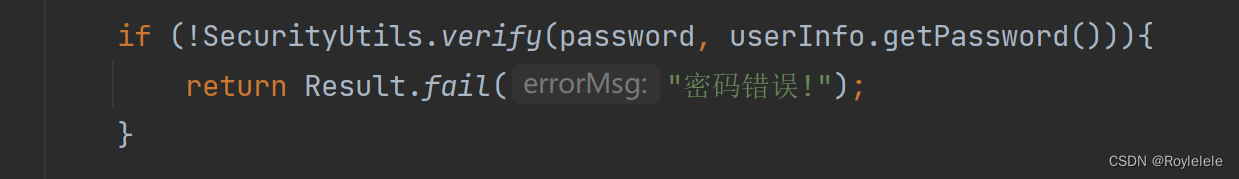
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、用例
- 小根堆管理定时器事件
- 小根堆和链表管理定时器事件
- 区别
- 二、基本数据结构介绍
- 结构体成员分析
- 小根堆和链表common_timeout图示
- 三、源码分析
- 小根堆管理定时器事件
- event_new
- event_add
- event_dispatch
- 链表common_timeout管理定时器事件
- event_base_init_common_timeout
- event_add
- event_dispatch
- 总结
前言
libevent中对三类事件进行了封装,io事件、信号事件、定时器事件,libevent源码分析系列文章会分别分析这三类事件,本文分析定时器事件。
本文通过例子展现了两种定时器的使用方法,同时通过源码分析了两种定时器事件的原理。
一、用例
小根堆管理定时器事件
#include <event.h>
void time_cb(evutil_socket_t s,short w, void *arg)
{
printf("====time_cb======\n");
}
一个单独的定时器事件
int main()
{
timeval t = {0,1};
event_base *base = event_base_new(); //初始化reactor对象,epoll_create
event* ev_t = evtimer_new(base, time_cb, NULL);//初始化一个定时器事件
evtimer_add(ev_t,&t); //将定时器事件注册到reactor中
event_base_dispatch(base); //事件主循环,epoll_wait
}
一个fd的超时事件:如果fd在设定的超时时间没有数据到达,则也会触发回调函数
int main()
{
event_base *base = event_base_new(); //初始化reactor对象,epoll_create
event *ev_t = event_new(base,sock,EV_READ|EV_TIMEOUT,time_cb,base); //初始化一个fd的超时事件
timeval t = {0,1};
event_add(ev_t,&t); //将事件加入io事件队列中并且加入到定时器结构中
event_base_dispatch(base); //时间主循环,epoll_wait
}
小根堆和链表管理定时器事件
int main()
{
timeval t = {0,1};
event_base *base = event_base_new(); //初始化reactor对象,epoll_create
event* ev_t = evtimer_new(base, time_cb, NULL);//初始化一个定时器事件
event_base_init_common_timeout(base,&t); //将超时时间标记上common_timeout标记
evtimer_add(ev_t,&t); //将定时器事件注册到reactor中
event_base_dispatch(base); //事件主循环,epoll_wait
}
区别
小根堆是用在:多个超时event的相对超时时间是随机的。而common-timeout则是用在: 大量的超时event具有相同的相对超时时间。绝对超时时间 = 相对超时时间+ 调用event_add时间。
原因:
小根堆每次删除堆顶超时的event时间复杂度只需要O(logn),假设有m个event超时了需要同时处理,需要花费的时间就是O(mlogn);如果有大量相同的超时时长,并且绝对超时时间一致,使用小根堆和链表则需要花费的时间是O(m+logn),能够提升超时时间处理效率。
二、基本数据结构介绍
结构体成员分析
typedef struct min_heap
{
struct event** p;
unsigned n, a;
} min_heap_t; //小根堆
struct common_timeout_list {
struct event_list events; //相同相对超时时间的事件组成链表
struct timeval duration; //该链表的相对超时时间
struct event timeout_event; //同一链表中绝对超时时间最小的事件
struct event_base *base;
};
struct event {
...
union {
TAILQ_ENTRY(event) ev_next_with_common_timeout; //超时链表的节点
int min_heap_idx;
} ev_timeout_pos;
...
union {
struct {
TAILQ_ENTRY(event) ev_io_next; //io事件队列的节点
struct timeval ev_timeout; //相对超时时间
} ev_io;
...
