目录
- 一 Select
- 1.1 参数的对应解析convertArgsToSqlCommandParam
- 1.2 ID获取对应的MappedStatement
- 1.3 MappedStatement交给执行器执行
- 1.4 根据参数获取BoundSql
- 1.5 SqlNode节点的解析
- 1.5.1 MixedSqlNode
- 1.5.2 IfSqlNode
- 1.5.3 StaticTextSqlNode
- 1.5.4 TextSqlNode
- 1.6 执行器执行查询
官网:mybatis – MyBatis 3 | 简介
参考书籍:《通用源码阅读指导书:MyBatis源码详解》 易哥
参考文章:
- Mybatis源码解析
上一篇文章我们分析到了MapperMethod的Insert执行流程,Update,Delete 语句执行过程其实都差不多,我们来看看Select语句?
/**
* 执行映射接口中的方法
* @param sqlSession sqlSession接口的实例,通过它可以进行数据库的操作
* @param args 执行接口方法时传入的参数
* @return 数据库操作结果
*/
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) { // 根据SQL语句类型,执行不同操作
case INSERT: { // 如果是插入语句
// 将参数顺序与实参对应好
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 执行操作并返回结果
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: { // 如果是更新语句
// 将参数顺序与实参对应好
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 执行操作并返回结果
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: { // 如果是删除语句MappedStatement
// 将参数顺序与实参对应好
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 执行操作并返回结果
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT: // 如果是查询语句
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) { // 方法返回值为void,且有结果处理器
// 使用结果处理器执行查询
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) { // 多条结果查询
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) { // Map结果查询
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) { // 游标类型结果查询
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else { // 单条结果查询
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH: // 清空缓存语句
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default: // 未知语句类型,抛出异常
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
// 查询结果为null,但返回类型为基本类型。因此返回变量无法接收查询结果,抛出异常。
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
一 Select
1.1 参数的对应解析convertArgsToSqlCommandParam
// 参数转换
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
- 具体的参考流程请参考前面的解析
1.2 ID获取对应的MappedStatement
// 执行查询操作,并返回一个结果,param:是通过convertArgsToSqlCommandParam转换的参数
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
我们看到是通过sqlSession来执行查询的,并且传入的参数为command.getName()和param,也就是namespace.methodName(com.shu.UserMapper.queryById)和方法的运行参数。我们知道了,所有的数据库操作都是交给sqlSession来执行的,那我们就来看看sqlSession的方法。
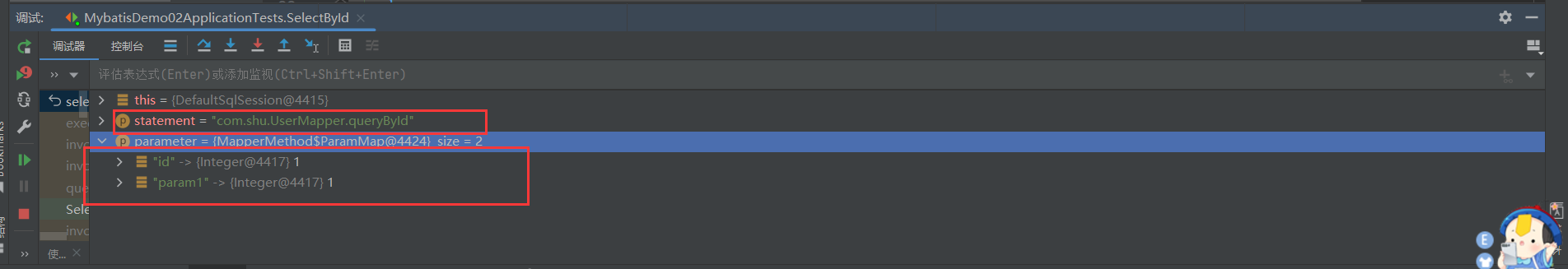
// 调用DefaultSqlSession的selectOne的方法
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
selectOne 方法在内部调用 selectList 了方法,并取 selectList 返回值的第1个元素作为自己的返回值。如果 selectList 返回的列表元素大于1,则抛出异常。下面我们来看看 selectList 方法的实现。
/**
* 查询结果列表
* @param <E> 返回的列表元素的类型
* @param statement SQL语句
* @param parameter 参数对象
* @param rowBounds 翻页限制条件
* @return 结果对象列表
*/
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
// 获取查询语句eg:com.shu.UserMapper.queryById,通过MappedStatement的Id获取 MappedStatement
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 交由执行器进行查询
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
- 通过Id获取MappedStatement的过程请参考前面的教程。
