4.2 synchronized 解决方案
应用之互斥
为了避免临界区的竞态条件发生,有多种手段可以达到目的。
-
阻塞式的解决方案:synchronized,Lock
-
非阻塞式的解决方案:原子变量
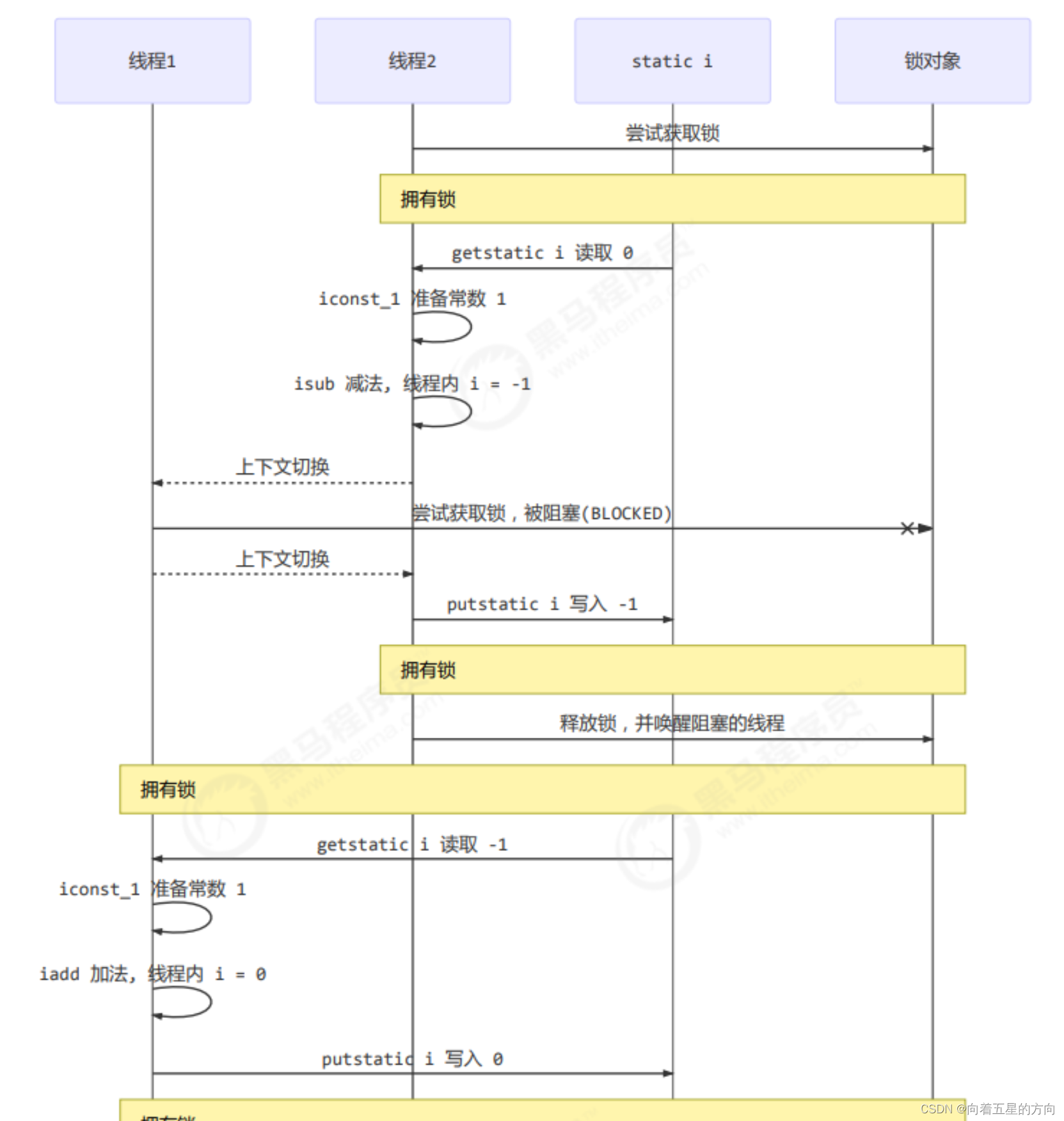
本次课使用阻塞式的解决方案:synchronized,来解决上述问题,即俗称的【对象锁】,它采用互斥的方式让同一 时刻至多只有一个线程能持有【对象锁】,其它线程再想获取这个【对象锁】时就会阻塞住。这样就能保证拥有锁 的线程可以安全的执行临界区内的代码,不用担心线程上下文切换
注意
虽然 java 中互斥和同步都可以采用 synchronized 关键字来完成,但它们还是有区别的:
互斥是保证临界区的竞态条件发生,同一时刻只能有一个线程执行临界区代码
同步是由于线程执行的先后、顺序不同、需要一个线程等待其它线程运行到某个点
synchronized
语法
synchronized(对象) // 线程1, 线程2(blocked)
{
临界区
}解决
static int counter = 0;
static final Object room = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
synchronized (room) {
counter++;
}
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
synchronized (room) {
counter--;
}
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
log.debug("{}",counter);
}图示流程
思考
synchronized 实际是用对象锁保证了临界区内代码的原子性,临界区内的代码对外是不可分割的,不会被线程切 换所打断。
为了加深理解,请思考下面的问题
-
如果把 synchronized(obj) 放在 for 循环的外面,如何理解?-- 原子性
-
如果 t1 synchronized(obj1) 而 t2 synchronized(obj2) 会怎样运作?-- 锁对象
-
如果 t1 synchronized(obj) 而 t2 没有加会怎么样?如何理解?-- 锁对象
面向对象改进
把需要保护的共享变量放入一个类
class Room {
int value = 0;
public void increment() {
synchronized (this) {
value++;
}
}
public void decrement() {
synchronized (this) {
value--;
}
}
public int get() {
synchronized (this) {
return value;
}
}
}
@Slf4j
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Room room = new Room();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 5000; j++) {
room.increment();
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 5000; j++) {
room.decrement();
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
log.debug("count: {}" , room.get());
}
}4.3 方法上的 synchronized
class Test{
public synchronized void test() {
}
}
//等价于
class Test{
public void test() {
synchronized(this) {
}
}
}class Test{
public synchronized static void test() {
}
}
等价于
class Test{
public static void test() {
synchronized(Test.class) {
}
}
}不加 synchronized 的方法
不加 synchronzied 的方法就好比不遵守规则的人,不去老实排队(好比翻窗户进去的)
所谓的“线程八锁”
其实就是考察 synchronized 锁住的是哪个对象
情况1:12 或 21
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number{
public synchronized void a() {
log.debug("1");
}
public synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Number n1 = new Number();
new Thread(()->{ n1.a(); }).start();
new Thread(()->{ n1.b(); }).start();
}情况2:1s后12,或 2 1s后 1