} _ev;
...
struct timeval ev_timeout; //绝对超时时间
};
struct event_base {
...
struct common_timeout_list **common_timeout_queues; //存放超时链表的数组
int n_common_timeouts; //使用的数组大小
int n_common_timeouts_allocated; //总共分配的数组大小
struct timeval event_tv; //存放上次的时间,用于检测当前系统的时间是否回拨,当前时间如果小于这个时间则表示系统时间回拨了
struct min_heap timeheap; //最小堆
struct timeval tv_cache; //存放时间的缓存,用于在很短时间中大量获取当前系统时间减少系统调用
};
小根堆和链表common_timeout图示
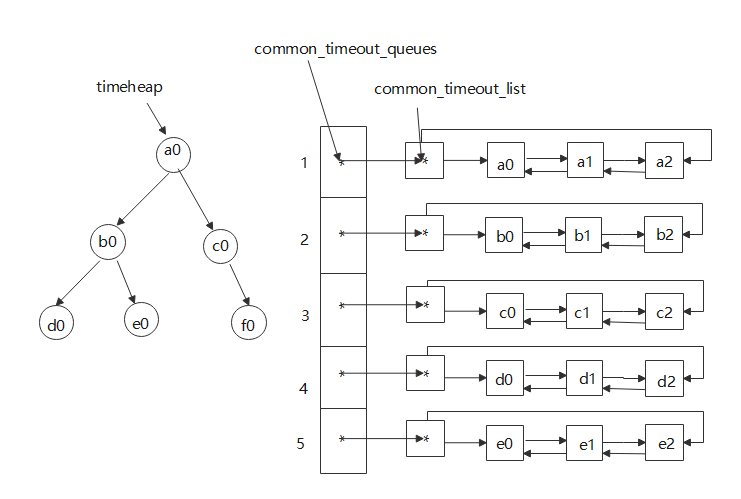
timeheap:按照绝对超时时间组织起来的小根堆,堆顶为最早过期的定时事件;common_timeout_queues将具有相同相对超时时间的超时事件组织成同一链表,如a0 a1 a2具有相同的相对超时时间,同时链表按照绝对超时时间进行排序,a0 a1 a2中的绝对超时时间依次增大或者相同,所以链表中从左到右依次过期,将链表中最早过期的超时事件放入小根堆中。
三、源码分析
小根堆管理定时器事件
主要解分析使用小根堆管理定时器事件的详细流程,占时忽略common_timeout这种情况。
event_new
初始化一个超时事件
int
event_assign(struct event *ev, struct event_base *base, evutil_socket_t fd, short events, void (*callback)(evutil_socket_t, short, void *), void *arg)
{
if (!base)
base = current_base;
ev->ev_flags = EVLIST_INIT;
...
if (events & EV_SIGNAL) {
...
ev->ev_closure = EV_CLOSURE_SIGNAL;
} else {
if (events & EV_PERSIST) {
evutil_timerclear(&ev->ev_io_timeout);
ev->ev_closure = EV_CLOSURE_PERSIST;
} else {
ev->ev_closure = EV_CLOSURE_NONE; //事件结束关闭的标志
}
}
min_heap_elem_init(ev); //初始化最小堆
...
return 0;
}
event_add
将该超时事件加入到注册事件队列、(io事件队列)、最小堆中
static inline int
event_add_internal(struct event *ev, const struct timeval *tv,
int tv_is_absolute)
{
struct event_base *base = ev->ev_base;
if (tv != NULL && !(ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_TIMEOUT)) {
if (min_heap_reserve(&base->timeheap,
1 + min_heap_size(&base->timeheap)) == -1) //给最小堆分配一个存放定时事件的空间
return (-1); /* ENOMEM == errno */
}
...
if ((ev->ev_events & (EV_READ|EV_WRITE|EV_SIGNAL)) &&
!(ev->ev_flags & (EVLIST_INSERTED|EVLIST_ACTIVE))) {
if (ev->ev_events & (EV_READ|EV_WRITE))
res = evmap_io_add(base, ev->ev_fd, ev); //EV_READ|EV_TIMEOUT 这种参数会将定时器事件插入io事件队列中
else if (ev->ev_events & EV_SIGNAL)
res = evmap_signal_add(base, (int)ev->ev_fd, ev);
if (res != -1)
event_queue_insert(base, ev, EVLIST_INSERTED); //定时器事件插入注册事件队列中
...
