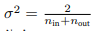上篇中记录了AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的创建以及注册,主要是
1、@EnableAspectJAutoProxy 注解会开启AOP功能
2、然后这个注解会往容器中注册一个AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator组件。
3、之后在容器创建过程中,注册后置处理器,创建AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator对象,这个也是一个后置处理器。
目录
一、finishBeanFactoryInitialization详解
一、遍历获取容器中所有的Bean,依次创建对象getBean(beanName);
二、创建bean
一、先从缓存中获取当前bean,如果能获取到,说明bean是之前被创建过的,直接使用,否则再创建;另外只要创建好的Bean都会被缓存起来
二、createBean();创建bean;
1、resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
二、resolveBeforeInstantiation详解
一、applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation
二、applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
三、创建代理对象
一、每一个bean创建之前,都会调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation()
一、 postProcessBeforeInstantiation源码讲解
二、isInfrastructureClass,判断是否是基础类型Advice、Pointcut、Advisor、AopInfrastructureBean, 或者是否是切面(@Aspect)
三、this.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)是否需要跳过
四、findCandidateAdvisors(获取所有的增强器)
五、buildAspectJAdvisors
六、getAdvisors获取所有增强器
二、postProcessAfterInitialization
一 、postProcessAfterInitialization源码
一、wrapIfNecessary(包装目标类,如果需要的话),返回代理对象
getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean:获取当前Bean 的所有增强器(通知方法)
findEligibleAdvisors(找到合适的增强器)
findAdvisorsThatCanApply(找到能够应用的增强器)
静态方法findAdvisorsThatCanApply(找到能够应用的增强器)
canApply(能够应用的增强器)
静态方法canApply(能够应用的增强器)
getClassFilter(获取切点表达式)
obtainPointcutExpression(获取切入点表达式)
buildPointcutExpression,解析表达式
matches(匹配当前类)
couldMatchJoinPointsInType(判断当前类是否可以匹配切入点),仅仅是去匹配当前类是否符合规则
二、createProxy,创建代理对象
getProxy:取决于 createAopProxy 返回的是 CGlib 还是JDK 代理
createAopProxy
四、目标方法的执行
一、CglibAopProxy.intercept();拦截目标方法的执行
二、根据ProxyFactory对象获取将要执行的目标方法拦截器链
一、ListinterceptorList保存所有拦截器,长度为5,遍历所有的增强器,将其转为Interceptor
二、getInterceptors获取所有的MethodInterceptor[]数组,也就是Interceptor拦截器数组,也就是最后的拦截器链
三、adapter.getInterceptor(advisor),转化MethodInterceptor逻辑
三、如果没有拦截器链,直接执行目标方法
四、如果有拦截器链,把需要执行的目标对象,目标方法,拦截器链等信息传入创建一个 CglibMethodInvocation 对象,并调用 Object retVal = mi.proceed();
五、执行拦截器链
一、proceed()
二、 proceed()里面的dm.interceptor.invoke(this)方法
五、最后做一个总结
一、finishBeanFactoryInitialization详解
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)主要是完成BeanFactory初始化工作;创建剩下的单实例bean。之前有一部分bean在this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);中就已经提前创建了。

一、遍历获取容器中所有的Bean,依次创建对象getBean(beanName);
一、代码进入流程:
1、finishBeanFactoryInitialization
2、beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();-》
3、if (isEagerInit) { this.getBean(beanName); }
二、创建对象流程:
getBean->doGetBean()->getSingleton()->
二、创建bean
一、先从缓存中获取当前bean,如果能获取到,说明bean是之前被创建过的,直接使用,否则再创建;另外只要创建好的Bean都会被缓存起来
二、createBean();创建bean;
1、resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);

解析BeforeInstantiation ,希望后置处理器在此能返回一个代理对象;如果能返回代理对象就使用,如果不能就继续
2、执行doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args)方法去真正的去创建一个bean实例
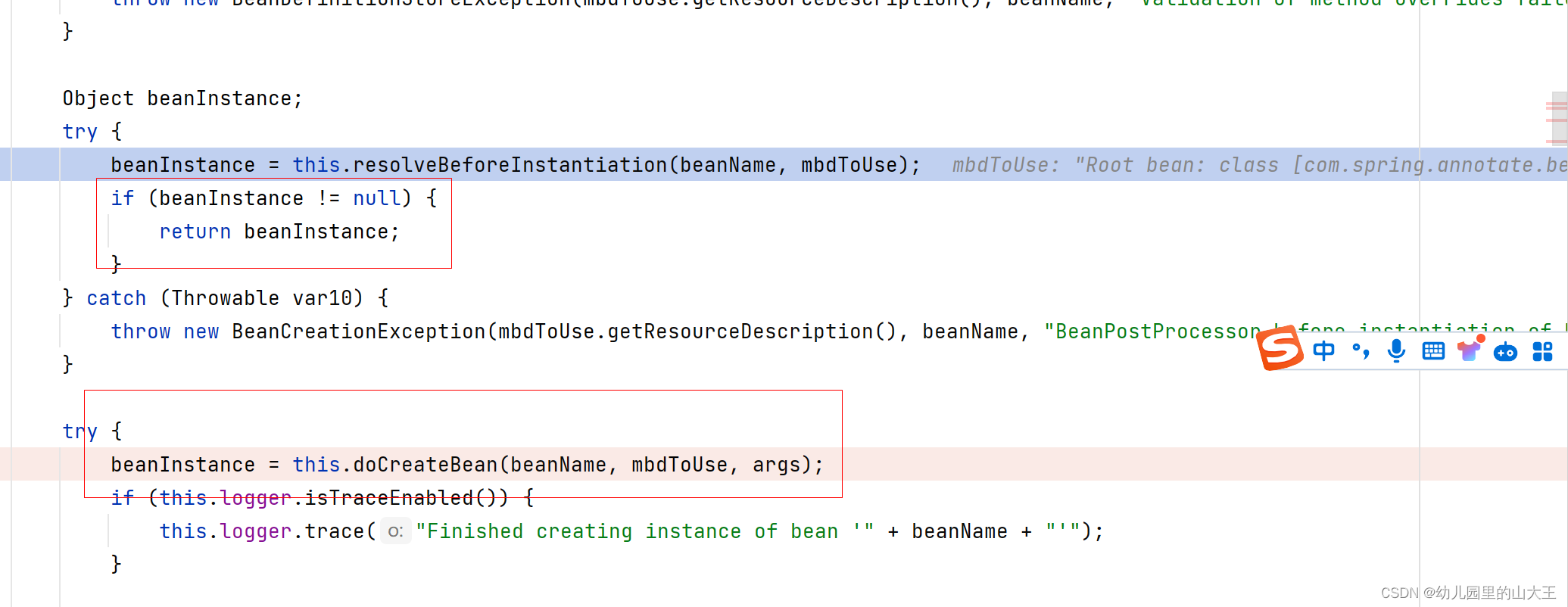
二、resolveBeforeInstantiation详解
创建bean之前,会从后置处理器中尝试获取一个代理对象,如果获取到了,就不会去创建bean对象了。
一、applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation
首先会去执行applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation这个方法

protected Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// 拿到所有后置处理器,如果是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
// 就执行postProcessBeforeInstantiation
Iterator var3 = this.getBeanPostProcessors().iterator();
while(var3.hasNext()) {
BeanPostProcessor bp = (BeanPostProcessor)var3.next();
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor)bp;
Object result = ibp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
return null;
}
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation:
遍历所有的后置处理器,如果对象是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,那么执行这个对象的postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName)方法。
注意:InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor也是一个后置处理器,但是他与BeanPostProcessor不一样。
BeanPostProcessor:是在Bean对象创建完成初始化前后调用的
