本文旨在补充@gwpscut创作的博文学习笔记之——3D Gaussian Splatting源码解读。
Gaussian Splatting Github地址:https://github.com/graphdeco-inria/gaussian-splatting
论文地址:https://repo-sam.inria.fr/fungraph/3d-gaussian-splatting/3d_gaussian_splatting_high.pdf
目录
- 一、预备知识:球谐(Spherical Harmonics)
- 二、高斯场景类:`GaussianModel`
- 1. `def setup_functions(self)`
- 2. `def __init__(self, sh_degree : int)`
- 3. `def create_from_pcd(self, pcd : BasicPointCloud, spatial_lr_scale : float)`
- 4. `ply`文件相关:`def construct_list_of_attributes(self)`、`def save_ply(self, path)`和`def load_ply(self, path)`
- 5. 优化器和学习率相关
- 6. 重置不透明度:`def reset_opacity(self)`
- 7. Gaussian的删除和新增
一、预备知识:球谐(Spherical Harmonics)
这部分可以参考PlenOctrees论文的附录B。
有时候从不同的角度看同一个物体看到的景象是不一样的(比如激光笔,它只朝一个固定的方向发光),所以需要定义从一个三维单位球体上各点观察一个物体所得的颜色函数。记这样的一个函数为 L ( θ , φ ) L(\theta,\varphi) L(θ,φ),其中 θ ∈ [ 0 , π ] \theta\in[0,\pi] θ∈[0,π]是纬度, φ ∈ [ 0 , 2 π ) \varphi\in[0,2\pi) φ∈[0,2π)是经度。任何从 [ 0 , π ] × [ 0 , 2 π ) [0,\pi]\times [0,2\pi) [0,π]×[0,2π)映射到 C \mathbb{C} C的函数都可以经过傅里叶变换表达为一系列函数 Y l m Y^m_l Ylm的线性组合,其中 l ∈ N l\in\mathbb{N} l∈N称为度数(degree), m ∈ { − l , − l + 1 , ⋯ , 0 , ⋯ , l − 1 , l } m\in\{-l,-l+1,\cdots,0,\cdots,l-1,l\} m∈{−l,−l+1,⋯,0,⋯,l−1,l}称为阶数(order)。 Y l m Y^m_l Ylm定义为 Y l m ( θ , φ ) = 2 l + 1 4 π ( l − m ) ! ( l + m ) ! P l m ( cos θ ) e i m φ Y^m_l(\theta,\varphi)=\sqrt{\frac{2l+1}{4\pi}\frac{(l-m)!}{(l+m)!}} P_l^m(\cos\theta)e^{im\varphi} Ylm(θ,φ)=4π2l+1(l+m)!(l−m)!Plm(cosθ)eimφ其中 P l m ( cos θ ) e i m φ P_l^m(\cos\theta)e^{im\varphi} Plm(cosθ)eimφ是勒让德多项式。当然这里的 Y l m Y^m_l Ylm是复数,我们可以定义对应的实数版本 Y l m ( θ , φ ) = { 2 ( − 1 ) m Im [ Y l ∣ m ∣ ] , m < 0 Y l 0 , m = 0 2 ( − 1 ) m Re [ Y l m ] , m > 0 Y^m_l(\theta,\varphi)=\begin{cases}\sqrt{2}(-1)^m\operatorname{Im}[Y_l^{|m|}],&m<0\\ Y_l^0,&m=0\\ \sqrt{2}(-1)^m\operatorname{Re}[Y_l^{m}],&m>0 \end{cases} Ylm(θ,φ)=⎩ ⎨ ⎧2(−1)mIm[Yl∣m∣],Yl0,2(−1)mRe[Ylm],m<0m=0m>0任何实的求函数 L : [ 0 , π ] × [ 0 , 2 π ) → R L:[0,\pi]\times [0,2\pi)\to\mathbb{R} L:[0,π]×[0,2π)→R都可以用球谐基来表达: L ( θ , φ ) = ∑ l = 0 ∞ ∑ m = − l l k l m Y l m ( θ , φ ) L(\theta,\varphi)=\sum\limits_{l=0}^\infty\sum\limits_{m=-l}^l k_l^m Y_l^m(\theta,\varphi) L(θ,φ)=l=0∑∞m=−l∑lklmYlm(θ,φ)其中 k l m k_l^m klm是对应的傅里叶系数。特别地,直流分量 Y 0 0 = 1 2 π Y_0^0=\frac{1}{2\sqrt\pi} Y00=2π1。当然我们不可能真的把 l l l考虑到无穷;一般来说 l l l是有限值就可以了,再高的频率也用不到。如果我们令最高度数为 l m a x l_\mathrm{max} lmax,则一共需要 ∑ l = 0 l m a x ( 2 l + 1 ) = ( l m a x + 1 ) 2 \sum\limits_{l=0}^{l_\mathrm{max}}(2l+1)=(l_\mathrm{max}+1)^2 l=0∑lmax(2l+1)=(lmax+1)2个系数。
