52. N 皇后 II,53. 最大子数组和,54. 螺旋矩阵,每题做详细思路梳理,配套Python&Java双语代码, 2024.03.20 可通过leetcode所有测试用例。
目录
52. N 皇后 II
解题思路
完整代码
Python
Java
53. 最大子数组和
解题思路
完整代码
Python
Java
54. 螺旋矩阵
解题思路
完整代码
Python
Java
52. N 皇后 II
n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将
n个皇后放置在n × n的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。给你一个整数
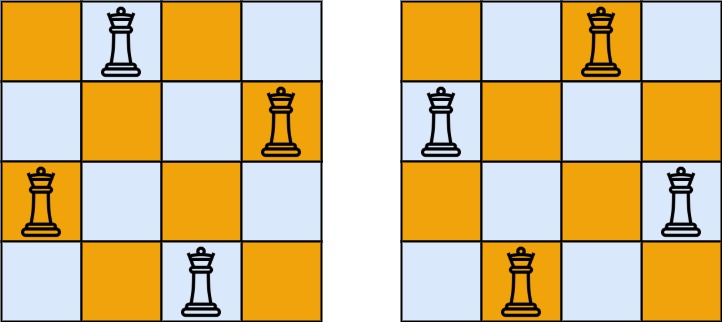
n,返回 n 皇后问题 不同的解决方案的数量。示例 1:
输入:n = 4 输出:2 解释:如上图所示,4 皇后问题存在两个不同的解法。示例 2:
输入:n = 1 输出:1提示:
1 <= n <= 9
解题思路
可以使用回溯法,类似于解决 n 皇后问题摆放方案的方法,但这次我们只需要计算不同解决方案的数量。关键点在于合理地放置皇后,以避免她们相互攻击。
-
初始化数据结构:使用数组或其他数据结构来标记哪些列、对角线(左上到右下和右上到左下)已经被占用。
-
递归回溯:从第一行开始,尝试在每一列放置皇后。对于放置在
(row, col)的皇后,需要标记第col列、(row + col)的左上到右下对角线和(row - col)的右上到左下对角线为占用状态。 -
检查冲突:在尝试放置每个皇后之前,检查当前列和两个对角线是否已经被其他皇后占用。
-
统计解决方案数量:每当成功放置了
n个皇后(即达到了最后一行的下一行),就将解决方案数量加一。 -
回溯:尝试当前行的下一列或回到上一行,撤销当前放置的皇后,并尝试新的位置。
完整代码
Python
class Solution:
def totalNQueens(self, n: int) -> int:
def backtrack(row = 0, hills = 0, next_row = 0, dales = 0, count = 0):
if row == n: # 如果已经放置了 n 个皇后
count += 1 # 解决方案数量加一
else:
# 在所有可用的列中
free_columns = columns & ~(hills | next_row | dales)
while free_columns:
# 选择最右侧的可用列
curr_column = - free_columns & free_columns
# 放置皇后并去掉当前列
free_columns ^= curr_column
count = backtrack(row + 1,
(hills | curr_column) << 1,
next_row | curr_column,
(dales | curr_column) >> 1,
count)
return count
# 初始化可用列
columns = (1 << n) - 1
return backtrack()Java
public class Solution {
private int size;
private int count;
private void solve(int row, int ld, int rd) {
if (row == size) {
count++;
return;
}
int pos = size & ~(row | ld | rd);
while (pos != 0) {
int p = pos & -pos;
pos -= p; // 放置皇后并移除当前位置
solve(row | p, (ld | p) << 1, (rd | p) >> 1);
}
}
public int totalNQueens(int n) {
count = 0;
size = (1 << n) - 1;
solve(0, 0, 0);
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
int n = 4;
System.out.println(solution.totalNQueens(n));
}
}
53. 最大子数组和
给你一个整数数组
nums,请你找出一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。子数组
是数组中的一个连续部分。示例 1:
输入:nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4] 输出:6 解释:连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6 。示例 2:
输入:nums = [1] 输出:1示例 3:
输入:nums = [5,4,-1,7,8] 输出:23
解题思路
我们可以使用一个称为“Kadane算法”的高效方法。Kadane算法通过一次遍历数组来找到最大的连续子数组和。该算法的基本思想是维护一个局部最大和一个全局最大变量,随着数组的遍历,更新这两个变量。
-
初始化两个变量:
currentMax用于追踪当前位置的最大子数组和,globalMax用于记录迄今为止找到的最大子数组和。初始时,两个变量都设置为数组的第一个元素。 -
遍历数组:从数组的第二个元素开始遍历。
-
更新
currentMax:对于每个元素,更新currentMax为当前元素本身和当前元素加上之前的currentMax之间的较大者。这一步骤确保了currentMax总是维护着到当前位置为止的最大子数组和。currentMax = max(nums[i], currentMax + nums[i]) -
更新
globalMax:如果更新后的currentMax大于globalMax,则更新globalMax为currentMax的值。这确保了globalMax总是全局最大子数组和。globalMax = max(globalMax, currentMax) -
返回结果:遍历完成后,
globalMax将包含整个数组的最大子数组和。
完整代码
Python
class Solution:
def maxSubArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
currentMax = globalMax = nums[0]
for num in nums[1:]:
currentMax = max(num, currentMax + num)
globalMax = max(globalMax, currentMax)
return globalMaxJava
public class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int currentMax = nums[0];
int globalMax = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
currentMax = Math.max(nums[i], currentMax + nums[i]);
globalMax = Math.max(globalMax, currentMax);
}
return globalMax;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[] nums = {-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4};
System.out.println(solution.maxSubArray(nums));
}
}
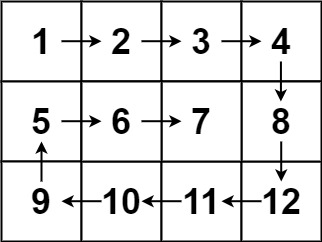
54. 螺旋矩阵
给你一个
m行n列的矩阵matrix,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。示例 1:
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] 输出:[1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]示例 2:
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]] 输出:[1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]提示:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100
解题思路
要按顺时针螺旋顺序返回矩阵中的所有元素,我们可以模拟整个过程,遵循从左到右、从上到下、从右到左、从下到上的顺序,每完成一圈后,缩小遍历的范围。
-
初始化四个方向的边界:
top、bottom、left、right分别代表了上下左右四个方向的边界。初始化时,top = 0,bottom = m-1,left = 0,right = n-1。 -
按顺序遍历矩阵:按照顺时针方向遍历矩阵的外围,然后逐层向内缩小范围,直到遍历完所有元素。具体步骤如下:
a. 从左到右遍历上层元素(
top行),遍历完成后top++。b. 从上到下遍历右侧元素(
right列),遍历完成后right--。c. 如果
top <= bottom,从右到左遍历底层元素(bottom行),遍历完成后bottom--。d. 如果
left <= right,从下到上遍历左侧元素(left列),遍历完成后left++。 -
收集元素:在每个方向上遍历时,将遍历到的元素添加到结果列表中。
-
返回结果:当上述遍历完成后,结果列表中将包含按顺时针螺旋顺序的所有矩阵元素。
完整代码
Python
class Solution:
def spiralOrder(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
result = []
if not matrix:
return result
top, bottom, left, right = 0, len(matrix) - 1, 0, len(matrix[0]) - 1
while left <= right and top <= bottom:
# 从左到右
for i in range(left, right + 1):
result.append(matrix[top][i])
top += 1
# 从上到下
for i in range(top, bottom + 1):
result.append(matrix[i][right])
right -= 1
# 从右到左
if top <= bottom:
for i in range(right, left - 1, -1):
result.append(matrix[bottom][i])
bottom -= 1
# 从下到上
if left <= right:
for i in range(bottom, top - 1, -1):
result.append(matrix[i][left])
left += 1
return resultJava
public class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) return result;
int top = 0, bottom = matrix.length - 1, left = 0, right = matrix[0].length - 1;
while (left <= right && top <= bottom) {
// 从左到右
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
result.add(matrix[top][i]);
}
top++;
// 从上到下
for (int i = top; i <= bottom; i++) {
result.add(matrix[i][right]);
}
right--;
// 从右到左
if (top <= bottom) {
for (int i = right; i >= left; i--) {
result.add(matrix[bottom][i]);
}
bottom--;
}
// 从下到上
if (left <= right) {
for (int i = bottom; i >= top; i--) {
result.add(matrix[i][left]);
}
left++;
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[][] matrix = {{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}};
System.out.println(solution.spiralOrder(matrix));
}
}