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor:是在创建Bean实例之前先尝试用后置处理器返回对象的
也就是说AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator在所有bean创建之前会有一个拦截,InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,会调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation()
1、SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor继承了
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
2、AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现了SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
3、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator继承了AbstractAutoProxyCreator
二、applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
一、执行applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation,里面会执行一个postProcessBeforeInstantiation,这个方法会在第三大项AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator中讲解
二、之后会执行applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法,里面会执行postProcessAfterInitialization方法,这个方法也会在第三大项AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator中讲解
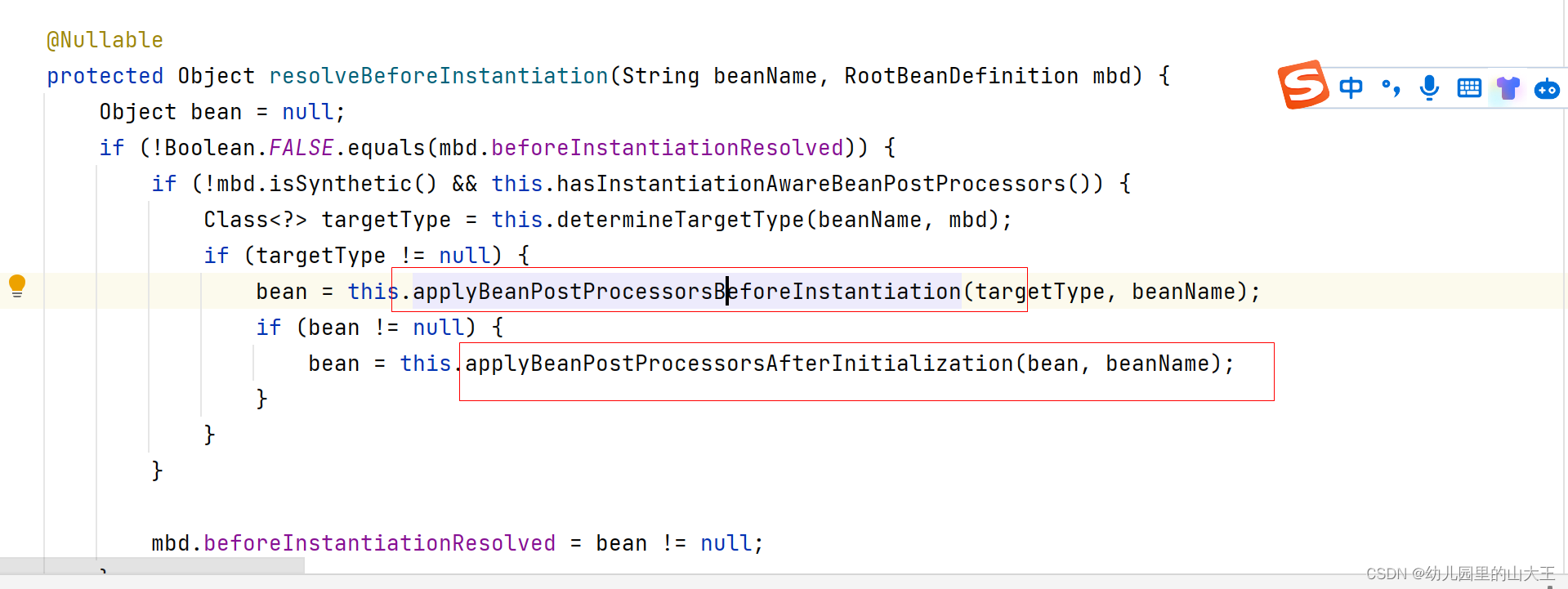
三、创建代理对象
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator其实就是一个实现InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的后置处理器
一、每一个bean创建之前,都会调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation()
这里呢,只需要关注MathCalculator和LogAspect的创建就好,这是由于其他bean都不会产生代理对象。
1、判断当前bean是否在advisedBeans中(保存了所有需要增强bean)
2、判断当前bean是否是基础类型的Advice、Pointcut、Advisor、AopInfrastructureBean,
或者是否是切面(@Aspect)3、是否需要跳过
1)获取候选的增强器(切面里面的通知方法)【List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors】每一个封装的通知方法的增强器是 InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisor;判断每一个增强器是否是 AspectJPointcutAdvisor 类型的;返回true
2)永远返回false

一、 postProcessBeforeInstantiation源码讲解
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
Object cacheKey = this.getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName);
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
// 判断当前bean是否在advisedBeans中(保存了所有需要增强bean)
if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) {
return null;
}
// 判断当前bean是否是基础类型的Advice、Pointcut、Advisor、AopInfrastructureBean,或者是否是切面(@Aspect)或者 是否需要跳过
if (this.isInfrastructureClass(beanClass)
//判断是不是需要跳过,如果返回true则就会将 这个 name 进行缓存
// 这里其实是将 切面 Bean 的BeanName 缓存起来,代表这个 Bean 不进行 增强操作
|| this.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return null;
}
}
// 如果我们有自定义的TargetSource,请在此处创建代理。
// 禁止目标Bean的不必要的默认实例化: TargetSource 将以自定义方式处理目标实例。
TargetSource targetSource = this.getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);
if (targetSource != null) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName)) {
this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);
}
Object[] specificInterceptors = this.getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource);
//创建代理对象
Object proxy = this.createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
} else {
return null;
}
}
二、isInfrastructureClass,判断是否是基础类型Advice、Pointcut、Advisor、AopInfrastructureBean, 或者是否是切面(@Aspect)
protected boolean isInfrastructureClass(Class<?> beanClass) {
boolean retVal = Advice.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || Pointcut.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || Advisor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || AopInfrastructureBean.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass);
if (retVal && this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Did not attempt to auto-proxy infrastructure class [" + beanClass.getName() + "]");
}
return retVal;
}
三、this.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)是否需要跳过
protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// 获取候选的增强器(切面里面的通知方法)【List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors】
// 每一个封装的通知方法的增强器是 InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisor类型
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = this.findCandidateAdvisors();
Iterator var4 = candidateAdvisors.iterator();
Advisor advisor;
// 循环所有 增强器
do {
if (!var4.hasNext()) {
// 这里基本返回 false..
