目录
编辑
一,线程的创建
二,线程的退出
1,在子线程内return
2,使用pthread_exit(void*)
三,线程等待
四,线程获取自己的id值
五,线程取消
六,线程分离
一,线程的创建
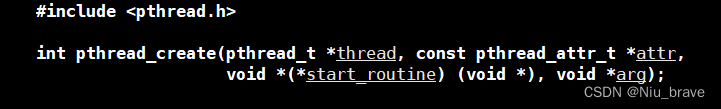
在对进程控制之前,首先要做的便是创建一个线程。创建方法如下:
使用的创建方法叫做pthread_create。
参数介绍:
thread:线程idattr:线程属性,直接设为nullstart_routine:函数指针arg:这个参数会传递进start_routine的void*参数中。
例子:
#include<iostream>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<unistd.h>
using namespace std;
void* hander(void* args)//新线程执行的方法
{
while(true)
{
sleep(1);
cout << "i am new thread" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t td;
pthread_create(&td, nullptr, hander, nullptr);//创建好新线程以后,新线程会去执行传入的hander方法。
while(true)//主线程会继续向下执行自己的方法
{
sleep(1);
cout << "i am main thread" << endl;
}
return 0;
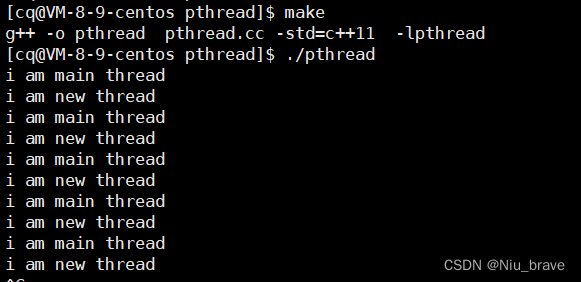
}执行这个代码以后结果如下:
在这里要注意,在使用g++编译时要加上-lpthread。因为线程库是一个第三方库,但是是安装在系统中的所以只需要-l便可以连接到pthread库。
二,线程的退出
1,在子线程内return
线程的退出有多种方式,先来看看最基本的一种退出方式,代码如下:
void *hander(void *args)
{
string name = static_cast<const char *>(args);
int cnt = 5;
while (cnt--)
{
cout << "i am new thread" << name << endl;
sleep(1);
}
return nullptr;//最基本的退出线程的方式便是直接在子线程内部使用return的方式退出
}
class data
{
public:
char buf[64];
int i;
};
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= NUM; i++) // 创建一批线程
{
data *m = new data();
snprintf(m->buf, sizeof(m->buf), "%s:%d", "new thread", i);
pthread_t td;
pthread_create(&td, nullptr, hander, (void *)m->buf);
}
while (true)
{
cout << "-- -- -- -- -- -- -- --sucess -- -- -- -- -- -- -- " << endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
在使用这种方式退出时,主线程在子线程退出以后还会继续执行。但是如果是子线程不退出而主线程先退出呢?像这样:
void *hander(void *args)
{