}
if (res != -1 && tv != NULL) { //设置了超时时间
struct timeval now;
int common_timeout;
if (ev->ev_closure == EV_CLOSURE_PERSIST && !tv_is_absolute)
ev->ev_io_timeout = *tv; //设置io事件的相对超时时间
if (ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_TIMEOUT) { //该超时时间已经被添加过一次
/* XXX I believe this is needless. */
if (min_heap_elt_is_top(ev))
notify = 1;
event_queue_remove(base, ev, EVLIST_TIMEOUT); //从定时器容器中移除定时事件
}
if ((ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_ACTIVE) &&
(ev->ev_res & EV_TIMEOUT)) {
... //如果该事件是激活事件并且是超时事件,则从激活事件队列中删除该事件
event_queue_remove(base, ev, EVLIST_ACTIVE);
}
gettime(base, &now); //获取当前时间
common_timeout = is_common_timeout(tv, base); //时间带有common_timeout标记
if (tv_is_absolute) {
ev->ev_timeout = *tv; //绝对超时时间直接赋值
} else if (common_timeout) {
...
} else { //传入的时间是相对超时时间
evutil_timeradd(&now, tv, &ev->ev_timeout); //利用相对超时时间更新当前的绝对超时时间
}
event_queue_insert(base, ev, EVLIST_TIMEOUT); //将定时器事件加入到小根堆中,ev_flags设置成EV_TIMEOUT
if (common_timeout) {
...
} else {
if (min_heap_elt_is_top(ev))
notify = 1;
}
}
...
return (res);
}
//事件加入到注册事件队列和最小堆中
static void
event_queue_insert(struct event_base *base, struct event *ev, int queue)
{
...
switch (queue) {
case EVLIST_INSERTED: //定时器事件加入到注册事件队列当中
TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&base->eventqueue, ev, ev_next);
break;
case EVLIST_ACTIVE:
base->event_count_active++;
TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&base->activequeues[ev->ev_pri],
ev,ev_active_next);
break;
case EVLIST_TIMEOUT: {
if (is_common_timeout(&ev->ev_timeout, base)) {
...
} else
min_heap_push(&base->timeheap, ev); //定时器事件加入最小堆中
break;
}
default:
event_errx(1, "%s: unknown queue %x", __func__, queue);
}
}
event_dispatch
从最小堆中获取超时时间最短的绝对超时事件,得到相对超时时间加入epoll_wait中,epoll_wait返回超时的事件加入激活事件队列当中,然后挨着处理激活队列中的激活事件。如果超时事件有persist标记则需要重新更新时间然后加入到最小堆,注册事件队列、(io事件队列)中,等待下一次的超时触发;如果没有则从最小堆、注册事件队列、(Io事件队列)中删除该事件,该事件只触发一次。
int
event_base_loop(struct event_base *base, int flags)
{
const struct eventop *evsel = base->evsel;
struct timeval tv;
struct timeval *tv_p;
int res, done, retval = 0;
...
clear_time_cache(base); //清空缓存的时间,让timeout_correct调用gettimeofday系统调用获取到当前时间
...
base->event_gotterm = base->event_break = 0;
while (!done) {
...