你可能对这个形式感到很陌生,但如果你回忆一下量子力学就会感觉很亲切了。其实 l l l就是角量子数, m m m就是磁量子数, m m m的取值刚好就是 − l -l −l到 l l l。
二、高斯场景类:GaussianModel
首先我们当然要看一下GaussianModel类的定义,这个类描述了怎么定义一个包含大量Gaussians的场景。它在scene/gaussian_model.py中被定义。
我们选一些有意义的函数进行分析。
1. def setup_functions(self)
def setup_functions(self):
def build_covariance_from_scaling_rotation(scaling, scaling_modifier, rotation):
L = build_scaling_rotation(scaling_modifier * scaling, rotation)
actual_covariance = L @ L.transpose(1, 2)
symm = strip_symmetric(actual_covariance)
return symm
self.scaling_activation = torch.exp
self.scaling_inverse_activation = torch.log
self.covariance_activation = build_covariance_from_scaling_rotation
self.opacity_activation = torch.sigmoid
self.inverse_opacity_activation = inverse_sigmoid
self.rotation_activation = torch.nn.functional.normalize
这个方法主要是初始化一些GaussianModel类涉及的函数。将缩放的激活函数设置为指数函数,我猜测其原因可能是缩放必须是正数,而指数函数的返回值一定是正数。用Sigmoid作为不透明度的激活函数是因为不透明度必须在0到1之间。旋转的激活函数是归一化。
协方差的激活函数比较复杂:首先从缩放及其修饰项、旋转参数得到
L
L
L矩阵,将其与自己的转置相乘得到一个对称矩阵,最后用strip_symmetric函数截取其下三角部分来节省空间(可能吧?)。论文第4节提到,协方差矩阵
Σ
=
R
S
S
T
R
T
\Sigma=RSS^T R^T
Σ=RSSTRT,其中
S
S
S是缩放矩阵,
R
R
R是旋转矩阵。缩放矩阵用3D向量
s
s
s表示得到,旋转用四元数
q
q
q得到。
q
q
q必须经过归一化,这就是为什么旋转的激活函数是归一化。根据utils/general_utils.py的build_scaling_rotation函数,
S
=
diag
(
s
)
=
diag
(
s
0
,
s
1
,
s
2
)
S=\operatorname{diag}(s)=\operatorname{diag}(s_0,s_1,s_2)
S=diag(s)=diag(s0,s1,s2),
R
R
R与
q
q
q的关系很复杂(见build_rotation函数),其中
q
q
q是四维向量。
2. def __init__(self, sh_degree : int)
这是类的初始化方法。代码如下:
def __init__(self, sh_degree : int):
self.active_sh_degree = 0 # 目前的球谐阶数,在`oneupSHdegree()`方法中加一
# SH = Sphere Harmonics
self.max_sh_degree = sh_degree # 最大可能达到的的球谐阶数
self._xyz = torch.empty(0) # 每个Gaussian的中心坐标
self._features_dc = torch.empty(0) # 球谐的直流分量(dc = Direct Current)
self._features_rest = torch.empty(0) # 球谐的其他高阶特征
self._scaling = torch.empty(0) # 缩放参数
self._rotation = torch.empty(0) # 旋转参数(一系列四元数)
self._opacity = torch.empty(0) # 不透明度(经历sigmoid前的)
self.max_radii2D = torch.empty(0) # 在某个相机视野里出现过的(像平面上的)最大2D半径,详见train.py里面gaussians.max_radii2D[visibility_filter] = ...一行
self.xyz_gradient_accum = torch.empty(0) # 每个Gaussian的坐标梯度积累,当它太大的时候要对Gaussian进行分裂或复制(见论文5.2节)
self.denom = torch.empty(0) # 与累积梯度配合使用,表示统计了多少次累积梯度,算平均梯度时除掉这个(denom = denominator,分母)
self.optimizer = None # 优化器(论文中采用Adam,见附录B Algorithm 1的伪代码)
self.percent_dense = 0 # 参与控制Gaussian密集程度的超参数
self.spatial_lr_scale = 0 # 坐标的学习率要乘上这个,抵消在不同尺度下应用同一个学习率带来的问题
self.setup_functions()
其中目前能推断出的变量含义已写在注释中。我们将会更进一步地探讨变量的具体含义。
3. def create_from_pcd(self, pcd : BasicPointCloud, spatial_lr_scale : float)
