文章目录
- gray_closing_shape 使用选定的掩码执行灰度值关闭
- create_planar_uncalib_deformable_model 为未校准的透视匹配创建一个可变形的模型
- get_deformable_model_params 返回可变形模型的参数
- find_planar_uncalib_deformable_model 在图像中寻找平面投影不变变形模型的最佳匹配
- get_deformable_model_contours 返回可变形模型的轮廓表示形式。
- projective_trans_contour_xld 对XLD轮廓应用投影变换
- clear_deformable_model 清除模板
- get_region_runs 访问区域的运行长度编码
- 示例
gray_closing_shape 使用选定的掩码执行灰度值关闭
gray_closing_shape(Image : ImageClosing : MaskHeight, MaskWidth, MaskShape : )
Image (input_object): 需要计算最小灰度值的图像。
ImageClosing (output_object): 包含最小灰度值的图像。
MaskHeight (input_control): 滤波器掩模的高度。
默认值: 11
建议值: 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15
典型取值范围: 1.0 ≤ MaskHeight ≤ 511.0
MaskWidth (input_control): 滤波器掩模的宽度。
默认值: 11
建议值: 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15
典型取值范围: 1.0 ≤ MaskWidth ≤ 511.0
MaskShape (input_control): 控制滤波器掩模形状的参数。
默认值: 'octagon'
可选值: 'octagon', 'rectangle', 'rhombus'
create_planar_uncalib_deformable_model 为未校准的透视匹配创建一个可变形的模型
create_planar_uncalib_deformable_model(Template : : NumLevels, AngleStart, AngleExtent, AngleStep, ScaleRMin, ScaleRMax, ScaleRStep, ScaleCMin, ScaleCMax, ScaleCStep, Optimization, Metric, Contrast, MinContrast, GenParamName, GenParamValue : ModelID)
Image (input_object): 输入图像,模型应在其中查找目标。
ModelID (input_control): 模型的标识符。
AngleStart (input_control): 模型的最小旋转角度。
AngleExtent (input_control): 旋转角度的范围。
ScaleRMin/ScaleRMax/ScaleCMin/ScaleCMax (input_control): 模型在行和列方向上的最小和最大比例。
MinScore (input_control): 实例的最低得分阈值。
NumMatches (input_control): 要找到的模型实例数量。
MaxOverlap (input_control): 实例之间的最大重叠度量。
NumLevels (input_control): 在匹配中使用的金字塔级别数。
Greediness (input_control): 搜索启发式算法的“贪婪度”。
GenParamName/GenParamValue (input_control): 一般参数名称和值。
HomMat2D (output_control): 模型实例与找到的实例之间的变换矩阵。
Score (output_control): 找到的模型实例的得分。
get_deformable_model_params 返回可变形模型的参数
get_deformable_model_params( : : ModelID, GenParamName : GenParamValue)
这段参数描述了一个可变形模型(deformable model)的相关控制参数:
ModelID (input_control): 模型的标识符。
GenParamName (input_control): 要查询可变形模型的通用参数的名称列表。
默认值: 'angle_start'
可选值: 'angle_extent', 'angle_start', 'angle_step', 'cam_param', 'cam_param_rect', 'created_from_xld', 'get_deformable_model_contours_coord_system', 'metric', 'min_contrast', 'min_size', 'model_col', 'model_pose', 'model_row', 'model_type', 'num_levels', 'optimization', 'reference_pose', 'scale_c_max', 'scale_c_min', 'scale_c_step', 'scale_r_max', 'scale_r_min', 'scale_r_step'
GenParamValue (output_control): 通用参数的值。
find_planar_uncalib_deformable_model 在图像中寻找平面投影不变变形模型的最佳匹配
find_planar_uncalib_deformable_model(Image : : ModelID, AngleStart, AngleExtent, ScaleRMin, ScaleRMax, ScaleCMin, ScaleCMax, MinScore, NumMatches, MaxOverlap, NumLevels, Greediness, GenParamName, GenParamValue : HomMat2D, Score)
Image:输入图像,模型应该在其中被找到。
