接着上篇博客机器学习-训练模型做进一步说明。
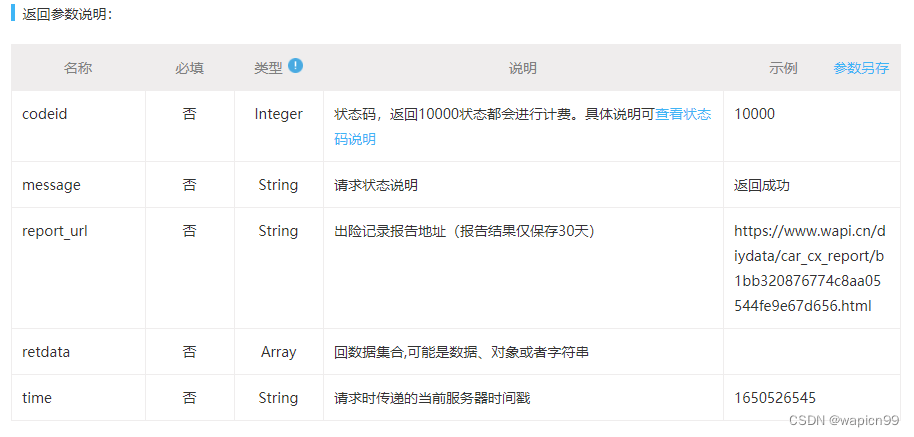
There are three things to make predictions (also called performing inference) with a PyTorch model:
- Set the model in evaluation mode (
model.eval()) - Make the predictions using the inference mode context manager (
with torch.inference_mode(): ...) - All predictions should be made with objects on the same device (e.g. data and model on GPU only or data and model on CPU only).
The first two items make sure all helpful calculations and settings PyTorch uses behind the scenes during training but aren’t necessary for inference are turned off (this results in faster computation). And the third ensures that you won’t run into cross-device errors.
下面代码片段是连接之前的博客
import torch
# 1. Set the model in evaluation mode
model_0.eval()
# 2. Setup the inference mode context manager
with torch.inference_mode():
# 3. Make sure the calculations are done with the model and data on the same device
y_preds = model_0(X_test)
print(y_preds)
plot_predictions(predictions=y_preds)
# 结果如下
tensor([[0.8685],
[0.8825],
[0.8965],
[0.9105],
[0.9245],
[0.9384],
[0.9524],
[0.9664],
[0.9804],
[0.9944]])
在下图,能看到预测点跟测试点很靠近,这结果挺理想的

这里稍微介绍一下 torch.inference_mode()
torch.inference.mode() 是一个上下文管理器,用于控制推断模式下的模型行为。在深度学习中,模型在训练和推断 (或称为预测) 阶段有不同的行为。在推断阶段,通常不需要计算梯度,也不需要跟踪计算图,这样可以提高推断速度并减少内存占用。torch.inference_mode() 上下文管理器就是为了控制模型在推断阶段的行为。
当进入torch.inference_mode() 上下文环境时,PyTorch会关闭梯度跟踪,并且禁用自动微分机制。这意味着在此环境中,无法调用backward()方法计算梯度,也无法通过梯度进行参数更新。这样可以确保模型在推断阶段不会意外地计算梯度,提高了推断的速度和效率。
都看到这里,点个赞支持一下呗~