vue2
- 简介
- 第一天
- 第二天
- 第三天
- 第四天
- 第五天
- 第六天
- 第七天
- 第八天
- 第九天
网课链接(半个月拿下)
简介
需要提前会的东西

中文文档链接点下面
vue.js
要会查文档用API
第一天
清除提示1
再文档中下载开发版本+浏览器安装vue devtools插件
打开允许访问URL

浏览器链接位置
……///……
这个直接在浏览器中安装的拓展在后续学习中时不时出现问题,建议直接从网盘下载工具
网盘链接如下
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ev2zbUIghU_Eo264_ArPWw?pwd=4dzp 提取码: 4dzp 复制这段内容后打开百度网盘手机App,操作更方便哦
……///……
清除提示2
直接写入下面代码,如果没有清除直接回vue.js文档改为txt格式用快捷键ctrl f 查找productionTip,把true改为false,再把文件后缀改回去
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //以阻止 vue 在启动时生成生产提示。
</script>
hello小案例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h1>hello,{{name}}</h1>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //以阻止 vue 在启动时生成生产提示。
//创建vue实例
const x = new Vue({
el:'#root', //el用于指定当前vue实例为哪个容器服务
data:{ //data用于存储数据数据供el所指定容器使用
name:'你好'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
分析
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h1>hello,{{name.toUpperCase()}},{{address}}</h1>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //以阻止 vue 在启动时生成生产提示。
//创建vue实例
const x = new Vue({
el:'#root', //el用于指定当前vue实例为哪个容器服务
data:{ //data用于存储数据数据供el所指定容器使用
name:'你好',
address:'长沙'
}
})
</script>
</body>

第二天
模板语法

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h1>插值语法</h1>
<h3>你好,{{name}}</h3>
<hr/>
<h1>指令语法</h1>
<a v-bind:href="school.url.toUpperCase()" x="hello">点我学习vue{{school.name}}</a>
<a :href="school.url" x="hello">快去学习{{school.name}}</a>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //以阻止 vue 在启动时生成生产提示。
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'jack',
school:{
name:'哈哈',
url:'http://www.atguigu.com'
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
数据绑定

<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<!-- 简写 -->
单向数据绑定:<input type="text" :value="name"><br/>
双向数据绑定:<input type="text" v-model="name"><br/>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //以阻止 vue 在启动时生成生产提示。
new Vue({
el:'#root', //el用于指定当前vue实例为哪个容器服务
data:{ //data用于存储数据数据供el所指定容器使用
name:'你好'
}
})
</script>
el与data的两种写法
学到组件data必须使用函数式

<body>
<div id="root">
<h1>你好,{{name}}</h1>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //以阻止 vue 在启动时生成生产提示。
//el两种写法
/* 第一种
new Vue({
el:'#root', //el用于指定当前vue实例为哪个容器服务
data:{ //data用于存储数据数据供el所指定容器使用
name:'你好'
}
}) */
/* 第二种
const v = new Vue({
data:{
name:'哈哈'
}
})
console.log(v)
v.$mount('#root') //挂载 */
//data两种写法
new Vue({
el:'#root',
//第一种写法,对象式
/* data:{ //data用于存储数据数据供el所指定容器使用
name:'你好'
} */
//第二种,函数式
data:function(){
return{
name:'哈哈'
}
}
})
</script>
第三天
object.defineProperty方法
<script type="text/javascript">
let number = 18
let person = {
name:'张三',
sex:'男',
}
Object.defineProperty(person,'age',{
/* value:18,
enumerable:true, //控制属性是否可以枚举
writable:true, //控制属性是否可以被修改
configurable:true //控制属性是否可以被删除
*/
get(){
console.log('有人读取了age属性了')
return number
},
set(value){
console.log('有人修改了age属性,且值是',value)
number = value
}
})
</script>
数据代理
<script type="text/javascript">
let obj = {x:100}
let obj2 = {y:200}
Object.defineProperty(obj2,'x',{
get(){
return obj.x
},
set(value){
obj.x = value
}
})
</script>
vue中的数据代理
<div id="root">
<h2>学校名称:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷',
address:'长沙',
}
})
</script>
事件处理
<div id="root">
<h2>欢迎来到{{name}}学习</h2>
<button v-on:click="showInfo">点我提示信息</button>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷'
},
methods: {
showInfo(event){
// console.log(this)//此处this是vm
alert('同学你好')
}
},
})
</script>
<div id="root">
<h2>欢迎来到{{name}}学习</h2>
<!-- <button v-on:click="showInfo">点我提示信息</button> -->
<button @click="showInfo1">点我提示信息1</button>
<button @click="showInfo2(66,$event)">点我提示信息2(传参)</button>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷'
},
methods: {
showInfo1(event){
// console.log(this)//此处this是vm
alert('同学你好')
},
showInfo2(number,a){
console.log(number,a)
}
}
})
</script>
事件修饰符

<div id="root">
<h2>欢迎来到{{name}}学习</h2>
<a href="http://www/atguigu.com" @click.prevent="shoowInfo">点我提示信息</a>
<!-- 阻止事件冒泡 -->
<div class="demo1" @click="showInfo">
<button @click.stop="showInfo">点我提示信息</button>
</div>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷'
},
methods: {
showInfo(e){
e.stopPropagation()
alert('同学你好!')
}
},
})
</script>
键盘事件