其中BasicPointCloud的定义如下(utils/graphic_utils.py):
class BasicPointCloud(NamedTuple):
points : np.array
colors : np.array
normals : np.array
create_from_pcd在scene/__init__.py中Scene类的构造函数
def __init__(self, args : ModelParams, gaussians : GaussianModel, load_iteration=None, shuffle=True, resolution_scales=[1.0])
中被调用。
- 首先,如果
load_iteration参数不是None,Scene.__init__会在输出文件夹下的point_cloud/文件夹搜索迭代次数最大的iteration_xxx文件夹(例如有iteration_7000和iteration_30000的文件夹则选取后者),将最大的迭代次数记录到self.loaded_iter。 - 然后构造函数会判断
args.source_path对应的文件夹是COLMAP的输出还是Blender的输出,并从中读取场景信息到变量scene_info。 - 最后,如果
self.loaded_iter有值,则直接读取对应的(已经迭代出来的)场景;如果没有,也就意味着load_iteration = None,换言之,模型还没有训练过,此时就调用GaussianModel.create_from_pcd从scene_info.point_cloud中建立模型。
我们重点关注scene_info.point_cloud是SfM工具COLMAP输出结果的情形。论文多处提到Gaussian Splatting用COLMAP的稀疏输出来初始化Gaussians的位置。此时,用于加载COLMAP输出的函数是scene.dataset_readers.sceneLoadTypeCallbacks["Colmap"],也就是scene/dataset_readers.py中的readColmapSceneInfo函数。COLMAP的输出中有一个sparse/0文件夹,其中有三个文件:
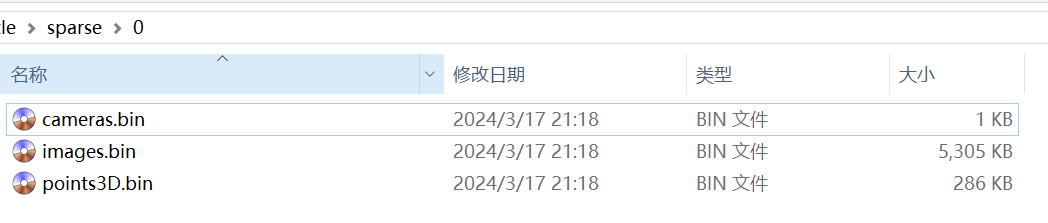
cameras.bin和images.bin分别是相机的内外参,points3D.bin是COLMAP产生的稀疏点云,由scene.colmap_loader.read_points3D_binary函数读取,它会返回各点的xyz、rgb和意义不明的error。我推测scene_info.point_cloud.points是稀疏点云中各点的3D坐标,scene_info.point_cloud.colors是各点的颜色。
现在我们终于可以回到create_from_pcd方法了。该方法的代码以及我的注释讲解如下(令
N
N
N为点的个数):
def create_from_pcd(self, pcd : BasicPointCloud, spatial_lr_scale : float):
self.spatial_lr_scale = spatial_lr_scale
'''
根据scene.Scene.__init__以及
scene.dataset_readers.SceneInfo.nerf_normalization,
即scene.dataset_readers.getNerfppNorm的代码,
这个值似乎是训练相机中离它们的坐标平均值(即中心)最远距离的1.1倍,
根据命名推断应该与学习率有关,防止固定的学习率适配不同尺度的场景时出现问题。
'''
fused_point_cloud = torch.tensor(np.asarray(pcd.points)).float().cuda()
'''
不清楚这里"fused"(融合)的用意。不过它实际上就是稀疏点云的3D坐标。大小为(N, 3)
'''
fused_color = RGB2SH(torch.tensor(np.asarray(pcd.colors)).float().cuda())
'''
应为球谐的直流分量,大小为(N, 3)
RGB2SH(x) = (x - 0.5) / 0.28209479177387814
看样子pcd.colors的原始范围应该是0到1。
0.28209479177387814是1 / (2*sqrt(pi)),是直流分量Y(l=0,m=0)的值。
'''
features = torch.zeros((fused_color.shape[0], 3, (self.max_sh_degree + 1) ** 2)).float().cuda()
features[:, :3, 0 ] = fused_color
features[:, 3:, 1:] = 0.0
'''
RGB三通道球谐的所有系数,大小为(N, 3, (最大球谐阶数 + 1)²)
'''
print("Number of points at initialisation : ", fused_point_cloud.shape[0])
dist2 = torch.clamp_min(distCUDA2(torch.from_numpy(np.asarray(pcd.points)).float().cuda()), 0.0000001)
'''
dist2的大小应该是(N,)。
首先可以明确的是这句话用来初始化scale,且scale(的平方)不能低于1e-7。
我阅读了一下submodules/simple-knn/simple_knn.cu,大致猜出来了这个是什么意思。
(cu文件里面一句注释都没有,读起来真折磨!)