ModelID:模型的标识符。
AngleStart:模型的最小旋转角度。
AngleExtent:旋转角度的范围。
ScaleRMin:模型在行方向上的最小比例。
ScaleRMax:模型在行方向上的最大比例。
ScaleCMin:模型在列方向上的最小比例。
ScaleCMax:模型在列方向上的最大比例。
MinScore:要找到的模型实例的最小分数。
NumMatches:要找到的模型实例的数量(或者为所有匹配项设置为0)。
MaxOverlap:要找到的模型实例的最大重叠。
NumLevels:在匹配中使用的金字塔级别数。
Greediness:搜索启发式算法的“贪婪度”。
GenParamName:通用参数名称。
GenParamValue:通用参数值。
HomMat2D:模型和找到的实例之间的Homographies。
Score:找到的模型实例的分数。
get_deformable_model_contours 返回可变形模型的轮廓表示形式。
get_deformable_model_contours( : ModelContours : ModelID, Level : )
ModelContours:可变形模型的轮廓表示。
ModelID:模型的标识符。
Level:应返回轮廓表示的金字塔级别。默认为1,建议值为1至10之间的整数,且必须大于等于1
projective_trans_contour_xld 对XLD轮廓应用投影变换
projective_trans_contour_xld(Contours : ContoursProjTrans : HomMat2D : )
Contours:输入的轮廓。
ContoursProjTrans:输出的轮廓。
HomMat2D:齐次投影变换矩阵。
clear_deformable_model 清除模板
clear_deformable_model( : : ModelID : )
ModelID :模板句柄
get_region_runs 访问区域的运行长度编码
get_region_runs(Region : : : Row, ColumnBegin, ColumnEnd)
Region:输入的区域。
Row:弦线的行号。
ColumnBegin:弦线起点的列号。
ColumnEnd:弦线终点的列号
示例
determine_area_of_interest (Image, Rectangle, AreaOfInterest) 函数
* 裁剪不重要的部分
reduce_domain (Image, Rectangle, ImageReduced)
*分成RGB三个图片
decompose3 (ImageReduced, ImageR, ImageG, ImageB)
*将图片转换为HSV
trans_from_rgb (ImageR, ImageG, ImageB, ImageH, ImageS, ImageV, 'hsv')
* 阈值处理
threshold (ImageS, HighSat, 130, 255)
* 膨胀
dilation_circle (HighSat, HighSatD, 2.0)
* 将图片填充
fill_up (HighSatD, HighSatD)
*填充后的图片裁剪
reduce_domain (ImageH, HighSatD, HighHue)
* 阈值处理
threshold (HighHue, ColoredAreaOfInterest, [230,145], [255,162])
* 填充图片
fill_up (ColoredAreaOfInterest, ImageFilled)
* 膨胀
dilation_circle (ImageFilled, ImageDilated, 3.0)
* 将图片联合
union1 (ImageDilated, AreaOfInterest)
return ()
* This example shows an application case from the automobile
* industry. A monitoring system in a car checks the sidewalk
* for roadsigns to support the driver in case of any inattention.
* To show the imaging process we focus on two road signs,
* the attention and the dead end road sign. First the models
* of both signs are generated and then detected in a street
* sequence.
*
* 读取图片
dev_close_window ()
* Read in model images.
* While the attention sign is from a synthetic source,
* the model for the dead end sign is from another sequence.
* 读取路标图片
read_image (ImageAttentionSign, 'road_signs/attention_road_sign')
* 读取街道图片
read_image (ImageInit, 'road_signs/street_01')
dev_open_window_fit_image (ImageInit, 0, 0, -1, -1, WindowHandle)
dev_update_off ()
dev_set_line_width (2)
dev_set_color ('green')
dev_set_draw ('margin')
set_display_font (WindowHandle, 14, 'mono', 'true', 'false')
*
* Some values for the later matching process are initialized
* The Attention sign has a significant red part, the
* dead end sign a blue one. Hence, we can extract the respective
* channels from the color images.