return super.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName);
}
advisor = (Advisor)var4.next();
//判断我们的增强器是不是 AspectJPointcutAdvisor 这个类型,并且 增强的名称和我们的BeanName 是一致
} while(!(advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor) || !((AspectJPointcutAdvisor)advisor).getAspectName().equals(beanName));
return true;
}
// 父类的方法
protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// 判断是不是 原始的实例,也就是说是不需要进行代理的实例
return AutoProxyUtils.isOriginalInstance(beanName, beanClass);
}
static boolean isOriginalInstance(String beanName, Class<?> beanClass) {
// 如果 BeanName 不正常 返回 false
// beanName 的长度不是 bean全限定类名+ ORIGINAL_INSTANCE_SUFFIX(原始后缀),也返回 false
// 也就是说这里基本会返回 false 那什么时候返回 True 呢 当我们的Bean 是全限定类名 + ORIGINAL_INSTANCE_SUFFIX 的时候...
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) || beanName.length() !=
beanClass.getName().length() + AutowireCapableBeanFactory.ORIGINAL_INSTANCE_SUFFIX.length()) {
return false;
}
return (beanName.startsWith(beanClass.getName()) &&
beanName.endsWith(AutowireCapableBeanFactory.ORIGINAL_INSTANCE_SUFFIX));
}
四、findCandidateAdvisors(获取所有的增强器)
注意这里由于下面的代码都是在
TargetSource targetSource = this.getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);
if (targetSource != null) {}
这段代码里面的,所以这里只有我们有自定义的TargetSource,才会在此处创建代理。否则会在postProcessAfterInitialization中创建代理
调用
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.findCandidateAdvisors()1、调用父类的
findCandidateAdvisors()方法获取的是 实现了 Advisor 接口的Bean2、获取的是注解 切面里面所有的 Advisor,
// AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类下的
// 获取所有 实现 Advisor 接口的类,
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) {
// 建立 切面增强器
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
}
return advisors;
}五、buildAspectJAdvisors
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {
// 因为解析会很消耗性能,所以 Spring 会使用 aspectBeanNames 保存解析结果
List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
// 如果==null 代表没处理过,因为第二次肯定不为 null,在 进入这个条件后,就会创建 ArrayList
if (aspectNames == null) {
// 进行加锁处理,防止多线程情况下一起操作解析
synchronized (this) {
// 二次赋值,防治以及操作过了
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
//双重非空判断,避免再次解析
if (aspectNames == null) {
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
// 创建切面集合
aspectNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 查找所有的 BeanName 包括父类
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
//排除不合法的ban,由子类定义规则,默认返回true
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {
continue;
}
// 根据Name获取Class类型
Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName);
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
// 判断 是否存在 @Aspect 注解 并且判断 目标类上所有的属性不包含 "ajc$"
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
// 将 切面的 BeanName 放入到集合中
aspectNames.add(beanName);
// 包装成 AspectMetadata
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
//检查 @Aspect 注解的value值,验证生成的增强是否是单例
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
// 创建一个工厂..
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
// 获取标记 Aspect 注解的增强方法,获取所有增强器
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
//如果bean是单例,则缓存bean的增强器
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
// 将 切面 BeanName 和 增强器 进行缓存
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
}
// bean非单例,只缓存bean对应的增强器创建工厂
else {
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
}
// 将获取的 增强器 放入到集合中
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
}
else {
// 切面创建模式非单例,这里的Else 基本不会进来...
// 如果切面是非单例,但是bean是单例,抛出异常
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
}
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
//获取所有切面
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
}
//将已经解析过的切面 Bean 进行缓存
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
return advisors;
}
}
}
// 如果是 null 就会直接返回...
if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) {
// 如果是一个空的就返回一个空集合
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
// 循环 切面的Name
for (String aspectName : aspectNames) {
// 根据切面的Name 获取 增强器
List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);
if (cachedAdvisors != null) {
advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);
}
else {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
// 返回~~~~
return advisors;
}
六、getAdvisors获取所有增强器
public List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {
// 获取 切面的 Class
Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
// 获取 切面的 Name
String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();
// 对切面进行校验
validate(aspectClass);
// We need to wrap the MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory with a decorator
// so that it will only instantiate once.
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =
new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取 切面的所有方法,排除 @Pointcut
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) {
// Prior to Spring Framework 5.2.7, advisors.size() was supplied as the declarationOrderInAspect
// to getAdvisor(...) to represent the "current position" in the declared methods list.
// However, since Java 7 the "current position" is not valid since the JDK no longer
// returns declared methods in the order in which they are declared in the source code.
// Thus, we now hard code the declarationOrderInAspect to 0 for all advice methods
// discovered via reflection in order to support reliable advice ordering across JVM launches.
// Specifically, a value of 0 aligns with the default value used in
// AspectJPrecedenceComparator.getAspectDeclarationOrder(Advisor).
// 尝试解析每个方法,找到方法对应的切点和通知
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, 0, aspectName);
if (advisor != null) {
// 解析完后放入集合
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
// 这里的分支一般不会走进..所以直接略过吧,别问,问了就是我大致略了一眼就不想看了
if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {
Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);
advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);
}
// 处理 @DeclareParents 注解
for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields()) {
Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
return advisors;
}
二、postProcessAfterInitialization

一 、postProcessAfterInitialization源码
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
// 判断这个对象是否创建成功..
if (bean != null) {
// 获取一个 key ,用于缓存..
