid[nx][ny]==1:
grid[nx][ny]=0
dfs(nx,ny)
for i in [0,n-1] :
for j in range(m):
if grid[i][j]==1:
ans+=1
grid[i][j]=0
dfs(i,j)
for i in range(n):
for j in [0,m-1]:
if grid[i][j]==1:
ans+=1
grid[i][j]=0
dfs(i,j)
return sum(sum(g) for g in grid)
class Solution {
public static int[][] dirs={{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
private int n,m;
private boolean[][] visted;
public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {
n = grid.length;
m=grid[0].length;
visted = new boolean[n][m];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
dfs(grid,i,0);
dfs(grid,i,m-1);
}
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
dfs(grid,0,j);
dfs(grid,n-1,j);
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j =0;j<m;j++){
if(grid[i][j]==1 && !visted[i][j]){
ans+=1;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
public void dfs(int[][]grid,int x,int y){
if (x<0 || x>=n || y<0 || y>=m || grid[x][y]==0 || visted[x][y]){
return;
}
visted[x][y]=true;
for(int[] dir:dirs){
dfs(grid,x+dir[0],y+dir[1]);
}
}
}
例题5 被围绕的区域
https://leetcode.cn/problems/surrounded-regions/description/
class Solution:
def solve(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
n=len(board)
m=len(board[0])
visted=[[0]*m for _ in range(n)]
def dfs(x,y):
if 0<=x<n and 0<=y<m and board[x][y]=='O' and not visted[x][y]:
visted[x][y]=1
for dx,dy in (0,1),(0,-1),(1,0),(-1,0):
dfs(x+dx,y+dy)
else:
return
for i in range(n):
dfs(i,0)
dfs(i,m-1)
for j in range(m):
dfs(0,j)
dfs(n-1,j)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if board[i][j]=='O' and visted[i][j]==0 :
board[i][j]='X'
例题6 太平洋大西洋水流问题
https://leetcode.cn/problems/pacific-atlantic-water-flow/description/
class Solution:
def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
n=len(heights)
m=len(heights[0])
pacific =[[0]*m for _ in range(n)]
atlantic=[[0]*m for _ in range(n)]
ans=[]
def dfs(x,y,grid):
grid[x][y]=1
for dx,dy in (0,1),(0,-1),(1,0),(-1,0):
nx=x+dx
ny=y+dy
if 0<=nx<n and 0<=ny<m and heights[nx][ny]>=heights[x][y] and grid[nx][ny]==0:
dfs(nx,ny,grid)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if j==0 or i==0:
dfs(i,j,pacific)
if i==n-1 or j==m-1:
atlantic[i][j]=1
dfs(i,j,atlantic)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if pacific[i][j]==1 and atlantic[i][j]==1:
ans.append([i,j])
return ans
例题7 钥匙和房间
https://leetcode.cn/problems/keys-and-rooms/
class Solution:
def canVisitAllRooms(self, rooms: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
n=len(rooms)
visted=[0]*n
def dfs(x):
if visted[x]:
return
visted[x]=1
for nx in rooms[x]:
dfs(nx)
dfs(0)
return sum(visted)==n
例题8 寻找图中是否存在路径
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-if-path-exists-in-graph/description/
class Solution:
def validPath(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], source: int, destination: int) -> bool:
parent=[i for i in range(n)]
def find(x):
if x==parent[x]:
return x
parent[x]=find(parent[x])
return find(parent[x])
def union(x,y):
px=find(x)
py=find(y)
if px!=py:
parent[px]=py
for u,v in edges:
if find(u)!=find(v):
union(u,v)
return find(source)==find(destination)
例题9 冗余连接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/redundant-connection/description/
class Solution:
def findRedundantConnection(self, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
n=len(edges)
parent=[i for i in range(n+1)]
def find(x):
if x==parent[x]:
return x
parent[x]=find(parent[x])
return find(parent[x])
def union(x,y):
px=find(x)
py=find(y)
if px !=py:
parent[px]=py
for u,v in edges:
if find(u)==find(v):
return [u,v]
else:
union(u,v)
例题10 课程表 拓扑排序
https://leetcode.cn/problems/course-schedule/description/
import collections
class Solution:
def canFinish(self, numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
edges=collections.defaultdict(list)
visted=[0]*numCourses
restult=[]
valid = True
for u,v in prerequisites:
edges[v].append(u)
def dfs(u):
nonlocal valid
visted[u]=1
for v in edges[u]:
if visted[v]==0:
dfs(v)
if not valid:
return
elif visted[v]==1:
valid=False
return
visted[u]=2
restult.append(u)
for i in range(numCourses):
if valid and not visted[i]:
dfs(i)
return valid
import collections
class Solution:
def canFinish(self, numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
edges=collections.defaultdict(list)
indeg=[0]*numCourses
for u,v in prerequisites:
edges[v].append(u)
indeg[u]+=1
queue = [u for u in range(numCourses) if indeg[u]==0]
visted =0
while queue:
u = queue.pop(0)
visted+=1
for v in edges[u]:
indeg[v]-=1
if indeg[v]==0:
queue.append(v)
return visted==numCourses
例题11 单词接龙
https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-ladder/description/
class Solution:
def ladderLength(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
wordList = set(wordList)
if endWord not in wordList:
return 0
q = deque([(beginWord, 1)])
while q:
cur, step = q.popleft()
for i, x in enumerate(cur):
for y in [chr(ord('a')+i) for i in range(26)]:
if y != x:
nxt = cur[:i] + y + cur[i+1:]
if nxt == endWord:
return step + 1
if nxt in wordList:
wordList.remove(nxt)
q.append((nxt, step+1))
return 0
例题12 最小高度树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-height-trees/description/
import collections
class Solution:
def findMinHeightTrees(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
graph=collections.defaultdict(list)
res=[]
for u,v in edges:
graph[u].append(v)
graph[v].append(u)
def dfs(u):
ans=1
visted[u]=1
for v in graph[u]:
if visted[v]==0:
vh=dfs(v)
# print(u,v,vh)
ans=max(ans,vh+1)
return ans
visted=[0]*n
res.append([0,dfs(0)])
for i in range(1,n):
visted=[0]*n
tmp=dfs(i)
if tmp<res[-1][-1]:
res=[[i,tmp]]
elif tmp==res[-1][-1]:
res.append([i,tmp])
return [u for u,v in res]
例题13 省份数量
https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-provinces/description/
1.利用并查集
class Solution:
def findCircleNum(self, isConnected: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n=len(isConnected)
par=[i for i in range(n+1)]
def find(x):
if x==par[x]:
return x
par[x]=find(par[x])
return find(par[x])
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if i!=j and isConnected[i][j]==1:
pi=find(i+1)
pj= find(j+1)
par[pi]=pj
for i in range(n+1):
par[i]=find(i)
return len(set(par))-1
class Solution:
def findCircleNum(self, isConnected: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n=len(isConnected)
visted=[0]*n
ans=0
def dfs(x):
visted[x]=1
for j in range(n):
if isConnected[x][j]==1 and visted[j]==0:
dfs(j)
for i in range(n):
if visted[i]==0:
dfs(i)
ans+=1
return ans


![[BT]BUUCTF刷题第6天(3.24)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/a0b2b2c123d146f0bf6c1177fe622ab0.png)