<div id="root">
<h2>欢迎来到{{name}}学习</h2>
<input type="text" placeholder="按下回车提示输入" @keyup.caps-lock="showInfo">
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷'
},
methods: {
showInfo(e){
console.log(e.target.value)
}
},
})
</script>
计算属性
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
姓: <input type="text" v-model="firstName"><br><br>
名: <input type="text" v-model="lastName"><br><br>
<!-- 拼接姓名实现"张-三"联动 -->
<!-- 第一种实现:使用插值语法(字符串的slice方法,左闭右开截取字符串) ,麻烦-->
姓名: <span>{{firstName.slice(0,3)}}-{{lastName}}</span><br><br>
<!-- 第二种实现:使用methods,每次用到都会调用一次,而计算属性只调用第一次就欧了-->
姓名: <span>{{fullName()}}</span><br><br>
姓名: <span>{{fullName()}}</span><br><br>
姓名: <span>{{fullName()}}</span><br><br>
姓名: <span>{{fullName()}}</span><br><br>
姓名: <span>{{fullName()}}</span>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
firstName: '张',
lastName: '三'
},
methods: {
fullName() {
console.log('调用')
return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName;
}
}
})
</script>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
姓: <input type="text" v-model="firstName"><br><br>
名: <input type="text" v-model="lastName"><br><br>
<!-- 拼接姓名实现"张-三"联动 -->
<!-- 使用计算属性,只调用一次,非常奈斯,节省内存 -->
姓名: <span>{{fullName}}</span><br><br>
姓名: <span>{{fullName}}</span><br><br>
姓名: <span>{{fullName}}</span><br><br>
姓名: <span>{{fullName}}</span><br><br>
姓名: <span>{{fullName}}</span><br><br>
姓名: <span>{{fullName}}</span>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
firstName: '张',
lastName: '三'
},
computed: {
//计算属性里面的属性要写成对象的形式,每个对象里面都有getter和setter
//这个fullName实际上就是firstName和lastName经过一番计算得到的玩意儿,直接给到vm身上
fullName: {
//get有什么用?当有人读取fullName时,get调用,返回值作为fullName的值
//get什么时候调用? 1.初次读取fullName 2.get里用到的数据发生了改变
get() {
console.log('fullName被读了');
// console.log(this);//此处的this是vm
return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName;
},
//set什么时候调用? fullName被手动修改时调用
//这里边呢有个连锁反应,我手动修改vm.fullName导致firstName和lastName被修改,Vue模板重新解析
//页面刷新,firstName和lastName的修改又导致get被重新执行(依赖的数据变了),返回新的fullName
//计算属性计算属性,就是一直在计算,所以要想改fullName,必须改它依赖的值
set(val) {
let arr = val.split('-');
this.firstName = arr[0];
this.lastName = arr[1];
}
}
}
})
</script>
简写
只考虑读取不考虑修改时可使用
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
姓: <input type="text" v-model="firstName"><br><br>
名: <input type="text" v-model="lastName"><br><br>
<!-- 拼接姓名实现"张-三"联动 -->
<!-- 使用计算属性,只调用一次,非常奈斯,节省内存 -->
姓名: <span>{{fullName}}</span>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
firstName: '张',
lastName: '三'
},
computed: {
fullName() {
console.log('fullName被读了');
return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName;
}
}
})
</script>
天气案例
<div id="root">
<!-- 实现点击按钮切换天气 -->
<!-- 写法1:利用插值语法和三元表达式 -->
<h2>今天天气很{{isHot ? '炎热': '寒冷'}}</h2>
<!-- 写法2:利用计算属性 -->
<h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2>
<!-- 绑定事件的时候:@xxx="yyy" yyy可以写一些简单的语句,但是最好别这么干-->
<!-- <button @click="isHot = !isHot">切换天气</button>-->
<button @click='change'>点击切换天气</button>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
isHot: true
},
methods: {
change() {
this.isHot = !this.isHot;
}
},
computed: {
info() {
//注意这里的isHot要加this
return this.isHot ? '炎热' : '寒冷';
}
},
})
</script>
监视属性
<div id="root">
<!-- 实现点击按钮切换天气 -->
<!-- 写法1:利用插值语法和三元表达式 -->
<h2>今天天气很{{isHot ? '炎热': '寒冷'}}</h2>
<!-- 写法2:利用计算属性 -->
<h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2>
<!-- 绑定事件的时候:@xxx="yyy" yyy可以写一些简单的语句,但是最好别这么干-->
<!-- <button @click="isHot = !isHot">切换天气</button>-->
<button @click='change'>点击切换天气</button>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
isHot: true
},
methods: {
change() {
this.isHot = !this.isHot;
}
},
computed: {
info() {
//注意这里的isHot要加this
return this.isHot ? '炎热' : '寒冷';
}
},
watch: {
isHot: {
immediate: true, //初始化时先调用一次handler
//当isHot被修改时调用handler函数
handler(newVal, oldVal) {
console.log('isHot被修改了', '改之前是' + oldVal, '改之后是' + newVal);
}
},
//watch不只可以监视data中的属性,还可以监视计算属性
info: {
immediate: true, //初始化时先调用一次handler
//当isHot被修改时调用handler函数
handler(newVal, oldVal) {
console.log('info被修改了', '改之前是' + oldVal, '改之后是' + newVal);
}
}
}
})
</script>
通过vm.$watch监视
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
isHot: true
},
methods: {
change() {
this.isHot = !this.isHot;
}
},
computed: {
info() {
//注意这里的isHot要加this
return this.isHot ? '炎热' : '寒冷';
}
}
})
vm.$watch('isHot', {
immediate: true, //初始化时先调用一次handler
//当isHot被修改时调用handler函数
handler(newVal, oldVal) {
console.log('isHot被修改了', '改之前是' + oldVal, '改之后是' + newVal);
}
})
vm.$watch('info', {
immediate: true, //初始化时先调用一次handler
//当isHot被修改时调用handler函数
handler(newVal, oldVal) {
console.log('info被修改了', '改之前是' + oldVal, '改之后是' + newVal);
}
})
深度监视
<!-- 准备一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h3>a的值是:{{numbers.a}}</h3>
<button @click="numbers.a++">点我实现a+1</button>
<h3>b的值是:{{numbers.b}}</h3>
<button @click="numbers.b++">点我实现b+1</button>
<h3>我tm就非要强制让number变</h3>
<button @click="numbers = {a:666, b:999}">点我改变numbers</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
isHot: true,
numbers: {
a: 1,
b: 2
}
},
watch: {
//监视多级结构中某个属性的变化,使用引号包起来(之前不加引号都是简写形式)
'numbers.a': {
handler() {
console.log('a被改变了');
}
},
//如果下面这么写,即使ab变了也不会执行handler,因为这么写意思是监视numbers这个属性
//而这个属性值是一个对象,只要numbers对象的地址不变就不变,除非像上面div写的暴力方法
numbers: {
handler() {
console.log('numbers改变了');
}
},
//但是如果加个deep,就可以监视多级结构中某个属性的变化,ab变了numbers也变
numbers: {
deep: true,
handler() {
console.log('numbers改变了');
}
},
}
})
</script>
简写
//复杂形式
vm.$watch('isHot', {
//当isHot被修改时调用handler函数
handler(newVal, oldVal) {
console.log('isHot被修改了', '改之前是' + oldVal, '改之后是' + newVal);
}
})
//简写形式
vm.$watch('isHot',function (newVaule,oldVaule) {
console.log(newVaule,oldVaule);
})
计算属性对比监视属性
计算
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
firstName: '张',
lastName: '三'
},
computed: {
fullName() {
console.log('fullName被读了');
return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName;
}
}
})
监视
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
firstName: '张',
lastName: '三',
fullName: '张-三'
},
watch: {
firstName: {
handler(newVal, oldVal) {
this.fullName = newVal + '-' + this.lastName;
}
},
lastName: {
handler(newVal, oldVal) {
this.fullName = this.firstName + '-' + newVal;
}
},
}
})
computed能完成的功能,watch都可以完成
第四天
绑定class样式
<div id="root">
<!-- 1. 绑定class样式--字符串写法,适用于样式的类名不确定,需要动态指定-->
<div class="basic" :class="mood" @click="changeMood">{{name}}</div>
<!-- 2. 绑定class样式--数组写法,适用于要绑定的样式个数不确定,名字也不确定-->
<div class="basic" :class="classArr" @click="removeStyle3">{{name}}</div><br>
<!-- 3. 绑定class样式--对象写法,适用于要绑定的样式个数确定,名字也确定,要动态决定用不用-->
<div class="basic" :class="classObj">{{name}}</div><br>
<button @click="useStyle1">点击添加样式1</button>
<button @click="useStyle2">点击添加样式2</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
name: 'zzy',
mood: 'normal',
classArr: ['style1', 'style2', 'style3'],
classObj: {
style1: false,
style2: false
}
},
methods: {
changeMood() {
// this.mood = 'happy';
//点击实现随机切换样式
const arr = ['happy', 'sad', 'normal'];
const index = Math.floor(Math.random() * 3); //获取0-3之间的整数不包括3
this.mood = arr[index];
},
//点击去掉style3样式
removeStyle3() {
this.classArr.pop();
},
//点击添加样式1
useStyle1() {
this.classObj.style1 = true;
// this.classObj.style2 = true;
},
//点击添加样式2
useStyle2() {
// this.classObj.style1 = true;
this.classObj.style2 = true;
}
}
})
</script>
绑定style样式
<!-- 绑定style样式--对象写法-->
<div class="basic" :class="classArr" :style="styleObj" >{{name}}</div><br>
<!-- 绑定style样式--数组写法(非常不常用)-->
<div class="basic" :class="classArr" :style="[styleObj,styleObj2]" >{{name}}</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data: {
name: 'zzy',
styleObj:{
//驼峰命名法
fontSize:'50px',
color:'red'
},
styleObj2:{
//驼峰命名法
backgroundColor:'green'
}
}
})
</script>
条件渲染
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<!-- 1.v-show="false" => 相当于display:none -->
<h2 v-show="false">我的名字叫{{name}}</h2>
<h2 v-show="1 === 3">我的名字叫{{name}}</h2>
<!-- 等价于<h2 style="display: none;">我的名字叫{{name}}</h2> -->
<!-- 2.v-if="false" => 彻底删除标签了 -->
<h2 v-if="false">我的名字叫{{name}}</h2>
<h2 v-if="1 === 3">我的名字叫{{name}}</h2>
<!-- 实现功能:随着n递增展示不同的div -->
<h2>当前n的值是:{{n}}</h2>
<button v-on:click="n++">点击n+1</button>
<!-- 这里的v-if,v-else-if,v-else和基础js里的一样儿 -->
<div v-if="n === 1">Angular</div>
<div v-else-if="n === 2">React</div>
<div v-else-if="n === 3">Vue</div>
<div v-else>哈哈</div>
<!-- v-if和template的配合使用(v-show不行)
template不会影响页面结构,页面运行后会自动去掉,但是可以配合v-if控制多个元素整体显示
而且不会影响css拿节点-->
<template v-if="n === 1">
<div>哈哈1</div>
<div>哈哈2</div>
<div>哈哈3</div>
</template>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
name: 'zzy',
n: 0
}
})
</script>
列表渲染
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) in persons" :key="p.id">
<!-- 遍历数组的话,index是索引值,p是数组每个元素 -->
{{p.name}}----{{p.age}}----{{index}}
</li>
<li v-for="(p,index) of games" :key="index">
<!-- 遍历对象的话,index就是属性名,p是属性值 -->
{{p}}---{{index}}
</li>
<li v-for="(p,index) of str" :key="index">
<!-- 遍历字符串的话,index就是索引值,p是每个字符 -->
{{p}}---{{index}}
</li>
<li v-for="(p,index) of 5" :key="index">
<!-- 遍历指定次数的话,index就是索引值,p是从1开始数 -->
{{p}}---{{index}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
//下面同上
key作用和原理
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h1>人员列表</h1>
<button @click="add">点击添加老刘</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) in persons" :key="p.id">
<!-- 遍历数组的话,index是索引值,p是数组每个元素 -->
{{p.name}}----{{p.age}}----{{index}}
<input type="text">
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
persons: [
{ id: '001', name: '张三', age: 23 },
{ id: '002', name: '李四', age: 18 },
{ id: '003', name: '王五', age: 10 }
]
},
methods: {
add() {
const p = { id: 004, name: '老刘', age: 90 };
this.persons.unshift(p);
}
},
})
</script>