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
// 这里就是去搞代理去了
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
一、wrapIfNecessary(包装目标类,如果需要的话),返回代理对象
一、获取当前bean的所有增强器(通知方法) getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
1、找到候选的所有的增强器(找哪些通知方法是需要切入当前bean方法的),findCandidateAdvisors()2、获取到能在当前bean使用的增强器。findAdvisorsThatCanApply
3、给增强器排序 this.sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors)
二、保存当前bean在advisedBeans中;
三、如果当前bean需要增强,创建当前bean的代理对象
1、获取所有增强器(通知方法)
2、保存到proxyFactory
3、创建代理对象:Spring自动决定
JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);jdk动态代理;如果这个类有实现接口使用jdk
ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);cglib的动态代理;四、给容器中返回当前组件使用cglib增强了的代理对象
五、以后容器中获取到的就是这个组件的代理对象,执行目标方法的时候,代理对象就会执行通知方法的流程
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 判断 beanName是正常的 并且 targetSourcedBeans 已经存在则会直接返回
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
//判断 Bean 是不是 不需要增强,如果不需要直接返回
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
//判断 是不是 切面 这里上面已经分析过了....
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
// 如果是 切面 放入到集合当中,
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
// 创建代理对象
// 1. 获取当前Bean 的所有增强器(通知方法)
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
// 如果不是 null 则会去生成代理对象,否则则标记当前类不需要进行代理.
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
// 将其放入到集合当中代表已经增强过了...
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 创建代理
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
// 将数据进行缓存
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
// 返回代理对象...
return proxy;
}
// 如果不需要代理则设置为 False 当下次进来的时候会直接返回(细节)
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean:获取当前Bean 的所有增强器(通知方法)
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
//获取这个类型的所有增强器
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
// 如果是一个空的 则返回 一个空的 数组
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
// 将其转换成数组返回
return advisors.toArray();
}
findEligibleAdvisors(找到合适的增强器)
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
//获取所有的增强器,这里之前已经分析过了就不分析了..
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
//找到适合的增强器
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
// 对增强器进行 排序
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
findAdvisorsThatCanApply(找到能够应用的增强器)
protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName);
try {
// 返回当前Bean能用的增强器
return AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass);
}
finally {
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(null);
}
}
静态方法findAdvisorsThatCanApply(找到能够应用的增强器)
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
// 如果是空..就直接返回..
if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
return candidateAdvisors;
}
//存放 合格的 增强器
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>();
//循环所有的增强器
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
//判断类型是不是整个类型的
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor
// 去应用..
&& canApply(candidate, clazz)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();
// 循环所有的增强器
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
//判断如果是这个类型的就跳过,因为上个循环已经处理过了
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// already processed
continue;
}
// 判断是不是能用的增强器,如果是能用的则添加到集合当中去
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
canApply(能够应用的增强器)
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
// 判断 是不是这个类型的
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);
}
// 判断 是不是这个类型的
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
// 判断切入点表达式是否匹配
return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
// 它没有切入点,因此我们假设它适用。
return true;
}
}
静态方法canApply(能够应用的增强器)
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
// 这一步会去解析 切入点表达式...
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
}
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// 判断是否是 Proxy 的子类并且 proxyClassCache 存在 这个类
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass));
}
// 返回当前类的所实现的所有的接口..
classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
// 获取当前类上包括父类的所有方法
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
// 循环所有方法
for (Method method : methods) {
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) :
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
getClassFilter(获取切点表达式)
public ClassFilter getClassFilter() {
obtainPointcutExpression();
return this;
}
obtainPointcutExpression(获取切入点表达式)
private PointcutExpression obtainPointcutExpression() {
// 如果表达式不存在 抛出异常...
if (getExpression() == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Must set property 'expression' before attempting to match");
}
// 如果 切入点表达式 是null 去进行解析,因为我们的表达式可能是 通过@Pointcut 的方式
if (this.pointcutExpression == null) {
this.pointcutClassLoader = determinePointcutClassLoader();
this.pointcutExpression = buildPointcutExpression(this.pointcutClassLoader);
}
return this.pointcutExpression;
}
buildPointcutExpression,解析表达式
private PointcutExpression buildPointcutExpression(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 初始化基础的Aspect切入点解析器
PointcutParser parser = initializePointcutParser(classLoader);
// 获取切入点参数...
PointcutParameter[] pointcutParameters = new PointcutParameter[this.pointcutParameterNames.length];
for (int i = 0; i < pointcutParameters.length; i++) {
// 将参数和类型包装一下 放入到数组中
pointcutParameters[i] = parser.createPointcutParameter(
this.pointcutParameterNames[i], this.pointcutParameterTypes[i]);
}
// 这里嵌套了3个方法....而且还异常复杂我都不忍心看...
return parser.parsePointcutExpression(replaceBooleanOperators(resolveExpression()),
this.pointcutDeclarationScope, pointcutParameters);
}
private String resolveExpression() {
// 获取表达式
String expression = getExpression();
Assert.state(expression != null, "No expression set");
// 返回表达式
return expression;
}
private String replaceBooleanOperators(String pcExpr) {
// 将表达式中的 and 替换
String result = StringUtils.replace(pcExpr, " and ", " && ");
// 将表达式中的 or 替换
result = StringUtils.replace(result, " or ", " || ");
// 将表达式中的 not 替换
result = StringUtils.replace(result, " not ", " ! ");
return result;
}
public PointcutExpression parsePointcutExpression(String expression, Class<?> inScope, PointcutParameter[] formalParameters)
throws UnsupportedPointcutPrimitiveException, IllegalArgumentException {
PointcutExpressionImpl pcExpr = null;
try {
// 这里是对表达式的进行处理,具体的可以自己深究去
Pointcut pc = resolvePointcutExpression(expression, inScope, formalParameters);
// 将表达式具体化,比如我使用的是 @Before("方法()") 这里是去将 "方法()" 转换成具体的 表达式
pc = concretizePointcutExpression(pc, inScope, formalParameters);
// again, because we have now followed any ref'd pcuts
validateAgainstSupportedPrimitives(pc, expression);
// 包装成 对象返回
pcExpr = new PointcutExpressionImpl(pc, expression, formalParameters, getWorld());
} catch (ParserException pEx) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(buildUserMessageFromParserException(expression, pEx));
} catch (ReflectionWorld.ReflectionWorldException rwEx) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(rwEx.getMessage());
}
return pcExpr;
}
matches(匹配当前类)
public boolean matches(Class<?> targetClass) {
// 这里是去获取 切入点表达式.. 也包括了解析(这里其实在 getClassFilter) 已经解析过了~~
PointcutExpression pointcutExpression = obtainPointcutExpression();
try {
try {
//根据表达式的解析实例,验证此类是否匹配
return pointcutExpression.couldMatchJoinPointsInType(targetClass);
}
catch (ReflectionWorldException ex) {
logger.debug("PointcutExpression matching rejected target class - trying fallback expression", ex);
// Actually this is still a "maybe" - treat the pointcut as dynamic if we don't know enough yet
PointcutExpression fallbackExpression = getFallbackPointcutExpression(targetClass);
if (fallbackExpression != null) {
return fallbackExpression.couldMatchJoinPointsInType(targetClass);
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.debug("PointcutExpression matching rejected target class", ex);
}
return false;
}
couldMatchJoinPointsInType(判断当前类是否可以匹配切入点),仅仅是去匹配当前类是否符合规则
public boolean couldMatchJoinPointsInType(Class aClass) {
ResolvedType matchType = world.resolve(aClass.getName());
if (matchType.isMissing() && (world instanceof ReflectionWorld)) {
// Class is a generated class that cannot be 'looked up' via getResource.
