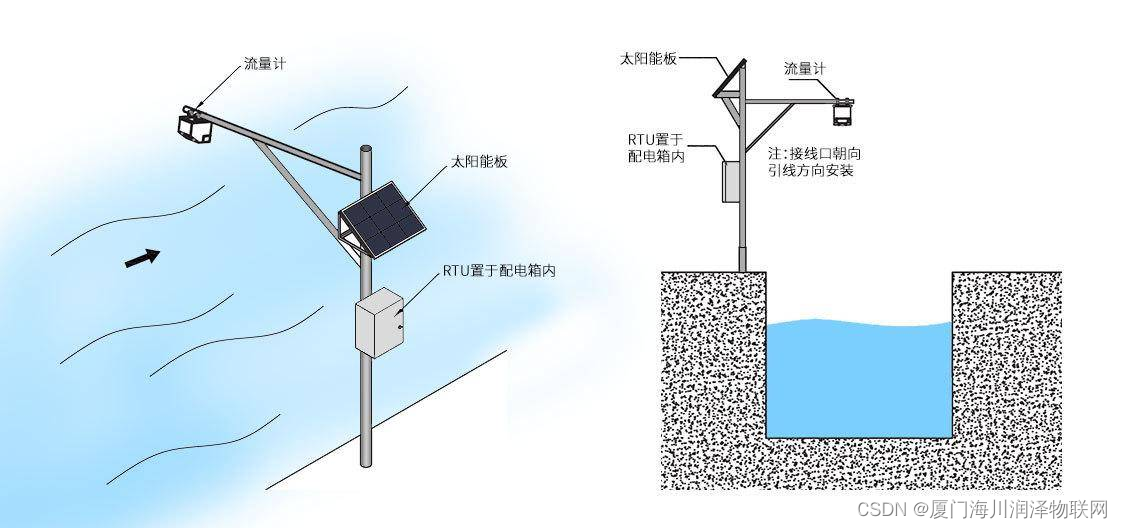
所有泛型算法,除了少数例外,前两个参数均为一组iterator,用来标识欲遍历容器元素的范围,范围从第一个iterator所指位置开始,至第二个iterator所指位置(并不包括)结束
如
int arr[3]={1,2,3}
vector<int> v1(arr,arr+3);
sort(v1.begin(),v2.begin());
算法通常有两个重载的版本,版本之一使用底层元素所属之类型的内置运算符,包括equlity运算符和less-than运算符,版本之二接收function object或function pointer的传入。例如,默认情形下sort会使用less-than运算符由低到高进行排序,如果改变这一行为,我们可以传入预先定义好的greater function object
sort(v1.begin(),v1.end())// 由低到高
sort(v1.begin(),v1.end(),greater<int>()) //由高到低
不过另一些算法干脆以不同名称区分不同版本,以形成两个函数,以_if为名称,便可以“指定特定行为的”那个版本。举个例子,如果我们想找出小于10的每一个元素,可以这么写
find_if(vec.begin(),vec.end(),bind2nd(less<int>,10))
许多“会改变容器自身内容”的算法会提供两个版本,一份为in-place(就地)版本,其必会改变容器内容,另一种为copy版本,不改变传入容器的内容,而是先为它制作一份副本,再改变副本的内容,然后返回该副本,例如replace()和replace_copy()两个算法,copy版本接收第三个iterator参数,用以指向改变容器的第一个元素。
头文件
#include<algortihm>
#include<numeric>
stable_sort()
稳定版的排序
stable_sort(vec1.begin(),vec1.end())
acumlate 累加(可以实现 累计 操作)
//累加
int a= accumlate(vec.begin(),vec.end())
//累乘
int b=accumlate(vec.begin(),vec.end(),mutiples<int>())
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-U71e3E0b-1673318674195)(https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/secure.notion-static.com/8aa1b2ad-a9e9-4a6e-a793-8238d7eeede7/Untitled.png)]
adjacent_difference() 相邻元素的差值(相邻元素处理)
除了第一个元素为原本的值外,其他元素均代表与上一个元素的差值
如{0,2,3,4,5,6}
返回{0,2,1,1,1,1}
该函数不会改变原本容器内容,第三个参数为新的容器的第一个元素
第四个参数还可以改变 默认的运算符 如 上一个元素与本元素相乘(multiplies) 等等
adjacent_difference(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin(),multiplies<int>)
adjacent_find() 相邻元素且重复
adjacent_find,在一个数组中寻找两个相邻的元素。如果相等,就返回这两个相等元素第一个元素的迭代器,不等的话,就返回v.end().