distCUDA2函数由simple_knn.cu的SimpleKNN::knn函数实现。
KNN意思是K-Nearest Neighbor,即求每一点最近的K个点。
simple_knn.cu中令k=3,求得每一点最近的三个点距该点的平均距离。
算法并没有实现真正的KNN,而是近似KNN。
原理是把3D空间中的每个点用莫顿编码(Morton Encoding)转化为一个1D坐标
(详见https://www.fwilliams.info/point-cloud-utils/sections/morton_coding/,
用到了能够填满空间的Z曲线),
然后对1D坐标进行排序,从而确定离每个点最近的三个点。
simple_knn.cu实际上还用了一种加速策略,是将点集分为多个大小为1024的块(box),
在每个块内确定3个最近邻居和它们的平均距离。用平均距离作为Gaussian的scale。
(我的解读不一定准确,如有错误请指正)
'''
scales = torch.log(torch.sqrt(dist2))[...,None].repeat(1, 3)
'''
因为scale的激活函数是exp,所以这里存的也不是真的scale,而是ln(scale)。
注意dist2其实是距离的平方,所以这里要开根号。
repeat(1, 3)标明三个方向上scale的初始值是相等的。
scales的大小:(N, 3)
'''
rots = torch.zeros((fused_point_cloud.shape[0], 4), device="cuda")
'''
旋转矩阵,大小为(N, 4)
'''
rots[:, 0] = 1
'''
初始化表示旋转的四元数为1(第0维为1,其他维为0)
'''
opacities = inverse_sigmoid(0.1 * torch.ones((fused_point_cloud.shape[0], 1), dtype=torch.float, device="cuda"))
'''
不透明度在经历sigmoid前的值,大小为(N, 1)
inverse_sigmoid是sigmoid的反函数,等于ln(x / (1 - x))。
这里把不透明度初始化为0.1(原因不明),但存储的时候要取其经历sigmoid前的值:
inverse_sigmoid(0.1) = -2.197
'''
self._xyz = nn.Parameter(fused_point_cloud.requires_grad_(True))
'''
作为参数的高斯椭球体中心坐标,(N, 3)
'''
self._features_dc = nn.Parameter(features[:,:,0:1].transpose(1, 2).contiguous().requires_grad_(True))
'''
RGB三个通道的直流分量,(N, 3, 1)
'''
self._features_rest = nn.Parameter(features[:,:,1:].transpose(1, 2).contiguous().requires_grad_(True))
'''
RGB三个通道的高阶分量,(N, 3, (最大球谐阶数 + 1)² - 1)
'''
self._scaling = nn.Parameter(scales.requires_grad_(True))
'''
作为参数的缩放
'''
self._rotation = nn.Parameter(rots.requires_grad_(True))
'''
作为参数的旋转四元数,(N, 4)
'''
self._opacity = nn.Parameter(opacities.requires_grad_(True))
'''
作为参数的不透明度(经过sigmoid之前),(N, 1)
'''
self.max_radii2D = torch.zeros((self.get_xyz.shape[0]), device="cuda")
'''
最大半径?初始化为0,大小为(N,)
'''
4. ply文件相关:def construct_list_of_attributes(self)、def save_ply(self, path)和def load_ply(self, path)
注意到模型被保存到了/point_cloud/iteration_xxx/point_cloud.ply文件中。我测试了一个火车场景并获得了一个这样的ply文件。用plyfile模块打开该文件:
p = PlyData.read('point_cloud.ply')
打印p.elements[0]的属性,得到:
('vertex',
(PlyProperty('x', 'float'),
PlyProperty('y', 'float'),
PlyProperty('z', 'float'),
PlyProperty('nx', 'float'),
PlyProperty('ny', 'float'),
PlyProperty('nz', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_dc_0', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_dc_1', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_dc_2', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_0', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_1', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_2', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_3', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_4', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_5', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_6', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_7', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_8', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_9', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_10', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_11', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_12', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_13', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_14', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_15', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_16', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_17', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_18', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_19', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_20', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_21', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_22', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_23', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