// For example a proxy or lambda.
// Use the class itself in this case
matchType = ((ReflectionWorld)world).resolveUsingClass(aClass);
}
ReflectionFastMatchInfo info = new ReflectionFastMatchInfo(matchType, null, this.matchContext, world);
//根据切入点和 目标类,判断类 package 是否匹配
boolean couldMatch = pointcut.fastMatch(info).maybeTrue();
return couldMatch;
}
上面主要是为了去进行匹配符合规则的类,当匹配成功的时候才会去创建代理对象
二、createProxy,创建代理对象
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
//创建 代理工厂
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
// 将当前类的一些配置进行 复制 ,简单来说就是获取 XML 或者注解配置的属性..
// 这里可以参考一下:
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
// 判断是否是通过接口 默认是 False
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
//根据最开始@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解中的proxyTargetClass参数判断是否应该使用cglib代理
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
//标识 使用cglib动态代理
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
} else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
// 获取到增强器
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
// 放入到 代理工厂
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
// 设置 目标 对象
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
// 留个子类去实现的一个方法,也就是说我们可以通过重写这个方法进行定制
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
getProxy:取决于 createAopProxy 返回的是 CGlib 还是JDK 代理
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
// createAopProxy() 获取AOP 工厂判断 CGlib还是JDK
return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);
}
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
if (!this.active) {
activate();
}
// 获取到 AOP 代理工厂
// 然后判断 是 Cglib 还是JDK
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
}
createAopProxy
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (!IN_NATIVE_IMAGE &&
(config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config))) {
// optimize 默认是 false
// ProxyTargetClass 默认是 false
// hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces 被代理的类没有实现接口
// 获取目标 Class
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
// 判断当前类是不是接口
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
四、目标方法的执行
容器中保存了组件的代理对象(cglib增强后的对象),这个对象里面保存了详细信息(比如增强器,目标对象,xxx)
 一、CglibAopProxy.intercept();拦截目标方法的执行
一、CglibAopProxy.intercept();拦截目标方法的执行
从目标方法执行中进去是CglibAopProxy对象中的intercept()方法,拦截目标方法的执行。
二、根据ProxyFactory对象获取将要执行的目标方法拦截器链
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);

一、List<Object> interceptorList保存所有拦截器,长度为5,遍历所有的增强器,将其转为Interceptor
一个默认的ExposeInvocationInterceptor 和 4个增强器;
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Advised config, Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance();
Advisor[] advisors = config.getAdvisors();
// 保存所有拦截器,长度为5
List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList(advisors.length);
Class<?> actualClass = targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass();
Boolean hasIntroductions = null;
Advisor[] var9 = advisors;
int var10 = advisors.length;
// 循环之前获取到的所有增强方法
for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) {
Advisor advisor = var9[var11];
// 如果类型是PointcutAdvisor,进入此逻辑