timeout_correct(base, &tv); //通过获取到的当前时间和上次保存的时间判断时间是否回拨,没有回拨则直接保存当前时间用于下次比较,回拨了则要更新最小堆和通用定时器中所有事件的超时时间
tv_p = &tv;
if (!N_ACTIVE_CALLBACKS(base) && !(flags & EVLOOP_NONBLOCK)) {
timeout_next(base, &tv_p);//激活队列中没有激活事件,则从小根堆中获得绝对超时时间最短的超时事件,计算出相对超时时间,epoll_wait等待这个相对超时时间后返回,这个超时事件就会放入激活事件队列中
} else {
evutil_timerclear(&tv); //如果激活队列中有事件则tv设置成0,让epoll_wait立即返回,马上处理还没有处理完的事件
}
/* If we have no events, we just exit */
if (!event_haveevents(base) && !N_ACTIVE_CALLBACKS(base)) { //注册事件队列和激活事件队列都没有事件则直接退出
event_debug(("%s: no events registered.", __func__));
retval = 1;
goto done;
}
/* update last old time */
gettime(base, &base->event_tv); //获取当前时间更新event_tv(用于判断系统时间是否回拨)
clear_time_cache(base); //清空时间缓存
res = evsel->dispatch(base, tv_p); //调用epoll_wait等待最短的相对超时时间,返回后一定有至少一个超时时间超时了
if (res == -1) {
event_debug(("%s: dispatch returned unsuccessfully.",
__func__));
retval = -1;
goto done;
}
update_time_cache(base); //获取当前时间作为缓存时间
timeout_process(base); //超时事件加入激活事件队列中,同时从注册事件队列、最小堆、(io事件队列)中删除该事件
if (N_ACTIVE_CALLBACKS(base)) {
int n = event_process_active(base); //处理激活事件的回调函数,如果是一次性定时器事件则直接调用回调函数,如果是重复的定时器事件则还需要更新定时器事件的时间,然后加入注册事件队列,最小堆,(io事件队列)中
if ((flags & EVLOOP_ONCE)
&& N_ACTIVE_CALLBACKS(base) == 0
&& n != 0)
done = 1;
} else if (flags & EVLOOP_NONBLOCK)
done = 1;
}
done:
clear_time_cache(base);
base->running_loop = 0;
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
return (retval);
}
//调用epoll_wait等待最短的超时时间
static int
epoll_dispatch(struct event_base *base, struct timeval *tv)
{
struct epollop *epollop = base->evbase;
struct epoll_event *events = epollop->events;
int i, res;
long timeout = -1;
if (tv != NULL) {
timeout = evutil_tv_to_msec(tv); //转换成时间戳
if (timeout < 0 || timeout > MAX_EPOLL_TIMEOUT_MSEC) { //时间戳大于临界值
/* Linux kernels can wait forever if the timeout is
* too big; see comment on MAX_EPOLL_TIMEOUT_MSEC. */
timeout = MAX_EPOLL_TIMEOUT_MSEC;
}
}
...
res = epoll_wait(epollop->epfd, events, epollop->nevents, timeout);//如果有超时事件则等待timeout返回,如果没有timeout=-1则一直等到fd有事件才会返回
if (res == -1) {
if (errno != EINTR) {
event_warn("epoll_wait");
return (-1);
}
return (0);
}
...
return (0);
}
//将超时事件加入到激活事件队列中
static void
timeout_process(struct event_base *base)
{
/* Caller must hold lock. */
struct timeval now;
struct event *ev;
if (min_heap_empty(&base->timeheap)) { //没有超时事件直接返回
return;
}
gettime(base, &now); //直接从缓存中获取当前时间减少系统调用
while ((ev = min_heap_top(&base->timeheap))) {
if (evutil_timercmp(&ev->ev_timeout, &now, >))//最小堆中的最小绝对超时时间都大于当前时间则没有超时事件需要处理,直接返回
break;
/* delete this event from the I/O queues */
event_del_internal(ev); //从最小堆、注册事件队列、(激活事件队列)、(io事件队列)中删除超时事件
event_active_nolock(ev, EV_TIMEOUT, 1); //定时事件加入到激活事件队列中
}
}
//处理超时事件
static int
event_process_active(struct event_base *base)
{
/* Caller must hold th_base_lock */
struct event_list *activeq = NULL;
int i, c = 0;
for (i = 0; i < base->nactivequeues; ++i) {
if (TAILQ_FIRST(&base->activequeues[i]) != NULL) { //从index=0开始遍历激活事件队列
base->event_running_priority = i;
activeq = &base->activequeues[i]; //获得某个index对应的链表
c = event_process_active_single_queue(base, activeq); //挨着处理链表中所有激活事件的回调函数
if (c < 0) {
base->event_running_priority = -1;
return -1;
} else if (c > 0)
break;
}
}
event_process_deferred_callbacks(&base->defer_queue,&base->event_break);
base->event_running_priority = -1;
return c;
}
static int
event_process_active_single_queue(struct event_base *base,
struct event_list *activeq)
{
struct event *ev;
int count = 0;
EVUTIL_ASSERT(activeq != NULL);
for (ev = TAILQ_FIRST(activeq); ev; ev = TAILQ_FIRST(activeq)) {
if (ev->ev_events & EV_PERSIST)
event_queue_remove(base, ev, EVLIST_ACTIVE); //有persist标记只移除激活事件队列中的事件
else
event_del_internal(ev); //否则要移除激活事件队列,注册事件队列,(io事件队列)中对应的事件
if (!(ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_INTERNAL))
++count;
...