列表过滤
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h1>人员列表</h1>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入关键字" v-model="keyword" @keyup.enter="search">
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) in newPersons" :key="p.id">
{{p.name}}----{{p.age}}----{{p.sex}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
keyword: '',
persons: [
{ id: '001', name: '冯万宁儿', age: 23, sex: '男' },
{ id: '002', name: '屁及万儿', age: 18, sex: '男' },
{ id: '003', name: '及丽热巴', age: 10, sex: '女' },
{ id: '004', name: '冯小刚儿', age: 60, sex: '男' }
],
newPersons: []
},
methods: {
search() {
this.newPersons = this.persons.filter((ele, index) => {
const arr = ele.name.split(''); //先把每个对象的name分割为数组
//数组里是不包含空字符串的,所以这样如果keyword=''是筛不出来东西的
const flag = arr.includes(this.keyword); //判断数组中是否包含当前vue中的keyword
return flag; //筛选出来包含keyword的对象,组成一个新数组
})
}
},
})
</script>
用watch瑕疵实现
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h1>人员列表</h1>
<!-- <input type="text" placeholder="请输入关键字" v-model="keyword" @keyup.enter="search"> -->
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入关键字" v-model="keyword">
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) in newPersons" :key="p.id">
{{p.name}}----{{p.age}}----{{p.sex}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
keyword: '',
persons: [
{ id: '001', name: '冯万宁儿', age: 23, sex: '男' },
{ id: '002', name: '屁及万儿', age: 18, sex: '男' },
{ id: '003', name: '及丽热巴', age: 10, sex: '女' },
{ id: '004', name: '冯小刚儿', age: 60, sex: '男' }
],
newPersons: []
},
watch: {
keyword: {
//页面上来由于newPersons是空,不会显示数据,想要让页面初始化就显示所有人,就要加个immediate: true
//这样就可以让handler函数初始化时先调用一次,由于开始keyword=''
// 而字符串里都包含空字符串,就可以先筛选出来,初始化所有人物信息
immediate: true,
handler(newVal, oldVal) {
this.newPersons = this.persons.filter((ele) => {
//判断keyword变化后的新值在不在每个对象的name中,并返回一个新的数组
return ele.name.includes(newVal);
//有个点要注意,字符串里面是有空字符串的
});
}
}
}
})
</script>
用computed完美实现
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h1>人员列表</h1>
<!-- <input type="text" placeholder="请输入关键字" v-model="keyword" @keyup.enter="search"> -->
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入关键字" v-model="keyword">
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) in newPersons" :key="p.id">
{{p.name}}----{{p.age}}----{{p.sex}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
keyword: '',
persons: [
{ id: '001', name: '冯万宁儿', age: 23, sex: '男' },
{ id: '002', name: '屁及万儿', age: 18, sex: '男' },
{ id: '003', name: '及丽热巴', age: 10, sex: '女' },
{ id: '004', name: '冯小刚儿', age: 60, sex: '男' }
],
//newPersons: []
},
computed: {
newPersons: {
get() {
return this.persons.filter((ele) => {
return ele.name.includes(this.keyword);
})
}
}
}
})
</script>
列表排序
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h1>人员列表</h1>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入关键字" v-model="keyword">
<button @click="sortType = 0">原顺序</button>
<button @click="sortType = 1">年龄降序</button>
<button @click="sortType = 2">年龄升序</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) in newPersons" :key="p.id">
{{p.name}}----{{p.age}}----{{p.sex}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
sortType: 0, //0原顺序,1年龄降序,2年龄升序
keyword: '',
persons: [
{ id: '001', name: '冯万宁儿', age: 23, sex: '男' },
{ id: '002', name: '屁及万儿', age: 18, sex: '男' },
{ id: '003', name: '及丽热巴', age: 10, sex: '女' },
{ id: '004', name: '冯小刚儿', age: 60, sex: '男' }
],
},
computed: {
newPersons() {
//先过滤,再排序
const arr = this.persons.filter((p) => {
return p.name.indexOf(this.keyword) !== -1
})
// 或者if(this.sortType)
if (this.sortType !== 0) {
arr.sort((a, b) => this.sortType === 1 ? b.age - a.age : a.age - b.age)
}
return arr
}
}
})
</script>
更新时的问题
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h1>人员列表</h1>
<button @click="updateNing">更新冯万宁儿</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) in persons" :key="p.id">
{{p.name}}----{{p.age}}----{{p.sex}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
persons: [
{ id: '001', name: '冯万宁儿', age: 23, sex: '男' },
{ id: '002', name: '屁及万儿', age: 18, sex: '男' },
{ id: '003', name: '及丽热巴', age: 10, sex: '女' },
{ id: '004', name: '冯小刚儿', age: 60, sex: '男' }
],
},
methods: {
updateNing() {
// this.persons[0].name = '冯千宁儿'; //奏效
// this.persons[0].age = 66; //奏效
// this.persons[0].sex = '女'; //奏效
this.persons[0] = { id: '001', name: '冯千宁儿', age: 66, sex: '女' };
//上面这么写,也奏效,数据实际上已经改了,但是Vue监测不到所以没更新到页面,为啥捏?
}
}
})
</script>

监测数据的原理
let data = {
name: 'zzy',
age: 18
}
//创建一个监视的实例对象,用来监视data中数据的变化
const obs = new Observer(data);
const vm = {};
vm._data = obs;
//创建一个类似vm._data的构造函数
function Observer(obj) {
//1.创建一个数组接收传入对象的属性名
let arr = Object.keys(obj); //['name','age']
//2.遍历属性名,让Observer实例对data中的每个数据进行数据代理
arr.forEach((k) => {
Object.defineProperty(this, k, {
get() {
//有人想读实例中的属性值,我就把data中对应的属性值拿过来
return obj[k];
},
set(val) {
//有人想改实例中的属性值,我就把data中对应的属性值更改(数据代理)
console.log(`${k}被改了,我要重新解析模板,生成虚拟DOM,开始diff算法`);
obj[k] = val;
}
})
})
}
案例Vue.set()使用
<div id="root">
<h2>我的名字:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>我的年龄:{{age}}</h2>
<h3 v-if="sex">我的性别:{{sex}}</h3>
<button @click="addmySex">点击添加我的性别</button>
<hr>
<h2>她的名字:{{girlfriend.name}}</h2>
<button @click="addherSex">点击添加性别,属性值为女</button>
<h2 v-if="girlfriend.sex">她的性别:{{girlfriend.sex}}</h2> <!-- undefined不显示,也不报错 -->
<h2>她的年龄:对外{{girlfriend.age.fakeAge}},真实{{girlfriend.age.realAge}}</h2>
<h2>朋友们</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="p in girlfriend.friends" :key="p.id">
{{p.name}}----{{p.age}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
name: 'zzy',
age: 18,
girlfriend: {
name: 'ht',
// sex: '女',
age: {
realAge: 23,
fakeAge: 18
}
}
},
methods: {
addherSex() {
// Vue.set(this.girlfriend, 'sex', '女');
this.$set(this.girlfriend, 'sex', '女'); //vm.$set(vm.girlfriend, 'sex', '女');
},
addmySex() {
Vue.set(this, 'sex', '男');
}
},
})
</script>
(说实话,我没听懂……)所以我又听了一遍
Vue监测数组
<div id="root">
<h2>我的名字:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>我的年龄:{{age}}</h2>
<hr>
<h2>她的名字:{{girlfriend.name}}</h2>
<button @click="addHobby">点击替换'跳'的爱好</button>
<h2>爱好</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="(h,index) in girlfriend.hobby" :key="index">
{{h}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
name: 'zzy',
age: 18,
girlfriend: {
name: 'ht',
hobby: ['唱', '跳', 'rap']
}
},
methods: {
addHobby() {
//除了那7个方法外,set方法也可以改变数组实现响应式
Vue.set(this.girlfriend.hobby, 1, '打游戏');
}
},
})
</script>
案例
<div id="root">
<button @click="addSex">添加一个性别属性,默认为女</button>
<button @click="addHeight">添加一个身高属性,默认为170</button><br>
<button @click="girlfriend.age.realAge--">年龄-1</button>
<button @click="addFriend">在列表前加一个朋友</button><br>
<button @click="updateFriend">修改第一个朋友的名字为张三</button>
<button @click="addHobby">添加一个爱好</button><br>
<button @click="updateHobby">修改第一个爱好为散步</button>
<button @click="removeHobby">过滤掉爱好中的跳</button>
<h2>名字:{{girlfriend.name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:对外{{girlfriend.age.fakeAge}},真实{{girlfriend.age.realAge}}</h2>
<h2 v-if="girlfriend.sex">性别:{{girlfriend.sex}}</h2>
<h2 v-if="girlfriend.height">身高:{{girlfriend.height}}</h2>
<h2>朋友们</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="p in girlfriend.friends" :key="p.id">
{{p.name}}----{{p.age}}
</li>
</ul>
<h2>爱好</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="(h,index) in girlfriend.hobby" :key="index">
{{h}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
name: 'zzy',
age: 18,
girlfriend: {
name: 'ht',
// sex: '女',
age: {
realAge: 23,
fakeAge: 18
},
friends: [
{ id: 001, name: 'jack', age: 10 },
{ id: 002, name: 'rose', age: 8 },
],
hobby: ['唱', '跳', 'rap']
}
},
methods: {
addSex() {
Vue.set(this.girlfriend, 'sex', '女');
},
addHeight() {
this.$set(this.girlfriend, 'height', 170);
},
addFriend() {
this.girlfriend.friends.unshift({ id: '003', name: 'alice', age: 5 }); //有效写法
},
updateFriend() {
this.girlfriend.friends[0].name = '张三';
},
addHobby() {
this.girlfriend.hobby.push('打游戏');
},
updateHobby() {
// this.girlfriend.hobby[0] = '散步'; //无效写法
// this.girlfriend.hobby.splice(0, 1, '散步'); //有效写法
Vue.set(this.girlfriend.hobby, 0, '散步'); //有效写法
},
removeHobby() {
// 变更方法,顾名思义,会变更调用了这些方法的原始数组。相比之下,也有非变更方法
// 例如 filter()、concat() 和 slice()。它们不会变更原始数组,而总是返回一个新数组。
// 当使用非变更方法时,可以用新数组替换旧数组:
this.girlfriend.hobby = this.girlfriend.hobby.filter((ele) => {
return ele !== '跳';
})
}
},
})
</script>
**代码参考与——DantinZhang
**
第五天
收集表单数据
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<form v-on:submit.prevent="demo">
<!-- v-model.trim去掉收集的首尾空格 -->
账号:<input type="text" v-model.trim="userInfo.account"> <br><br>
密码:<input type="password" v-model="userInfo.password"><br><br>
<!--下面是 双向绑定修饰符:收集到的必须是数字类型(Vue内部做了数据转换) -->
年龄:<input type="number" v-model.number="userInfo.age"><!-- v-model.number经常和type="number"一起用 --><br><br>
性别:
男<input type="radio" name="sex" value="male" v-model="userInfo.sex">
女<input type="radio" name="sex" value="female" v-model="userInfo.sex"><br><br>
爱好:
抽烟<input type="checkbox" value="smoke" v-model="userInfo.hobby">
喝酒<input type="checkbox" value="drink" v-model="userInfo.hobby">
跳舞<input type="checkbox" value="dance" v-model="userInfo.hobby"><br><br>
玩哪个游戏?
<select v-model="userInfo.game">
<option value="saibo">赛博朋克2077</option>
<option value="ditie">地铁:离去</option>
<option value="dipingxian">地平线4</option>
<option value="nfsmw">极品飞车21:热度</option>
<option value="dabiaoge">荒野大镖客2</option>
</select><br><br>
<!-- v-model.lazy可以实现不用实时收集,输入框焦点离开了再收集 -->
其他信息: <textarea v-model.lazy="userInfo.other"></textarea><br><br>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="userInfo.agree">阅读并接受<a href="http://www.baidu.com">用户协议</a>
<button>提交</button>
</form>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
userInfo: {
account: '',
password: '',
age: '',
sex: 'female',
//hobby的数据类型影响着多选框收集到的数据类型
hobby: [],
game: 'nf smw',
other: '',
agree: '',
},
},
methods: {
demo() {
// console.log(JSON.stringify(this._data)); //一般不建议直接访问_data,建议用个对象包住数据
console.log(JSON.stringify(this.userInfo)); //只是这么写的话,所有双向绑定都要加userInfo前缀
}
},
})
</script>
v-model的三个修饰符
v-model.lazy:实现不用实时收集,输入框失去焦点再收集
v-model.number:输入的字符串收集为数字(Vue内部做了数据转换),经常和type="number"一起用
v-model.trim:收集时去掉输入的首尾空格
过滤器格式化时间戳
dayjs
<!-- 准备一个容器 -->
<div id="hello">
<h1>当前时间是:{{time}}</h1>
<!-- 计算属性实现 -->
<h1>当前时间是:{{formatTime}}</h1>
<!-- 方法实现 -->
<h1>当前时间是:{{getformatTime()}}</h1>
<!-- 过滤器实现 time传给timeFormater,然后返回值替换整个部分-->
<h1>当前时间是:{{time | timeFormater}}</h1>
<!-- 过滤器实现(传参)-->
<h1>当前时间是:{{time | timeFormater('YYYY——MM——DD')}}</h1>
<!-- 过滤器的串联,一层一层往后传,后面的接受的是前面的返回值-->
<h1>当前时间是:{{time | timeFormater('YYYY——MM——DD') | mySlice}}</h1>
<!-- 下面这个打开控制台看元素节点就明白了 -->
<h3 :x="name | mySlice">DJ</h3>
</div>
<script>
// 全局过滤器
Vue.filter('mySlice', function (val) {
return val.slice(0, 4);
})
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#hello',
data: {
time: 1660472948789,
name: 'zhangziying'
},
computed: {
formatTime: {
get() {
return dayjs(this.time).format('YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss');
}
}
},
methods: {
getformatTime() {
return dayjs(this.time).format('YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss');
}
},
// 局部过滤器
filters: {
//第一个参数是管道符 | 前边那玩意儿
//第二个参数str来个默认值,如果传了str就给,不传就用默认值
timeFormater(val, str = 'YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss') {
// console.log(val);
return dayjs(this.time).format(str);
},
mySlice(val) {
//这里的val是上一个过滤器的返回值
return val.slice(0, 4);
}
}
})
</script>
内置指令
v-bind : 单向绑定解析表达式, 可简写为 :xxx
v-model : 双向数据绑定
v-for : 遍历数组/对象/字符串
v-on : 绑定事件监听, 可简写为@
v-if : 条件渲染(动态控制节点是否存存在)
v-else : 条件渲染(动态控制节点是否存存在)
v-show : 条件渲染 (动态控制节点是否展示)
v-text指令:
1.作用:向其所在的节点中渲染文本内容。
2.与插值语法的区别:v-text会替换掉节点中的所有内容,{{xx}}则不会
v-html指令:
作用:向指定节点中渲染包含html结构的内容。
与插值语法的区别:
(1)v-html会替换掉节点中所有的内容,{{xx}}则不会,这点和v-text一样。
(2)v-html可以识别html结构,这点和v-text区别,v-text不能渲染标签。
严重注意:v-html有安全性问题!!!!
(1)在网站上动态渲染任意HTML是非常危险的,容易导致XSS攻击。
(2)一定要在可信的内容上使用v-html,永不要用在用户提交的内容上!
v-cloak指令(没有值):
(1)本质是一个特殊属性,Vue实例创建完毕并接管容器后,会删掉v-cloak属性。
(2)使用css配合v-cloak可以解决网速慢时页面展示出{{xxx}}的问题,先隐藏标签,然后Vue渲染完了之后删除v-cloak,那么就能显示渲染完之后的页面了
v-once指令:
(1)v-once所在节点在初次动态渲染后,就视为静态内容了,也就是只读一次。
(2)以后数据的改变不会引起v-once所在结构的更新,可以用于优化性能。
v-pre指令:
(1)跳过其所在节点的编译过程。
(2)可利用它跳过:没有使用指令语法、没有使用插值语法的节点,会加快编译。
cookie