if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor)advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher();
boolean match;
if (mm instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
if (hasIntroductions == null) {
hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(advisors, actualClass);
}
match = ((IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher)mm).matches(method, actualClass, hasIntroductions);
} else {
match = mm.matches(method, actualClass);
}
if (match) {
// 将增强方法转换成MethodInterceptor
MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
if (mm.isRuntime()) {
MethodInterceptor[] var17 = interceptors;
int var18 = interceptors.length;
for(int var19 = 0; var19 < var18; ++var19) {
MethodInterceptor interceptor = var17[var19];
interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm));
}
} else {
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
}
// IntroductionAdvisor类型进入
} else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor)advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
} else {
// 直接转换为MethodInterceptor放入拦截器数组中,然后放入拦截器链集合
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
return interceptorList;
}二、getInterceptors获取所有的MethodInterceptor[]数组,也就是Interceptor拦截器数组,也就是最后的拦截器链
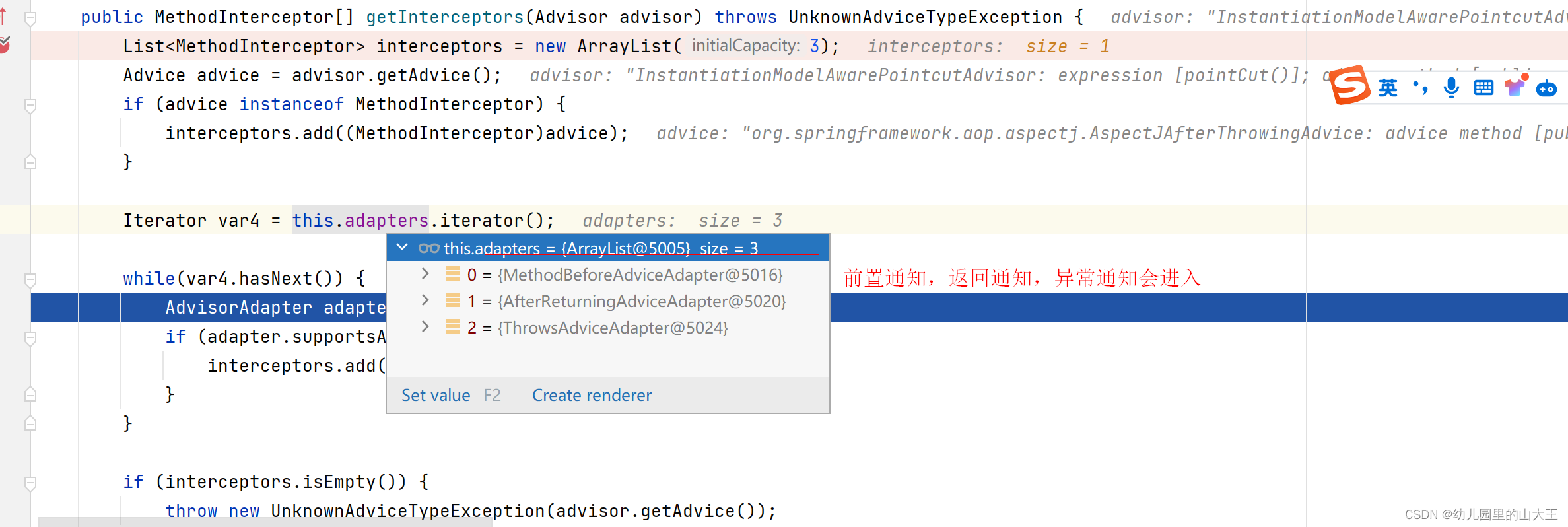
public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {
List<MethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList(3);
Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice();
// 如果增强器实现了MethodInterceptor,也就是是MethodInterceptor类型的直接加入
if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {
interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor)advice);
}
Iterator var4 = this.adapters.iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
AdvisorAdapter adapter = (AdvisorAdapter)var4.next();
// 如果是前置通知、返回通知、异常通知,则进入下面进行适配器转换成MethodInterceptor
if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {
interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor));
}
}
if (interceptors.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice());
} else {
return (MethodInterceptor[])interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[0]);
}
}
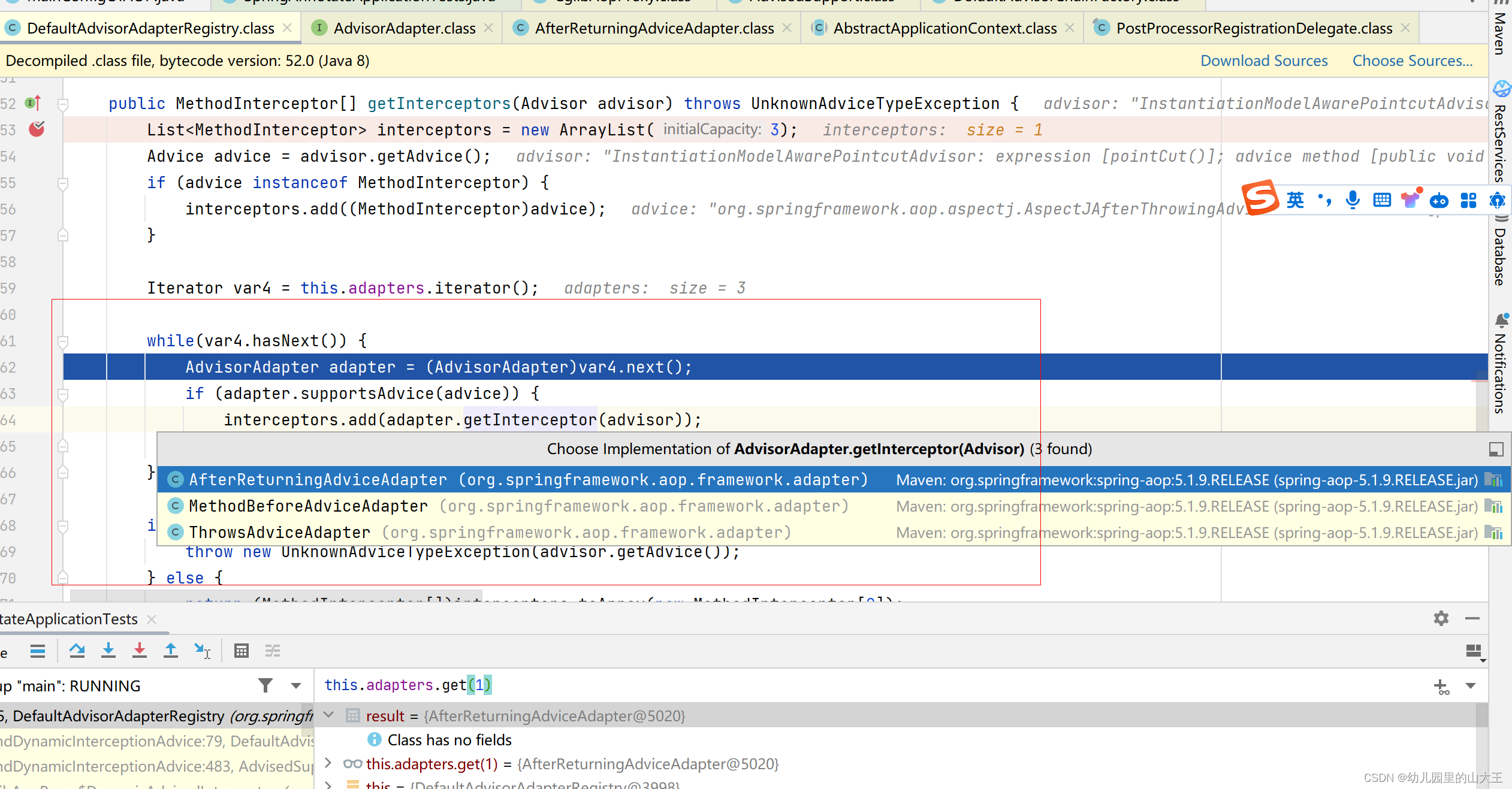
三、adapter.getInterceptor(advisor),转化MethodInterceptor逻辑
1、如果是MethodInterceptor,直接加入到集合中
2、如果不是,使用AdvisorAdapter将增强器转为MethodInterceptor, 转换完成返回MethodInterceptor数组;一般前置通知、返回通知、异常通知会走这一步,
if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) { interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor)); }其中adapter.getInterceptor(advisor)有三个实现类,前置通知、返回通知、异常通知实现类
前置通知转换实现类,MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter
class MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter implements AdvisorAdapter, Serializable {
MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter() {
}
public boolean supportsAdvice(Advice advice) {
return advice instanceof MethodBeforeAdvice;
}
public MethodInterceptor getInterceptor(Advisor advisor) {
// 其实就是一个强转,再封装
MethodBeforeAdvice advice = (MethodBeforeAdvice)advisor.getAdvice();
return new MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(advice);
