哨兵位:
通俗的话讲就是额外开辟一块空间,指向链表的头部。
合并两个有序链表
已解答
简单
相关标签
相关企业
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
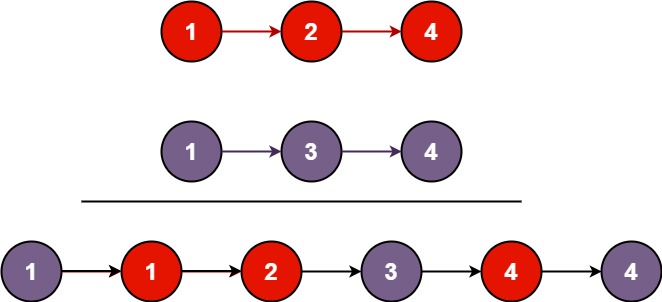
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]
提示:
- 两个链表的节点数目范围是
[0, 50] -100 <= Node.val <= 100l1和l2均按 非递减顺序 排列
解答:
目录
一、不带哨兵位
二、带哨兵位
三、哨兵位的优缺
一、不带哨兵位
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
//链表本身就可能为空!!! 一定不可省略!!!
if(list1 == NULL)
return list2;
else if(list2 == NULL)
return list1;
struct ListNode* cur1 = list1;
struct ListNode* cur2 = list2;
struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;
struct ListNode* tail = NULL;
while(cur1 && cur2){
if(cur1->val <= cur2->val){
if(newhead == NULL)
{
newhead = tail = cur1;
}
else
{
tail->next = cur1;
tail = tail->next;
}
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
else
{
if(newhead == NULL)
{
newhead = tail = cur2;
}
else
{
tail->next = cur2;
tail = tail->next;
}
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
}
//跳出循环,意味着某个链表结束
if(cur2) //cur1 为空,cur2不能为空!
tail->next = cur2;
else if(cur1)
tail->next = cur1;
return newhead;
}二、带哨兵位
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
//链表本身就可能为空!!! 一定不可省略!!!
if(list1 == NULL)
return list2;
else if(list2 == NULL)
return list1;
struct ListNode* cur1 = list1;
struct ListNode* cur2 = list2;
struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;
struct ListNode* tail = NULL;
//创建哨兵位,头和尾指向哨兵位
newhead = tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
while(cur1 && cur2){
if(cur1->val <= cur2->val){
// if(newhead == NULL) //不用判断是不是空
// {
// newhead = tail = cur1;
// }
tail->next = cur1;
tail = tail->next;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
else
{
// if(newhead == NULL)
// {
// newhead = tail = cur2;
// }
// else
// {
tail->next = cur2;
tail = tail->next;
// }
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
}
//跳出循环,意味着某个链表结束
if(cur2) //cur1 为空,cur2不能为空!
tail->next = cur2;
else if(cur1)
tail->next = cur1;
struct ListNode* del = newhead; //释放哨兵位节点
newhead = newhead->next;
free(del);
return newhead;
}三、哨兵位的优缺
优:可以省去判断是否为空的步骤。
缺:需要主动释放。






![[HackMyVM]靶场 XMAS](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ab385716590a4dea88cf09a6212f5831.png)