0. 背景
在高速公路监控视频场景下,图像分辨率大都是1920 * 1080或者2560 * 1440,远处的物体(车辆和行人等)都比较小。考虑需要对图像进行拆分,然后把拆分后的数据统一送入模型中,推理的结果然后再做nms,恢复到原始图片数据中。
这个过程中牵涉到两个方面的内容,一个是多batch推理,一个是nms。
1. 多batch
例如使用1920*1080分辨率的图片数据,把该分辨率的数据分为4份。
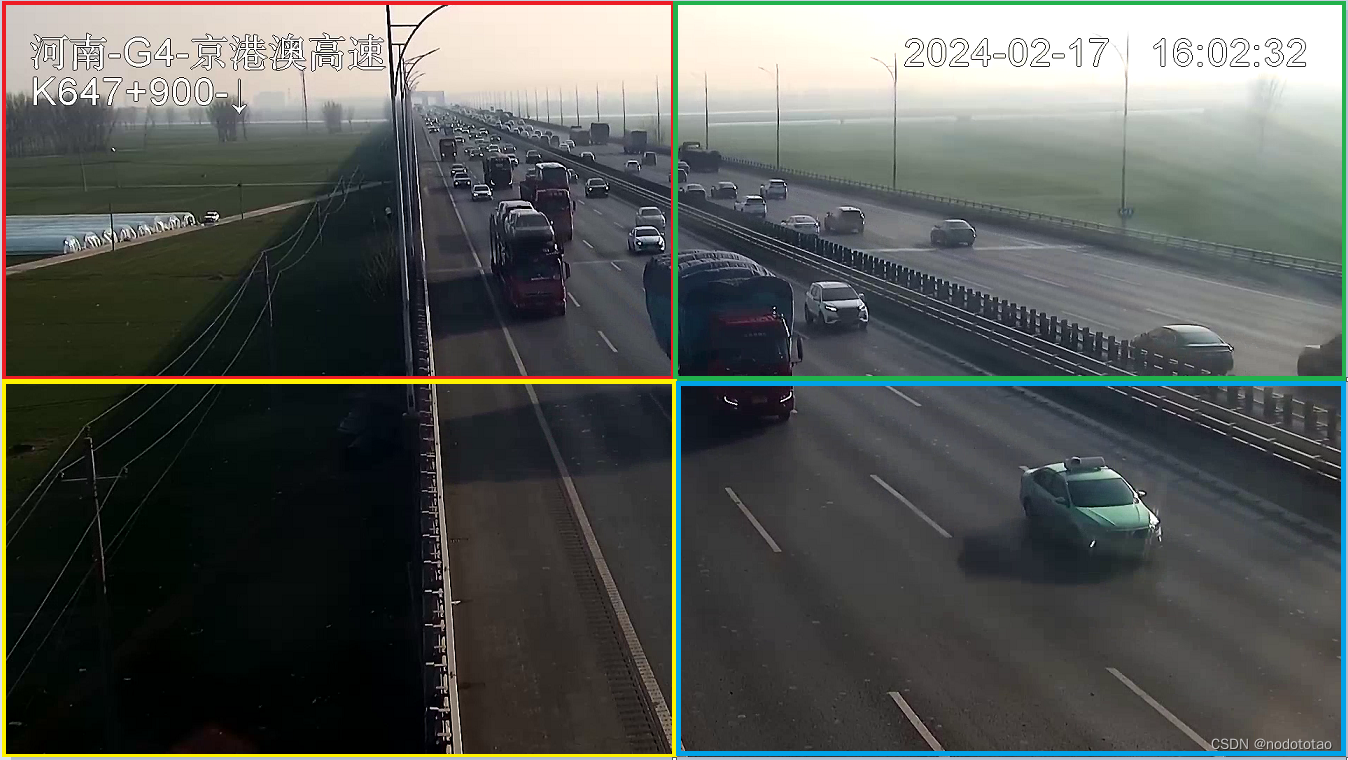
如果只是平均分车4份,当一个物体(比如车辆)正好处于图片中心时,则可能被拆分到4个区域,这样当后续这4个区域分别得到检测框后,无法对同一个拆分的物体进行完美覆盖。所以在拆分图片是,可用适当的大一些。
1.1 平均拆分
1.2 建议拆分
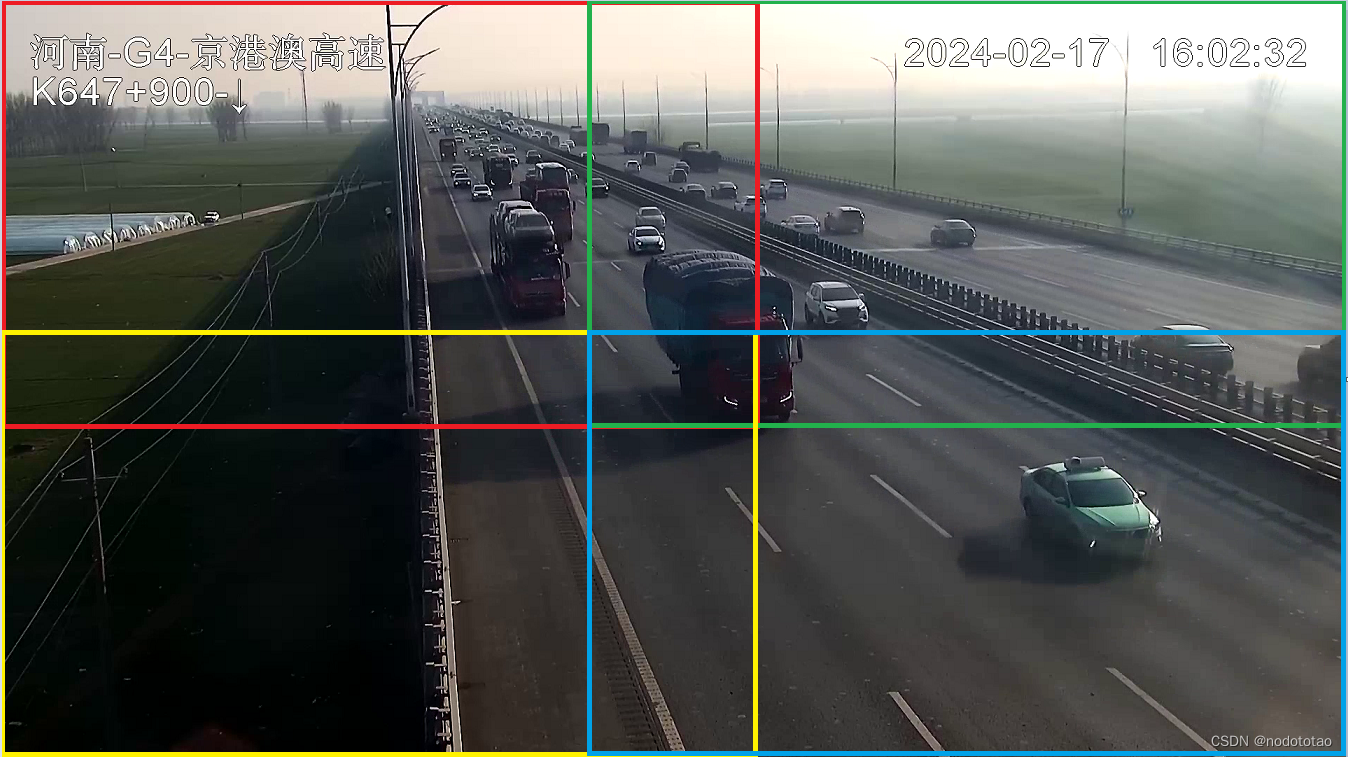
例如:1920*1080分辨率的图片,进行拆分
h1 = int(1080 * 7 / 16)
h2 = int(1080 * 9 / 16)
w1 = int(1920 * 7 / 16)
w2 = int(1920 * 9 / 16)
img0 = frame[0:h_2, 0:w_2].copy()
img1 = frame[0:h_2, w_1:w].copy()
img2 = frame[h_1:h, 0:w_2].copy()
img3 = frame[h_1:h, w_1:w].copy()
2. yolov8中多batch推理的方式
因为刚使用yolov8不久,推理过程中的数据加载逻辑重新梳理了一下,做个记录
1)推理调用入口
results = model(source=frame, save=False, conf=conf, iou=nms, save_txt=False,
show=False)
2)model定义
model = YOLO(MODEL)
3)YOLO类 (ultralytics/models/yolo/model.py)
from ultralytics import YOLO
class YOLO(Model):
4) Model基类
class Model(nn.Module):
(4.1)super().__init__()
self._load(model, task)
(4.2)def __call__(self, source=None, stream=False, **kwargs):
"""Calls the 'predict' function with given arguments to perform object detection."""