批量编辑器
自定义指令
函数式
<!-- 准备一个容器 -->
<div id="hello">
<h1>当前n值是:<span v-text="n"></span></h1>
<h1>放大十倍后的n值是:<span v-big="n"></span></h1>
<button @click="n++">点我n+1</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#hello',
data: {
n: 1
},
directives: {
//一、函数式
// 需求1:定义一个v-big指令,和v-text功能类似,但会把绑定的数值放大10倍。
//第一个参数是指令所在的标签,第二个参数是一个存着指令值的对象
big(element, binding) {
//big函数何时会被调用?
//1.指令与元素成功绑定时(一上来,没放入页面之前) 2.指令所在的模板被重新解析时
console.log('我被调用了');
element.innerText = binding.value * 10;
},
}
})
</script>
对象式
<!-- 准备一个容器 -->
<div id="hello">
<h1>当前n值是:<span v-text="n"></span></h1>
<button @click="n++">点我n+1</button>
<!-- 在输入框中显示n的值动态变化 -->
<input v-fbind:value="n">
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#hello',
data: {
n: 1
},
directives: {
// 需求2:定义一个v-fbind指令,和v-bind功能类似,但可以让其所绑定的input元素默认获取焦点。
//函数无法实现该需求
// fbind(element, binding) {
// element.innerText = binding.value * 10;
// //下面这个focus,必须在放到页面之后才调用
// element.focus(); //不奏效,因为big函数调用时还没放入页面
// }
//二、对象式
fbind: {
// 指令与元素成功绑定时(一上来,没放入页面之前)
bind(element, binding) {
element.value = binding.value;
},
// 指令所在元素被插入页面时
inserted(element, binding) {
element.focus();
},
// 指令所在的模板被重新解析时
update(element, binding) {
element.value = binding.value;
}
}
}
})
</script>
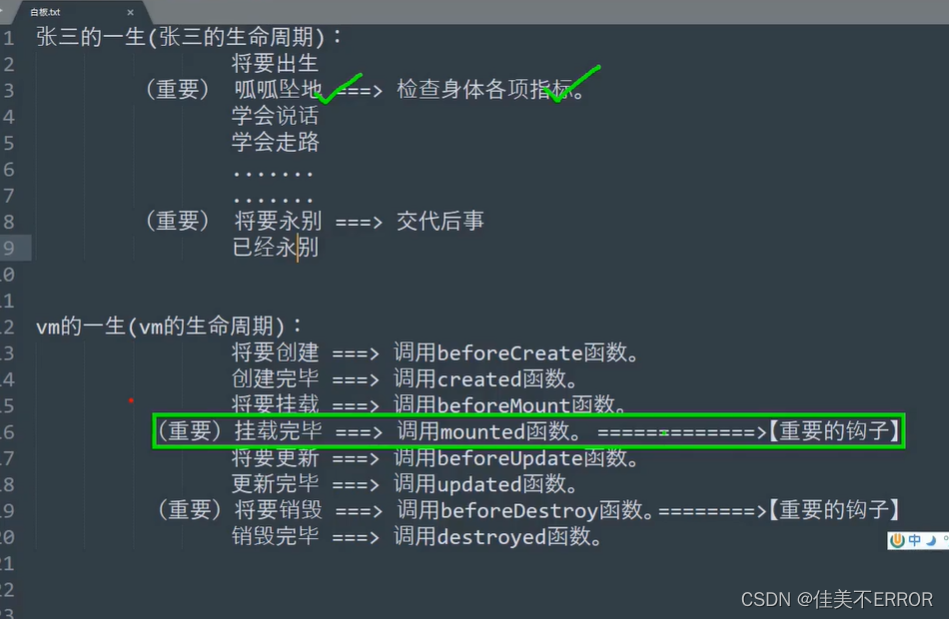
生命周期
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
a:false,
opacity:1
},
methods: {
},
mounted() {
console.log('mounted',this)
setInterval(()=>{
this.opacity -=0.01
if(this.opacity<=0) this.opacity = 1
},16)
},
})
</script>
生命周期图示
八个钩子
<!-- 准备一个容器 -->
<div id="hello">
<h1>欢迎来到{{n}}年代</h1>
<button @click="add">点击n+1</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#hello',
data: {
n: 1
},
methods: {
add() {
this.n++;
}
},
beforeCreate() {
console.log('beforeCreate');
console.log(this);
// debugger;
},
created() {
console.log('created');
},
beforeMount() {
console.log('beforeMount');
},
mounted() {
console.log('mounted');
},
beforeUpdate() {
console.log('beforeUpdate');
},
updated() {
console.log('updated');
},
beforeDestroy() {
console.log('beforeDestroy');
},
destryed() {
console.log('destryed');
}
})
</script>
案例
<!-- 准备一个容器 -->
<div id="hello">
<h1 :style="{opacity: opacity}">欢迎来到2024</h1>
<button @click="stop">点击停止闪烁</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#hello',
data: {
opacity: 1
},
methods: {
stop() {
// clearInterval(this.timer); vm自杀可以这么写,他杀需要写在beforeDestroy中
this.$destroy(); //vm自杀
}
},
//挂载意思就是放在页面上
//挂载函数,Vue完成模板的解析并把*初始的(只调用一次)*真实DOM放入页面后(完成挂载)调用mounted
mounted() {
this.timer = setInterval(() => {
console.log('计时器调用');
this.opacity -= 0.01;
if (this.opacity <= 0) this.opacity = 1; //js里玩儿小数一般碰不到0
}, 16)
},
beforeDestroy() {
console.log('vm即将被销毁');
// 为什么vm的后事需要写在这里,是因为vm很有可能是被别人干掉的
clearInterval(this.timer);
},
})
//通过外部的定时器实现(不推荐)
// setInterval(() => {
// vm.opacity -= 0.01;
// if (vm.opacity <= 0) vm.opacity = 1; //js里玩儿小数一般碰不到0
// }, 16);
</script>
第六天
使用组件
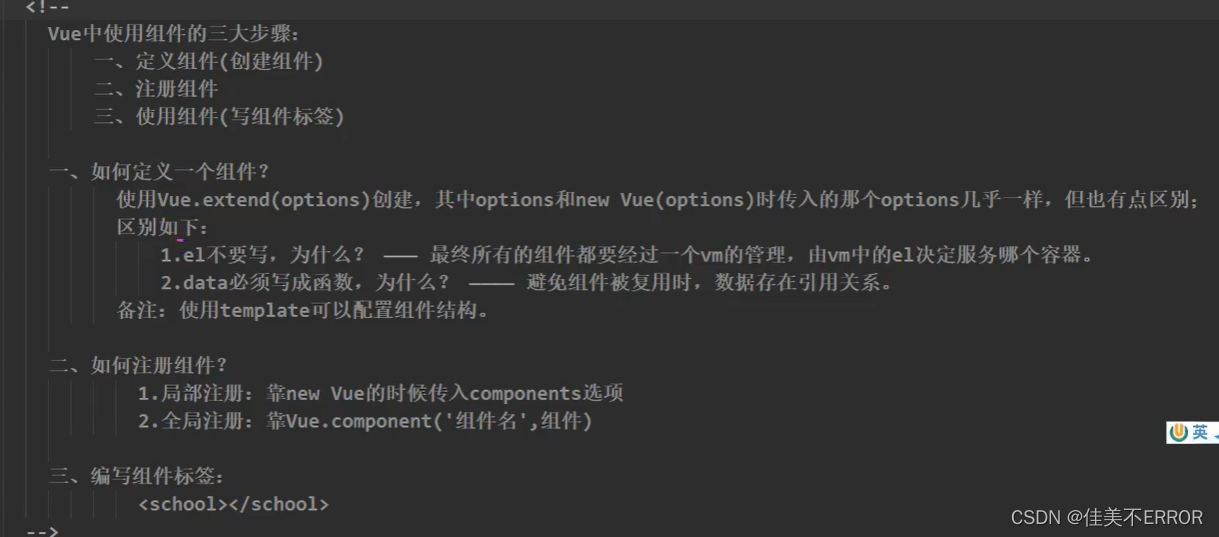
<div id="root">
<hello></hello>
<hr>
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
<school></school>
<hr>
<student></student>
</div>
<div id="root2">
<hello></hello>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
//创建school组件
const school = Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<h2>学校名称:{{schoolName}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
<button @click="showName">点我提示校名</button>
</div>
`,
data(){
return{
schoolName:'尚硅谷',
address:'长沙'
}
},
methods: {
showName(){
alert(this.schoolName)
}
},
})
//创建student组件
const student = Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<h2>学生姓名:{{studentName}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄:{{age}}</h2>
</div>
`,
data(){
return{
studentName:'张三',
age:18
}
}
})
const hello = Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<h2>你好啊!</h2>
</div>
`,
data(){
return{
name:'Tom'
}
}
})
//全局注册组件
Vue.component('hello',hello)
//创建vm
new Vue({
el:'#root',
//注册组件(局部注册)
components:{
school,
student
}
})
new Vue({
el:'#root2',
})
</script>
注意点
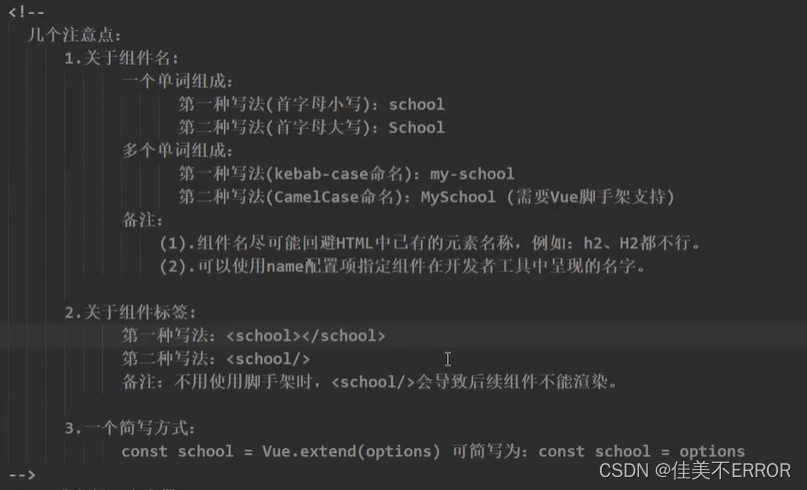
组件的嵌套
<div id="root">
<app></app>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
//定义student组件
const student = Vue.extend({
name:'student',
template:`
<div>
<h2>学生姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄:{{age}}</h2>
</div>
`,
data(){
return{
name:'张三',
age:18
}
}
})
//定义school组件
const school = Vue.extend({
name:'school',
template:`
<div>
<h2>学校名称:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
<student></student>
</div>
`,
data(){
return{
name:'尚硅谷',
address:'北京'
}
},
//注册组件(局部)
components:{
student
}
})
//定义hello组件
const hello = Vue.extend({
template:`
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
`,
data(){
return{
msg:'欢迎来到尚硅谷学习'
}
}
})
//定义app组件
const app = Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<hello></hello>
<school></school>
</div>
`,
components:{
school,
hello
}
})
//创建vm
new Vue({
el:'#root',
//注册组件(局部)
components:{
app
}
})
</script>
VueComponent
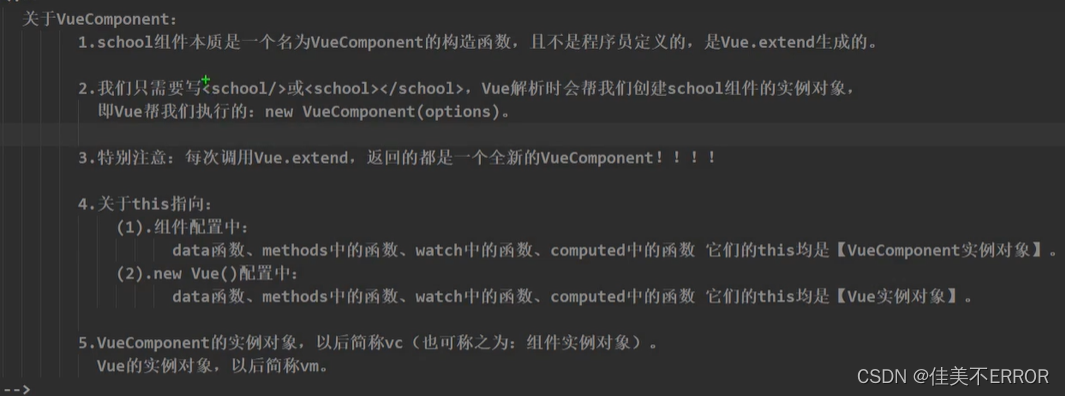
<div id="root">
<hello></hello>
<school></school>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
//定义student组件
//定义school组件
const school = Vue.extend({
name:'school',
template:`
<div>
<h2>学校名称:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
<button @click="showName">点我提示学校名</button>
</div>
`,
data(){
return{
name:'尚硅谷',
address:'北京'
}
},
methods: {
showName(){
// alert(this.name)
console.log('showName',this)
}
},
})
const test = Vue.extend({
template:`<span>hahahaha</span>`,
})
//定义hello组件
const hello = Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<test></test>
</div>
`,
data(){
return{
msg:'你好'
}
},
components:{
test
}
})
// console.log('@',school)
// console.log('#',hello)
//定义app组件
//创建vm
new Vue({
el:'#root',
//注册组件(局部)
components:{
school,
hello
}
})
</script>
重要的内置关系