Channel := [3,1]
* In this example, we have significant scalings of the road signs.
ScaleRMin := [0.5,0.4]
ScaleRMax := [0.8,2.0]
* One could add an anisotropic scaling for the exhaustive search.
* However, this makes the detection slower and is not required here.
ScaleCMin := [1.0,1.0]
ScaleCMax := [1.0,1.0]
* Add names to the signs.
RoadSign := ['Attention','Dead end']
HFac := [47.0,50.0]
*
* Prepare the attention sign picture for the model
* creation process.
* 创建通道
access_channel (ImageAttentionSign, Image, Channel[0])
* 放大图片
zoom_image_factor (Image, ImageZoomed, 0.1, 0.1, 'weighted')
* 将放大后的图片插入到轮廓识别算法中
inspect_shape_model (ImageZoomed, ModelImages, ModelRegions, 3, 20)
* 创建一个可变形的模板
create_planar_uncalib_deformable_model (ImageZoomed, 3, [], [], 0.1, ScaleRMin[0], [], 0.05, ScaleCMin[0], [], 0.5, 'none', 'use_polarity', 'auto', 'auto', [], [], ModelID)
Models := ModelID
*
*
*
*读取路标图片
read_image (ImageDeadEnd, 'road_signs/dead_end_road_sign')
* 获取通道1
access_channel (ImageDeadEnd, Image, Channel[1])
* 使用选定的掩码执行灰度值关闭
gray_closing_shape (Image, ImageClosing, 5, 5, 'octagon')
* 图片放大
zoom_image_factor (ImageClosing, ImageZoomed, 0.4, 0.4, 'weighted')
gen_rectangle1 (Rectangle1, 28, 71, 69, 97)
* 裁剪
reduce_domain (ImageZoomed, Rectangle1, ImageReduced)
* 将裁剪的标识创建一个可变形的模板
create_planar_uncalib_deformable_model (ImageReduced, 3, [], [], 0.1, ScaleRMin[1], [], 0.05, ScaleRMin[1], [], 0.1, 'none', 'use_polarity', 'auto', 'auto', [], [], ModelID)
*
* The following three lines theoretically show how to
* query specific parameters of a model.
* Practically, the derived information is not needed
* within the program.
* 获取模板参数
get_deformable_model_params (ModelID, 'angle_step', AngleStep)
get_deformable_model_params (ModelID, 'scale_r_step', ScaleRStep)
Models := [Models,ModelID]
*
* Generate ROI in which the road signs are expected.
* We can discard not significant parts of the image, in which
* no road sign can be located.
*丢弃图像中不重要的部分
gen_rectangle1 (Rectangle, 115, 0, 360, 640)
*
* Search in image sequence
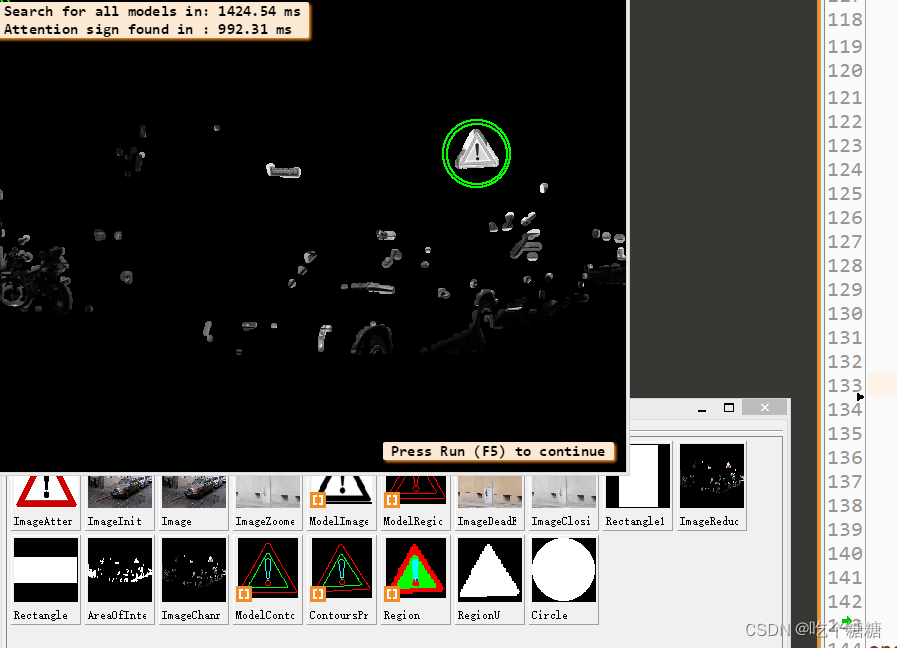
for Index := 1 to 16 by 1
OutputString := []
TotalTime := 0
* 读取街道图片
read_image (Image, 'road_signs/street_' + Index$'.02')
* We are using color images, hence the ROI of the search image
* can significantly be reduced based on the color.
