目录
一、信号的阻塞
二、信号集操作函数
三、sigprocmask函数
四、pause函数
五、sigsuspend函数
一、信号的阻塞
有时候不希望在接到信号时就立即停止当前执行,去处理信号,同时也不希望忽略该信号,而是延时一段时间去调用信号处理函数。这种情况可以通过阻塞信号实现。
信号的阻塞概念:信号的”阻塞“是一个开关动作,指的是阻止信号被处理,但不是阻止信号产生。

信号的状态:
信号递达(Delivery ):实际信号执行的处理过程(3种状态:忽略,执行默认动作,捕获)、信号未决(Pending):从产生到递达之间的状态。
二、信号集操作函数
sigset_t set; 自定义信号集。 是一个32bit 64bit 128bit的数组。
sigemptyset(sigset_t *set); 清空信号集
sigfillset(sigset_t *set); 全部置1
sigaddset(sigset_t *set, int signum); 将一个信号添加到集合中
sigdelset(sigset_t *set, int signum); 将一个信号从集合中移除
sigismember(const sigset_t *set,int signum); 判断一个信号是否在集合中。
三、sigprocmask函数
#include <signal.h>
int sigprocmask( int how,
const sigset_t *restrict set,
sigset_t *restrict oset );
返回值:若成功则返回0,若出错则返回-1
首先,若oset是非空指针,那么进程的当前信号屏蔽字通过oset返回。
其次,若set是一个非空指针,则参数how指示如何修改当前信号屏蔽字。
how可选用的值:(注意,不能阻塞SIGKILL和SIGSTOP信号)
SIG_BLOCK : 把参数set中的信号添加到信号屏蔽字中
SIG_UNBLOCK: 从信号屏蔽字中删除参数set中的信号
SIG_SETMASK: 把信号屏蔽字设置为参数set中的信号
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<signal.h>
#include<unistd.h>
void handle(int sig)
{
printf("I get the sig = %d\n",sig);
}
int main()
{
struct sigaction act;
act.sa_handler = handle;
act.sa_flags = 0;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
sigaction(SIGINT,&act,NULL);
sigset_t set;
sigemptyset(&set);
sigaddset(&set,SIGINT);
sigprocmask(SIG_BLOCK,&set,NULL);
sleep(5);
sigprocmask(SIG_UNBLOCK,&set,NULL);
while(1)
{
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
这段代码注册了一个信号处理函数 handle() 来处理 SIGINT 信号。
然后它创建了一个 sigset_t 类型的信号集 set,并将 SIGINT 添加到这个信号集中。
接着,通过 sigprocmask(SIG_BLOCK, &set, NULL) 调用,程序阻塞了 SIGINT 信号。
这意味着在这个代码块中,SIGINT 信号将被暂时屏蔽,不会触发信号处理函数。
随后,程序调用 sleep(5) 函数来暂停执行 5 秒钟。在此期间,由于 SIGINT 被阻塞,即使用户发送 SIGINT 信号(通常是通过按下 Ctrl+C),信号处理函数 handle() 也不会执行。
然后,通过 sigprocmask(SIG_UNBLOCK, &set, NULL) 调用,解除了对 SIGINT 信号的阻塞。
最后,程序进入一个无限循环,每次循环调用 sleep(1) 函数来保持进程处于活动状态。
运行结果:
linux@linux:/mnt/hgfs/linuxshare/linux_code/message2$ ./sigmask_new_t
^C^C^C^C^C^C^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^\Quit (core dumped)
四、pause函数
调用该函数可以造成进程主动挂起,等待信号唤醒。