<div id="root">
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
//定义一个构造函数
function Demo(){
this.a = 1
this.b = 1
}
//创建一个Demo的实例对象
const d = new Demo()
console.log(Demo.prototype)//显示原型属性
console.log(d._proto_)//隐式原型属性
console.log(Demo.prototype === d._proto_)
//程序员通过显示原型属性对象,追加一个x属性,值为99
Demo.prototype.x = 99
console.log('@',d)
</script>
单文件组件
School.vue
<template>
<div class="demo">
<h2>学校名称:{{schoolName}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
<button @click="showName">点我提示校名</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//组件交互相关代码(数据、方法等等)
//Vue.extend可省略
export default {
name:'School',
data(){
return{
schoolName:'尚硅谷',
address:'长沙'
}
},
methods: {
showName(){
alert(this.schoolName)
}
},
}
// export default school 默认暴露
</script>
<style>
/* 组件样式 */
.demo{
background-color:pink;
}
</style>
app.vue
<v +回车 调出架子
<template>
<div>
<School></School>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//引入组件
import School from './School.vue'
export default {
name:'App',
components:{
School
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
main.js
import App from './App.vue'
new Vue({
el:'#root',
template:`<App></App>`,
components:{App},
})
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- <App></App> -->
</div>
<!-- <script type="text/javascript" src="../vue.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="./main.js"></script> -->
</body>
</html>
Vue脚手架
是Vue官方提供的标准化开发工具
开发文档
建议先安装node.js
教程
vue安装步骤:
npm install -g @vue/cli
vue
一定要记得目录,别待会找不到
vue create name
选好用2还是3
再按指示操作
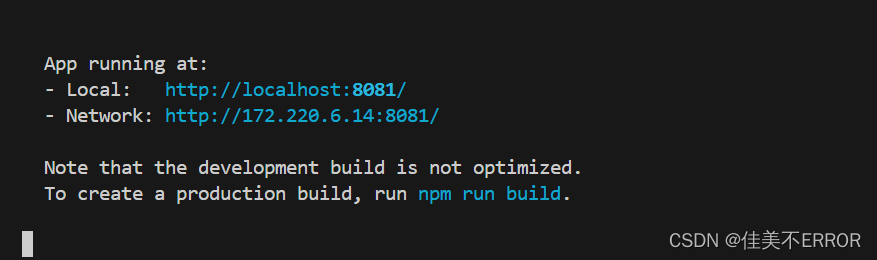
npm run serve
单词别写错了

