Java注解
- 注解介绍
- 元注解
- @Retention
- @Target
- @Documented
- @Inherited
- 接口
- 类
- 测试结果
注解介绍
Java注解(Annotation)是一种元数据(Metadata)的形式,它可以被添加到Java代码中的类、方法、变量、参数等元素上,以提供关于程序代码的额外信息。
在Java中,注解并不是一个Java类,而是一个特殊的接口类型(默认继承java.lang.annotation.Annotation接口),其实例在编译时被创建,并且在程序运行过程中可以通过反射获取相关信息。
注解里面定义的方法,代表的注解的成员属性,可以指定默认值(不指定默认值时,使用时必须指定对应的值)。在注解被使用时可以指定具体的的值,在编译时,会自动创建代理的注解对象,这个对象的属性不可修改(immutable)。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional({OnClassCondition.class})
public @interface ConditionalOnClass {
Class<?>[] value() default {};
String[] name() default {};
}
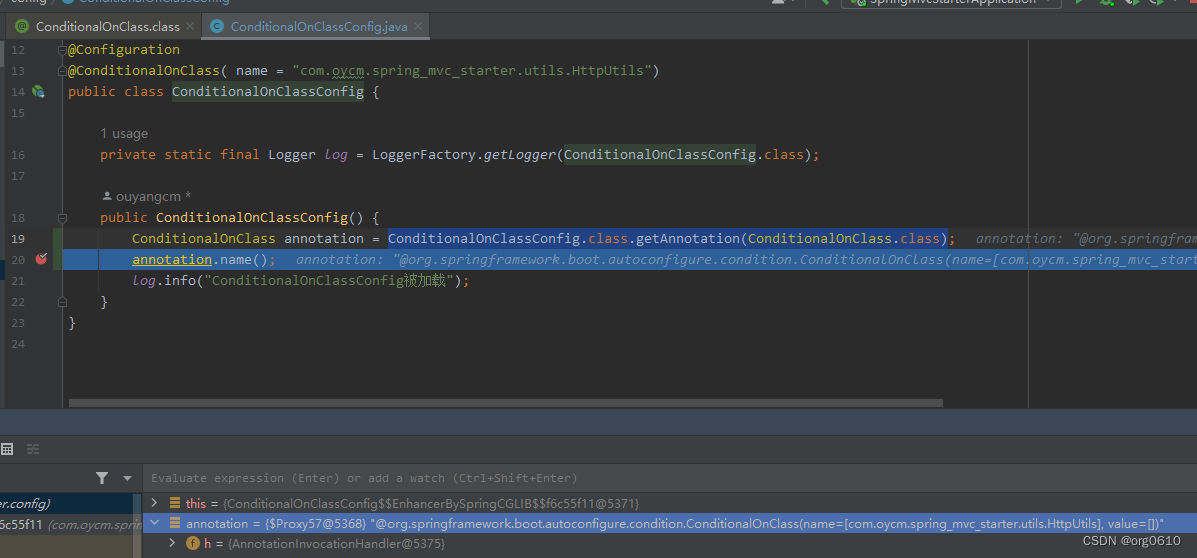
元注解
Java中,元注解是用来修饰其它注解的注解。元注解是用来定义其它注解行为的注解。Java提供了常用的元注解:@Retention、@Target、@Documented、@Inherited。
@Retention
retention:保留;保持。
@Retention保留注解策略,只有这个元注解作用于注解时才有效;如果将元注解类型作用于另一个注解类型的成员属性(成员变量),则无效。
保留策略:RetentionPolicy.SOURCE、RetentionPolicy.CLASS、RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME。
- RetentionPolicy.SOURCE:注解在编译时会被丢弃。只保留在源代码级别,可以用于编译器的静态检查和处理。
- RetentionPolicy.CLASS:注解被保留在class文件中,但是运行时不可见,不能通过反射获取。对编译器可见,但是运行时不会产生任何效果。缺省的默认保留策略。
- RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME:编译后被保存在class文件中,并且运行时能提供反射获取到。
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Retention {
// 返回注解保留的策略
RetentionPolicy value();
}
继承Retention注解
package com.oycm.spring_data_jpa.annotations.retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface RetentionSource {
}
package com.oycm.spring_data_jpa.annotations.retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface RetentionClass {
}
package com.oycm.spring_data_jpa.annotations.retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface RetentionRuntime {
Class<RetentionClass> value();
}
package com.oycm.spring_data_jpa.annotations.retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
/**
* @author ouyangcm
* create 2024/2/26 15:52
*/
@RetentionSource
@RetentionClass
@RetentionRuntime(value = RetentionClass.class)
public class RetentionTest {
@RetentionSource
@RetentionClass
@RetentionRuntime(value = RetentionClass.class)
private String member;
@RetentionSource
@RetentionClass
@RetentionRuntime(value = RetentionClass.class)
private static String staticMember;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<RetentionRuntime> runtimeClass = RetentionRuntime.class;
Class<RetentionTest> clazz = RetentionTest.class;
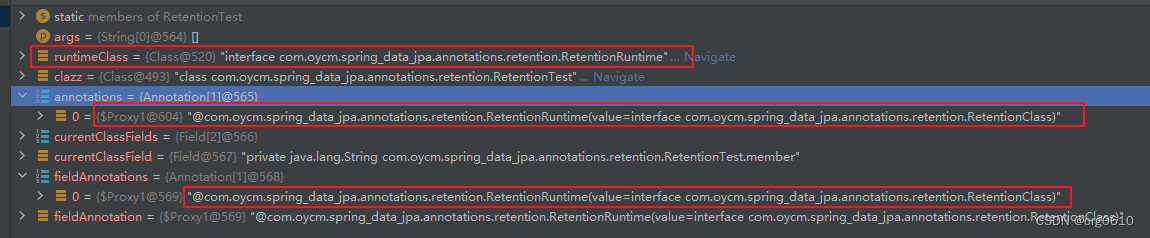
Annotation[] annotations = clazz.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
Field[] currentClassFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field currentClassField : currentClassFields) {
System.out.println("属性名: " + currentClassField.getName());
Annotation[] fieldAnnotations = currentClassField.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation fieldAnnotation : fieldAnnotations) {
System.out.println("注解: " + fieldAnnotation.annotationType().getName());
}
}
}
}
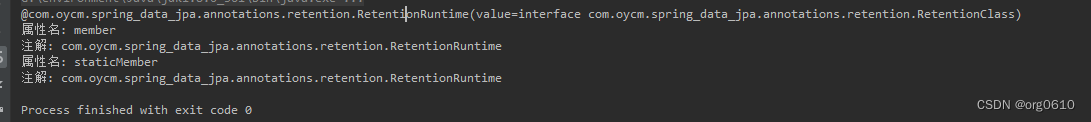
注意:反射获取的Annotation是一个代理对象,可以使用annotationType()方法获取真正的注解对象类信息。
@Target
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Target {
// 注解目标类型数组
ElementType[] value();
}