return self.predict(source, stream, **kwargs)
(4.3)def predict(self, source=None, stream=False, predictor=None, **kwargs):
if not self.predictor:
self.predictor = (predictor or self._smart_load('predictor'))(overrides=args, _callbacks=self.callbacks)
self.predictor.setup_model(model=self.model, verbose=is_cli)
(4.4)def _smart_load(self, key):
"""Load model/trainer/validator/predictor."""
try:
return self.task_map[self.task][key] #detect\predictor
# 根据(3)中YOLO类中的task_mape
'detect': {
'model': DetectionModel,
'trainer': yolo.detect.DetectionTrainer,
'validator': yolo.detect.DetectionValidator,
'predictor': yolo.detect.DetectionPredictor, },
# 调用接口为yolo.detect.DetectionPredictor
5)class DetectionPredictor(BasePredictor)
6)BasePredictor
#因为DetectionPredictor中只有后处理的方式,数据预处理的内容在BasePredictor基类中
(6.1)def __call__(self, source=None, model=None, stream=False, *args, **kwargs):
"""Performs inference on an image or stream."""
self.stream = stream
if stream:
return self.stream_inference(source, model, *args, **kwargs)
else:
return list(self.stream_inference(source, model, *args, **kwargs)) # merge list of Result into one
(6.2)def stream_inference(self, source=None, model=None, *args, **kwargs):
# Setup source every time predict is called
self.setup_source(source if source is not None else self.args.source)
(6.3)def setup_source(self, source):
self.dataset = load_inference_source(source=source,
imgsz=self.imgsz,
vid_stride=self.args.vid_stride,
buffer=self.args.stream_buffer)
7) 数据处理方式
from ultralytics.data import load_inference_source
def load_inference_source(source=None, imgsz=640, vid_stride=1, buffer=False):
dataset = LoadPilAndNumpy(source, imgsz=imgsz)
8)最终的数据处理
class LoadPilAndNumpy:
def __init__(self, im0, imgsz=640):
"""Initialize PIL and Numpy Dataloader."""
if not isinstance(im0, list):
im0 = [im0]
self.paths = [getattr(im, 'filename', f'image{i}.jpg') for i, im in enumerate(im0)]
self.im0 = [self._single_check(im) for im in im0]
#print(self.im0)
self.imgsz = imgsz
self.mode = 'image'