adjacent_find(vec1.begin(),vec2.begin())
binary_search() 二元搜索
cpp
cpp外层二分搜索使用STL库的
binary_search bool 如果搜到了该数 则返回True
lower_bound 返回第一个等于或大于该元素的指针
upper_bound 返回第一个大于该元素的指针
若要索引减去指针第一个位置即可
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[100]= {4,10,11,30,69,70,96,100};
int b=binary_search(a,a+9,4);//查找成功,返回1
cout<<"在数组中查找元素4,结果为:"<<b<<endl;
int c=binary_search(a,a+9,40);//查找失败,返回0
cout<<"在数组中查找元素40,结果为:"<<c<<endl;
int d=lower_bound(a,a+9,10)-a;
cout<<"在数组中查找第一个大于等于10的元素位置,结果为:"<<d<<endl;
int e=lower_bound(a,a+9,101)-a;
cout<<"在数组中查找第一个大于等于101的元素位置,结果为:"<<e<<endl;
int f=upper_bound(a,a+9,10)-a;
cout<<"在数组中查找第一个大于10的元素位置,结果为:"<<f<<endl;
int g=upper_bound(a,a+9,101)-a;
cout<<"在数组中查找第一个大于101的元素位置,结果为:"<<g<<endl;
}
copy() 复制一个容器的内容到另一容器中
copy(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin()); //vec1 复制到vec2中
类似于vector的成员函数assign()
copy_backward() 逆向复制
copy_backward(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin())
count() 计数
count(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),5);
count() 条件计数
count_if(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),bind2nd(less<than>,10))
// 比10小的数字个数
equal() 两数列是否相等(不考虑第二数列的多的部分)
相等返回true
不等返回false
第四个参数可传入二元运算符
equal(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin())
equal(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin(),Even2())
class Even2
{
public:
bool operator2(int val1,int val2){return val1-val2}
}
fill() 将容器内元素更改为某值
fill(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),10)
fill_n() 更改为n个值
fill(vec1.begin(),count,value)
find() 找到某个值
找到则返回指向该元素的iterator
没找到指向end()
auto l1=find(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),10)
find_if() 找到满足条件的某个值
第三个参数输入一元运算符
find_if(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),bind2nd(less<int>,val))
search() 寻找子序列的第一次出现的位置
如果没有该子序列 则返回end()
auto l1=search(l1.begin(),l1.end(),l2.begin(),l2.end())
find_end() 寻找子序列的最后一次出现的位置‘
如果没有该子序列 则返回end()
auto l1=find_end(l1.begin(),l1.end(),l2.begin(),l2.end())
find_first_of 找寻某些元素第一次出现的地点
比如在[1,2,3,4,5,6,7]中找[6,2,5]第一次出现的位置,自然是nums[1]
find_first_of(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin(),vec2.end())
for_each() 以功能函数遍历不得改变原函数
void newfunction (int k)
{
std::cout << " " <<k;
}
for_each(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),newfunction)
transform() 以功能函数遍历容器并赋值给另一个容器
int myfun(int val)
{
return -val;
}
transform(vec1.begin(),ve1.end(),vec2.begin(),myfun)
includes 线性时间复杂度 在有序序列中找有序元素
// initializing 1st container
vector<int> arr1 = { 1, 4, 6, 3, 2 };
// initializing 2nd container
vector<int> arr2 = { 1, 2, 4 };
// sorting initial containers
sort(arr1.begin(), arr1.end());
sort(arr2.begin(), arr2.end());
// using include() check if all elements
// of arr2 lie in arr1
// using comparator function
if (includes(arr1.begin(), arr1.end(), arr2.begin(),
arr2.end(), comp))
cout << "All elements of 2nd container are in 1st "
"container";
else
cout << "All elements of 2nd container are not in "
"1st container";
return 0;
inner_product() 两个容器的内积
[1,2,3,4]
[5,6,7,8] 初值+(15)+ (26) +(37)+(48)