string name = static_cast<const char *>(args);
int cnt = 5;
while (true)//子线程一直在死循环
{
cout << "i am new thread" << name << endl;
sleep(1);
}
return nullptr;
}
class data
{
public:
char buf[64];
int i;
};
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= NUM; i++) // 创建一批线程
{
data *m = new data();
snprintf(m->buf, sizeof(m->buf), "%s:%d", "new thread", i);
pthread_t td;
pthread_create(&td, nullptr, hander, (void *)m->buf);
}
int cnt = 5;
while (cnt--)//主线程在cnt减到零时就退出
{
cout << "-- -- -- -- -- -- -- --sucess -- -- -- -- -- -- -- " << endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
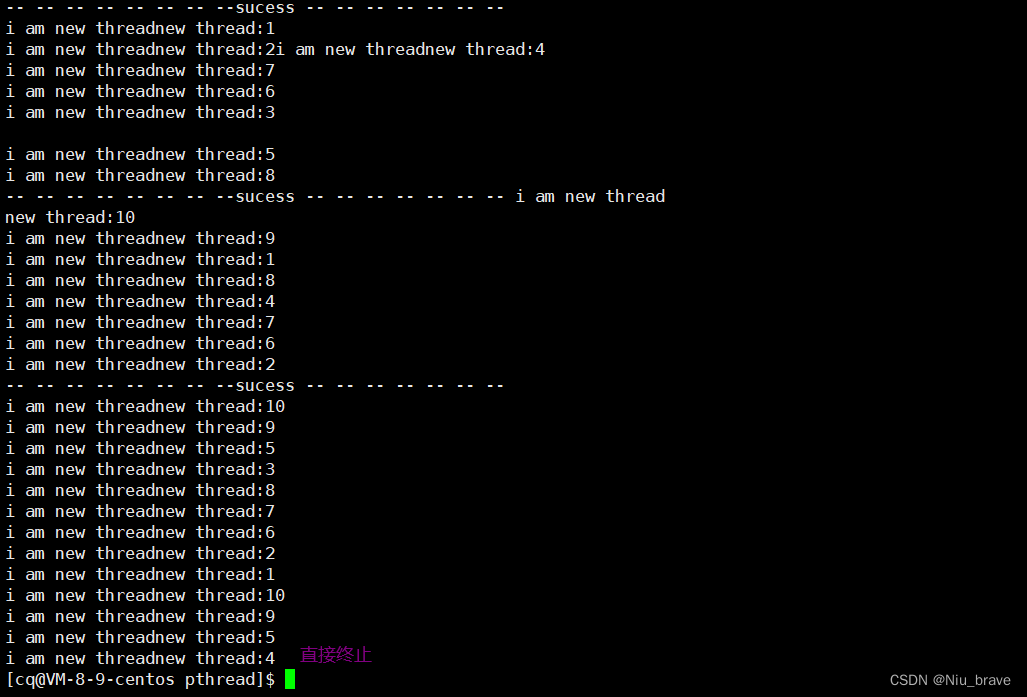
这样的话只要主线程退出了,这个进程都会直接结束。 如下:
2,使用pthread_exit(void*)
这个函数是线程库提供给我们的专门用于线程退出的函数,他的参数可以直接设置为nullptr。使用方式如下:
void *hander(void *args)
{
string name = static_cast<const char *>(args);
int cnt = 5;
while (cnt--)
{
cout << "i am new thread" << name << endl;
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(nullptr);//使用pthread_exit()退出线程。
}
class data
{
public:
char buf[64];
int i;
};
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= NUM; i++) // 创建一批线程
{
data *m = new data();
snprintf(m->buf, sizeof(m->buf), "%s:%d", "new thread", i);
pthread_t td;
pthread_create(&td, nullptr, hander, (void *)m->buf);
}
while (true)
{
cout << "-- -- -- -- -- -- -- --sucess -- -- -- -- -- -- -- " << endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}使用pthread_exit退出的效果和在子线程内使用return退出的效果一样。
##注意## 线程的退出不能使用exit,因为exit的本质其实是向进程发信号,所以exit是专门用于进程退出的。同样的,线程的退出也不需要返回errno,因为如果一个线程因为异常退出的话整个进程都会退出,进程返回errno就可以了。
三,线程等待
和进程一样,线程也需要等待。等待的目的如下:
1,回收新线程对应的内核资源。