# Generate fake paths
self.bs = len(self.im0)
从上面的数据执行逻辑可用看出,推理入口的数据格式可以是一个列表形式。
这个列表中包含拆分后多个区域的数据
# 例如上面拆分为了4个部分,img0, img1, img2, img3
imgs = []
imgs.append(img0)
imgs.append(img1)
imgs.append(img2)
imgs.append(img3)
resultss = model(source=imgs, save=False, conf=conf, iou=nms, save_txt=False,
show=False)
最后的结果为4个batch图片数据对应的检测结果
ress0 = resultss[0].tojson()
datas0 = json.loads(ress0)
ress1 = resultss[1].tojson()
datas1 = json.loads(ress1)
ress2 = resultss[2].tojson()
datas2 = json.loads(ress2)
ress3 = resultss[3].tojson()
datas3 = json.loads(ress3)
3. nms处理
因为4部分区域拆分时,是有重合的部分,故在4部分区域推理出结果后,还需要进行一次NMS。
# results:为4个拆分区域检测结果的合集,iou_thresh: iou计算的阈值
def nms(results, iou_thresh):
grouped_results = {}
# 把results的内容,根据cls的分类情况组合。因为最终做nms时需要区分是不是同一个类别
for cls_boxes in results:
x1, y1, x2, y2, score, cls = cls_boxes
if cls not in grouped_results:
grouped_results[cls] = []
grouped_results[cls].append([x1, y1, x2, y2, score])
#print(grouped_results)
keep_boxes = []
# 遍历所有的键值对
for cls, boxes_l in grouped_results.items():