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number{
public synchronized void a() {
sleep(1);
log.debug("1");
}
public synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Number n1 = new Number();
new Thread(()->{ n1.a(); }).start();
new Thread(()->{ n1.b(); }).start();
}情况3:3 1s 12 或 23 1s 1 或 32 1s 1
@
Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number{
public synchronized void a() {
sleep(1);
log.debug("1");
}
public synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
public void c() {
log.debug("3");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Number n1 = new Number();
new Thread(()->{ n1.a(); }).start();
new Thread(()->{ n1.b(); }).start();
new Thread(()->{ n1.c(); }).start();
}情况4:2 1s 后 1
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number{
public synchronized void a() {
sleep(1);
log.debug("1");
}
public synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Number n1 = new Number();
Number n2 = new Number();
new Thread(()->{ n1.a(); }).start();
new Thread(()->{ n2.b(); }).start();
}情况5:2 1s 后 1
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number{
public static synchronized void a() {
sleep(1);
log.debug("1");
}
public synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Number n1 = new Number();
new Thread(()->{ n1.a(); }).start();
new Thread(()->{ n1.b(); }).start();
}情况6:1s 后12, 或 2 1s后 1
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number{
public static synchronized void a() {
sleep(1);
log.debug("1");
}
public static synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Number n1 = new Number();
new Thread(()->{ n1.a(); }).start();
new Thread(()->{ n1.b(); }).start();
}情况7:2 1s 后 1
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number{
public static synchronized void a() {
sleep(1);
log.debug("1");
}
public synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Number n1 = new Number();
Number n2 = new Number();
new Thread(()->{ n1.a(); }).start();
new Thread(()->{ n2.b(); }).start();
}情况8:1s 后12, 或 2 1s后 1
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number{
public static synchronized void a() {
sleep(1);
log.debug("1");
}
public static synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Number n1 = new Number();
Number n2 = new Number();
new Thread(()->{ n1.a(); }).start();
new Thread(()->{ n2.b(); }).start();
}