_24', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_25', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_26', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_27', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_28', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_29', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_30', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_31', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_32', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_33', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_34', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_35', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_36', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_37', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_38', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_39', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_40', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_41', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_42', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_43', 'float'),
PlyProperty('f_rest_44', 'float'),
PlyProperty('opacity', 'float'),
PlyProperty('scale_0', 'float'),
PlyProperty('scale_1', 'float'),
PlyProperty('scale_2', 'float'),
PlyProperty('rot_0', 'float'),
PlyProperty('rot_1', 'float'),
PlyProperty('rot_2', 'float'),
PlyProperty('rot_3', 'float')))
其中每一项数据的大小应该都是(N,)。我们看到x,y,z,四个rot,三个scale,以及RGB三个通道的球谐参数:f_dc_x为直流分量,f_rest_xx为其他高阶分量。关于球谐的参数共有48个,每个通道16个,据此得知球谐的最高度数为3。nx、ny、nz打印出来都是全0,我也不知道是干什么的。
这样就不难理解下面的construct_list_of_attributes函数:
def construct_list_of_attributes(self): # 构建ply文件的键列表
l = ['x', 'y', 'z', 'nx', 'ny', 'nz']
# All channels except the 3 DC
for i in range(self._features_dc.shape[1]*self._features_dc.shape[2]):
l.append('f_dc_{}'.format(i))
'''
注意self._features_dc: (N, 3, 1)
'''
for i in range(self._features_rest.shape[1]*self._features_rest.shape[2]):
l.append('f_rest_{}'.format(i))
'''
self._features_rest: (N, 3, (最大球谐阶数 + 1)² - 1)
'''
l.append('opacity')
for i in range(self._scaling.shape[1]): # shape[1]: 3
l.append('scale_{}'.format(i))
for i in range(self._rotation.shape[1]): # shape[1]: 4
l.append('rot_{}'.format(i))
return l
以及save_ply函数:
def save_ply(self, path):
mkdir_p(os.path.dirname(path))
xyz = self._xyz.detach().cpu().numpy()
normals = np.zeros_like(xyz) # nx, ny, nz;全是0,不知何用
f_dc = self._features_dc.detach().transpose(1, 2).flatten(start_dim=1).contiguous().cpu().numpy()
f_rest = self._features_rest.detach().transpose(1, 2).flatten(start_dim=1).contiguous().cpu().numpy()
opacities = self._opacity.detach().cpu().numpy()
scale = self._scaling.detach().cpu().numpy()
rotation = self._rotation.detach().cpu().numpy()
dtype_full = [(attribute, 'f4') for attribute in self.construct_list_of_attributes()]
elements = np.empty(xyz.shape[0], dtype=dtype_full)
attributes = np.concatenate((xyz, normals, f_dc, f_rest, opacities, scale, rotation), axis=1) # 所有要保存的值合并成一个大数组
elements[:] = list(map(tuple, attributes))
el = PlyElement.describe(elements, 'vertex')
PlyData([el]).write(path)
而load_ply函数的作用也就是读取ply文件并把数据转换成torch.nn.Parameter等待优化:
def load_ply(self, path):
plydata = PlyData.read(path)
xyz = np.stack((np.asarray(plydata.elements[0]["x"]),
np.asarray(plydata.elements[0]["y"]),
np.asarray(plydata.elements[0]["z"])), axis=1)
opacities = np.asarray(plydata.elements[0]["opacity"])[..., np.newaxis]
features_dc = np.zeros((xyz.shape[0], 3, 1))
features_dc[:, 0, 0] = np.asarray(plydata.elements[0]["f_dc_0"])
features_dc[:, 1, 0] = np.asarray(plydata.elements[0]["f_dc_1"])
features_dc[:, 2, 0] = np.asarray(plydata.elements[0]["f_dc_2"])
extra_f_names = [p.name for p in plydata.elements[0].properties if p.name.startswith("f_rest_")]