boxes = np.array(boxes_l)
# 每个 box 的坐标和置信度
x1 = boxes[:, 0]
y1 = boxes[:, 1]
x2 = boxes[:, 2]
y2 = boxes[:, 3]
scores = boxes[:, 4]
# 每个 box 的面积
areas = (y2 - y1 + 1) * (x2 - x1 + 1)
# keep_boxes 用于存放执行 NMS 后剩余的 boxes
# 取出置信度从大到小排列的索引,其中 scores.argsort() 返回的是数组值从小到大的索引
index = scores.argsort()[::-1]
while len(index) > 0:
# 取出置信度最大的 box,将其放入 keep 中,并判断其他 box 是否可以与之合并
i = index[0]
boxes_l[i].append(cls)
keep_boxes.append(boxes_l[i])
# np.maximum(arr:list, x:int)表示计算arr中每一个元素与常数 x 之间的最大值
x1_overlap = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[index[1:]])
y1_overlap = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[index[1:]])
x2_overlap = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[index[1:]])
y2_overlap = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[index[1:]])
# 计算重叠部分的面积,若没有不重叠部分则面积为 0
w = np.maximum(0, x2_overlap - x1_overlap + 1)
h = np.maximum(0, y2_overlap - y1_overlap + 1)
overlap_area = w * h
# 计算 iou(交并比)
ious = overlap_area / (areas[i] + areas[index[1:]] - overlap_area)