2,接收新线程返回的数据。
线程等待函数: int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval)
thread:表示要等待线程的pid
reval:接收数据并将数据带出。
使用如下:
class thread
{
public:
int _num; // 线程的编号
char _buf[64]; // 线程的名字
pthread_t _tid; // 线程的id
};
void *start_routine(void *args)
{
int cnt = 5;
while (cnt--)
{
sleep(1);
thread *_td = static_cast<thread *>(args);
cout << "i am new thread:" << _td->_buf << ":" << _td->_num
<< ":" << _td->_tid << endl;
}
pthread_exit(nullptr);//线程退出
}
int main()
{
vector<thread*> threads;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)//创建线程
{
thread *td = new thread;
td->_num = i;
snprintf(td->_buf, sizeof(td->_buf), "%s-%d", "thread:", i);
pthread_create(&td->_tid, nullptr, start_routine, (void *)td);
threads.push_back(td);
}
for(auto e:threads)
{
void *ret = nullptr;
pthread_join(e->_tid, &ret);//回收线程
cout << "等待成功"
<< " tid:" << e->_tid << endl;
}
cout << "等待结束" << endl;
return 0;
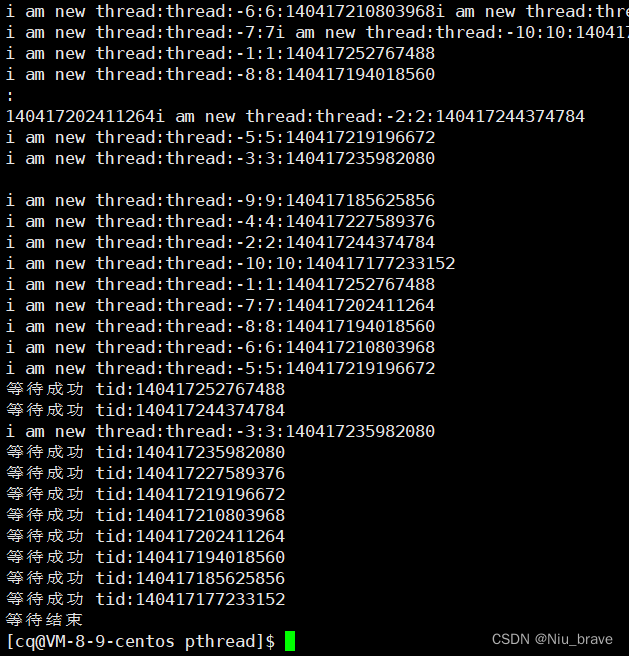
}以上的代码便演示了如何用pthread_join进行线程的等待效果如下:
那该函数里面的里面的返回值有什么作用呢?其实这个返回值就是用来带出退出码的。过程如下:

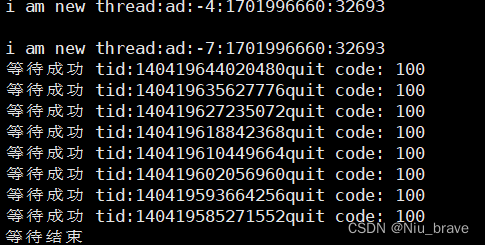
添加打印退出码的信息以后结果如下:
那为什么reval的类型是二级指针类型呢?这其实是因为线程结束后,退出信息会写入到线程库内部。线程库内部的退出码便是void*类型的。此时我们要想的便是获取这个退出码了,如何获取呢?因为pthread_join()的返回值是int类型的,所以我们便不能直接让pthread_join()直接返回一个void*类型的变量,所以只能自己在用户层定义一个void*类型的retval然后retval的地址传入进去获取返回值了。
四,线程获取自己的id值
使用 pthread_t pthread_self(void)可以获取到当前线程的id值。
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <vector>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
void *Done(void *args)
{
uint64_t i = (uint64_t)args;
string name = "thread_" + to_string(i);
sleep(1);
