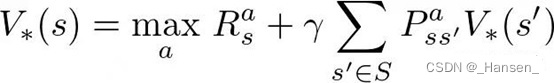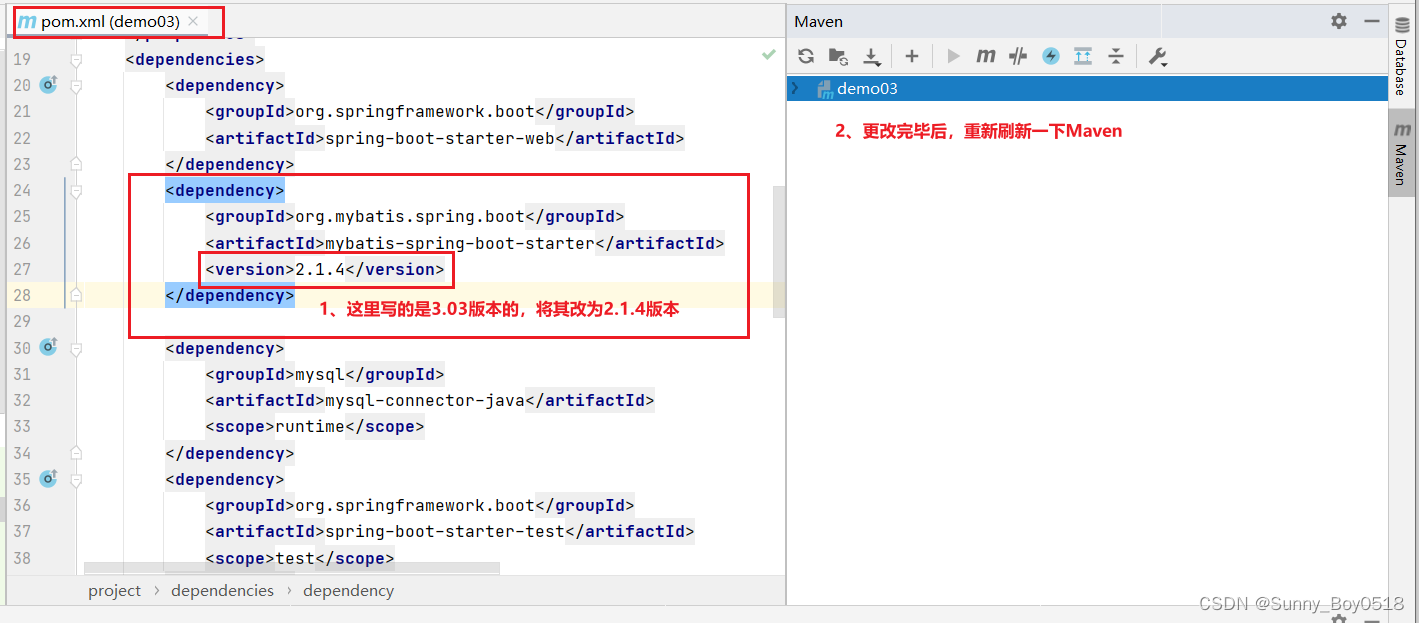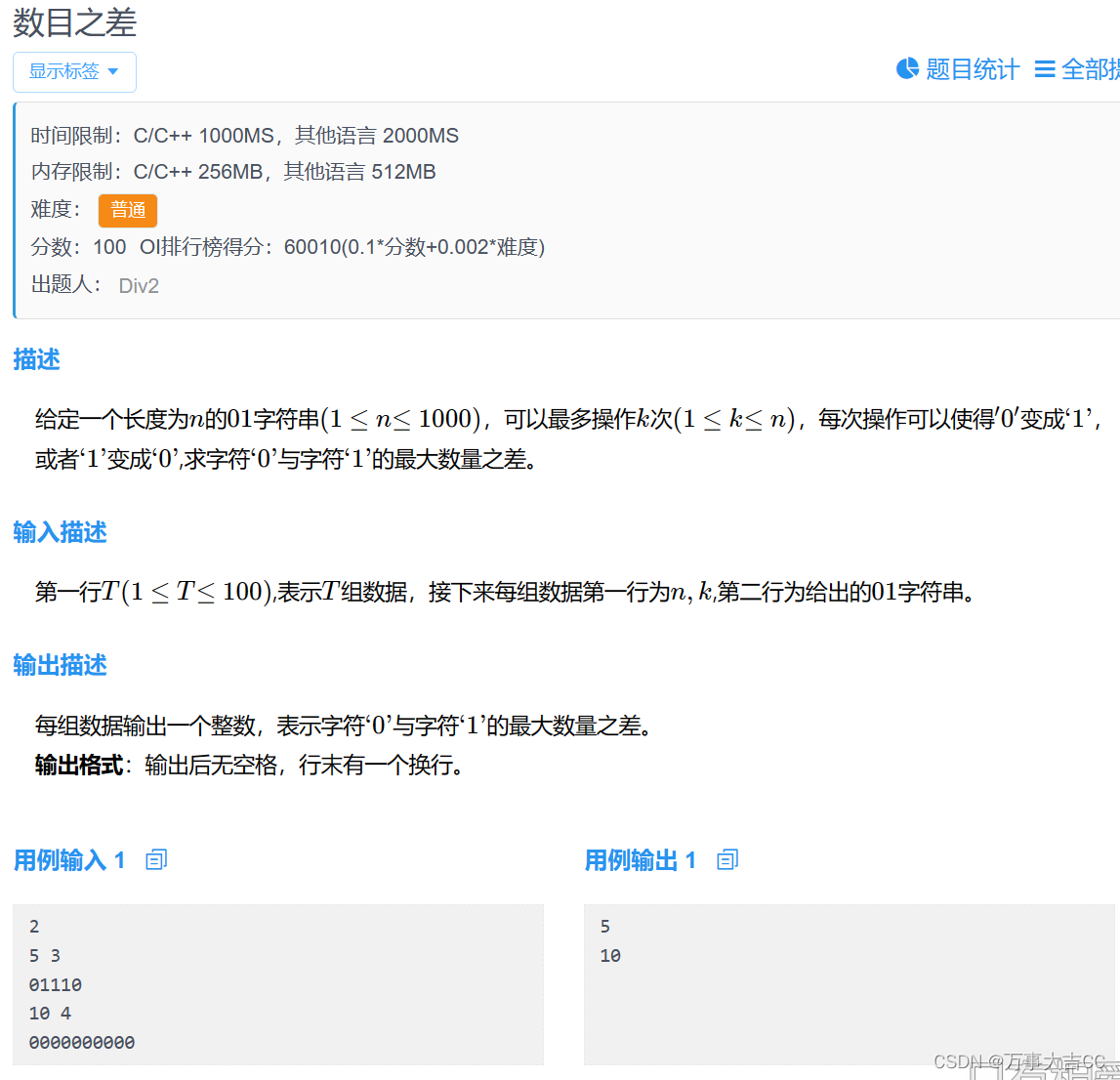
解法一:
显然只需让多的在限度内最多即可
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
void solve() {
int n, k, num0 = 0, num1 = 0;
cin >> n >> k;
string s;
cin >> s;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (s[i] == '0') num0++;
else if (s[i] == '1') num1++;
}
int mx = max(num0, num1);
int mn = min(num0, num1);
while (mn > 0 && k > 0) {
mx++, mn--, k--;
}
cout << mx - mn << endl;
}
int main() {
int t; cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}解法二:
#include <iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t, n, k;
string str;
cin >> t;
for (int i = 1; i <= t; i++) {
int tong[100] = { 0 };
cin >> n >> k >> str;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
tong[str[j] - '0']++;
if (tong[1] >= tong[0]) {
if ((tong[1] + k) > n) cout << n << endl;
else cout << tong[1] + 2 * k - tong[0] << endl;
}
else {
if ((tong[0] + k) > n) cout << n << endl;
else cout << tong[0] - tong[1] + 2 * k << endl;
}
}
}