一.LayoutLMv3介绍
LayoutLMv3(文档基础模型)
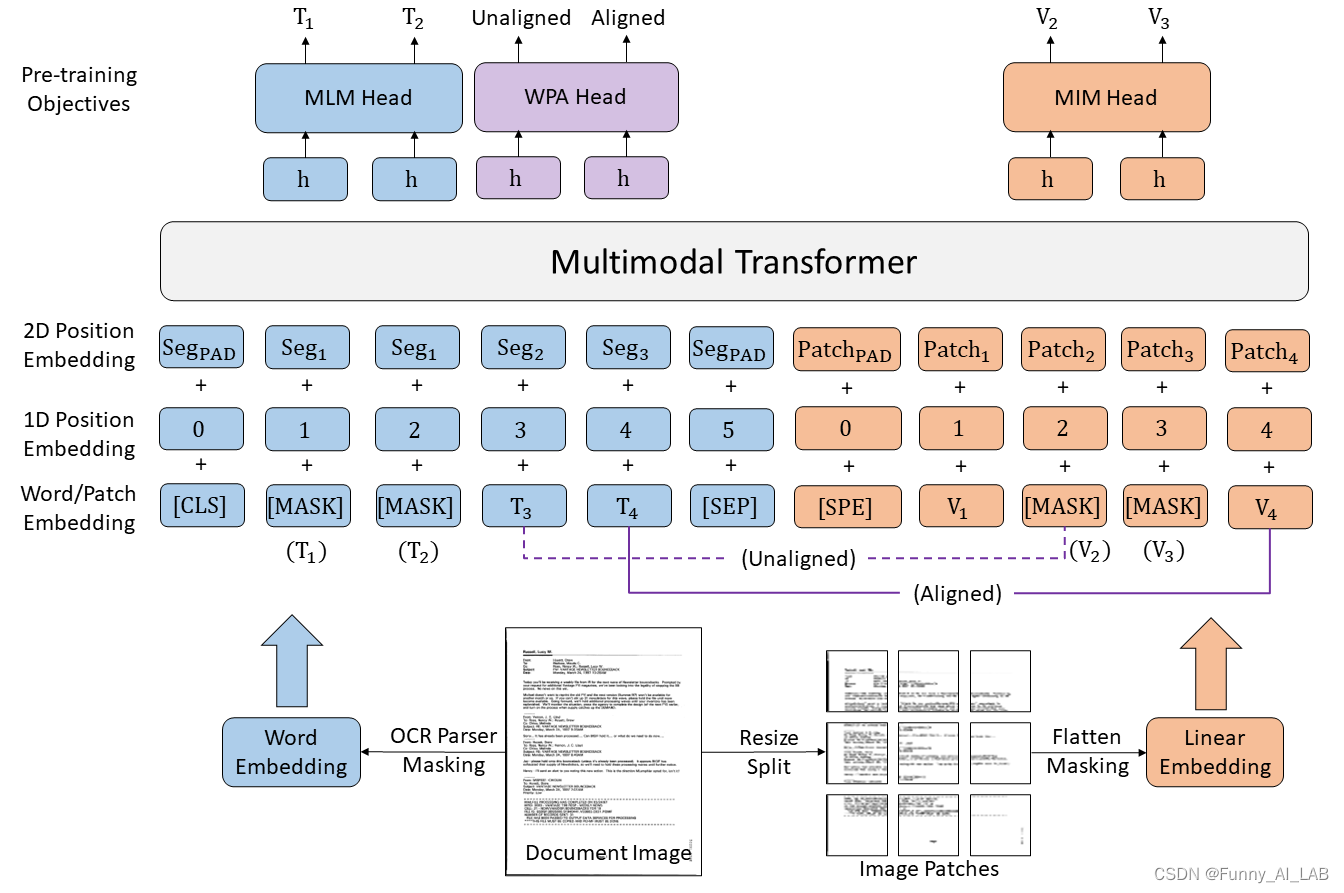
自监督预训练技术在文档人工智能方面取得了显着的进步。大多数多模态预训练模型使用掩码语言建模目标来学习文本模态的双向表示,但它们在图像模态的预训练目标上有所不同。这种差异增加了多模态表示学习的难度。
在本文中,微软提出LayoutLMv3来通过统一的文本和图像掩码来预训练文档 AI 的多模态 Transformer。此外,LayoutLMv3 还使用单词补丁对齐目标进行了预训练,通过预测文本单词的相应图像补丁是否被屏蔽来学习跨模态对齐。简单的统一架构和训练目标使 LayoutLMv3 成为适用于以文本为中心和以图像为中心的文档 AI 任务的通用预训练模型。实验结果表明,LayoutLMv3 不仅在以文本为中心的任务(包括表单理解、收据理解和文档视觉问答)中实现了最先进的性能,而且在以图像为中心的任务(如文档图像分类和文档布局)中也实现了最先进的性能分析。
二.环境配置
conda create --name layoutlmv3 python=3.7
conda activate layoutlmv3
git clone https://github.com/microsoft/unilm.git
cd unilm/layoutlmv3
pip install -r requirements.txt
# install pytorch, torchvision refer to https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/
pip install torch==1.10.0+cu111 torchvision==0.11.1+cu111 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html
# install detectron2 refer to https://detectron2.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorials/install.html
python -m pip install detectron2 -f https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/detectron2/wheels/cu111/torch1.10/index.html
pip install -e .