emmmmNetwork: unavailable怎么解决……
等大佬救我……
解决了,这个IP号填错了,每个wifi有对应的号,点开wifi进入属性,看ipv4复制就行
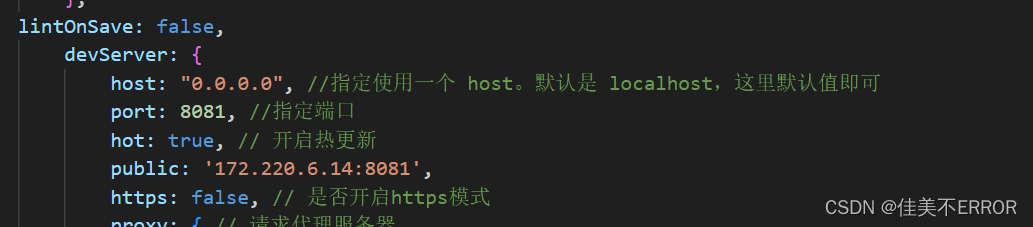
本地存储也跟着解决了,,,,加油加油
然后复制链接回车
停止工程可以按两次ctrl +c
(报错可能是权限问题,命令提示符用管理员身份进)
进入文件
调出终端快捷键:ctrl + ~
├── node_modules
├── public
│ ├── favicon.ico: 页签图标
│ └── index.html: 主页面
├── src
│ ├── assets: 存放静态资源
│ │ └── logo.png
│ │── component: 存放组件
│ │ └── HelloWorld.vue
│ │── App.vue: 汇总所有组件
│ │── main.js: 入口文件
├── .gitignore: git版本管制忽略的配置
├── babel.config.js: babel的配置文件
├── package.json: 应用包配置文件
├── README.md: 应用描述文件
├── package-lock.json:包版本控制文件
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<!-- 针对IE浏览器的一个特殊配置,含义是让IE浏览器以最高的渲染级别渲染页面 -->
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<!-- 开启移动端的理想视口 -->
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<!-- 配置页签图标 --> -->
<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL %>favicon.ico">
<!-- 配置网页标题 -->
<title><%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %></title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 当浏览器不支持js时noscript中元素就会被渲染 -->
<noscript>
<strong>We're sorry but <%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %> doesn't work properly without JavaScript enabled. Please enable it to continue.</strong>
</noscript>
<!-- 容器 -->
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- built files will be auto injected -->
</body>
</html>
main.js
//入口文件
//引入Vue
import Vue from 'vue'
//引入App组件,它是所有组件的父组件
import App from './App.vue'
//关闭vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
//创建Vue实例对象---vm
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
render函数
扮演了vue中解析template模板的那块儿代码
ref属性
被用来给元素或子组件注册引用信息(id的替代者)
应用在html标签上获取的是真实DOM元素,应用在组件标签上是组件实例对象(vc)
使用方式:
1、打标识:
…
或2、获取:this.$refs.xxx
<template>
<div>
<h1 v-text="msg" ref="title"></h1>
<button @click="showDom" ref="btn">点我输出上方的DOM元素</button>
<MySchool111 ref="school" id="school"></MySchool111>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 如果组件没写名字,那么就用的import后面起的名字
import MySchool111 from './compoments/MySchool.vue';
export default {
name: 'Appppp', //这里如果写名字,开发者工具里看的就是这个名字
components: {
MySchool111
},
data() {
return {
msg: '从蓬莱写到仙台,哥们儿代码信手拈来'
}
},
methods: {
showDom() {
// console.log(document.getElementById('title')); //这种写法拿不到组件
console.log(this.$refs.title); //拿到h1真实DOM元素标签
console.log(this.$refs.btn); //拿到button真实DOM元素标签
console.log(this.$refs.school); //拿到组件的实例(MySchool的vc)
//如果这么写,拿到的是组件template中的内容,相当于给根的div加了个id="school"
console.log(document.getElementById('school'));
}
},
}
</script>
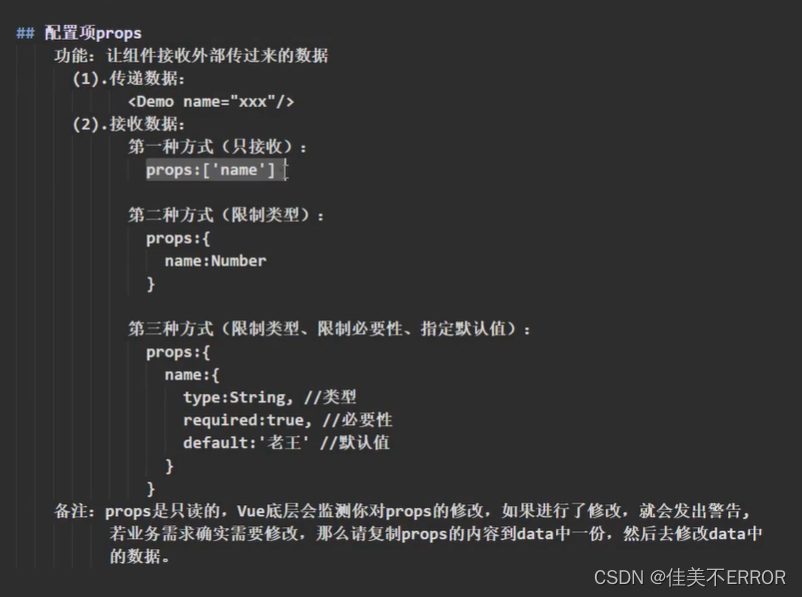
props配置
让组件接收外部传过来的数据。
props这个配置项就类似微信转账,App那边的标签里传过来,这边得接一下子
<template>
<div>
<!-- 加个单项数据绑定,引号里面就不是字符串了,就是表达式了 -->
<Student name="李四" sex="女" :age="20"></Student>
<Student name="王五" sex="男" :age="20 + 1" />
<!-- <Student name="zzy" sex="男" age="20" /> -->
</div>
</template>
简单接收
props: ['name', 'age', 'sex']
接收的同时对数据进行类型限制
props: {
name: String,
age: Number,
sex: String
}
接收时同时对数据:进行类型校验+默认值指定+必要性限制
props: {
name: {
type: String, //name的类型是字符串
required: true //name是必须填的
},
age: {
type: Number, //age的类型时数值
default: 99 //age可以不填,不填就是99
},
sex: {
type: String, //sex的类型是字符串
required: true //sex是必须填的
}
}
Student.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
<h2>学生名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>学生性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
<!-- 实现年龄+1 要加v-bind把引号里的东西变成js表达式,否则是字符串+1-->
<!-- <h2>学生年龄:{{ age*1+1 }}</h2> 强制类型转换一下-->
<h2>学生年龄age:{{ age + 1 }}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄myAge:{{ myAge + 1 }}</h2>
<button @click="updateAge">尝试修改收到的年龄</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Student',
data() {
return {
msg: '从蓬莱写到仙台,哥们儿代码信手拈来',
//想要修改age,就要用一个新的变量myAge来接收传进来的值
//然后页面显示myAge就能实现修改,props里的东西是只读的
myAge: this.age
// name: 'zzy',
// age: 18,
// sex: '男'
}
},
methods: {
updateAge() {
// this.age++; //会报错但是能改但是不建议改
this.myAge++;
}
},
//props这个配置项就类似微信转账,App那边的标签里传过来,这边得接一下子
//props中的内容优先级最高,先接这边的数据放vc里,再去读data,若有重复不会覆盖
props: ['name', 'age', 'sex']
}
</script>
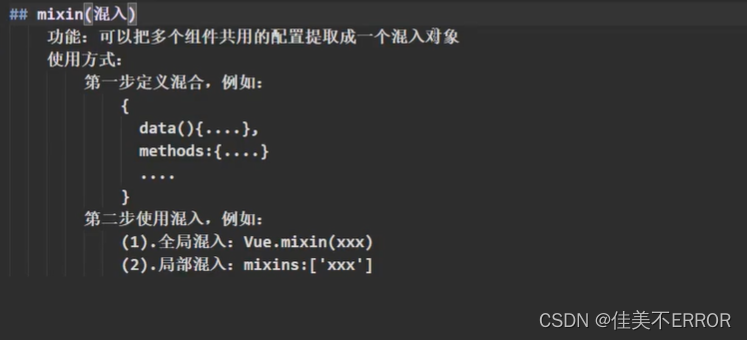
mixin(混入)
功能:可以把多个组件共用的配置提取成一个混入对象
Student.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2 @click="showName">学生姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生性别:{{sex}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {hunhe,hunhe2}from '../mixin'
export default {
name:'Student',
data(){
return{
name:'张三',
sex:'男'
}
},
mixins:[hunhe,hunhe2]
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
School.vue
<template>
<div >
<h2 @click="showName">学校名称:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
<!-- <button @click="showName">点我提示校名</button> -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
//组件交互相关代码(数据、方法等等)
//Vue.extend可省略
import {hunhe,hunhe2}from '../mixin'
export default {
name:'School',
data(){
return{
name:'尚硅谷',
address:'长沙'
}
},
mixins:[hunhe,hunhe2]
}
// export default school 默认暴露
</script>
<style>
</style>
mixin.js
export const hunhe = {
methods: {
showName(){
alert(this.name)
}
},
mounted() {
console.log('你好')
},
}
export const hunhe2 = {
data(){
return{
x:100,
y:200
}
}
}
插件
功能:用于增强Vue
本质:包含install方法的一个对象,install的第一个参数是Vue,第二个以后的参数是插件使用者传递的数据。
使用插件Vue.use()
//在main.js中引入插件并起个名儿
import plugins from './plugins';
//使用插件,要在new Vue之前使用
Vue.use(plugins, 1, 2, 3);
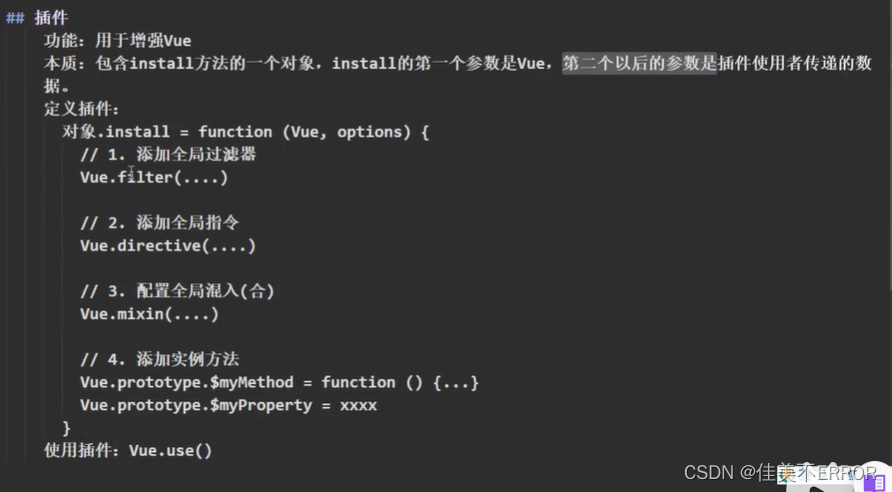
定义插件:可以在另一个js中配置插件,然后通过import引入到main.js中
const plusobj = {
install(Vue, x, y, z) {
console.log(Vue); //第一个参数是Vue构造函数
console.log(x, y, z); //后面的参数是使用者传进来的东西123
//1.定义一个全局过滤器
Vue.filter('mySlice', function (val) {
return val.slice(0, 4); //返回值别忘了
});
//2.定义一个全局自定义指令,元素默认获取焦点
Vue.directive('fbind', {
bind(el, binding) {
el.value = binding.value;
},
inserted(el) {
el.focus();
},
update(el, binding) {
el.value = binding.value;
}
})
//3.定义一个全局混合,不用引入就能给所有的vm和vc
Vue.mixin({
data() {
return {
x: 1,
y: 2
}
}
})
//4.给Vue的原型对象添加实例方法,vm和vc都能用
Vue.prototype.hello = () => { alert('hello!') }
}
}
export default plusobj;
scoped样式
作用:让样式在局部生效,防止冲突。
写法:
指定使用 less写法:
备注:
查看webpack所有版本 当前项目文件目录>npm view webpack versions
安装less版本7当前项目文件目录>npm i less-loader@7
第七天
TodoList案例