- 我们之前创建DefaultSqlSession的时候,是创建了一个Executor的实例作为其属性的,我们看到通过MappedStatement的Id获取 MappedStatement后,就交由Executor去执行了。
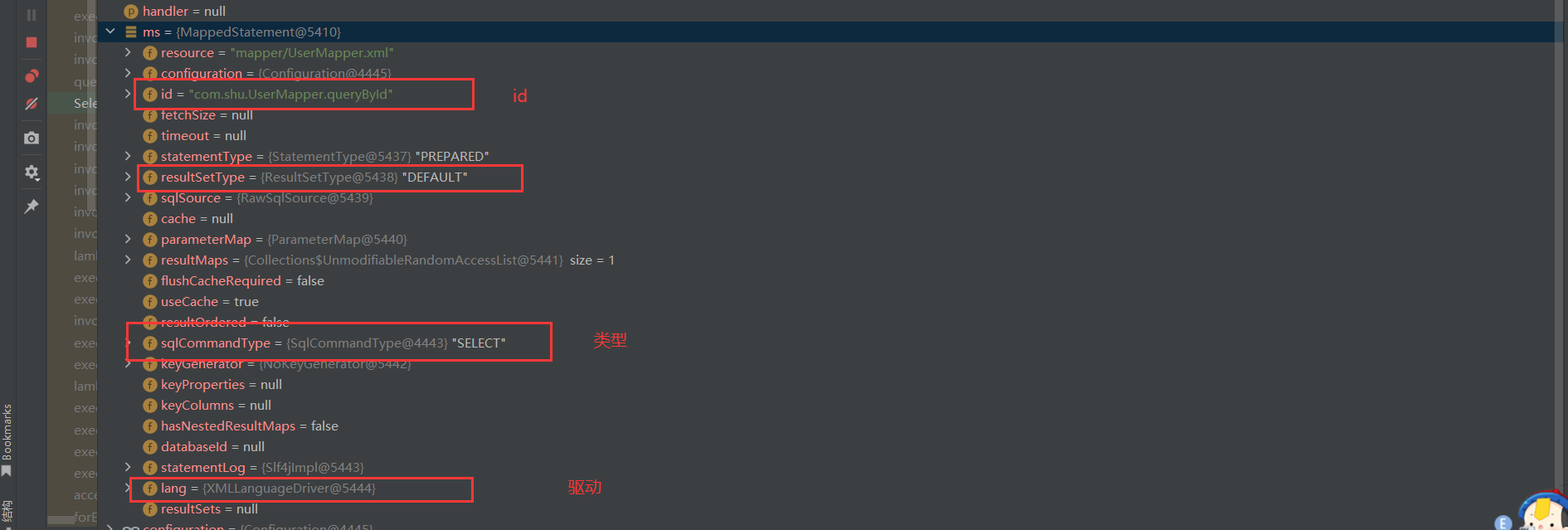
1.3 MappedStatement交给执行器执行
- 首先我们可以看看执行器的创建
/**
* 从数据源中获取SqlSession对象
* @param execType 执行器类型
* @param level 事务隔离级别
* @param autoCommit 是否自动提交事务
* @return SqlSession对象
*/
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
// 找出要使用的指定环境
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 从环境中获取事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
// 从事务工厂中生产事务
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 创建执行器
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
// 创建DefaultSqlSession对象
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
/**
* 创建一个执行器
* @param transaction 事务
* @param executorType 数据库操作类型
* @return 执行器
*/
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
// 根据数据操作类型创建实际执行器
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 根据配置文件中settings节点cacheEnabled配置项确定是否启用缓存
if (cacheEnabled) { // 如果配置启用缓存
// 使用CachingExecutor装饰实际执行器
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// 为执行器增加拦截器(插件),以启用各个拦截器的功能
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
CachingExecutor的query方法
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 获取 BoundSql
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 创建 CacheKey
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
// 调用重载方法
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
1.4 根据参数获取BoundSql
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 获取BoundSql
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 参数映射列表
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) {
boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);
}
// 循环遍历从configuration中获取隐射参数
// check for nested result maps in parameter mappings (issue #30)
for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
String rmId = pm.getResultMapId();
if (rmId != null) {
ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId);
if (rm != null) {
hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps();
}
}
}
return boundSql;
}
我们都知道 SQL 是配置在映射文件中的,但由于映射文件中的 SQL 可能会包含占位符 #{},以及动态 SQL 标签,比如 、 等。因此,我们并不能直接使用映射文件中配置的 SQL。MyBatis 会将映射文件中的 SQL 解析成一组 SQL 片段。我们需要对这一组片段进行解析,从每个片段对象中获取相应的内容。然后将这些内容组合起来即可得到一个完成的 SQL 语句,这个完整的 SQL 以及其他的一些信息最终会存储在 BoundSql 对象中。下面我们来看一下 BoundSql 类的成员变量信息,如下:
// 可能含有“?”占位符的sql语句
private final String sql;
// 参数映射列表
private final List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
// 实参对象本身
private final Object parameterObject;
// 实参
private final Map<String, Object> additionalParameters;
// additionalParameters的包装对象
private final MetaObject metaParameters;
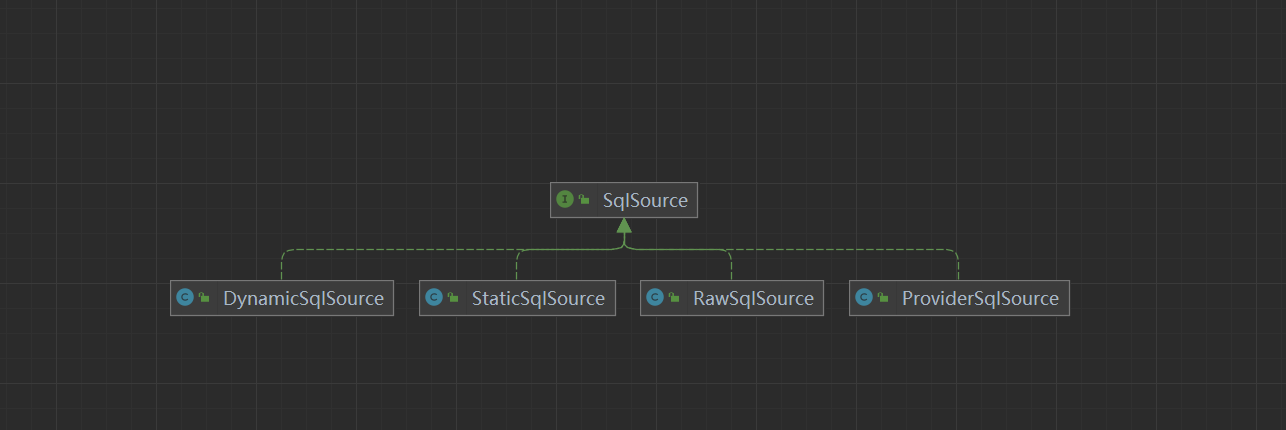
- DynamicSqlSource:针对动态 SQL 和 ${} 占位符的 SQL
- RawSqlSource:针对 #{}占位符的 SQL
- ProviderSqlSource:针对 @*Provider 注解 提供的 SQL
- StaticSqlSource:仅包含有 ?占位符的 SQL
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
- 首先我们需要看看sqlSource是如何进行创建的?
