接下来的日子会顺顺利利,万事胜意,生活明朗-----------林辞忧
引言
栈和队列作为数据结构的重要组成部分,可以用栈实现非递归等,为后面学习打基础。栈由数组来实现,队列由链表来实现,接下来将详细介绍
一:栈
1.定义:
栈是一种线性表结构,在栈顶插入和删除数据,栈底不做任何操作,不含任何元素的栈称为空栈,主要特性为后进先出(First in Last out)LIFO结构
2.特性
FILO结构,栈在栈顶插入数据称为入栈,栈顶删除数据称为出栈
3.栈的结构定义

4.数组实现栈
//栈的初始化
void STInit(ST* pst);
//入栈
void STPush(ST* pst,STDataType x);
//出栈
void STPop(ST* pst);
//栈的销毁
void STDestroy(ST* pst);
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
//显示栈顶元素
STDataType STTopData(ST* pst);
//判断开辟大小
int STSize(ST* pst);void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
pst->top = 0;//pst指向栈顶元素的下个位置
//pst->top=-1;//指向栈顶元素
}
//入栈
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)//判断空间大小,是否扩容
{
int newCapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
//开辟空间
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc failue\n");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newCapacity;
}
//入栈
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
//出栈
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!STEmpty(pst));
pst->top--;
}
//栈的销毁
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = pst->top = 0;
}
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
//显示栈顶元素
STDataType STTopData(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!STEmpty(pst));
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
//判断开辟大小
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}二:队列
1.定义:
队列是一种先进先出(First in First out)的线性表,简称FIFO.在队尾插入数据,队头删除数据,通常由单链表来实现
2.队列的结构定义:
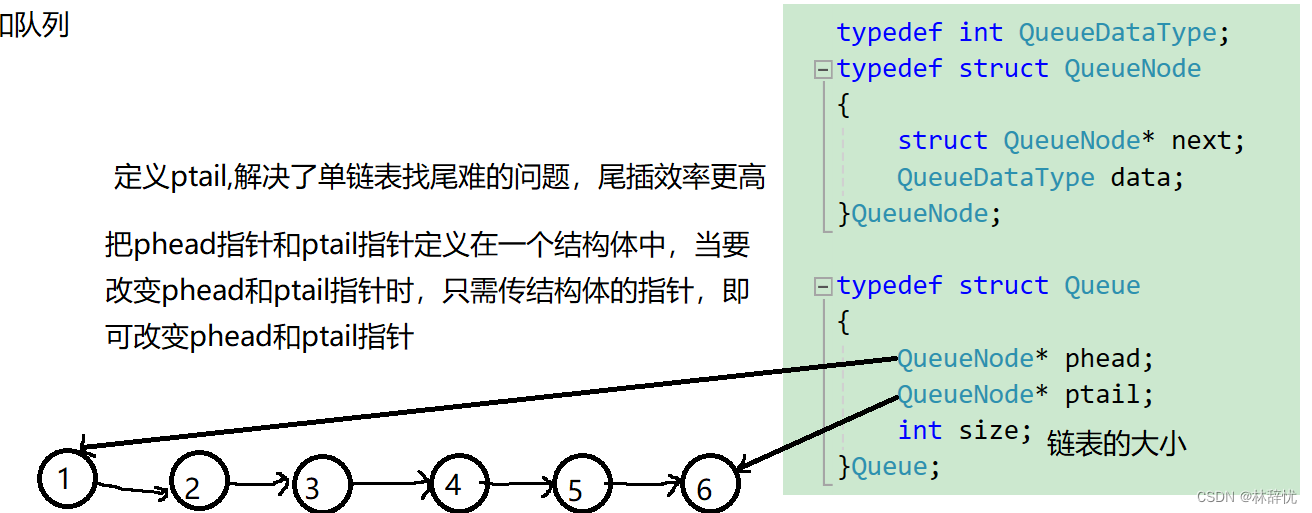
3.单链表实现队列
//队列之初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
//队列之销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
//队列之队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq,QueueDataType x);
//队列之队头的删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
//队列之队头数据
QueueDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
//队列之队尾数据
QueueDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
//队列之判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
//队列之大小
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);//队列之初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//队列之销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QueueNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead=pq->ptail=NULL:
pq->size = 0;
}
//队列之队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq,QueueDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail\n");
return;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)//空链表
{
assert(pq->phead == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else//非空链表
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
//队列之队头的删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//空链表不能删除
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)//一个节点
{
freee(pq->phead);
pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else//多个结点
{
Queue* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
//队列之队头数据
QueueDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}
//队列之队尾数据
QueueDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->data;
}
//队列之判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}
//队列之大小
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}三:总结
栈和队列作为重要的数据结构组成部分,将在后面学习中经常使用到