app.vue
<template>
<div id="root">
<div class="todo-container">
<div class="todo-wrap">
<MyHeader :addTodo="addTodo"/>
<MyList :todos="todos" :checkTodo="checkTodo" :deleteTodo="deleteTodo"/>
<MyFooter :todos="todos" :checkAllTodo="checkAllTodo" :clearAllTodo="clearAllTodo"/>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyHeader from './components/MyHeader'
import MyList from './components/MyList'
import MyFooter from './components/MyFooter.vue'
export default {
name:'App',
components:{MyHeader,MyList,MyFooter},
data() {
return {
//由于todos是MyHeader组件和MyFooter组件都在使用,所以放在App中(状态提升)
todos:[
{id:'001',title:'抽烟',done:true},
{id:'002',title:'喝酒',done:false},
{id:'003',title:'开车',done:true}
]
}
},
methods: {
//添加一个todo
addTodo(todoObj){
this.todos.unshift(todoObj)
},
//勾选or取消勾选一个todo
checkTodo(id){
this.todos.forEach((todo)=>{
if(todo.id === id) todo.done = !todo.done
})
},
//删除一个todo
deleteTodo(id){
this.todos = this.todos.filter( todo => todo.id !== id )
},
//全选or取消全选
checkAllTodo(done){
this.todos.forEach((todo)=>{
todo.done = done
})
},
//清除所有已经完成的todo
clearAllTodo(){
this.todos = this.todos.filter((todo)=>{
return !todo.done
})
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
/*base*/
body {
background: #fff;
}
.btn {
display: inline-block;
padding: 4px 12px;
margin-bottom: 0;
font-size: 14px;
line-height: 20px;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: middle;
cursor: pointer;
box-shadow: inset 0 1px 0 rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2), 0 1px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);
border-radius: 4px;
}
.btn-danger {
color: #fff;
background-color: #da4f49;
border: 1px solid #bd362f;
}
.btn-danger:hover {
color: #fff;
background-color: #bd362f;
}
.btn:focus {
outline: none;
}
.todo-container {
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.todo-container .todo-wrap {
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 5px;
}
</style>
MyFooter.vue
<template>
<div class="todo-footer" v-show="total">
<label>
<!-- <input type="checkbox" :checked="isAll" @change="checkAll"/> -->
<input type="checkbox" v-model="isAll"/>
</label>
<span>
<span>已完成{{doneTotal}}</span> / 全部{{total}}
</span>
<button class="btn btn-danger" @click="clearAll">清除已完成任务</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'MyFooter',
props:['todos','checkAllTodo','clearAllTodo'],
computed: {
//总数
total(){
return this.todos.length
},
//已完成数
doneTotal(){
//此处使用reduce方法做条件统计
/* const x = this.todos.reduce((pre,current)=>{
console.log('@',pre,current)
return pre + (current.done ? 1 : 0)
},0) */
//简写
return this.todos.reduce((pre,todo)=> pre + (todo.done ? 1 : 0) ,0)
},
//控制全选框
isAll:{
//全选框是否勾选
get(){
return this.doneTotal === this.total && this.total > 0
},
//isAll被修改时set被调用
set(value){
this.checkAllTodo(value)
}
}
},
methods: {
/* checkAll(e){
this.checkAllTodo(e.target.checked)
} */
//清空所有已完成
clearAll(){
this.clearAllTodo()
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
/*footer*/
.todo-footer {
height: 40px;
line-height: 40px;
padding-left: 6px;
margin-top: 5px;
}
.todo-footer label {
display: inline-block;
margin-right: 20px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.todo-footer label input {
position: relative;
top: -1px;
vertical-align: middle;
margin-right: 5px;
}
.todo-footer button {
float: right;
margin-top: 5px;
}
</style>
MyHeader.vue
<template>
<div class="todo-header">
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入你的任务名称,按回车键确认" v-model="title" @keyup.enter="add"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {nanoid} from 'nanoid'
export default {
name:'MyHeader',
//接收从App传递过来的addTodo
props:['addTodo'],
data() {
return {
//收集用户输入的title
title:''
}
},
methods: {
add(){
//校验数据
if(!this.title.trim()) return alert('输入不能为空')
//将用户的输入包装成一个todo对象
const todoObj = {id:nanoid(),title:this.title,done:false}
//通知App组件去添加一个todo对象
this.addTodo(todoObj)
//清空输入
this.title = ''
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
/*header*/
.todo-header input {
width: 560px;
height: 28px;
font-size: 14px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
padding: 4px 7px;
}
.todo-header input:focus {
outline: none;
border-color: rgba(82, 168, 236, 0.8);
box-shadow: inset 0 1px 1px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.075), 0 0 8px rgba(82, 168, 236, 0.6);
}
</style>
MyItem.vue
<template>
<li>
<label>
<input type="checkbox" :checked="todo.done" @change="handleCheck(todo.id)"/>
<!-- 如下代码也能实现功能,但是不太推荐,因为有点违反原则,因为修改了props -->
<!-- <input type="checkbox" v-model="todo.done"/> -->
<span>{{todo.title}}</span>
</label>
<button class="btn btn-danger" @click="handleDelete(todo.id)">删除</button>
</li>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'MyItem',
//声明接收todo、checkTodo、deleteTodo
props:['todo','checkTodo','deleteTodo'],
methods: {
//勾选or取消勾选
handleCheck(id){
//通知App组件将对应的todo对象的done值取反
this.checkTodo(id)
},
//删除
handleDelete(id){
if(confirm('确定删除吗?')){
//通知App组件将对应的todo对象删除
this.deleteTodo(id)
}
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
/*item*/
li {
list-style: none;
height: 36px;
line-height: 36px;
padding: 0 5px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ddd;
}
li label {
float: left;
cursor: pointer;
}
li label li input {
vertical-align: middle;
margin-right: 6px;
position: relative;
top: -1px;
}
li button {
float: right;
display: none;
margin-top: 3px;
}
li:before {
content: initial;
}
li:last-child {
border-bottom: none;
}
li:hover{
background-color: #ddd;
}
li:hover button{
display: block;
}
</style>
MyList.vue
<template>
<ul class="todo-main">
<MyItem
v-for="todoObj in todos"
:key="todoObj.id"
:todo="todoObj"
:checkTodo="checkTodo"
:deleteTodo="deleteTodo"
/>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
import MyItem from './MyItem'
export default {
name:'MyList',
components:{MyItem},
//声明接收App传递过来的数据,其中todos是自己用的,checkTodo和deleteTodo是给子组件MyItem用的
props:['todos','checkTodo','deleteTodo']
}
</script>
<style scoped>
/*main*/
.todo-main {
margin-left: 0px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 2px;
padding: 0px;
}
.todo-empty {
height: 40px;
line-height: 40px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 2px;
padding-left: 5px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
浏览器本地存储
上面Network: unavailable问题没解决下面也会有问题,服啦
localStorage.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>localStorage</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>localStorage</h2>
<button onclick="saveData()">点我保存一个数据</button>
<button onclick="readData()">点我读取一个数据</button>
<button onclick="deleteData()">点我删除一个数据</button>
<button onclick="deleteAllData()">点我清空一个数据</button>
<script type="text/javascript" >
let p = {name:'张三',age:18}
function saveData(){
localStorage.setItem('msg','hello!!!')
localStorage.setItem('msg2',666)
localStorage.setItem('person',JSON.stringify(p))
}
function readData(){
console.log(localStorage.getItem('msg'))
console.log(localStorage.getItem('msg2'))
const result = localStorage.getItem('person')
console.log(JSON.parse(result))
// console.log(localStorage.getItem('msg3'))
}
function deleteData(){
localStorage.removeItem('msg2')
}
function deleteAllData(){
localStorage.clear()
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
sessionStorage.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>sessionStorage</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>sessionStorage</h2>
<button onclick="saveData()">点我保存一个数据</button>
<button onclick="readData()">点我读取一个数据</button>
<button onclick="deleteData()">点我删除一个数据</button>
<button onclick="deleteAllData()">点我清空一个数据</button>
<script type="text/javascript" >
let p = {name:'张三',age:18}
function saveData(){
sessionStorage.setItem('msg','hello!!!')
sessionStorage.setItem('msg2',666)
sessionStorage.setItem('person',JSON.stringify(p))
}
function readData(){
console.log(sessionStorage.getItem('msg'))
console.log(sessionStorage.getItem('msg2'))
const result = sessionStorage.getItem('person')
console.log(JSON.parse(result))
// console.log(sessionStorage.getItem('msg3'))
}
function deleteData(){
sessionStorage.removeItem('msg2')
}
function deleteAllData(){
sessionStorage.clear()
}
</script>
</body>
</html>