switch (ev->ev_closure) {
case EV_CLOSURE_SIGNAL:
event_signal_closure(base, ev);
break;
case EV_CLOSURE_PERSIST: //重复定时器事件
event_persist_closure(base, ev);//执行定时事件回调函数,同时将定时事件更新时间后重新加入注册事件队列、最小堆、(io事件队列)中
break;
default:
case EV_CLOSURE_NONE: //一次性定时器事件
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
(*ev->ev_callback)(
ev->ev_fd, ev->ev_res, ev->ev_arg);//执行定时事件的回调函数
break;
}
...
}
return count;
}
static inline void
event_persist_closure(struct event_base *base, struct event *ev)
{
if (ev->ev_io_timeout.tv_sec || ev->ev_io_timeout.tv_usec) {
struct timeval run_at, relative_to, delay, now;
ev_uint32_t usec_mask = 0;
EVUTIL_ASSERT(is_same_common_timeout(&ev->ev_timeout,
&ev->ev_io_timeout));
gettime(base, &now);
if (is_common_timeout(&ev->ev_timeout, base)) {
...
} else {
delay = ev->ev_io_timeout; //相对超时时间
if (ev->ev_res & EV_TIMEOUT) {
relative_to = ev->ev_timeout; //获得绝对超时时间
} else {
relative_to = now;
}
}
evutil_timeradd(&relative_to, &delay, &run_at); //该事件过期的绝对超时时间
if (evutil_timercmp(&run_at, &now, <)) { //该事件的绝对超时时间<当前时间,证明该事件是超时触发的,则重新更新超时时间;如果不是超时触发的则沿用上之前的绝对超时时间
evutil_timeradd(&now, &delay, &run_at); //获取下一次的绝对超时时间
}
run_at.tv_usec |= usec_mask;
event_add_internal(ev, &run_at, 1); //重新将事件加入注册事件队列、最小堆、(io事件队列)中
}
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
(*ev->ev_callback)(ev->ev_fd, ev->ev_res, ev->ev_arg);//调用回调函数
}
链表common_timeout管理定时器事件
event_base_init_common_timeout
event_base_init_common_timeout将事件增加common_timeout标记,调用event add时就会将超时时间加入最小堆的同时加入到链表当中。
原理:
对一个struct timeval结构体,成员tv_usec的单位是微秒,所以最大也就是999999,只需低20比特位就能存储了。但成员tv_usec的类型是int或者long,肯定有32比特位。所以,就有高12比特位是空闲的。
Libevent就是利用那空闲的12个比特位做文章的。这12比特位是高比特位。Libevent使用最高的4比特位作为标志位,标志它是一个专门用于common-timeout的时间,下文将这个标志称为common-timeout标志。次8比特位用来记录该超时时长在common_timeout_queues数组中的位置,即下标值。这也限制common_timeout_queues数组的长度,最大为2的8次方,即256。
//将时间增加timeout标记和索引,并根据该时间初始化一个common_timeout_list链表,同时初始化一个内部超时时间timeout_event
const struct timeval *
event_base_init_common_timeout(struct event_base *base,
const struct timeval *duration)
{
int i;
struct timeval tv;
const struct timeval *result=NULL;
struct common_timeout_list *new_ctl;
EVBASE_ACQUIRE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
if (duration->tv_usec > 1000000) { //tv_usec进位到tv_sec
memcpy(&tv, duration, sizeof(struct timeval));
if (is_common_timeout(duration, base))
tv.tv_usec &= MICROSECONDS_MASK;
tv.tv_sec += tv.tv_usec / 1000000;
tv.tv_usec %= 1000000;
duration = &tv;
}
for (i = 0; i < base->n_common_timeouts; ++i) { //判断是否为这个相对超时时间分配过存放链表的空间
const struct common_timeout_list *ctl =
base->common_timeout_queues[i];
if (duration->tv_sec == ctl->duration.tv_sec &&
duration->tv_usec ==
(ctl->duration.tv_usec & MICROSECONDS_MASK)) { //&操作去掉common_timeout标记,比较分配空间的相对超时时间和传入的相对超时时间是否一致
EVUTIL_ASSERT(is_common_timeout(&ctl->duration, base));
result = &ctl->duration; //一致则直接返回分配过的带有common_timeout标记的相对超时时间
goto done;
}
}
...