determine_area_of_interest (Image, Rectangle, AreaOfInterest)
reduce_domain (Image, AreaOfInterest, ImageReduced)
dev_display (Image)
*
for Index2 := 0 to |Models| - 1 by 1
*
* Depending on the street sign to be found, we use different color
* channels of the image and the operator find_planar_uncalib_deformable_model
* with different parameters because of the varying dimensions of the models.
access_channel (ImageReduced, ImageChannel, Channel[Index2])
count_seconds (Time1)
* 查找匹配模板
find_planar_uncalib_deformable_model (ImageChannel, Models[Index2], 0, 0, ScaleRMin[Index2], ScaleRMax[Index2], ScaleCMin[Index2], ScaleCMax[Index2], 0.85, 1, 0, 2, 0.4, [], [], HomMat2D, Score)
count_seconds (Time2)
Time := Time2 - Time1
TotalTime := TotalTime + Time
*
* Display found models.
if (|HomMat2D|)
*发现轮廓
get_deformable_model_contours (ModelContours, Models[Index2], 1)
*将轮廓进行投影
projective_trans_contour_xld (ModelContours, ContoursProjTrans, HomMat2D)
* 产生亚像素轮廓
gen_region_contour_xld (ContoursProjTrans, Region, 'filled')
* 合并
union1 (Region, RegionU)
*获取中心点面积
area_center (RegionU, Area, R, C)
* 访问区域的长度
get_region_runs (RegionU, Row, ColumnBegin, ColumnEnd)
H := max(Row) - min(Row)
Fac := H / HFac[Index2]
gen_circle (Circle, R, C, 45 * Fac)
dev_display (Circle)
gen_circle (Circle, R, C, 50 * Fac)
dev_display (Circle)
dev_display (ContoursProjTrans)
if (Index2 == 0)
OutputString := 'Attention sign found in : ' + (Time * 1000)$'.2f' + ' ms \n'
else
OutputString := 'Dead end sign found in : ' + (Time * 1000)$'.2f' + ' ms \n'
endif
endif
endfor
if (|OutputString| == 0)
OutputString := 'No sign found in : ' + (Time * 1000)$'.2f' + ' ms \n'
endif
OutputString := ['Search for all models in: ' + (TotalTime * 1000)$'.2f' + ' ms',OutputString]
disp_message (WindowHandle, OutputString, 'window', 10, 10, 'black', 'true')
disp_continue_message (WindowHandle, 'black', 'true')
stop ()
endfor
dev_display (Image)
disp_message (WindowHandle, 'Program finished.\nPress \'Run\' to clear all deformable models.', 'window', 10, 10, 'black', 'true')
stop ()
* Clean the memory of the models.
for Index1 := 0 to 1 by 1
clear_deformable_model (Models[Index1])
endfor