// 处理各个数据库操作语句
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
// 从上下文构建语句
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
// 单条语句的解析器,解析类似:
// <select id="selectUser" resultType="com.example.demo.UserBean">
// select * from `user` where id = #{id}
// </select>
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
/**
* 解析select、insert、update、delete这四类节点
*/
public void parseStatementNode() {
// 读取当前节点的id与databaseId
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
// 验证id与databaseId是否匹配。MyBatis允许多数据库配置,因此有些语句只对特定数据库生效
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
// 读取节点名
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
// 读取和判断语句类型
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// 处理语句中的Include节点
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// 参数类型
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
// 语句类型
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// 处理SelectKey节点,在这里会将KeyGenerator加入到Configuration.keyGenerators中
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// 此时,<selectKey> 和 <include> 节点均已被解析完毕并被删除,开始进行SQL解析
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
// 判断是否已经有解析好的KeyGenerator
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
// 全局或者本语句只要启用自动key生成,则使用key生成
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
// 读取各个配置属性
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
if (resultSetTypeEnum == null) {
resultSetTypeEnum = configuration.getDefaultResultSetType();
}
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
// 在MapperBuilderAssistant的帮助下创建MappedStatement对象,并写入到Configuration中
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
请注意:SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);这个方法,在SqlSessionFactory的创建时就已经上生成了SqlSource,下面我们来看看具体的执行流程,首先我们要看看LanguageDriver这个接口,他负责在接口上注解的SQL语句,就是由它进行解析的,比如:@Select(“select * from user where id = #{id}”)
public interface LanguageDriver {
/**
* 创建参数处理器。参数处理器能将实参传递给JDBC statement。
* @param mappedStatement 完整的数据库操作节点
* @param parameterObject 参数对象
* @param boundSql 数据库操作语句转化的BoundSql对象
* @return 参数处理器
*/
ParameterHandler createParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql);
/**
* 创建SqlSource对象(基于映射文件的方式)。该方法在MyBatis启动阶段,读取映射接口或映射文件时被调用
* @param configuration 配置信息
* @param script 映射文件中的数据库操作节点
* @param parameterType 参数类型
* @return SqlSource对象
*/
SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType);
/**
* 创建SqlSource对象(基于注解的方式)。该方法在MyBatis启动阶段,读取映射接口或映射文件时被调用
* @param configuration 配置信息
* @param script 注解中的SQL字符串
* @param parameterType 参数类型
* @return SqlSource对象,具体来说是DynamicSqlSource和RawSqlSource中的一种
*/
SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String script, Class<?> parameterType);
}
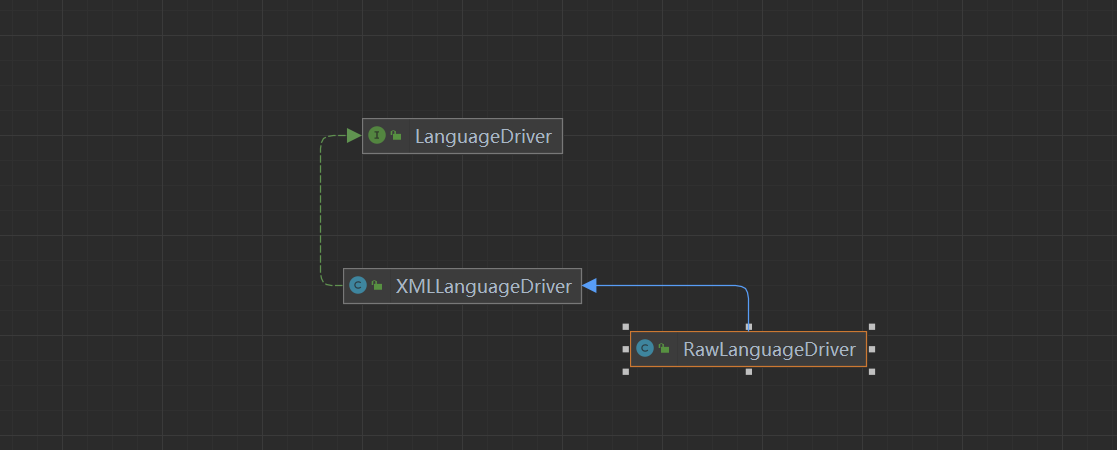
我们来看看他的实现类:XMLLanguageDriver,Mybatis默认的XML驱动为XMLLanguageDriver。
我们主要是看看他的createSqlSource()方法,主要有两种方式:XML式和注解式
/**
* 创建SqlSource对象(基于映射文件的方式)。该方法在MyBatis启动阶段,读取映射接口或映射文件时被调用
* @param configuration 配置信息
* @param script 映射文件中的数据库操作节点
* @param parameterType 参数类型
* @return SqlSource对象
*/
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) {
XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType);
return builder.parseScriptNode();
}
// 创建SQL源码(注解方式)
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String script, Class<?> parameterType) {
if (script.startsWith("<script>")) {
// 如果注解中的内容以<script>开头
XPathParser parser = new XPathParser(script, false, configuration.getVariables(), new XMLMapperEntityResolver());
return createSqlSource(configuration, parser.evalNode("/script"), parameterType);
} else {
// 如果注解中的内容不以<script>开头
script = PropertyParser.parse(script, configuration.getVariables());
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(script);
// 是不是动态节点
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
//返回针对动态 SQL 和 ${} 占位符的 SQL的DynamicSqlSource
return new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, textSqlNode);
} else {
//返回针对 #{}占位符的 SQL的RawSqlSource
return new RawSqlSource(configuration, script, parameterType);
}
}
}
/**
* 解析节点生成SqlSource对象
* @return SqlSource对象
*/
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
// 解析XML节点节点,得到节点树MixedSqlNode
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context);
SqlSource sqlSource;
// 根据节点树是否为动态,创建对应的SqlSource对象
if (isDynamic) {
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}
/**
* 将XNode对象解析为节点树
* @param node XNode对象,即数据库操作节点
* @return 解析后得到的节点树
*/
protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(XNode node) {
// XNode拆分出的SqlNode列表
List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<>();
// 输入XNode的子XNode
NodeList children = node.getNode().getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
// 循环遍历每一个子XNode
XNode child = node.newXNode(children.item(i));
if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE || child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) { // CDATASection类型或者Text类型的XNode节点
// 获取XNode内的信息
String data = child.getStringBody("");
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(data);
// 只要有一个TextSqlNode对象是动态的,则整个MixedSqlNode是动态的
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
contents.add(textSqlNode);
isDynamic = true;
} else {
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));
}
} else if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { // 子XNode仍然是Node类型
String nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName();
// 找到对应的处理器
NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);
if (handler == null) {
throw new BuilderException("Unknown element <" + nodeName + "> in SQL statement.");
}
// 用处理器处理节点
handler.handleNode(child, contents);
isDynamic = true;
}
}
// 返回一个混合节点,其实就是一个SQL节点树
return new MixedSqlNode(contents);
}
到这我们就可以发现SqlSource的创建:如果是动态的返回DynamicSqlSource,否则返回RawSqlSource,那如何来判断是否是动态语句?下面我们接着看?