extra_f_names = sorted(extra_f_names, key = lambda x: int(x.split('_')[-1]))
assert len(extra_f_names)==3*(self.max_sh_degree + 1) ** 2 - 3
features_extra = np.zeros((xyz.shape[0], len(extra_f_names)))
for idx, attr_name in enumerate(extra_f_names):
features_extra[:, idx] = np.asarray(plydata.elements[0][attr_name])
# Reshape (P,F*SH_coeffs) to (P, F, SH_coeffs except DC)
features_extra = features_extra.reshape((features_extra.shape[0], 3, (self.max_sh_degree + 1) ** 2 - 1))
scale_names = [p.name for p in plydata.elements[0].properties if p.name.startswith("scale_")]
scale_names = sorted(scale_names, key = lambda x: int(x.split('_')[-1]))
scales = np.zeros((xyz.shape[0], len(scale_names)))
for idx, attr_name in enumerate(scale_names):
scales[:, idx] = np.asarray(plydata.elements[0][attr_name])
rot_names = [p.name for p in plydata.elements[0].properties if p.name.startswith("rot")]
rot_names = sorted(rot_names, key = lambda x: int(x.split('_')[-1]))
rots = np.zeros((xyz.shape[0], len(rot_names)))
for idx, attr_name in enumerate(rot_names):
rots[:, idx] = np.asarray(plydata.elements[0][attr_name])
self._xyz = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor(xyz, dtype=torch.float, device="cuda").requires_grad_(True))
self._features_dc = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor(features_dc, dtype=torch.float, device="cuda").transpose(1, 2).contiguous().requires_grad_(True))
self._features_rest = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor(features_extra, dtype=torch.float, device="cuda").transpose(1, 2).contiguous().requires_grad_(True))
self._opacity = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor(opacities, dtype=torch.float, device="cuda").requires_grad_(True))
self._scaling = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor(scales, dtype=torch.float, device="cuda").requires_grad_(True))
self._rotation = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor(rots, dtype=torch.float, device="cuda").requires_grad_(True))
self.active_sh_degree = self.max_sh_degree
5. 优化器和学习率相关
def training_setup(self, training_args): # 初始化训练工作
self.percent_dense = training_args.percent_dense # 控制Gaussian的密度,在`densify_and_clone`中被使用
self.xyz_gradient_accum = torch.zeros((self.get_xyz.shape[0], 1), device="cuda") # 坐标的累积梯度
self.denom = torch.zeros((self.get_xyz.shape[0], 1), device="cuda") # 意义不明
l = [ # 设置分别对应于各个参数的学习率
{'params': [self._xyz], 'lr': training_args.position_lr_init * self.spatial_lr_scale, "name": "xyz"},
{'params': [self._features_dc], 'lr': training_args.feature_lr, "name": "f_dc"},
{'params': [self._features_rest], 'lr': training_args.feature_lr / 20.0, "name": "f_rest"},
{'params': [self._opacity], 'lr': training_args.opacity_lr, "name": "opacity"},
{'params': [self._scaling], 'lr': training_args.scaling_lr, "name": "scaling"},
{'params': [self._rotation], 'lr': training_args.rotation_lr, "name": "rotation"}
]
self.optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(l, lr=0.0, eps=1e-15)
self.xyz_scheduler_args = get_expon_lr_func(lr_init=training_args.position_lr_init*self.spatial_lr_scale,
lr_final=training_args.position_lr_final*self.spatial_lr_scale,
lr_delay_mult=training_args.position_lr_delay_mult,
max_steps=training_args.position_lr_max_steps)
# 坐标的学习率规划函数
def update_learning_rate(self, iteration): # 更新Gaussian坐标的学习率
''' Learning rate scheduling per step '''
for param_group in self.optimizer.param_groups:
if param_group["name"] == "xyz":
lr = self.xyz_scheduler_args(iteration)
param_group['lr'] = lr
return lr
def replace_tensor_to_optimizer(self, tensor, name):
# 看样子是把优化器保存的某个名为`name`的参数的值强行替换为`tensor`
# 这里面需要注意的是修改Adam优化器的状态变量:动量(momentum)和平方动量(second-order momentum)
optimizable_tensors = {}
for group in self.optimizer.param_groups:
if group["name"] == name:
stored_state = self.optimizer.state.get(group['params'][0], None)