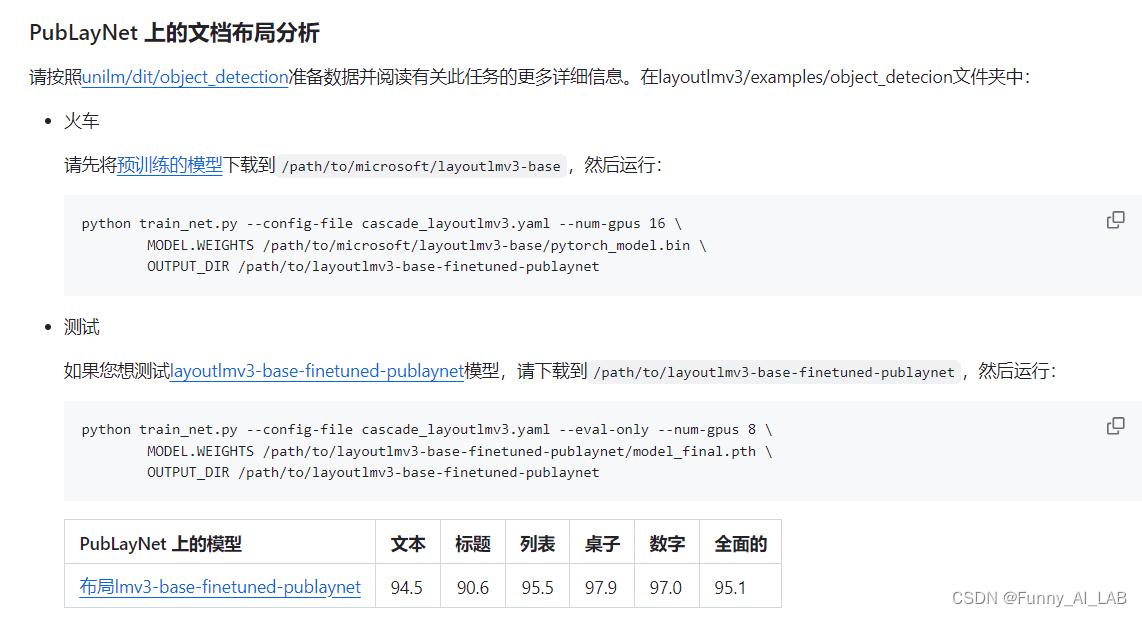
参考官网下载预训练:
三.CDLA数据转成coco格式
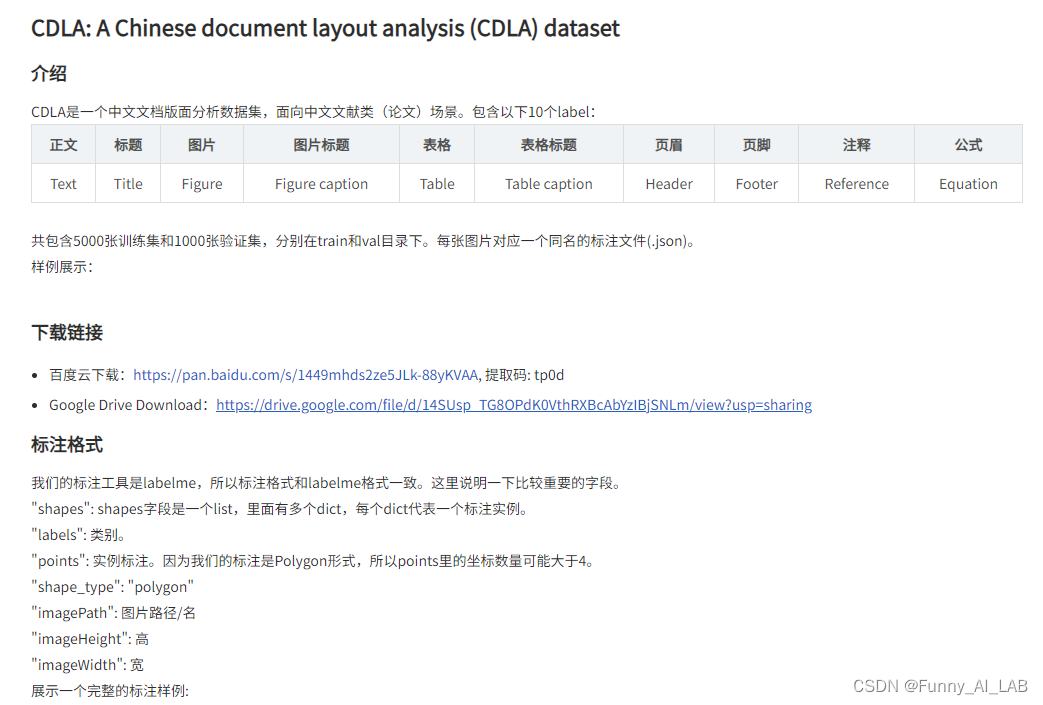
CDLA数据集介绍:CDLA数据集
由于CDLA的数据是由Labeme标注的,先将数据集格式转成coco的:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import argparse
import collections
import datetime
import glob
import json
import os
import os.path as osp
import sys
import uuid
import imgviz
import numpy as np
import labelme
try:
import pycocotools.mask
except ImportError:
print("Please install pycocotools:\n\n pip install pycocotools\n")
sys.exit(1)
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter
)
parser.add_argument("input_dir", help="input annotated directory")
parser.add_argument("output_dir", help="output dataset directory")
parser.add_argument("--labels", help="labels file", required=True)
parser.add_argument(
"--noviz", help="no visualization", action="store_true"
)
args = parser.parse_args()
if osp.exists(args.output_dir):
print("Output directory already exists:", args.output_dir)
sys.exit(1)
os.makedirs(args.output_dir)
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages"))
if not args.noviz:
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "Visualization"))
print("Creating dataset:", args.output_dir)
now = datetime.datetime.now()
data = dict(
info=dict(
description=None,
url=None,
version=None,
year=now.year,
contributor=None,
date_created=now.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f"),
),
licenses=[dict(url=None, id=0, name=None,)],
images=[
# license, url, file_name, height, width, date_captured, id
],
type="instances",
annotations=[
# segmentation, area, iscrowd, image_id, bbox, category_id, id
],
categories=[
# supercategory, id, name
],
)
class_name_to_id = {}
for i, line in enumerate(open(args.labels).readlines()):
