前言:本篇文章主要从代码实现角度研究 Bert Encoder和Transformer Encoder 有什么不同?应该可以帮助你:
- 深入了解Bert Encoder 的结构实现
- 深入了解Transformer Encoder的结构实现
本篇文章不涉及对注意力机制实现的代码研究。
注:本篇文章所得出的结论和其它文章略有不同,有可能是本人代码理解上存在问题,但是又没有找到更多的文章加以验证,并且代码也检查过多遍。
观点不太一致的文章:bert-pytorch版源码详细解读_bert pytorch源码-CSDN博客 这篇文章中,存在 “这个和我之前看的transformers的残差连接层差别还挺大的,所以并不完全和transformers的encoder部分结构一致。” 但是我的分析是:代码实现上不太一样,但是本质上没啥不同,只是Bert Encoder在Attention之后多了一层Linear。具体分析过程和结论可以阅读如下文章。
如有错误或问题,请在评论区回复。
1、研究目标
这里主要的观察对象是BertModel中Bert Encoder是如何构造的?从Bert Tensorflow源码,以及transformers库中源码去看。
然后再看TransformerEncoder是如何构造的?从pytorch内置的transformer模块去看。
最后再对比不同。
2、tensorflow中BertModel主要代码如下
class BertModel(object):
def __init__(...):
...得到了self.embedding_output以及attention_mask
# transformer_model就代表了Bert Encoder层的所有操作
self.all_encoder_layers = transformer_model(input_tensor=self.embedding_output, attention_mask=attention_mask,...)
# 这里all_encoder_layers[-1]是取最后一层encoder的输出
self.sequence_output = self.all_encoder_layers[-1]
...pooler层,对 sequence_output中的first_token_tensor,即CLS对应的表示向量,进行dense+tanh操作
with tf.variable_scope("pooler"):
first_token_tensor = tf.squeeze(self.sequence_output[:, 0:1, :], axis=1)
self.pooled_output = tf.layers.dense(
first_token_tensor,
config.hidden_size,
activation=tf.tanh,
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(config.initializer_range))
def transformer_model(input_tensor, attention_mask=None,...):
...
for layer_idx in range(num_hidden_layers):
# 如下(1)(2)(3)就是每一层Bert Encoder包含的结构和操作
with tf.variable_scope("layer_%d" % layer_idx):
# (1)attention层:主要包含两个操作,获取attention_output,对attention_output进行dense + dropout + layer_norm
with tf.variable_scope("attention"):
# (1.1)通过attention_layer获得 attention_output
attention_output
# (1.2)output层:attention_output需要经过dense + dropout + layer_norm操作
with tf.variable_scope("output"):
attention_output = tf.layers.dense(attention_output,hidden_size,...)
attention_output = dropout(attention_output, hidden_dropout_prob)
# “attention_output + layer_input” 表示 残差连接操作
attention_output = layer_norm(attention_output + layer_input)
# (2)intermediate中间层:对attention_output进行dense+激活(GELU)
with tf.variable_scope("intermediate"):
intermediate_output = tf.layers.dense(
attention_output,
intermediate_size,
activation=intermediate_act_fn,)
# (3)output层:对intermediater_out进行dense + dropout + layer_norm
with tf.variable_scope("output"):
layer_output = tf.layers.dense(
intermediate_output,
hidden_size,
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
layer_output = dropout(layer_output, hidden_dropout_prob)
# "layer_output + attention_output"是残差连接操作
layer_output = layer_norm(layer_output + attention_output)
all_layer_outputs.append(layer_output)3、pytorch的transformers库中的BertModel主要代码;
- 其中BertEncoder对应要研究的目标
class BertModel(BertPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config, add_pooling_layer=True):
self.embeddings = BertEmbeddings(config)
self.encoder = BertEncoder(config)
self.pooler = BertPooler(config) if add_pooling_layer else None
def forward(...):
# 这是嵌入层操作
embedding_output = self.embeddings(input_ids=input_ids,position_ids=position_ids,token_type_ids=token_type_ids,...)
# 这是BertEncoder层的操作
encoder_outputs = self.encoder(embedding_output,attention_mask=extended_attention_mask,...)
# 这里encoder_outputs是一个对象,encoder_outputs[0]是指最后一层Encoder(BertLayer)输出
sequence_output = encoder_outputs[0]
# self.pooler操作是BertPooler层操作,是先取first_token_tensor(即CLS对应的表示向量),然后进行dense+tanh操作
# 通常pooled_output用于做下游分类任务
pooled_output = self.pooler(sequence_output) if self.pooler is not None else None
class BertEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
...
self.layer = nn.ModuleList([BertLayer(config) for _ in range(config.num_hidden_layers)])
...
def forward(...):
for i, layer_module in enumerate(self.layer):
# 元组的append做法,将每一层的hidden_states保存到all_hidden_states;
# 第一个hidden_states是BertEncoder的输入,后面的都是每一个BertLayer的输出
if output_hidden_states:
all_hidden_states = all_hidden_states + (hidden_states,)
...