第八天
组件自定义事件

累了,毁灭吧
第九天
动画效果
Test.vue
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow =!isShow">显示/隐藏</button>
<transition name="hello" appear>
<h1 v-show="isShow" class="come">你好啊</h1>
</transition>
<!-- <transition name="h2" appear>
<h2 v-show="isShow">尚硅谷</h2>
</transition> -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'Test',
data(){
return{
isShow:true
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
h1{
border-color: orange;
}
.hello-enter-active{
animation: atguigu 1s linear;
}
.hello-leave-active{
animation: atguigu 1s linear reverse;
}
@keyframes atguigu {
from{
transform: translateX(-100px);
}
to{
transform: translateX(0px);
}
}
</style>
过渡效果
Test2.vue
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow =!isShow">显示/隐藏</button>
<transition name="hello" appear>
<h1 v-show="isShow">你好啊</h1>
</transition>
<!-- <transition name="h2" appear>
<h2 v-show="isShow">尚硅谷</h2>
</transition> -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'Test',
data(){
return{
isShow:true
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
h1{
border-color: orange;
transform: 0.5s linear;
}
.hello-enter,.hello-leave-to{
transform: translateX(-100%);
}
.hello-enter-active,.hello-leave-active{
transform: 0.5s linear;
}
.hello-enter-to,.hello-leave{
transform: translateX(0);
}
</style>
app.vue
<template>
<div >
<Test></Test>
<Test2></Test2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Test from './components/Test.vue'
import Test2 from './components/Test2.vue';
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Test,Test2
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
样式库
Animate.css
链接位置
安装npm install animate.css+引入import ‘animate.css’
Test3.vue
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow =!isShow">显示/隐藏</button>
<transition-group
appear
name="animate_animated animate_bounce"
enter-active-class="animate_swing"
leave-active-class="animate_backOutUp"
>
<h1 v-show="!isShow" key="1">你好啊</h1>
<h1 v-show="isShow" key="2">尚硅谷</h1>
</transition-group>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import 'animate.css'
export default {
name:'Test',
data(){
return{
isShow:true
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
h1{
border-color: orange;
transform: 0.5s linear;
}
</style>
配置代理
引入axios
npm i axios
app.vue
<template>
<div >
<button @click="getStudents">获取学生信息</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
name: 'App',
methods:{
getStudents(){
axios.get('http://localhost:8080/students').then(
response =>{
console.log('请求成功了',response.data)
},
error=>{
console.log('请求失败了',error.message)
}
)
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
vue.config.js
module.exports = {
pages:{
index:{
entry:'src/main.js',
},
},
lintOnSave:false,
devServer: {
proxy: 'http://localhost:5000'
}
}
第二种配置代理
app.vue
<template>
<div >
<button @click="getStudents">获取学生信息</button>
<button @click="getCars">获取汽车信息</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
name: 'App',
methods:{
getStudents(){
axios.get('http://localhost:8080/atguigu/students').then(
response =>{
console.log('请求成功了',response.data)
},
error=>{
console.log('请求失败了',error.message)
}
)
},
getCars(){
axios.get('http://localhost:8080/demo/cars').then(
response =>{
console.log('请求成功了',response.data)
},
error=>{
console.log('请求失败了',error.message)
}
)
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
vue.config.js
module.exports = {
pages:{
index:{
entry:'src/main.js',
},
},
lintOnSave:false,
devServer: {
proxy: {
'/atguigu': {
target: 'http://localhost:5000',
pathRewrite:{'^/atguigu':''},
/* ws: true, //用于支持websocket
changeOrigin: true */
},
'/demo':{
target:'http://localHost:5001',
pathRewrite:{
'^/demo':''
},
}
/* '/foo': {
target: '<other_url>'
} */
}
}
}

github案例
List.vue
<template>
<div class="row">
<!-- 展示用户列表 -->
<div v-show="info.users.length" class="card" v-for="user in info.users" :key="user.login">
<a :href="user.html_url" target="_blank">
<img :src="user.avatar_url" style='width: 100px'/>
</a>
<p class="card-text">{{user.login}}</p>
</div>
<!-- 展示欢迎词 -->
<h1 v-show="info.isFirst">欢迎使用!</h1>
<!-- 展示加载中 -->
<h1 v-show="info.isLoading">加载中....</h1>
<!-- 展示错误信息 -->
<h1 v-show="info.errMsg">{{info.errMsg}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'List',
data(){
info:{
return{
isFirst:true,
isLoading:false,
errMsg:'',
users:[]
}
}
},
mounted(){
/* this.$bus.$on('getUsers',(isFirst,isLoading,errMsg,users)=>{
console.log('我是List组件',users)
this.isFirst=isFirst
this.isLoading=isLoading
this.errMsg=errMsg
this.users=users
}) */
this.$bus.$on('updateListDate',(dataObj)=>{
this.info={
...this.info,...dataObj
}
console.log(this)
})
/* this.$bus.$on('getFirst',(isFirst)=>{
this.isFirst=isFirst
}) */
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
Search.vue
<template>
<section class="jumbotron">
<h3 class="jumbotron-heading">Search Github Users</h3>
<div>
<input type="text" placeholder="enter the name you search" v-model="keyWord"/>
<button @click="searchUsers">Search</button>
</div>
</section>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
name:'Search',
data() {
return {
keyWord:''
}
},
methods: {
searchUsers(){
//请求前更新List的数据
this.$bus.$emit('updateListData',{isLoading:true,errMsg:'',users:[],isFirst:false})
axios.get(`https://api.github.com/search/users?q=${this.keyWord}`).then(
response => {
console.log('请求成功了')
//请求成功后更新List的数据
this.$bus.$emit('updateListData',{isLoading:false,errMsg:'',users:response.data.items})
},
error => {
//请求后更新List的数据
this.$bus.$emit('updateListData',{isLoading:false,errMsg:error.message,users:[]})
}
)
}
},
}
</script>
vue-resource
安装
npm i vue-resource
这个文档太长了,,,换个新文档写了