if (base->n_common_timeouts_allocated == base->n_common_timeouts) { //数组分配的空间和使用空间相等了
int n = base->n_common_timeouts < 16 ? 16 : //重新分配2倍的空间
base->n_common_timeouts*2;
struct common_timeout_list **newqueues =
mm_realloc(base->common_timeout_queues,
n*sizeof(struct common_timeout_queue *));
if (!newqueues) {
event_warn("%s: realloc",__func__);
goto done;
}
base->n_common_timeouts_allocated = n;
base->common_timeout_queues = newqueues;
}
new_ctl = mm_calloc(1, sizeof(struct common_timeout_list)); //分配存放链表节点的空间
if (!new_ctl) {
event_warn("%s: calloc",__func__);
goto done;
}
TAILQ_INIT(&new_ctl->events);
new_ctl->duration.tv_sec = duration->tv_sec;
new_ctl->duration.tv_usec =
duration->tv_usec | COMMON_TIMEOUT_MAGIC |
(base->n_common_timeouts << COMMON_TIMEOUT_IDX_SHIFT); //给链表节点的时间增加timeout标记和索引位置的标记
evtimer_assign(&new_ctl->timeout_event, base,
common_timeout_callback, new_ctl); //初始化链表中绝对超时时间最小的事件,设置回调common_timeout_callback
new_ctl->timeout_event.ev_flags |= EVLIST_INTERNAL; //内部事件
event_priority_set(&new_ctl->timeout_event, 0); //最高优先级
new_ctl->base = base;
base->common_timeout_queues[base->n_common_timeouts++] = new_ctl; //链表节点加入数组中
result = &new_ctl->duration; //返回带有标记的时间
done:
return result;
}
//这时内部超时时间timeout_event触发的,遍历对应的common_timeout_list中的事件,加入激活事件队列中,更新时间重新将timeout_event事件加入最小堆中
static void
common_timeout_callback(evutil_socket_t fd, short what, void *arg)
{
struct timeval now;
struct common_timeout_list *ctl = arg;
struct event_base *base = ctl->base;
struct event *ev = NULL;
EVBASE_ACQUIRE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
gettime(base, &now);
while (1) {
//挨着遍历timeout_event对应的链表
ev = TAILQ_FIRST(&ctl->events);
if (!ev || ev->ev_timeout.tv_sec > now.tv_sec ||
(ev->ev_timeout.tv_sec == now.tv_sec &&
(ev->ev_timeout.tv_usec&MICROSECONDS_MASK) > now.tv_usec))
break; //链表中的事件没有超时则直接退出,因为链表按绝对超时时间升序排列
event_del_internal(ev); //从common_timeout_list中删除对应的事件,如果设置成persist标记,后面更新了事件就会重新添加该事件
event_active_nolock(ev, EV_TIMEOUT, 1); //将common_timeout_list中的事件加入到激活事件队列中
}
if (ev)
common_timeout_schedule(ctl, &now, ev); //如果链表中还有事件没发生,则重新将该链表的timeout_event事件加入到最小堆中,事件为当前链表头结点的绝对时间
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
}
event_add
将超时事件加入到对应的common_timeout_list中,同时将timeout_event事件加入到最小堆中
static inline int
event_add_internal(struct event *ev, const struct timeval *tv,
int tv_is_absolute)
{
struct event_base *base = ev->ev_base;
if (tv != NULL && !(ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_TIMEOUT)) {
if (min_heap_reserve(&base->timeheap,
1 + min_heap_size(&base->timeheap)) == -1) //给最小堆分配一个存放定时事件的空间
return (-1); /* ENOMEM == errno */
}
...