/**
* 判断当前节点是不是动态的
* @return 节点是否为动态
*/
public boolean isDynamic() {
// 占位符处理器,该处理器并不会处理占位符,而是判断是不是含有占位符
DynamicCheckerTokenParser checker = new DynamicCheckerTokenParser();
GenericTokenParser parser = createParser(checker);
// 使用占位符处理器。如果节点内容中含有占位符,则DynamicCheckerTokenParser对象的isDynamic属性将会被置为true
parser.parse(text);
return checker.isDynamic();
}
/**
*
* @param text 输入:
* SELECT * FROM t_action
* WHERE `id`=#{id}
* ORDER BY `actionTime`
*
* @return 输出:
* SELECT * FROM t_action
* WHERE `id`=?
* ORDER BY `actionTime`
*/
public String parse(String text) {
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// search open token
int start = text.indexOf(openToken);
if (start == -1) {
return text;
}
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
int offset = 0;
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder expression = null;
while (start > -1) {
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
// this open token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
// found open token. let's search close token.
if (expression == null) {
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
offset = start + openToken.length();
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
while (end > -1) {
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
break;
}
}
if (end == -1) {
// close token was not found.
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
offset = src.length;
} else {
// 这里调用了传入的handler的方法
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
}
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
return builder.toString();
}
public String handleToken(String content) {
this.isDynamic = true;
return null;
}
}
到这我们知道了上面我们写的测试案例返回的是RawSqlSource,我们来你看看他的解析过程,我们可以发现他的构造器?
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, Class<?> parameterType) {
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> clazz = parameterType == null ? Object.class : parameterType;
// 处理RawSqlSource中的“#{}”占位符,得到StaticSqlSource
sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(sql, clazz, new HashMap<>());
}
我们可以发现他调用了父类的方法parse(),并返回了一个StaticSqlSource对象
public SqlSourceBuilder(Configuration configuration) {
super(configuration);
}
// 这里解析的对象是SqlNode拼接结束的,即<if> <where>等节点的结果都已经解析结束。然后在这里继续处理
/**
* 将DynamicSqlSource和RawSqlSource中的“#{}”符号替换掉,从而将他们转化为StaticSqlSource
* @param originalSql sqlNode.apply()拼接之后的sql语句。已经不包含<if> <where>等节点,也不含有${}符号
* @param parameterType 实参类型
* @param additionalParameters 附加参数
* @return 解析结束的StaticSqlSource
*/
public SqlSource parse(String originalSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
// 用来完成#{}处理的处理器
ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType, additionalParameters);
// 通用的占位符解析器,用来进行占位符替换
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler);
// 将#{}替换为?的SQL语句
String sql = parser.parse(originalSql);
// 生成新的StaticSqlSource对象
return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings());
}
接来下我们来看看ParameterMappingTokenHandler的处理过程,与上面判断是否是动态的过程大体一样
// 用以替换占位符的处理器
// 用来处理形如#{ id, javaType= int, jdbcType=NUMERIC, typeHandler=DemoTypeHandler }
private static class ParameterMappingTokenHandler extends BaseBuilder implements TokenHandler {
// 每个#{}中的东西对应一个ParameterMapping。所有的#{}都放在这个list
private List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = new ArrayList<>();
// 参数类型
private Class<?> parameterType;
// 参数的Meta对象
private MetaObject metaParameters;
//
public ParameterMappingTokenHandler(Configuration configuration, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
super(configuration);
this.parameterType = parameterType;
this.metaParameters = configuration.newMetaObject(additionalParameters);
}
}
接着调用GenericTokenParser的parse()方法,传入的TokenHandler不一样他的处理方式不一样
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler);
// 占位符的起始标志:#{
private final String openToken;
// 占位符的结束标志:}
private final String closeToken;
// 占位符处理器:ParameterMappingTokenHandler
private final TokenHandler handler;
public GenericTokenParser(String openToken, String closeToken, TokenHandler handler) {
this.openToken = openToken;
this.closeToken = closeToken;
this.handler = handler;
}
// 解析返回Sql语句
public String parse(String text) {
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// search open token
int start = text.indexOf(openToken);
if (start == -1) {
return text;
}
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
int offset = 0;
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder expression = null;
while (start > -1) {
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
// this open token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
// found open token. let's search close token.
if (expression == null) {
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
offset = start + openToken.length();
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
while (end > -1) {
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
break;
}
}
if (end == -1) {
// close token was not found.
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
offset = src.length;
} else {
// 这里调用了传入的handler的方法
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
}
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
return builder.toString();
}
/**
* 在这里,${}被替换为?