cout << name << "id :" << pthread_self() << endl;//使用pthread_self()打印线程id值。
}
int main()
{
vector<pthread_t> wait;
for (uint64_t i = 1; i <= 4; i++)
{
pthread_t td;
pthread_create(&td, nullptr, Done, (void *)i); // 创建线程
wait.push_back(td);
sleep(2);
}
for (auto e : wait) // 等待线程
{
pthread_join(e, nullptr);
}
return 0;
}
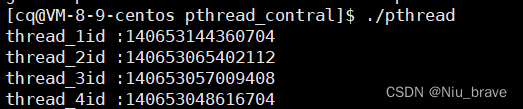
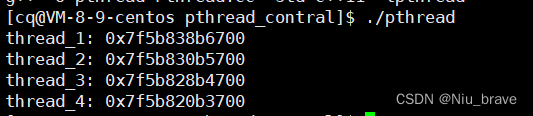
如果用16进制打印便是下面这样的:

其实线程的id就是一些地址。
五,线程取消
进行线程取消的函数叫做pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread)。线程取消的前提是线程先运行起来,然后才能取消。
实验代码:创建线程,然后取消一半线程,观察现象。
class thread
{
public:
int _num; // 线程的编号
char _buf[64]; // 线程的名字
pthread_t _tid; // 线程的id
};
void *start_routine(void *args)
{
int cnt = 5;
while (cnt--)
{
sleep(1);
thread *_td = static_cast<thread *>(args);
cout << "i am new thread:" << _td->_buf << ":" << _td->_num
<< ":" << _td->_tid << endl;
}
pthread_exit((void*)100);
}
int main()
{
vector<thread *> threads;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
thread *td = new thread;
td->_num = i;
snprintf(td->_buf, sizeof(td->_buf), "%s-%d", "thread:", i);
pthread_create(&td->_tid, nullptr, start_routine, (void *)td->_buf);
threads.push_back(td);
}
for (int i = 0;i<threads.size()/2;i++)//取消一半的线程
{
pthread_cancel(threads[i]->_tid);
}
for (auto e : threads)//等待
{
void *ret = nullptr;
pthread_join(e->_tid, &ret);
cout << "等待成功"
<< " tid:" << e->_tid << "quit code: " << (long long)(ret) << endl;
delete e;
}
cout << "等待结束" << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果如下:
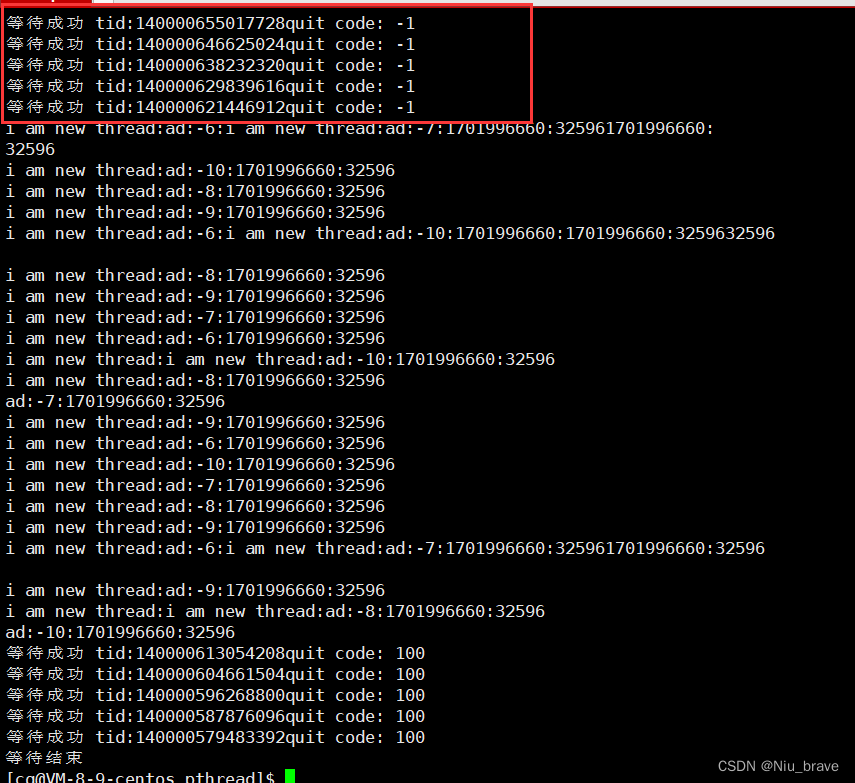
可以看到如果取消线程,那线程还是会被等待然后退出,退出码是-1。其实这是一个宏:
六,线程分离