# 因为在拆分时,某个物体可能只有很小一部分,这个小的区域的检测框与正常物体的检测框的
# 交集占比小于iou_thresh,则这边小的区域就不会被去除。所以添加下面两个iou数值,用于
# 判断某个重叠部分的区域是不是跟检测框的大小类似,从而去除该检测框的值。
iou1 = overlap_area / areas[i]
iou2 = overlap_area / areas[index[1:]]
# 合并重叠度最大的 box,即只保留 iou < iou_thresh 的 box
# 因为 np.where(ious <= iou_thresh) 的数据结构是 tuple 里面包含了一个 list,所以要用 [0] 取出 list
# 添加条件2,3是为了解决,同一个物体被分隔后,目标框只是物体的小一部分,nms时遗漏
condition1 = ious <= iou_thresh
condition2 = iou1 < 0.8
condition3 = iou2 < 0.8
idx = np.where(condition1 & condition2 & condition3)[0]
# 这里将需要idx + 1,由于index 是 ious 的索引,而 ious 是去除掉 index 的第一个元素对应的 box 得到的,
# 所以 ious 的索引 +1 对应的 box 才是 index 相同索引对应的 index
# 因为 len(ious)<=len(index),所以 len(index[idx + 1])<=len(index),所以 while 循环中 index 的元素数量越来越少
index = index[idx + 1]
return keep_boxes
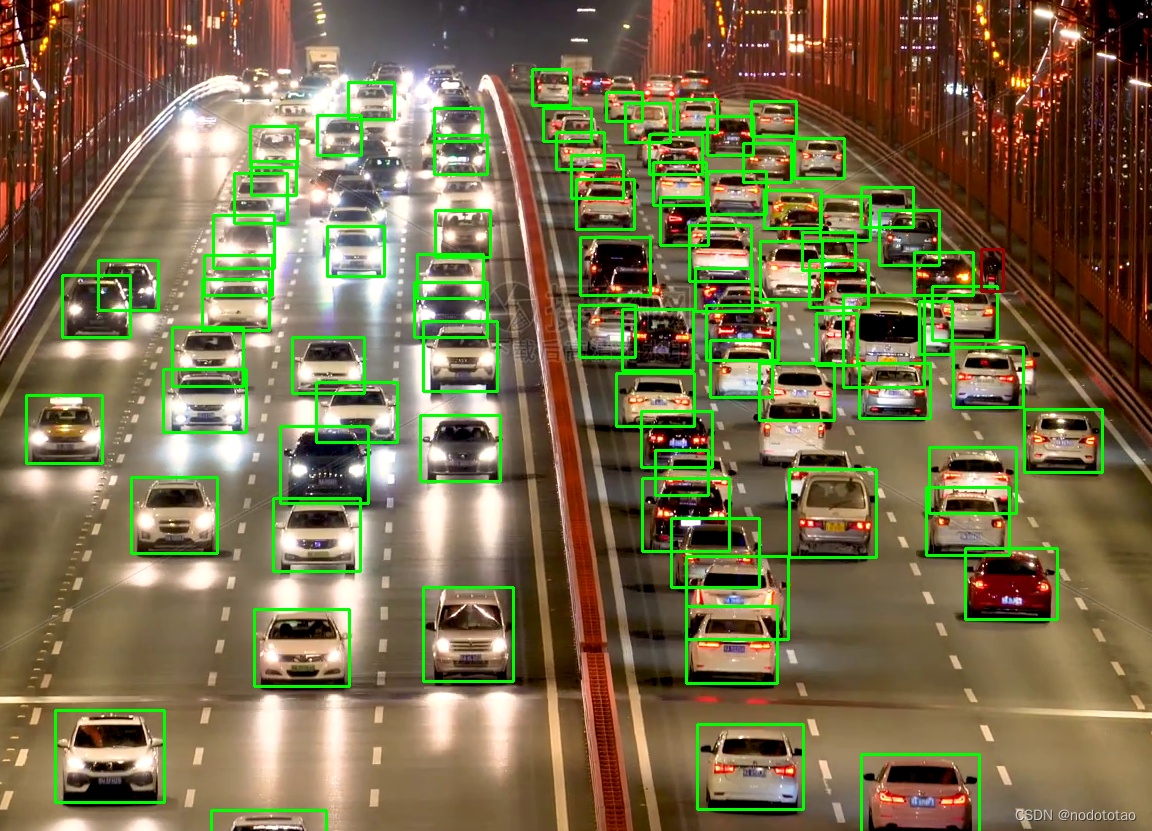
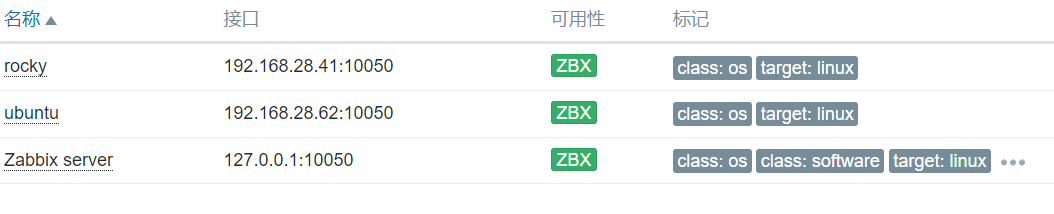
4. 示例
nms前
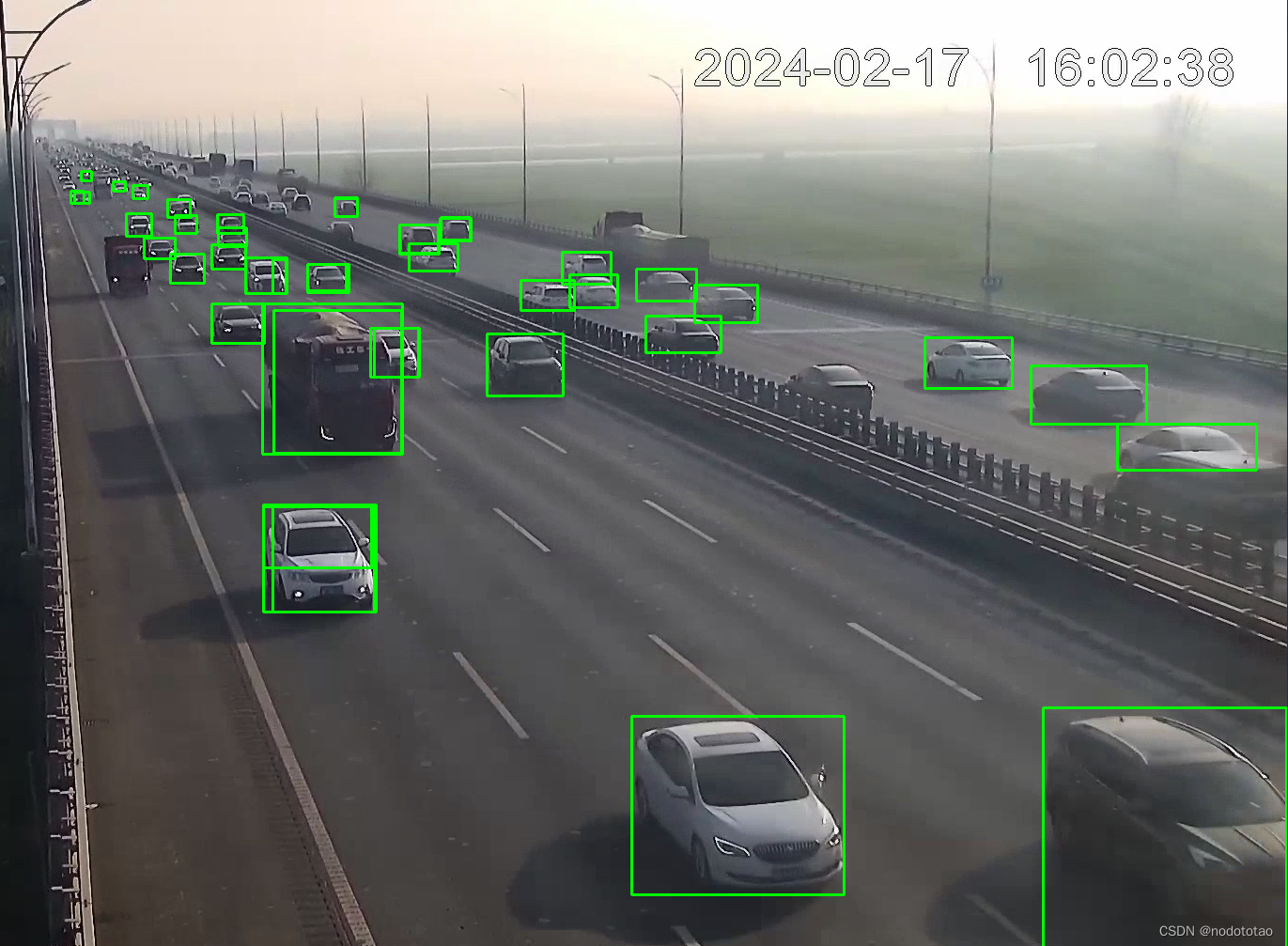
nms处理后
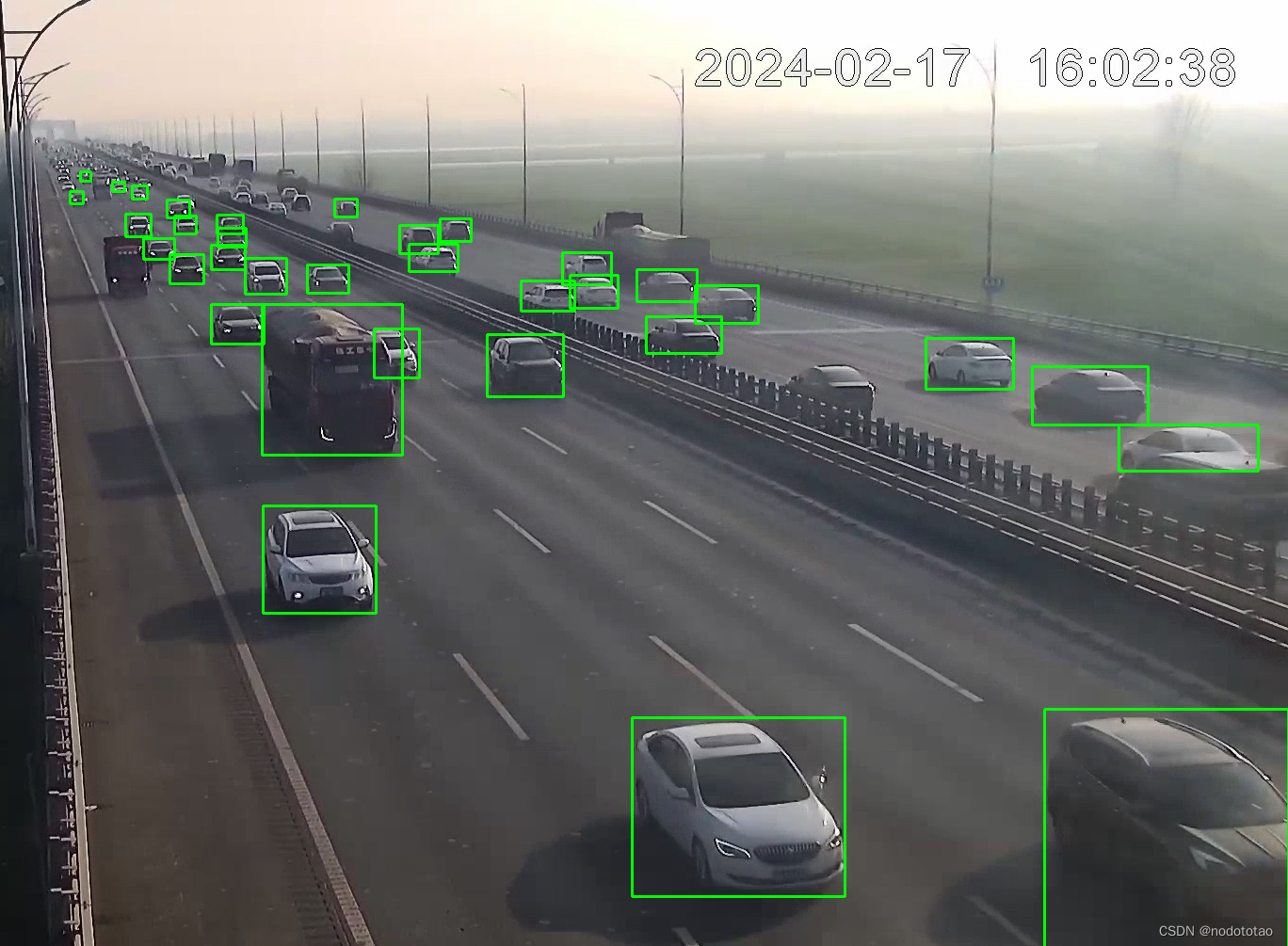
nms前
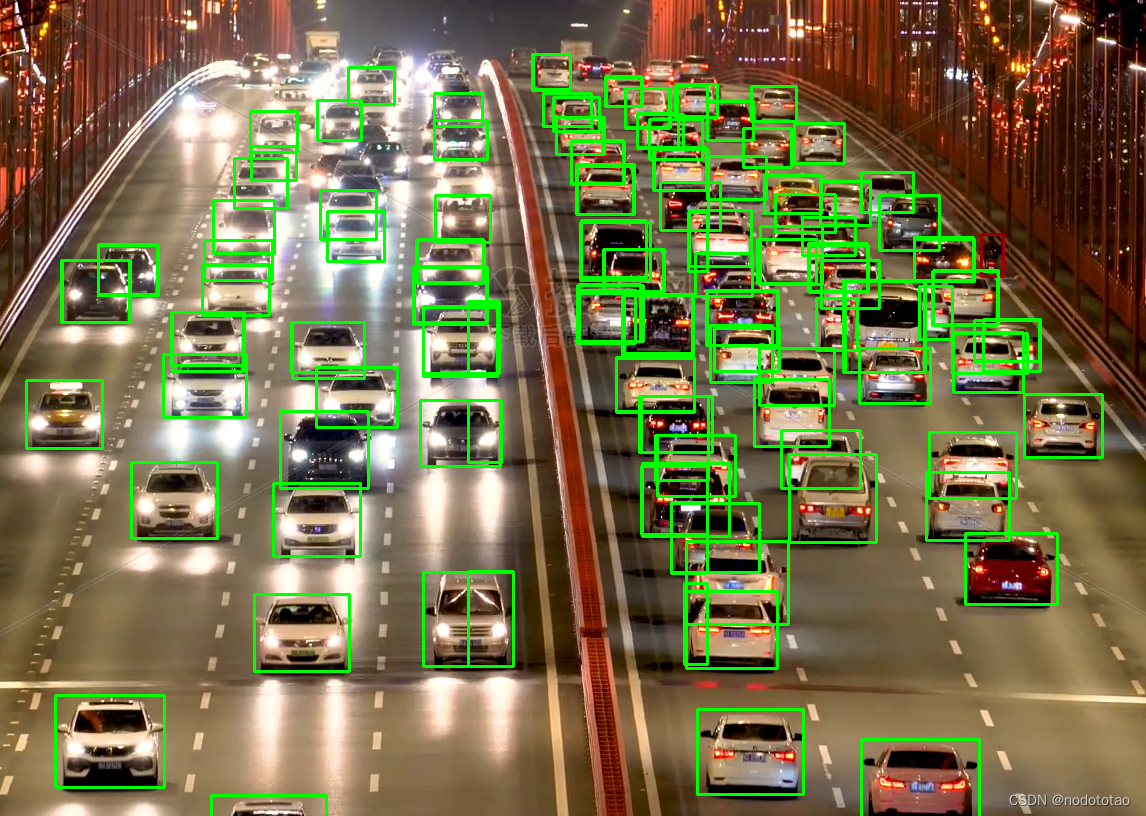

nms处理后