* 但同时,用户传入的实际参数也被记录了
* @param content 包含
* @return
*/
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
parameterMappings.add(buildParameterMapping(content));
return "?";
}
/**
*
* @param content 形如id, javaType= int, jdbcType=NUMERIC, typeHandler=DemoTypeHandler
* @return
*/
private ParameterMapping buildParameterMapping(String content) {
// 将参数转化为map
Map<String, String> propertiesMap = parseParameterMapping(content);
String property = propertiesMap.get("property");
Class<?> propertyType;
if (metaParameters.hasGetter(property)) { // issue #448 get type from additional params
propertyType = metaParameters.getGetterType(property);
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterType)) {
propertyType = parameterType;
} else if (JdbcType.CURSOR.name().equals(propertiesMap.get("jdbcType"))) {
propertyType = java.sql.ResultSet.class;
} else if (property == null || Map.class.isAssignableFrom(parameterType)) {
propertyType = Object.class;
} else {
MetaClass metaClass = MetaClass.forClass(parameterType, configuration.getReflectorFactory());
if (metaClass.hasGetter(property)) {
propertyType = metaClass.getGetterType(property);
} else {
propertyType = Object.class;
}
}
ParameterMapping.Builder builder = new ParameterMapping.Builder(configuration, property, propertyType);
Class<?> javaType = propertyType;
String typeHandlerAlias = null;
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : propertiesMap.entrySet()) {
String name = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
if ("javaType".equals(name)) {
javaType = resolveClass(value);
builder.javaType(javaType);
} else if ("jdbcType".equals(name)) {
builder.jdbcType(resolveJdbcType(value));
} else if ("mode".equals(name)) {
builder.mode(resolveParameterMode(value));
} else if ("numericScale".equals(name)) {
builder.numericScale(Integer.valueOf(value));
} else if ("resultMap".equals(name)) {
builder.resultMapId(value);
} else if ("typeHandler".equals(name)) {
typeHandlerAlias = value;
} else if ("jdbcTypeName".equals(name)) {
builder.jdbcTypeName(value);
} else if ("property".equals(name)) {
// Do Nothing
} else if ("expression".equals(name)) {
throw new BuilderException("Expression based parameters are not supported yet");
} else {
throw new BuilderException("An invalid property '" + name + "' was found in mapping #{" + content + "}. Valid properties are " + PARAMETER_PROPERTIES);
}
}
if (typeHandlerAlias != null) {
builder.typeHandler(resolveTypeHandler(javaType, typeHandlerAlias));
}
return builder.build();
}
private Map<String, String> parseParameterMapping(String content) {
try {
// content = id, javaType= int, jdbcType=NUMERIC, typeHandler=DemoTypeHandler ;
return new ParameterExpression(content);
} catch (BuilderException ex) {
throw ex;
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BuilderException("Parsing error was found in mapping #{" + content + "}. Check syntax #{property|(expression), var1=value1, var2=value2, ...} ", ex);
}
}
}
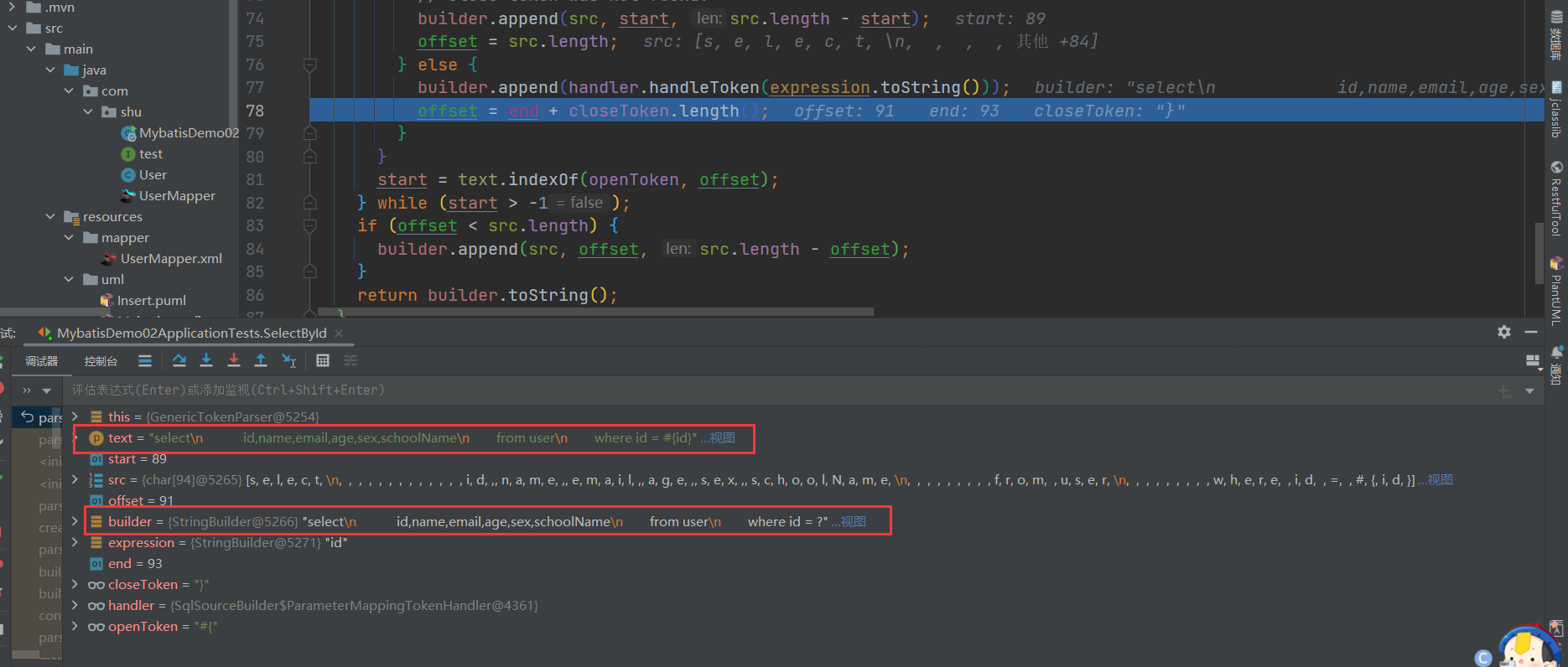
我们会发现他调用了ParameterMappingTokenHandler.handleToken()方法将#{}替换?接着构建StaticSqlSource对象
public StaticSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings) {
this.sql = sql;
this.parameterMappings = parameterMappings;
this.configuration = configuration;
}
/**
* 组建一个BoundSql对象
* @param parameterObject 参数对象
* @return 组件的BoundSql对象
*/
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
return new BoundSql(configuration, sql, parameterMappings, parameterObject);
}
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 获取BoundSql
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 参数映射列表
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) {
boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);
}
// 循环遍历从configuration中获取隐射参数
// check for nested result maps in parameter mappings (issue #30)
for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
String rmId = pm.getResultMapId();
if (rmId != null) {
ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId);
if (rm != null) {
hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps();
}
}
}
return boundSql;
}
到这我们会发现BoundSql的获取实际上是SqlSource干了所有事,就返回boundSql对象
1.5 SqlNode节点的解析
接下来我们来看看DynamicSqlSource动态节点的解析,首先看看他的成员变量。
private final Configuration configuration;
// 整个sqlSource的根节点。
// 举例子,例如: SELECT *
// FROM `user`
// WHERE id IN
// <foreach item="id" collection="array" open="(" separator="," close=")">
// #{id}
// </foreach>
// 那根节点是一个MixedSqlNode,其List分别是:
// StaticTextSqlNode: SELECT * FROM `user` WHERE id IN
// ForEachSqlNode:拆解后的foreachSqlNode信息
private final SqlNode rootSqlNode;
public DynamicSqlSource(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.rootSqlNode = rootSqlNode;
}
我们来看看他的getBoundSql()方法,返回BoundSql对象
/**
* 获取一个BoundSql对象
* @param parameterObject 参数对象
* @return BoundSql对象
*/
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 创建DynamicSqlSource的辅助类,用来记录DynamicSqlSource解析出来的
// * SQL片段信息
// * 参数信息
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
// 这里会逐层(对于mix的node而言)调用apply。最终不同的节点会调用到不同的apply,完成各自的解析
// 解析完成的东西拼接到DynamicContext中,里面含有#{}
// 在这里,动态节点和${}都被替换掉了。
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
// 处理占位符、汇总参数信息
// RawSqlSource也会焦勇这一步
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
// 使用SqlSourceBuilder处理#{},将其转化为?