}
}
MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor 再次封装对象,也就是把MethodBeforeAdvice作为成员对象放进去,然后在执行目标方法前调用。其他返回通知则是在执行完方法返回时执行。
public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, BeforeAdvice, Serializable {
private final MethodBeforeAdvice advice;
public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) {
Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null");
this.advice = advice;
}
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
return mi.proceed();
}
}
三、如果没有拦截器链,直接执行目标方法
拦截器链(每一个通知方法又被包装为方法拦截器,利用MethodInterceptor机制),
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
直接执行目标方法
四、如果有拦截器链,把需要执行的目标对象,目标方法,拦截器链等信息传入创建一个 CglibMethodInvocation 对象,并调用 Object retVal = mi.proceed();
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
// 直接执行拦截的目标方发生
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
} else {
// 如果有有拦截器链,把需要执行的目标对象,目标方法,拦截器链等信息传入创建一个 CglibMethodInvocation 对象,并调用 proceed(),逐个执行拦截器,这里其实就是触发拦截器链的执行
retVal = (new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy)).proceed();
}五、执行拦截器链
一、proceed()
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
/**currentInterceptorIndex 默认为-1,
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers就是增强方法的数量,也就是拦截器连的长度
这里意思就是当拦截器链执行到最后一个时,也就是0 - 1 等于currentInterceptorIndex时,也就是如果没有拦截器执行执行目标方法,或者拦截器的索引和拦截器数组-1大小一样(指定到了最后一个拦截器)执行目标方法
**/
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return this.invokeJoinpoint();
} else {
// 拿到第++this.currentInterceptorIndex 个拦截器,-1,0,1,2这种顺序
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm = (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher)interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
/* 上面进行一系列类型判断,然后调用拦截器的invoke方法,传入this
然后点击dm.interceptor.invoke(this),发现回去执行MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor对象里面的invoke方法
*/
Class<?> targetClass = this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass();
return dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments) ? dm.interceptor.invoke(this) : this.proceed();
} else {
return ((MethodInterceptor)interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
}
二、 proceed()里面的dm.interceptor.invoke(this)方法
dm.interceptor.invoke(this)有多个实现类,


会按照这个顺序去执行拦截器
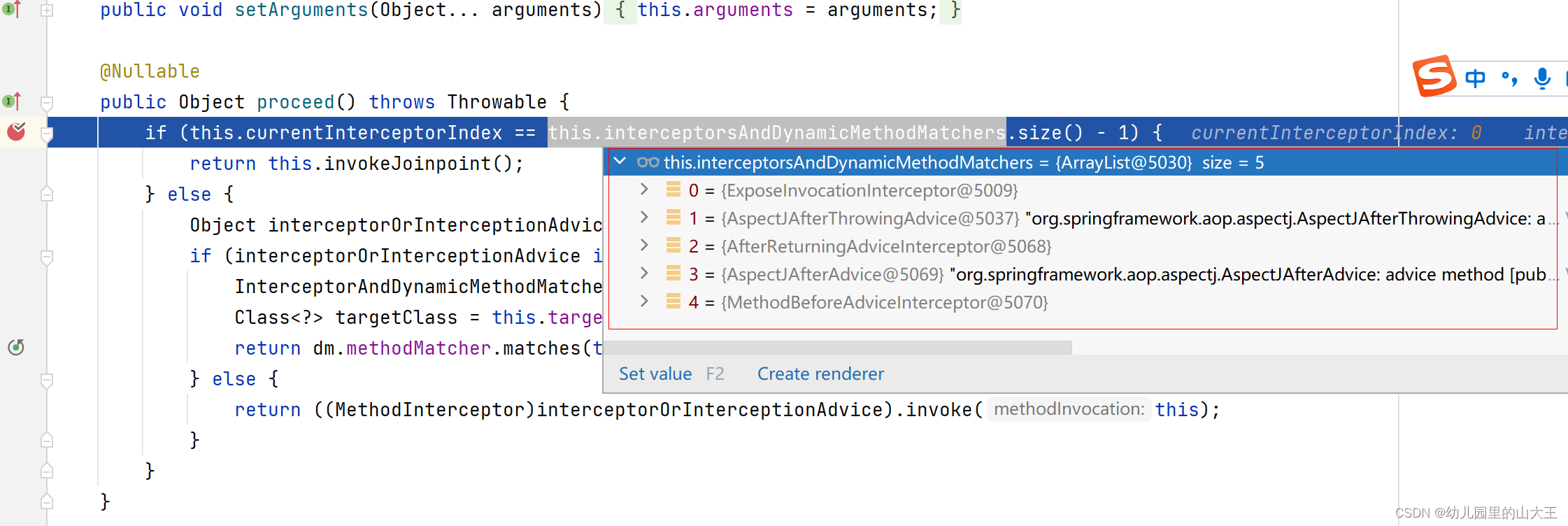
1、首先会去执行ExposeInvocationInterceptor对象的invoke方法,执行mi.proceed();会发现,又再一次进入了一里面的proceed()方法里,只不过这个时候,索引变了。currentInterceptorIndex变为了0,interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers将少了一个,再次调用invoke方法,进入2
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation oldInvocation = (MethodInvocation)invocation.get();
invocation.set(mi);
Object var3;
try {
var3 = mi.proceed();
} finally {
invocation.set(oldInvocation);
}
return var3;
}
2、执行AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice拦截器里面的invoke方法,然后进入mi.proceed(),currentInterceptorIndex变为了1,interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers将少了一个,再次调用invoke方法,进入3
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
return mi.proceed();
} catch (Throwable var3) {
if (this.shouldInvokeOnThrowing(var3)) {
this.invokeAdviceMethod(this.getJoinPointMatch(), (Object)null, var3);