common_timeout = is_common_timeout(tv, base); //时间带有common_timeout标记
if (tv_is_absolute) {
ev->ev_timeout = *tv; //绝对超时时间直接赋值
} else if (common_timeout) {
struct timeval tmp = *tv;
tmp.tv_usec &= MICROSECONDS_MASK; //去除标记取真正的时间
evutil_timeradd(&now, &tmp, &ev->ev_timeout); //算得绝对超时时间
ev->ev_timeout.tv_usec |=
(tv->tv_usec & ~MICROSECONDS_MASK); //绝对超时时间增加标记
} else {
evutil_timeradd(&now, tv, &ev->ev_timeout); //利用相对超时时间更新当前的绝对超时时间
}
event_queue_insert(base, ev, EVLIST_TIMEOUT); //将定时器事件加入到common_timeout容器中
if (common_timeout) {
struct common_timeout_list *ctl =
get_common_timeout_list(base, &ev->ev_timeout); //获取当前时间的common_timeout_list
if (ev == TAILQ_FIRST(&ctl->events)) { //从链表中取出头节点,绝对超时时间最小的事件
common_timeout_schedule(ctl, &now, ev); //设置timeout_event的超时时间加入到最小堆中
}
} else {
if (min_heap_elt_is_top(ev))
notify = 1;
}
}
...
return (res);
}
static void
event_queue_insert(struct event_base *base, struct event *ev, int queue)
{
...
switch (queue) {
...
case EVLIST_TIMEOUT: {
if (is_common_timeout(&ev->ev_timeout, base)) { //如果超时时间有common_timeout标记
struct common_timeout_list *ctl =
get_common_timeout_list(base, &ev->ev_timeout); //根据时间获取对应的common_timeout_list
insert_common_timeout_inorder(ctl, ev); //定时器事件插入链表common_timeout_list中
} else
min_heap_push(&base->timeheap, ev); //定时器事件加入最小堆中
break;
}
default:
event_errx(1, "%s: unknown queue %x", __func__, queue);
}
}
static void
insert_common_timeout_inorder(struct common_timeout_list *ctl,
struct event *ev)
{
struct event *e;
//遍历链表,按照绝对超时时间从小到大插入链表中,一般情况下直接插入到链表的尾部,但是在多线程中可能出现先调用evutil_timeradd的还没来的及插入,后面的先插入了,所以需要遍历。
TAILQ_FOREACH_REVERSE(e, &ctl->events,
event_list, ev_timeout_pos.ev_next_with_common_timeout) {
EVUTIL_ASSERT(
is_same_common_timeout(&e->ev_timeout, &ev->ev_timeout));
if (evutil_timercmp(&ev->ev_timeout, &e->ev_timeout, >=)) {
TAILQ_INSERT_AFTER(&ctl->events, e, ev,
ev_timeout_pos.ev_next_with_common_timeout);//从队列后面插入
return; //插入了直接返回
}
}
//新插入的绝对超时时间最小则从头部插入
TAILQ_INSERT_HEAD(&ctl->events, ev,
ev_timeout_pos.ev_next_with_common_timeout);
}
static void
common_timeout_schedule(struct common_timeout_list *ctl,
const struct timeval *now, struct event *head)
{
struct timeval timeout = head->ev_timeout;
timeout.tv_usec &= MICROSECONDS_MASK; //清除common-timeout标志
//用common_timeout_list结构体的一个event成员作为超时event调用event_add_internal
//由于已经清除了common-timeout标志,所以这次将最小超时事件timeout_event插入到小根堆中。
event_add_internal(&ctl->timeout_event, &timeout, 1);
}
event_dispatch
第一个循环是内部事件timeout_event事件触发,调用timeout_event_callback回调函数,该回调函数遍历common_timeout_list将触发的事件加入到激活事件队列中,第二个循环,激活队列中有事件则马上处理common_timeout_list中的事件,也就是外部注册的事件。
int
event_base_loop(struct event_base *base, int flags)
{
const struct eventop *evsel = base->evsel;
struct timeval tv;
struct timeval *tv_p;
int res, done, retval = 0;
while (!done) {
...