class_id = i - 1 # starts with -1
class_name = line.strip()
if class_id == -1:
assert class_name == "__ignore__"
continue
class_name_to_id[class_name] = class_id
data["categories"].append(
dict(supercategory=None, id=class_id, name=class_name,)
)
out_ann_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "annotations.json")
label_files = glob.glob(osp.join(args.input_dir, "*.json"))
for image_id, filename in enumerate(label_files):
print("Generating dataset from:", filename)
label_file = labelme.LabelFile(filename=filename)
base = osp.splitext(osp.basename(filename))[0]
out_img_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages", base + ".jpg")
img = labelme.utils.img_data_to_arr(label_file.imageData)
imgviz.io.imsave(out_img_file, img)
data["images"].append(
dict(
license=0,
url=None,
file_name=osp.relpath(out_img_file, osp.dirname(out_ann_file)),
height=img.shape[0],
width=img.shape[1],
date_captured=None,
id=image_id,
)
)
masks = {} # for area
segmentations = collections.defaultdict(list) # for segmentation
for shape in label_file.shapes:
points = shape["points"]
label = shape["label"]
group_id = shape.get("group_id")
shape_type = shape.get("shape_type", "polygon")
mask = labelme.utils.shape_to_mask(
img.shape[:2], points, shape_type
)
if group_id is None:
group_id = uuid.uuid1()
instance = (label, group_id)
if instance in masks:
masks[instance] = masks[instance] | mask
else:
masks[instance] = mask
if shape_type == "rectangle":
(x1, y1), (x2, y2) = points
x1, x2 = sorted([x1, x2])
y1, y2 = sorted([y1, y2])
points = [x1, y1, x2, y1, x2, y2, x1, y2]
else:
points = np.asarray(points).flatten().tolist()
segmentations[instance].append(points)
segmentations = dict(segmentations)
for instance, mask in masks.items():