// 相关参数放进了context.bindings
// *** 最终生成了StaticSqlSource对象,然后由它生成BoundSql
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 把context.getBindings()的参数放到boundSql的metaParameters中进行保存
context.getBindings().forEach(boundSql::setAdditionalParameter);
return boundSql;
}
根据带来我们可以看出DynamicSqlSource的解析依赖于DynamicContext,因此我们来看看DynamicContext这个类,下面是他的成员变量
public static final String PARAMETER_OBJECT_KEY = "_parameter";
public static final String DATABASE_ID_KEY = "_databaseId";
static {
OgnlRuntime.setPropertyAccessor(ContextMap.class, new ContextAccessor());
}
// 上下文环境
private final ContextMap bindings;
// 用于拼装SQL语句片段
private final StringJoiner sqlBuilder = new StringJoiner(" ");
// 解析时的唯一编号,防止解析混乱
private int uniqueNumber = 0;
/**
* DynamicContext的构造方法
* @param configuration 配置信息
* @param parameterObject 用户传入的查询参数对象
*/
public DynamicContext(Configuration configuration, Object parameterObject) {
if (parameterObject != null && !(parameterObject instanceof Map)) {
// 获得参数对象的元对象
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
// 判断参数对象本身是否有对应的类型处理器
boolean existsTypeHandler = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass());
// 放入上下文信息
bindings = new ContextMap(metaObject, existsTypeHandler);
} else {
// 上下文信息为空
bindings = new ContextMap(null, false);
}
// 把参数对象放入上下文信息
bindings.put(PARAMETER_OBJECT_KEY, parameterObject);
// 把数据库id放入上下文信息
bindings.put(DATABASE_ID_KEY, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
下面进入我们今天的正题:SQLNode的解析,首先我们看看SqlNode接口
// 在我们写动态的SQL语句时,<if></if> <where></where> 这些就是sqlNode
public interface SqlNode {
/**
* 完成该节点自身的解析
* @param context 上下文环境,节点自身的解析结果将合并到该上下文环境中
* @return 解析是否成功
*/
boolean apply(DynamicContext context);
}
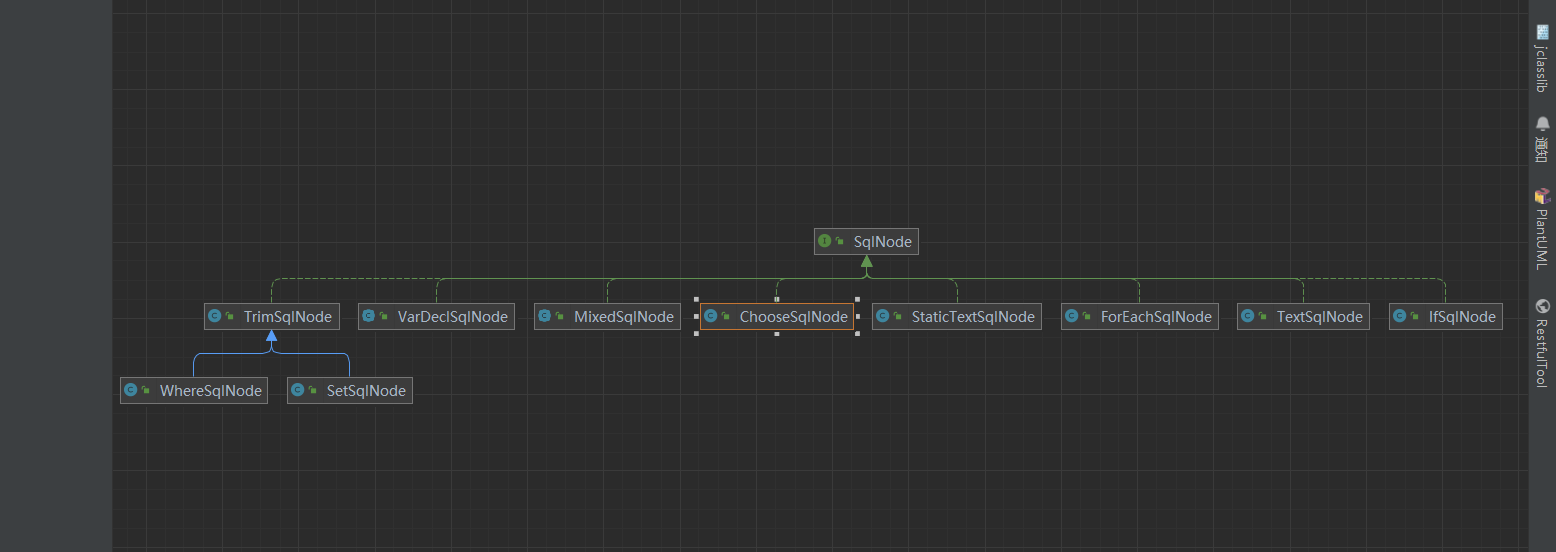
SqlNode的创建?