inner_product(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin(),初值)
自定义 单序列元素的符号ar1 两序列元素的符号 ar2
(1 ar2 5)ar1(2 ar2 6) ar1 …
inner_product(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin(),初值,ar1,ar2)
merge()
合并两个排序后的数列,结果亦经过排序。
可设定默认排序的方式
sort(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),greater<int>())
sort(vec2.begin(),vec2.end(),greater<int>())
merge(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin(),vec2.begin(),vec_rs.begin(),greater<int>());
iter_swap 元素互换
iter_swap(it1,it2);
max,min
返回两元素中较大较小者
max_element() min_element()
返回指向较大较小者的迭代器1
auto it =max_element(vec1.begin(),vec1.end())
partial_sum() 累计 斐波那契
[0,0,1,2,3] → [0,0,1,3,6]
该元素与之前所有元素的累加和
赋值给某个容器
partial_sum(a1.begin(),a1.end(),a2.begin())
partial_sort() 堆排序 排前k个数
容器前四个为排好的数
partial_sort(vec1.begin(),vec1.begin()+4,vec1.end())
partial_sort() 堆排序 排前k个数 复制给另一个容器
partial_sort_copy(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin(),vec2.end())
//通过vec2的长度指明k
remove() 和 erase()
remove 隔离某种元素
erase是vector的成员函数,删除某个范围
vector<int> vec1={0,2,0,,5};
auto it =remove(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),0).
//it 指向合格元素的下一个位置,即第一个0
-> vec1=[2,5,0,0]
vec1.erase(it,vec1.end()) // 抹去0, 0
remove_copy() 删除某个元素的序列赋值给另一个序列
[0,2,0,5] 删除0 赋值给vec2 -》 【2,5】
remove_copy(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin(),0)
remove_if remove_copy_if
用一个单元运算符代替0
auto it= remove_if(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),func)
remove_copy_if(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin(),func)
replace()
将old_val 替换成 new_val
replace(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),oldval,newval)
replace_if()
将满足单元运算符func的替换成newval
replace_if(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),func,newval)
reverse() reverse_copy()
颠倒原容器
颠倒容器赋值到另一个容器
reverse(vec1.begin(),vec1.end())
reverse(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin())
unique() unique_copy()
与remove remove_copy类似
复制给vec1
[1,2,3,1,1,3,5]
auto it =unique(vec1.begin(),vec1.end()) ->[1,2,3,5,1,1,3]
把唯一的元素移到前面
可以删除 vec1.erase(it,vec1.end())
unique(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec1.begin())
partition() stable_partition()
所有为true的元素会置于false的元素之前 func为1元运算符
stable为稳定版
partition(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),func)
random_shuffle()
随机重排
random_shuffle(vec1.begin(),vec1.end())
nth_element()
快排的一部分 将小于某个数的放在其前面,大于它的放在后面
nth_element(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec1.begin()+6)
set_difference() set_intersection set_union
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-j0CFY7Ud-1673318674196)(https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/secure.notion-static.com/d763ebcb-fdf0-463f-aa08-c69ee2ec87af/Untitled.png)]
// 交集
set_intersection(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin(),vec2.end(),vec3.begin())
// 并集
set_union(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin(),vec2.end(),vec3.begin())
// 差集
set_difference(vec1.begin(),vec1.end(),vec2.begin(),vec2.end(),vec3.begin())