stored_state["exp_avg"] = torch.zeros_like(tensor) # 把动量清零
stored_state["exp_avg_sq"] = torch.zeros_like(tensor) # 把平方动量清零
del self.optimizer.state[group['params'][0]]
group["params"][0] = nn.Parameter(tensor.requires_grad_(True))
self.optimizer.state[group['params'][0]] = stored_state
optimizable_tensors[group["name"]] = group["params"][0]
return optimizable_tensors
def _prune_optimizer(self, mask):
# 根据`mask`裁剪一部分参数及其动量和二阶动量
optimizable_tensors = {}
for group in self.optimizer.param_groups:
stored_state = self.optimizer.state.get(group['params'][0], None)
if stored_state is not None:
stored_state["exp_avg"] = stored_state["exp_avg"][mask]
stored_state["exp_avg_sq"] = stored_state["exp_avg_sq"][mask]
del self.optimizer.state[group['params'][0]]
group["params"][0] = nn.Parameter((group["params"][0][mask].requires_grad_(True)))
self.optimizer.state[group['params'][0]] = stored_state
optimizable_tensors[group["name"]] = group["params"][0]
else:
group["params"][0] = nn.Parameter(group["params"][0][mask].requires_grad_(True))
optimizable_tensors[group["name"]] = group["params"][0]
return optimizable_tensors
def cat_tensors_to_optimizer(self, tensors_dict):
# 把新的张量字典添加到优化器
optimizable_tensors = {}
for group in self.optimizer.param_groups:
assert len(group["params"]) == 1
extension_tensor = tensors_dict[group["name"]]
stored_state = self.optimizer.state.get(group['params'][0], None)
if stored_state is not None:
stored_state["exp_avg"] = torch.cat((stored_state["exp_avg"], torch.zeros_like(extension_tensor)), dim=0)
stored_state["exp_avg_sq"] = torch.cat((stored_state["exp_avg_sq"], torch.zeros_like(extension_tensor)), dim=0)
del self.optimizer.state[group['params'][0]]
group["params"][0] = nn.Parameter(torch.cat((group["params"][0], extension_tensor), dim=0).requires_grad_(True))
self.optimizer.state[group['params'][0]] = stored_state
optimizable_tensors[group["name"]] = group["params"][0]
else:
group["params"][0] = nn.Parameter(torch.cat((group["params"][0], extension_tensor), dim=0).requires_grad_(True))
optimizable_tensors[group["name"]] = group["params"][0]
return optimizable_tensors
6. 重置不透明度:def reset_opacity(self)
def reset_opacity(self):
opacities_new = inverse_sigmoid(torch.min(self.get_opacity, torch.ones_like(self.get_opacity)*0.01))
# get_opacity返回了经过exp的不透明度,是真的不透明度
# 这句话让所有不透明度都不能超过0.01
optimizable_tensors = self.replace_tensor_to_optimizer(opacities_new, "opacity") # 更新优化器中的不透明度
self._opacity = optimizable_tensors["opacity"]
7. Gaussian的删除和新增
def prune_points(self, mask): # 删除Gaussian并移除对应的所有属性
valid_points_mask = ~mask
optimizable_tensors = self._prune_optimizer(valid_points_mask)
# 重置各个参数
self._xyz = optimizable_tensors["xyz"]
self._features_dc = optimizable_tensors["f_dc"]
self._features_rest = optimizable_tensors["f_rest"]
self._opacity = optimizable_tensors["opacity"]
self._scaling = optimizable_tensors["scaling"]
self._rotation = optimizable_tensors["rotation"]
self.xyz_gradient_accum = self.xyz_gradient_accum[valid_points_mask]
self.denom = self.denom[valid_points_mask]
self.max_radii2D = self.max_radii2D[valid_points_mask]
def densification_postfix(self, new_xyz, new_features_dc, new_features_rest, new_opacities, new_scaling, new_rotation):
# 新增Gaussian,把新属性添加到优化器中
d = {"xyz": new_xyz,
"f_dc": new_features_dc,
"f_rest": new_features_rest,
"opacity": new_opacities,
"scaling" : new_scaling,
"rotation" : new_rotation}
optimizable_tensors = self.cat_tensors_to_optimizer(d)
self._xyz = optimizable_tensors["xyz"]
self._features_dc = optimizable_tensors["f_dc"]
self._features_rest = optimizable_tensors["f_rest"]
self._opacity = optimizable_tensors["opacity"]
self._scaling = optimizable_tensors["scaling"]
self._rotation = optimizable_tensors["rotation"]
self.xyz_gradient_accum = torch.zeros((self.get_xyz.shape[0], 1), device="cuda")