}
throw var3;
}
}
3、然后 AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor里面的invoke方法,再次进入mi.proceed()里面,currentInterceptorIndex变为了2,interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers将少了一个,再次调用invoke方法,进入4
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
Object retVal = mi.proceed();
this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
return retVal;
}
4、然后在AspectJAfterAdvice中的invoke方法执行mi.proceed(),然后currentInterceptorIndex变为了3,interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers将少了一个,再次调用一个拦截器
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
Object var2;
try {
var2 = mi.proceed();
} finally {
this.invokeAdviceMethod(this.getJoinPointMatch(), (Object)null, (Throwable)null);
}
return var2;
}
5、然后拿到最后一个拦截器MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor,执行里面的invoke方法,会先执行 this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());,currentInterceptorIndex变为了4,interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers将少了一个也就是5-1,再次调用invoke方法
1、执行前置通知方法
2、然后调用mi.proceed();,进去发现currentInterceptorIndex = interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers的大小了,然后直接执行proceed()里面的this.invokeJoinpoint();方法,这个方法是利用反射执行目标方法。
3、然后执行完以后,会返回上一个拦截器,AspectJAfterAdvice继续执行剩下逻辑,也就是finally里面的方法,意思就是不管有没有异常都执行invokeAdviceMethod方法,也就是后置通知。
4、再返回到AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor继续执行剩下的逻辑,但是如果mi.proceed()执行抛出异常,AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor并没有进行catch处理,而是直接抛出给上一层AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice处理。如果没有出现异常,AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor将会在mi.proceed()执行后执行afterReturning方法,也就是返回通知。
5、也就是说出现异常AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice处理,没有出现异常AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor处理。这是由于AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor有进行catch处理,执行里面的invokeAdviceMethod异常通知
public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, BeforeAdvice, Serializable {
private final MethodBeforeAdvice advice;
public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) {
Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null");
this.advice = advice;
}
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
return mi.proceed();
}
}
6、整个调用链执行也就是,链式获取每一个拦截器,拦截器执行invoke方法,每一个拦截器等待下一个拦截器执行完成返回以后再来执行;拦截器链的机制,保证通知方法与目标方法的执行顺序;
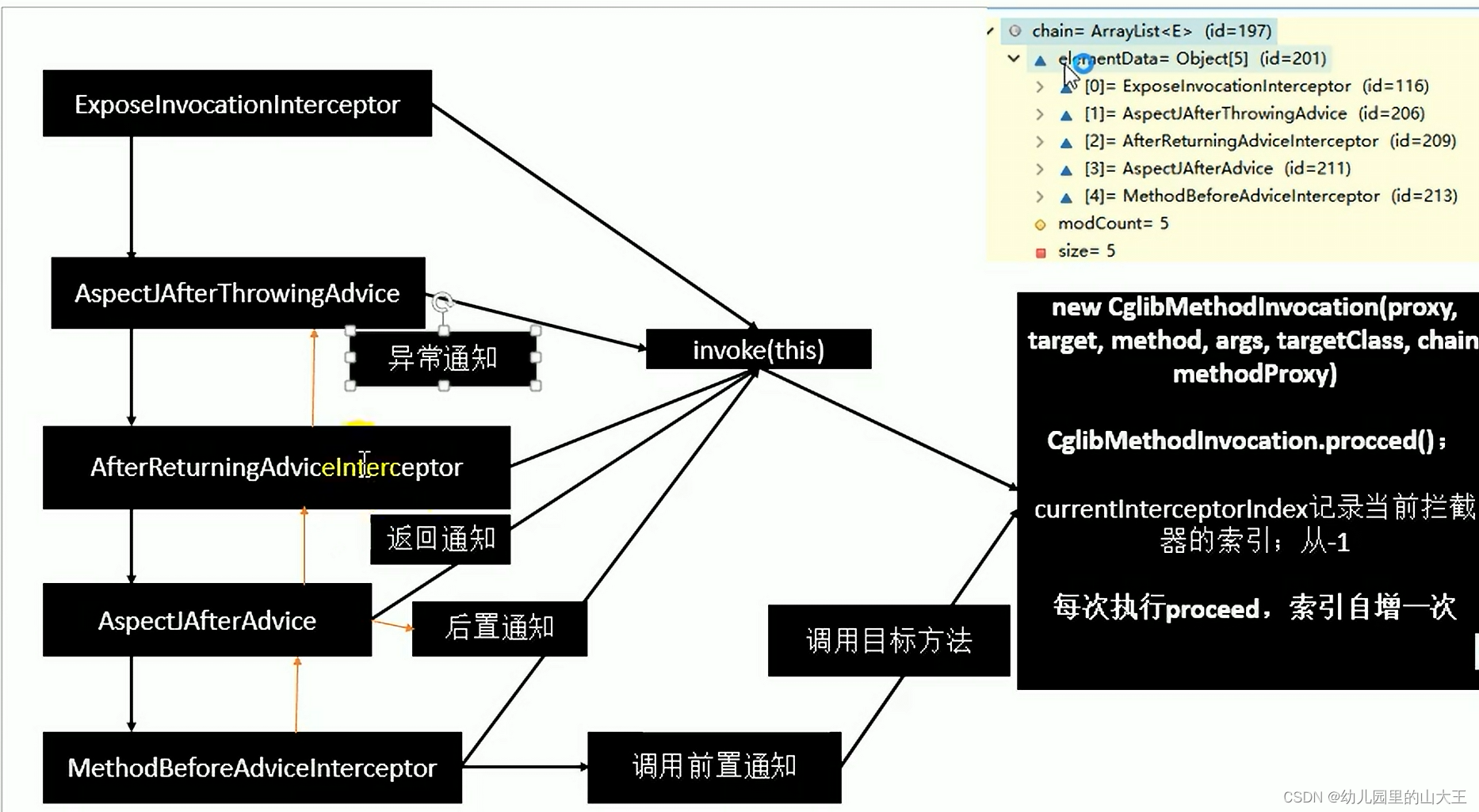
五、最后做一个总结
一、@EnableAspectJAutoProxy 开启AOP功能
二、@EnableAspectJAutoProxy 会给容器中注册一个组件 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
三、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator是一个后置处理器;
四、容器的创建流程:
1、registerBeanPostProcessors()注册后置处理器;创建AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator对象
2、finishBeanFactoryInitialization()初始化剩下的单实例bean
1)、创建业务逻辑组件和切面组件
2)、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator拦截组件的创建过程
3)、组件创建完之后,判断组件是否需要增强
是:切面的通知方法,包装成增强器(Advisor);给业务逻辑组件创建一个代理对象(cglib);五、执行目标方法:
1、代理对象执行目标方法
2、CglibAopProxy.intercept();1)、得到目标方法的拦截器链(增强器包装成拦截器MethodInterceptor)
2)、利用拦截器的链式机制,依次进入每一个拦截器进行执行;
3)、执行顺序:
正常执行:前置通知-》目标方法-》后置通知-》返回通知
出现异常:前置通知-》目标方法-》后置通知-》异常通知