调用该系统调用的进程将处于阻塞状态(主动放弃cpu) 直到有信号递达将其唤醒。
int pause(void); 返回值:-1 并设置errno为EINTRpause() 函数是一个系统调用,它的作用是使当前进程挂起,直到收到一个信号为止。
在收到信号之前,pause() 函数会一直阻塞当前进程。
一旦收到信号,pause() 函数会返回,并且不会执行任何其他代码,直接返回到信号处理函数(如果有的话)或者程序的主体部分。
如下代码中,pause() 函数用于等待SIGINT信号的到来。
一旦收到SIGINT信号(通常由用户在终端上按下Ctrl+C触发),pause() 函数会返回,然后程序会执行信号处理函数handle()。#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<signal.h>
#include<unistd.h>
void handle(int sig)
{
printf("I get the sig = %d\n",sig);
}
int main()
{
struct sigaction act;
act.sa_handler = handle;
act.sa_flags = 0;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
sigaction(SIGINT,&act,NULL);
pause();
printf("after pause\n");
while(1)
{
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
注意:第一次CTRL+C会调用handle回调函数且打印after pause,但是第二次CTRL+C后就不会打印after pause。
linux@linux:/mnt/hgfs/linuxshare/linux_code/message2$ ./pause_t
^CI get the sig = 2
after pause
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
^\Quit (core dumped)
linux@linux:/mnt/hgfs/linuxshare/linux_code/message2$
我们用一个测试程序测试一下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<signal.h>
#include<unistd.h>
void handle(int sig)
{
printf("I get the sig = %d\n",sig);
}
int main()
{
struct sigaction act;
act.sa_handler = handle;
act.sa_flags = 0;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
sigaction(SIGINT,&act,NULL);
pause();
printf("after pause\n");
while(1)
{
printf("test\n");
sleep(1);
printf("sleep\n");
}
return 0;
}
运行结果:
linux@linux:/mnt/hgfs/linuxshare/linux_code/message2$ ./pause_t
^CI get the sig = 2
after pause
test
sleep
test
sleep
test
sleep
test
sleep
test
sleep
test
sleep
test
^CI get the sig = 2
sleep
test
sleep
test
sleep
test
^CI get the sig = 2
sleep
test
^CI get the sig = 2
sleep
test
sleep
test
^\Quit (core dumped)
可以发现,当我用CTRL+C,接着运行,之后程序就运行到while(1)里了,当我再CTRL+C因为信号捕获的关系才会打印句柄里的语句I get the sig = 2。
而对于如下代码:
每次CTRL+C都会触发mytask中的语句和handle句柄中的打印语句。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<signal.h>
#include<unistd.h>
void handle(int sig)
{