self.denom = torch.zeros((self.get_xyz.shape[0], 1), device="cuda")
self.max_radii2D = torch.zeros((self.get_xyz.shape[0]), device="cuda")
def densify_and_split(self, grads, grad_threshold, scene_extent, N=2):
n_init_points = self.get_xyz.shape[0]
# Extract points that satisfy the gradient condition
padded_grad = torch.zeros((n_init_points), device="cuda")
padded_grad[:grads.shape[0]] = grads.squeeze()
selected_pts_mask = torch.where(padded_grad >= grad_threshold, True, False)
selected_pts_mask = torch.logical_and(selected_pts_mask,
torch.max(self.get_scaling, dim=1).values > self.percent_dense*scene_extent)
'''
被分裂的Gaussians满足两个条件:
1. (平均)梯度过大;
2. 在某个方向的最大缩放大于一个阈值。
参照论文5.2节“On the other hand...”一段,大Gaussian被分裂成两个小Gaussians,
其放缩被除以φ=1.6,且位置是以原先的大Gaussian作为概率密度函数进行采样的。
'''
stds = self.get_scaling[selected_pts_mask].repeat(N,1)
means = torch.zeros((stds.size(0), 3),device="cuda")
samples = torch.normal(mean=means, std=stds)
rots = build_rotation(self._rotation[selected_pts_mask]).repeat(N,1,1)
new_xyz = torch.bmm(rots, samples.unsqueeze(-1)).squeeze(-1) + self.get_xyz[selected_pts_mask].repeat(N, 1)
# 算出随机采样出来的新坐标
# bmm: batch matrix-matrix product
new_scaling = self.scaling_inverse_activation(self.get_scaling[selected_pts_mask].repeat(N,1) / (0.8*N))
new_rotation = self._rotation[selected_pts_mask].repeat(N,1)
new_features_dc = self._features_dc[selected_pts_mask].repeat(N,1,1)
new_features_rest = self._features_rest[selected_pts_mask].repeat(N,1,1)
new_opacity = self._opacity[selected_pts_mask].repeat(N,1)
self.densification_postfix(new_xyz, new_features_dc, new_features_rest, new_opacity, new_scaling, new_rotation)
prune_filter = torch.cat((selected_pts_mask, torch.zeros(N * selected_pts_mask.sum(), device="cuda", dtype=bool)))
self.prune_points(prune_filter)
def densify_and_clone(self, grads, grad_threshold, scene_extent):
# Extract points that satisfy the gradient condition
selected_pts_mask = torch.where(torch.norm(grads, dim=-1) >= grad_threshold, True, False)
selected_pts_mask = torch.logical_and(selected_pts_mask,
torch.max(self.get_scaling, dim=1).values <= self.percent_dense*scene_extent)
# 提取出大于阈值`grad_threshold`且缩放参数较小(小于self.percent_dense * scene_extent)的Gaussians,在下面进行克隆
new_xyz = self._xyz[selected_pts_mask]
new_features_dc = self._features_dc[selected_pts_mask]
new_features_rest = self._features_rest[selected_pts_mask]
new_opacities = self._opacity[selected_pts_mask]
new_scaling = self._scaling[selected_pts_mask]
new_rotation = self._rotation[selected_pts_mask]
self.densification_postfix(new_xyz, new_features_dc, new_features_rest, new_opacities, new_scaling, new_rotation)
def densify_and_prune(self, max_grad, min_opacity, extent, max_screen_size):
grads = self.xyz_gradient_accum / self.denom # 计算平均梯度
grads[grads.isnan()] = 0.0
self.densify_and_clone(grads, max_grad, extent) # 通过克隆增加密度
self.densify_and_split(grads, max_grad, extent) # 通过分裂增加密度
# 接下来移除一些Gaussians,它们满足下列要求中的一个:
# 1. 接近透明(不透明度小于min_opacity)
# 2. 在某个相机视野里出现过的最大2D半径大于屏幕(像平面)大小
# 3. 在某个方向的最大缩放大于0.1 * extent(也就是说很长的长条形也是会被移除的)
prune_mask = (self.get_opacity < min_opacity).squeeze()
if max_screen_size:
big_points_vs = self.max_radii2D > max_screen_size # vs = view space?
big_points_ws = self.get_scaling.max(dim=1).values > 0.1 * extent
prune_mask = torch.logical_or(torch.logical_or(prune_mask, big_points_vs), big_points_ws) # ws = world space?
self.prune_points(prune_mask)
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
def add_densification_stats(self, viewspace_point_tensor, update_filter):
# 统计坐标的累积梯度和均值的分母(即迭代步数?)
self.xyz_gradient_accum[update_filter] += torch.norm(viewspace_point_tensor.grad[update_filter,:2], dim=-1, keepdim=True)
self.denom[update_filter] += 1
下一部分:【计算机视觉】Gaussian Splatting源码解读补充(二)