tv_p = &tv;
if (!N_ACTIVE_CALLBACKS(base) && !(flags & EVLOOP_NONBLOCK)) {
timeout_next(base, &tv_p); //最小堆中的timeout_event中取出最短的相对超时时间
} else {
evutil_timerclear(&tv); //执行完内部超时时间timeout_event中的回调函数,会将common_timeout_list中的事件加入激活队列中,所以激活队列中还有事件则tv设置成0,让epoll_wait马上返回执行激活事件队列中的事件
}
res = evsel->dispatch(base, tv_p); //调用epoll_wait等待最短的相对超时时间,有一个timeout_event事件返回
if (res == -1) {
event_debug(("%s: dispatch returned unsuccessfully.",
__func__));
retval = -1;
goto done;
}
timeout_process(base); //第一次timeout_event事件加入激活事件队列中,并从最小堆中删除该事件,第二次由于最小堆的timeout_event事件没有超时这个函数直接返回
if (N_ACTIVE_CALLBACKS(base)) {
int n = event_process_active(base); //第一次调用timeout_event事件的回调函数,第二次调用用户注册的超时时间的回调函数
if ((flags & EVLOOP_ONCE)
&& N_ACTIVE_CALLBACKS(base) == 0
&& n != 0)
done = 1;
} else if (flags & EVLOOP_NONBLOCK)
done = 1;
}
done:
clear_time_cache(base);
base->running_loop = 0;
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
return (retval);
}
timeout_process(struct event_base *base)
{
...
while ((ev = min_heap_top(&base->timeheap))) {
if (evutil_timercmp(&ev->ev_timeout, &now, >))
break;
event_del_internal(ev); //timeout_event事件触发从最小堆中删除,然后common_timeou_list中的事件触发则从common_timeout_list链表中移除事件
event_debug(("timeout_process: call %p",
ev->ev_callback));
event_active_nolock(ev, EV_TIMEOUT, 1); //第一次将timeout_event事件加入激活事件队列中,然后timeout_event_callbak触发后将common_timeout_list中的事件加入到激活事件队列中,这里才是用户注册的超时时间
}
}
static void
event_queue_remove(struct event_base *base, struct event *ev, int queue)
{
...
ev->ev_flags &= ~queue;
switch (queue) {
...
case EVLIST_TIMEOUT:
if (is_common_timeout(&ev->ev_timeout, base)) { //common_timeout_list中链表中的事件
struct common_timeout_list *ctl =
get_common_timeout_list(base, &ev->ev_timeout);
TAILQ_REMOVE(&ctl->events, ev,
ev_timeout_pos.ev_next_with_common_timeout); //移除激活的common_timeout事件,也就是链表的首部
} else {
min_heap_erase(&base->timeheap, ev); //首先时内部的timout_event事件,从最小堆中删除
}
break;
default:
event_errx(1, "%s: unknown queue %x", __func__, queue);
}
}
//common_timeout超时时间中设置了persist标记
static inline void
event_persist_closure(struct event_base *base, struct event *ev)
{
if (ev->ev_io_timeout.tv_sec || ev->ev_io_timeout.tv_usec) {
struct timeval run_at, relative_to, delay, now;
ev_uint32_t usec_mask = 0;
EVUTIL_ASSERT(is_same_common_timeout(&ev->ev_timeout,
&ev->ev_io_timeout));
gettime(base, &now);
if (is_common_timeout(&ev->ev_timeout, base)) { //调用common_timeout_callback时触发的事件
delay = ev->ev_io_timeout; //获得相对超时时间
usec_mask = delay.tv_usec & ~MICROSECONDS_MASK; //取消common_timeout标记
delay.tv_usec &= MICROSECONDS_MASK; //增加common_timeout标记
if (ev->ev_res & EV_TIMEOUT) {
relative_to = ev->ev_timeout; //获得绝对超时时间
relative_to.tv_usec &= MICROSECONDS_MASK; //增加common_timeout标记
} else {
relative_to = now;
}
} else { //timeout_event事件被触发
delay = ev->ev_io_timeout;
if (ev->ev_res & EV_TIMEOUT) {
relative_to = ev->ev_timeout;
} else {
relative_to = now;
}
}
evutil_timeradd(&relative_to, &delay, &run_at);
if (evutil_timercmp(&run_at, &now, <)) {
evutil_timeradd(&now, &delay, &run_at); //获得下一次的绝对超时时间
}
run_at.tv_usec |= usec_mask;
event_add_internal(ev, &run_at, 1); //common_timeout_list中的事件触发,重新将事件加入common_timeout_list中
}
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
(*ev->ev_callback)(ev->ev_fd, ev->ev_res, ev->ev_arg); //common_timeout_list中的事件调用用户注册的回调函数
}
总结
在大多数应用中定时事件规模不大,我们一般是使用小根堆进行定时器事件的管理;libevent通过最小堆加上链表的方式提供了一种管理大规模定时器的高效方法。