printf("I get the sig = %d\n",sig);
}
void mytask()
{
printf("woshigedashabi\n");
}
int main()
{
struct sigaction act;
act.sa_handler = handle;
act.sa_flags = 0;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
sigaction(SIGINT,&act,NULL);
pause();
printf("after pause1\n");
while(1)
{
mytask();
pause();
}
printf("after pasue2\n");
while(1)
{
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}运行结果:
linux@linux:/mnt/hgfs/linuxshare/linux_code/message2$ ./test
^CI get the sig = 2
after pause1
woshigedashabi
^CI get the sig = 2
woshigedashabi
^CI get the sig = 2
woshigedashabi
^CI get the sig = 2
woshigedashabi
^CI get the sig = 2
woshigedashabi
^CI get the sig = 2
woshigedashabi
^\Quit (core dumped)
对代码进行一定的修改后:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<signal.h>
#include<unistd.h>
void handle(int sig)
{
printf("I get the sig = %d\n",sig);
}
void mytask()
{
printf("My task start\n");
sleep(3);
printf("My task end\n");
}
int main()
{
struct sigaction act;
act.sa_handler = handle;
act.sa_flags = 0;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
sigaction(SIGINT,&act,NULL);
sigaction(SIGHUP,&act,NULL);
sigset_t set;
sigaddset(&set,SIGHUP);
sigaddset(&set,SIGINT);
pause();
printf("after pause1\n");
while(1)
{
sigprocmask(SIG_BLOCK,&set,NULL);
mytask();
sigprocmask(SIG_UNBLOCK,&set,NULL);
pause();
}
/* while(1)
{
mytask();
pause();
}*/
printf("after pasue2\n");
return 0;
}运行结果:
第一次CTRL+C触发,打印完after pause1,程序进入while(1)循环,在5s内再按下CTRL+C会被堵塞,直达sigprocmask(SIG_UNBLOCK,&set,NULL);只要在5s内按下了CTRL+C就会信号捕获打印handle中的语句,且这个时候因为pause(),再按下CTRL+C会再次运行mytask()。
linux@linux:/mnt/hgfs/linuxshare/linux_code/message2$ ./test
^CI get the sig = 2
after pause1
My task start
^CMy task end
I get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
My task start
My task end
^CI get the sig = 2
My task start
My task end
^CI get the sig = 2
My task start
^C^C^C^C^CMy task end
I get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
My task start
My task end
^CI get the sig = 2
My task start