线程分离使用到的函数 int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread)。先来说明一下,新创建的线程默认是joinable的。但是如果我的主线程并不关心当前的线程的返回值,那当前的线程便与我无关。那我的主线程去等待当前的线程便对我的主线程是一种负担。这个时候便可以来进行线程分离。线程的分离方式有两种:1,主线程去分离子线程 2,子线程自己进行分离。
示例代码:
1,主线程进行分离
#include<iostream>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<vector>
#include<unistd.h>
using namespace std;
void* Done(void* args)
{
uint64_t i = (uint64_t)args;
string name = "thread_" + to_string(i);
int cnt = 5;
while (cnt--)
{
sleep(1);
cout << name << "running....." << endl;
sleep(3);
}
}
int main()
{
vector<pthread_t> wait;
for (uint64_t i = 1; i <= 4; i++)
{
pthread_t td;
pthread_create(&td, nullptr, Done, (void*)i);//创建线程
wait.push_back(td);
sleep(3);//先休眠三秒,再进行线程分离
pthread_detach(td);//主线程子集分离
}
for(auto e:wait)//等待线程
{
int n = pthread_join(e,nullptr);
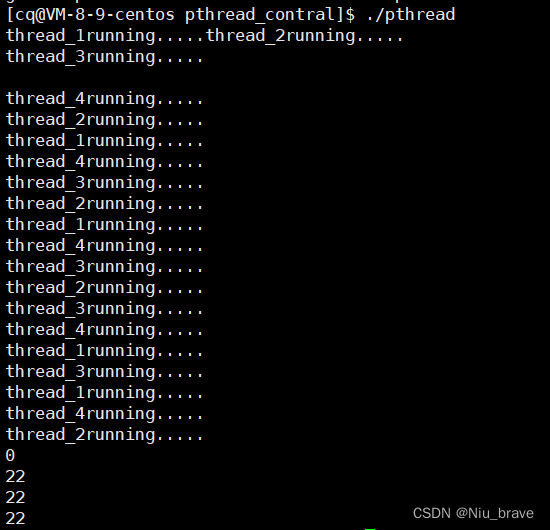
cout << n << " " << endl;//打印等待的返回值,0表示成功,其它表示失败。
}
return 0;
}
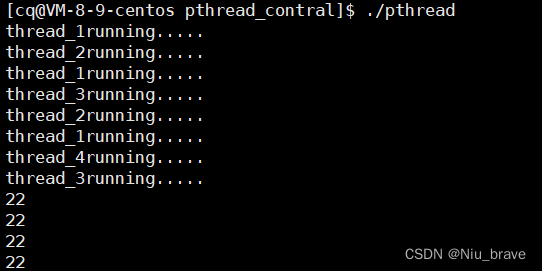
2,子线程自己主动分离
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <vector>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
void *Done(void *args)
{
uint64_t i = (uint64_t)args;
string name = "thread_" + to_string(i);
pthread_detach(pthread_self()); // 子线程自己自动分离
int cnt = 5;
while (cnt--)
{
cout << name << "running....." << endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
vector<pthread_t> wait;
for (uint64_t i = 1; i <= 4; i++)
{
pthread_t td;
pthread_create(&td, nullptr, Done, (void *)i); // 创建线程
wait.push_back(td);
}
for (auto e : wait) // 等待线程
{
int n = pthread_join(e, nullptr);
cout << n << " " << endl; // 打印等待的返回值,0表示成功,其它表示失败。
}
return 0;
}