cls_name, group_id = instance
if cls_name not in class_name_to_id:
continue
cls_id = class_name_to_id[cls_name]
mask = np.asfortranarray(mask.astype(np.uint8))
mask = pycocotools.mask.encode(mask)
area = float(pycocotools.mask.area(mask))
bbox = pycocotools.mask.toBbox(mask).flatten().tolist()
data["annotations"].append(
dict(
id=len(data["annotations"]),
image_id=image_id,
category_id=cls_id,
segmentation=segmentations[instance],
area=area,
bbox=bbox,
iscrowd=0,
)
)
if not args.noviz:
labels, captions, masks = zip(
*[
(class_name_to_id[cnm], cnm, msk)
for (cnm, gid), msk in masks.items()
if cnm in class_name_to_id
]
)
viz = imgviz.instances2rgb(
image=img,
labels=labels,
masks=masks,
captions=captions,
font_size=15,
line_width=2,
)
out_viz_file = osp.join(
args.output_dir, "Visualization", base + ".jpg"
)
imgviz.io.imsave(out_viz_file, viz)
with open(out_ann_file, "w") as f:
json.dump(data, f)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
四.修改配置文件
配置文件路径:/unilm/layoutlmv3/examples/object_detection/cascade_layoutlmv3.yaml
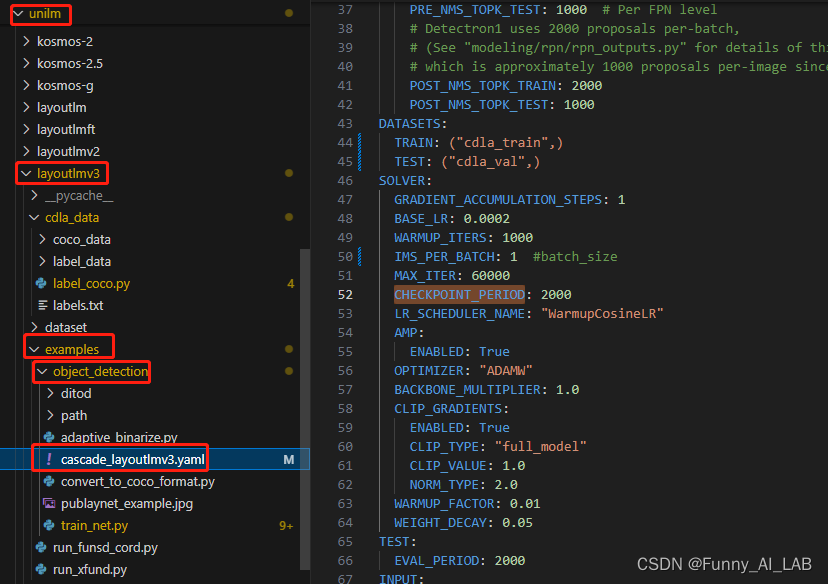
需要修改的位置:
WEIGHTS: "/microsoft/layoutlmv3-base-chinese/pytorch_model.bin" #预训练权重
NUM_CLASSES: 10 #标签数
IMS_PER_BATCH: 1 #batch_size
CHECKPOINT_PERIOD: 5000 # 每5000个epoch进行一次测试
PUBLAYNET_DATA_DIR_TRAIN: "/layoutlmv3/cdla_data/coco_data/train" #train
PUBLAYNET_DATA_DIR_TEST: "/layoutlmv3/cdla_data/coco_data/val" #val
相关参数的介绍:detectron2(目标检测框架):配置config解析
五.模型训练
train:
python train_net.py --config-file cascade_layoutlmv3.yaml MODEL.WEIGHTS /path/to/microsoft/layoutlmv3-base/pytorch_model.bin OUTPUT_DIR /path/to/layoutlmv3_train/
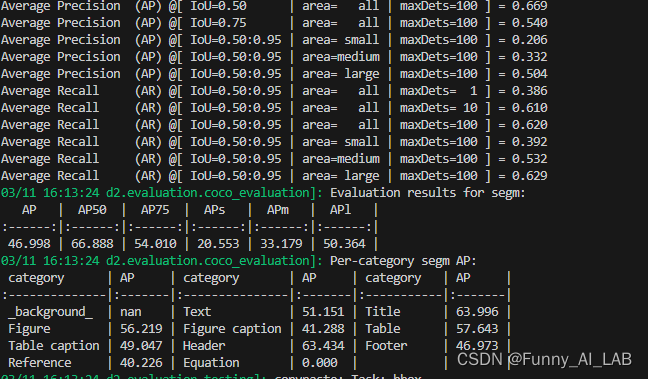
更多参考:
1.微调LayoutLM v3进行票据数据的处理和内容识别
2.yolov8训练CDLA数据文版版面分析
3.layoutlmv3 在中文文档上的应用