/**
* 创建SqlSource对象(基于映射文件的方式)。该方法在MyBatis启动阶段,读取映射接口或映射文件时被调用
* @param configuration 配置信息
* @param script 映射文件中的数据库操作节点
* @param parameterType 参数类型
* @return SqlSource对象
*/
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) {
XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType);
return builder.parseScriptNode();
}
// 创建SQL源码(注解方式)
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String script, Class<?> parameterType) {
if (script.startsWith("<script>")) {
// 如果注解中的内容以<script>开头
XPathParser parser = new XPathParser(script, false, configuration.getVariables(), new XMLMapperEntityResolver());
return createSqlSource(configuration, parser.evalNode("/script"), parameterType);
} else {
// 如果注解中的内容不以<script>开头
script = PropertyParser.parse(script, configuration.getVariables());
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(script);
// 是不是动态节点:就是<>
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
return new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, textSqlNode);
} else {
return new RawSqlSource(configuration, script, parameterType);
}
}
}
/**
* 将XNode对象解析为节点树
* @param node XNode对象,即数据库操作节点
* @return 解析后得到的节点树
*/
protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(XNode node) {
// XNode拆分出的SqlNode列表
List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<>();
// 输入XNode的子XNode
NodeList children = node.getNode().getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
// 循环遍历每一个子XNode
XNode child = node.newXNode(children.item(i));
if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE || child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) { // CDATASection类型或者Text类型的XNode节点
// 获取XNode内的信息
String data = child.getStringBody("");
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(data);
// 只要有一个TextSqlNode对象是动态的,则整个MixedSqlNode是动态的
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
contents.add(textSqlNode);
isDynamic = true;
} else {
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));
}
} else if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { // 子XNode仍然是Node类型
String nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName();
// 找到对应的处理器
NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);
if (handler == null) {
throw new BuilderException("Unknown element <" + nodeName + "> in SQL statement.");
}
// 用处理器处理节点
handler.handleNode(child, contents);
isDynamic = true;
}
}
// 返回一个混合节点,其实就是一个SQL节点树
return new MixedSqlNode(contents);
}
// 获取XNode内的信息
String data = child.getStringBody("");
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(data);
// 只要有一个TextSqlNode对象是动态的,则整个MixedSqlNode是动态的
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
contents.add(textSqlNode);
isDynamic = true;
} else {
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));
}
在这里我们可也以看到满足CDATASection类型或者Text类型的XNode节点如果是动态的就返回TextSqlNode,否则返回StaticTextSqlNode,否则调用自己的的处理器来生成对应的SqlNode,包装在MixedSqlNode中,MixedSqlNode 内部维护了一个 SqlNode 集合。
S tring nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName();
// 找到对应的处理器
NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);
if (handler == null) {
throw new BuilderException("Unknown element <" + nodeName + "> in SQL statement.");
}
// 用处理器处理节点
handler.handleNode(child, contents);
isDynamic = true;
比如:IfHandler的解析,其他的Handel可以自己查看
/**
* 该方法将当前节点拼装到节点树中
* @param nodeToHandle 要被拼接的节点
* @param targetContents 节点树
*/
@Override
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
// 解析该节点的下级节点
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
// 获取该节点的test属性
String test = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("test");
// 创建一个IfSqlNode
IfSqlNode ifSqlNode = new IfSqlNode(mixedSqlNode, test);
// 将创建的IfSqlNode放入到SQL节点树中
targetContents.add(ifSqlNode);
}
}
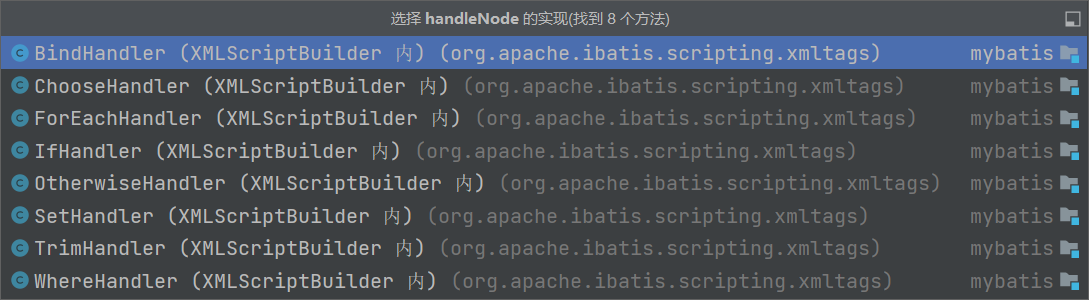

1.5.1 MixedSqlNode
- MixedSqlNode 内部维护了一个 SqlNode 集合,用于存储各种各样的 SqlNode。
- MixedSqlNode 可以看做是 SqlNode 实现类对象的容器,凡是实现了 SqlNode 接口的类都可以存储到 MixedSqlNode 中,包括它自己。MixedSqlNode 解析方法 apply 逻辑比较简单,即遍历 SqlNode 集合,并调用其他 SqlNode实现类对象的 apply 方法解析 sql。
public class MixedSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private final List<SqlNode> contents;
public MixedSqlNode(List<SqlNode> contents) {
this.contents = contents;
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
contents.forEach(node -> node.apply(context));
return true;
}
}
1.5.2 IfSqlNode
IfSqlNode 对应的是 节点,首先是通过 ONGL 检测 test 表达式是否为 true,如果为 true,则调用其子节点的 apply 方法继续进行解析。如果子节点是静态SQL节点,则子节点的文本值会直接拼接到DynamicContext中
<select id="findActiveBlogWithTitleLike"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE state = ‘ACTIVE’
<if test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</if>
</select>
public class IfSqlNode implements SqlNode {
// 表达式评估器
private final ExpressionEvaluator evaluator;
// if判断时的测试条件
private final String test;
// if成立时,要被拼接的SQL片段信息
private final SqlNode contents;
public IfSqlNode(SqlNode contents, String test) {
this.test = test;
this.contents = contents;
this.evaluator = new ExpressionEvaluator();
}
/**
* 完成该节点自身的解析
* @param context 上下文环境,节点自身的解析结果将合并到该上下文环境中
* @return 解析是否成功
*/
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 判断if条件是否成立
if (evaluator.evaluateBoolean(test, context.getBindings())) {
// 将contents拼接到context
contents.apply(context);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
1.5.3 StaticTextSqlNode
静态的SQL节点,直接追加到sql尾部即可
public class StaticTextSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private final String text;
public StaticTextSqlNode(String text) {
this.text = text;
}
@Override
// 最终调用到这里,将节点内容拼接到context后面
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
context.appendSql(text);
return true;
}
}
/**
* 增加拼接串
* @param sql
*/
public void appendSql(String sql) {
sqlBuilder.add(sql);
}
1.5.4 TextSqlNode
主要是包含${}占位符的动态sql节点解析,具体的请参考前面的RawSqlSource的解析
/**
* 判断当前节点是不是动态的
* @return 节点是否为动态
*/
public boolean isDynamic() {
// 占位符处理器,该处理器并不会处理占位符,而是判断是不是含有占位符
DynamicCheckerTokenParser checker = new DynamicCheckerTokenParser();
GenericTokenParser parser = createParser(checker);
// 使用占位符处理器。如果节点内容中含有占位符,则DynamicCheckerTokenParser对象的isDynamic属性将会被置为true
parser.parse(text);
return checker.isDynamic();
}
/**
* 完成该节点自身的解析
* @param context 上下文环境,节点自身的解析结果将合并到该上下文环境中