@Target注解用于指定注解可以应用的目标类型。类型有:ElementType.TYPE(类、接口(注解)、枚举等)、ElementType.FIELD(静态或非静态成员变量)、ElementType.METHOD(普通方法)、ElementType.PARAMETER(方法参数)、ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR(构造方法)、ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE(局部变量)、ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE(注解)、ElementType.PACKAGE(包)、ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER(泛型)、ElementType.TYPE_USE(用于使用类型的任何地方)。
// 不能作用于其他类型上,只能作为其他注解的变量使用
@Target({})
public @interface MemberType {
...
}
// 类型重复出现,编译报错
@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD})
public @interface Bogus {
...
}
@Documented
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Documented {
}
指示被标注的自定义注解是否应该包含再Java文档中。一个注解使用了@Document注解标注,那么使用javadoc工具生成文档时,这个注解的信息会被包含在文档中。
@Inherited
Inherited:继承的;遗传的。
表示类的注解是可继承的,使用getAnnotation()会自动查询该类的父类以获取所有的注解,直到Object类;这个元注解只在作用于类注解时才生效。
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Inherited {
}
@Inherited
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)// 不可省略,不然获取不到
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface MyInherited {
}
接口
package com.oycm.spring_data_jpa.annotations.inherited;
@MyInherited
public interface InheritedInterface {
}
package com.oycm.spring_data_jpa.annotations.inherited;
/**
* @author ouyangcm
* create 2024/2/26 17:22
*/
public class InheritedInterfaceImpl implements InheritedInterface{
}
类
package com.oycm.spring_data_jpa.annotations.inherited;
/**
* @author ouyangcm
* create 2024/2/26 17:22
*/
@MyInherited
public class InheritedSuper {
}
package com.oycm.spring_data_jpa.annotations.inherited;
/**
* @author ouyangcm
* create 2024/2/26 17:22
*/
public class InheritedSuperSub extends InheritedSuper{
}
测试结果
package com.oycm.spring_data_jpa.annotations.inherited;
/**
* @author ouyangcm
* create 2024/2/26 17:21
*/
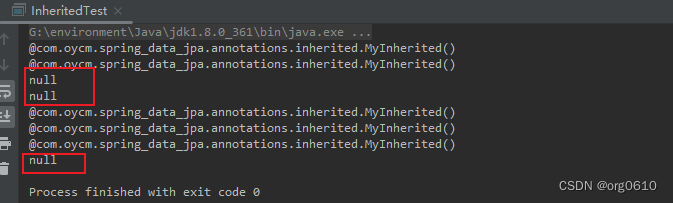
public class InheritedTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<InheritedInterface> inheritedInterfaceClass = InheritedInterface.class;
Class<InheritedInterfaceImpl> inheritedInterfaceClassImpl = InheritedInterfaceImpl.class;
// 这里获取到Annotation对象仍然是代理,不过两个是同一个对象.annotationType()可以获取真正的Class对象
System.out.println(inheritedInterfaceClass.getAnnotation(MyInherited.class));
System.out.println(inheritedInterfaceClass.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyInherited.class));
System.out.println(inheritedInterfaceClassImpl.getAnnotation(MyInherited.class));
System.out.println(inheritedInterfaceClassImpl.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyInherited.class));
Class<InheritedSuper> inheritedSuperClass = InheritedSuper.class;
Class<InheritedSuperSub> inheritedSuperSubClass = InheritedSuperSub.class;
System.out.println(inheritedSuperClass.getAnnotation(MyInherited.class));
System.out.println(inheritedSuperClass.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyInherited.class));
System.out.println(inheritedSuperSubClass.getAnnotation(MyInherited.class));
System.out.println(inheritedSuperSubClass.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyInherited.class));// 只能获得自己的注解
}
}