^C^C^C^C^C^C^C^CMy task end
I get the sig = 2
^CI get the sig = 2
My task start
^C^\Quit (core dumped)
如果上述代码去掉pause(),则输出结果为:则会一直运行mytest(),只是CTRL+C触发运行了handle中的打印语句。
linux@linux:/mnt/hgfs/linuxshare/linux_code/message2$ gcc -o test pause_t_new.c
linux@linux:/mnt/hgfs/linuxshare/linux_code/message2$ ./test
^CI get the sig = 2
after pause1
My task start
My task end
My task start
My task end
My task start
My task end
My task start
^CMy task end
I get the sig = 2
My task start
^C^C^C^C^C^C^C^C^C^CMy task end
I get the sig = 2
My task start
My task end
My task start
My task end
My task start
My task end
My task start
My task end
My task start
^\Quit (core dumped)
五、sigsuspend函数
int sigsuspend(const sigset_t *sigmask);
功能:将进程的屏蔽字替换为由参数sigmask给出的信号集,然后挂起进程的执行
参数:sigmask:希望屏蔽的信号
对比如下代码:
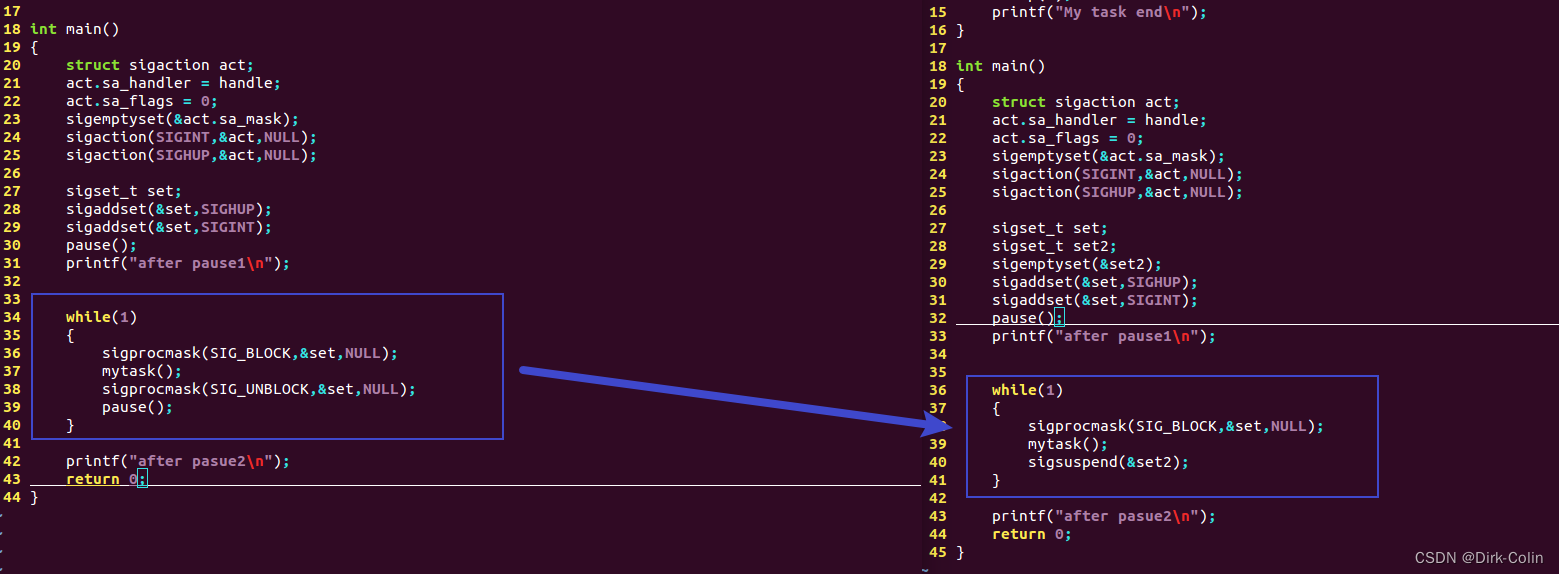
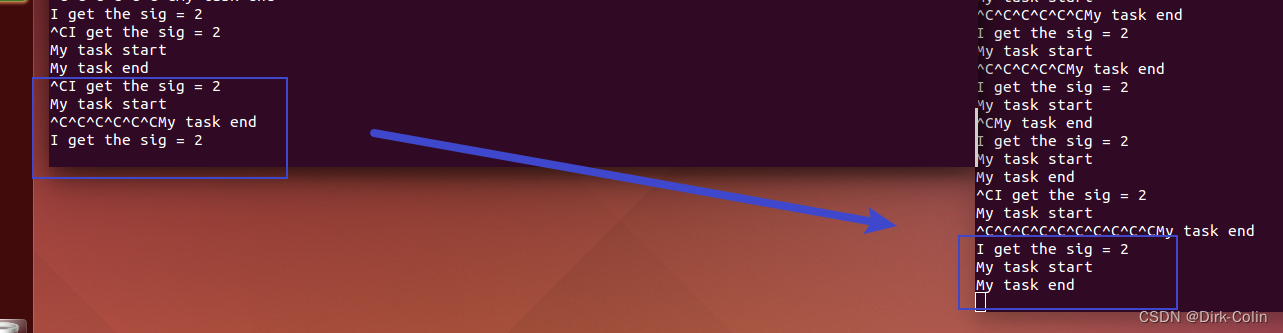
运行结果的区别:
左边运行结果表示你在阻塞期间按下CTRL+C只会捕获一次信号,但是不会认为你需要再执行一次mytask()。只有当运行了sigprocmask(SIG_UNBLOCK,&set,NULL)才有效。
但是右边在任务中间会接收任务,这是因为sigsuspend函数,set2是一个空的信号集。sigsuspend(&set2); 函数允许程序在任务执行的过程中等待信号,一旦收到信号,程序就会立即响应。
详细代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<signal.h>
#include<unistd.h>
void handle(int sig)
{
printf("I get the sig = %d\n",sig);
}
void mytask()
{
printf("My task start\n");
sleep(3);
printf("My task end\n");
}
int main()
{
struct sigaction act;
act.sa_handler = handle;
act.sa_flags = 0;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
sigaction(SIGINT,&act,NULL);
sigaction(SIGHUP,&act,NULL);
sigset_t set;
sigset_t set2;
sigemptyset(&set2);
sigaddset(&set,SIGHUP);
sigaddset(&set,SIGINT);
pause();
printf("after pause1\n");
while(1)
{
sigprocmask(SIG_BLOCK,&set,NULL);
mytask();
sigsuspend(&set2);
}
printf("after pasue2\n");
return 0;
}
先注册了两个信号处理函数 handle,分别用于处理 SIGINT 和 SIGHUP 信号
。然后定义了一个自定义函数 mytask(),它模拟了一个长时间运行的任务。
在 main() 函数中,创建了两个信号集 set 和 set2,set 中包含了 SIGHUP 和 SIGINT 信号。
然后调用了 pause() 函数来挂起进程,直到收到信号为止。
接着进入一个无限循环,在循环中,先将 set 中的信号阻塞,然后执行 mytask() 函数,模拟长时间运行的任务。
然后使用 sigsuspend() 函数挂起进程,等待收到 set2 中的信号。