* @return 解析是否成功
*/
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 创建通用的占位符解析器
GenericTokenParser parser = createParser(new BindingTokenParser(context, injectionFilter));
// 替换掉其中的${}占位符
context.appendSql(parser.parse(text));
return true;
}
/**
* 创建一个通用的占位符解析器,用来解析${}占位符
* @param handler 用来处理${}占位符的专用处理器
* @return 占位符解析器
*/
private GenericTokenParser createParser(TokenHandler handler) {
return new GenericTokenParser("${", "}", handler);
}
其他节点的解析,请读者自己查看源码分析,我们回到刚开始分析BoundSql 的获取完毕,CachingExecutor#query()方法
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 创建缓存
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
1.6 执行器执行查询
/**
* 查询数据库中的数据
* @param ms 映射语句
* @param parameterObject 参数对象
* @param rowBounds 翻页限制条件
* @param resultHandler 结果处理器
* @param key 缓存的键
* @param boundSql 查询语句
* @param <E> 结果类型
* @return 结果列表
* @throws SQLException
*/
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
// 获取MappedStatement对应的缓存,可能的结果有:该命名空间的缓存、共享的其它命名空间的缓存、无缓存
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
// 如果映射文件未设置<cache>或<cache-ref>则,此处cache变量为null
if (cache != null) { // 存在缓存
// 根据要求判断语句执行前是否要清除二级缓存,如果需要,清除二级缓存
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) { // 该语句使用缓存且没有输出结果处理器
// 二级缓存不支持含有输出参数的CALLABLE语句,故在这里进行判断
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
// 从缓存中读取结果
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) { // 缓存中没有结果
// 交给被包装的执行器执行
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
// 缓存被包装执行器返回的结果
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
// 交由被包装的实际执行器执行
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
上面的代码涉及到了二级缓存,若二级缓存为空,或未命中,则调用被装饰类的 query 方法。被装饰类为SimpleExecutor,而SimpleExecutor继承BaseExecutor,那我们来看看 BaseExecutor 的query方法
/**
* 查询数据库中的数据
* @param ms 映射语句
* @param parameter 参数对象
* @param rowBounds 翻页限制条件
* @param resultHandler 结果处理器
* @param key 缓存的键
* @param boundSql 查询语句
* @param <E> 结果类型
* @return 结果列表
* @throws SQLException
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
// 执行器已经关闭
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { // 新的查询栈且要求清除缓存
// 清除一级缓存
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
// 尝试从本地缓存获取结果
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
// 本地缓存中有结果,则对于CALLABLE语句还需要绑定到IN/INOUT参数上
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 本地缓存没有结果,故需要查询数据库
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
// 懒加载操作的处理
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
deferredLoads.clear();
// 如果本地缓存的作用域为STATEMENT,则立刻清除本地缓存
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
从一级缓存中查找查询结果。若缓存未命中,再向数据库进行查询。至此我们明白了一级二级缓存的大概思路,先从二级缓存中查找,若未命中二级缓存,再从一级缓存中查找,若未命中一级缓存,再从数据库查询数据,那我们来看看是怎么从数据库查询的。
/**
* 从数据库中查询结果
* @param ms 映射语句
* @param parameter 参数对象
* @param rowBounds 翻页限制条件
* @param resultHandler 结果处理器
* @param key 缓存的键
* @param boundSql 查询语句
* @param <E> 结果类型
* @return 结果列表
* @throws SQLException
*/
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
// 向缓存中增加占位符,表示正在查询
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
// 删除占位符
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 将查询结果写入缓存
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
调用了doQuery方法进行查询,最后将查询结果放入一级缓存,我们来看看doQuery,在SimpleExecutor中
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 创建 StatementHandler
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 创建 Statement
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 执行查询操作
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
// 关闭 Statement
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
tatementHandler有什么作用呢?通过这个对象获取Statement对象,然后填充运行时参数,最后调用query完成查询。我们来看看其创建过程?
- RoutingStatementHandler: RoutingStatementHandler 并没有对 Statement 对象进行使用,只是根据StatementType 来创建一个代理,代理的就是对应Handler的三种实现类。在MyBatis工作时,使用的StatementHandler 接口对象实际上就是 RoutingStatementHandler 对象。
- BaseStatementHandler: 是 StatementHandler 接口的另一个实现类.本身是一个抽象类.用于简化StatementHandler 接口实现的难度,属于适配器设计模式体现,它主要有三个实现类
- SimpleStatementHandler: 管理 Statement 对象并向数据库中推送不需要预编译的SQL语句。
- PreparedStatementHandler: 管理 Statement 对象并向数据中推送需要预编译的SQL语句。
- CallableStatementHandler:管理 Statement 对象并调用数据库中的存储过程。
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement,
Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
// 创建具有路由功能的 StatementHandler
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 应用插件到 StatementHandler 上
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
statementType 的默认类型为PREPARED,这里将会创建PreparedStatementHandler。所以我们看看
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
// 根据语句类型选择被代理对象
switch (ms.getStatementType()) {
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case PREPARED:
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
default:
throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
}
}
构造器
public PreparedStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
super(executor, mappedStatement, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
}
我们可以看到构造器中调用了父类的构造器方法、因此我们查看一下父类方法BaseStatementHandler:主要定义了从Connection中获取Statement的方法,而对于具体的Statement操作则未定义
protected BaseStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration();
this.executor = executor;
this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement;
this.rowBounds = rowBounds;
this.typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
this.objectFactory = configuration.getObjectFactory();
if (boundSql == null) { // issue #435, get the key before calculating the statement
// 如果是前置主键自增,则在这里进行获得自增的键值
generateKeys(parameterObject);
// 获取BoundSql对象
boundSql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
this.boundSql = boundSql;
this.parameterHandler = configuration.newParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
this.resultSetHandler = configuration.newResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql);
}
找了StatementHandler,创建 Statement 在 stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); 这句代码,那我们跟进去看看
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 获取数据库连接
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 创建 Statement,
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 为 Statement 设置参数
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
在上面的代码中我们终于看到了和jdbc相关的内容了,创建完Statement,最后就可以执行查询操作了。在下一篇文章我们来接受JDBC的操作