# 执行BertLayer的forward方法,包含BertAttention层 + BertIntermediate中间层 + BertOutput层
layer_outputs = layer_module(...)
# 当前BertLayer的输出
hidden_states = layer_outputs[0]
# 添加到all_hidden_states元组中
if output_hidden_states:
all_hidden_states = all_hidden_states + (hidden_states,)
class BertLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
self.attention = BertAttention(config)
self.intermediate = BertIntermediate(config)
self.output = BertOutput(config)
def forward(...):
# (1)Attention是指BertAttention
# BertAttention包含:BertSelfAttention + BertSelfOutput
# BertSelfAttention包括计算Attention+Dropout
# BertSelfOutput包含:dense+dropout+LayerNorm,LayerNorm之前会进行残差连接
self_attention_outputs = self.attention(...)
# self_attention_outputs是一个元组,取[0]获取当前BertLayer中的Attention层的输出
attention_output = self_attention_outputs[0]
# (2)BertIntermediate中间层包含:dense+gelu激活
# (3)BertOutput层包含:dense+dropout+LayerNorm,LayerNorm之前会进行残差连接
# feed_forward_chunk的操作是:BertIntermediate(attention_output) + BertOutput(intermediate_output, attention_output)
# BertIntermediate(attention_output)是:dense+gelu激活
# BertOutput(intermediate_output, attention_output)是:dense+dropout+LayerNorm;
# 其中LayerNorm(intermediate_output + attention_output)中的“intermediate_output + attention_output”是残差连接操作
layer_output = apply_chunking_to_forward(self.feed_forward_chunk, ..., attention_output)
4、pytorch中内置的transformer的TransformerEncoderLayer主要代码
- torch.nn.modules.transformer.TransformerEncoderLayer
class TransformerEncoderLayer(Module):
'''
Args:
d_model: the number of expected features in the input (required).
nhead: the number of heads in the multiheadattention models (required).
dim_feedforward: the dimension of the feedforward network model (default=2048).
dropout: the dropout value (default=0.1).
activation: the activation function of intermediate layer, relu or gelu (default=relu).
Examples::
>>> encoder_layer = nn.TransformerEncoderLayer(d_model=512, nhead=8)
>>> src = torch.rand(10, 32, 512)
>>> out = encoder_layer(src)
'''
def __init__(self, d_model, nhead, dim_feedforward=2048, dropout=0.1, activation="relu"):
super(TransformerEncoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.self_attn = MultiheadAttention(d_model, nhead, dropout=dropout)
# Implementation of Feedforward model
self.linear1 = Linear(d_model, dim_feedforward)
self.dropout = Dropout(dropout)
self.linear2 = Linear(dim_feedforward, d_model)
self.norm1 = LayerNorm(d_model)
self.norm2 = LayerNorm(d_model)
self.dropout1 = Dropout(dropout)
self.dropout2 = Dropout(dropout)
self.activation = _get_activation_fn(activation)
def forward(...):
# 过程:
# (1)MultiheadAttention操作:src2 = self.self_attn
# (2)Dropout操作:self.dropout1(src2)
# (3)残差连接:src = src + self.dropout1(src2)
# (4)LayerNorm操作:src = self.norm1(src)
# 如下是FeedForword:做两次线性变换,为了更深入的提取特征
# (5)Linear操作:src = self.linear1(src)
# (6)RELU激活(默认RELU)操作:self.activation(self.linear1(src))
# (7)Dropout操作:self.dropout(self.activation(self.linear1(src)))
# (8)Linear操作:src2 = self.linear2(...)
# (9)Dropout操作:self.dropout2(src2)
# (10)残差连接:src = src + self.dropout2(src2)
# (11)LayerNorm操作:src = self.norm2(src)
src2 = self.self_attn(src, src, src, attn_mask=src_mask,
key_padding_mask=src_key_padding_mask)[0]
src = src + self.dropout1(src2)
src = self.norm1(src)
src2 = self.linear2(self.dropout(self.activation(self.linear1(src))))
src = src + self.dropout2(src2)
src = self.norm2(src)
return src
5、区别总结
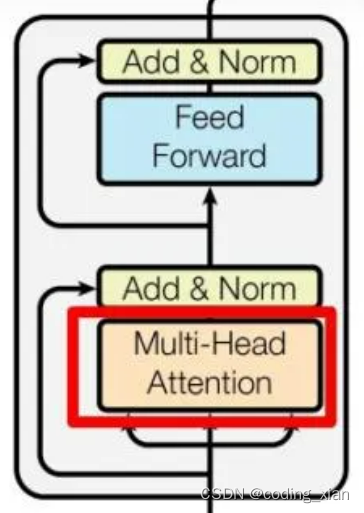
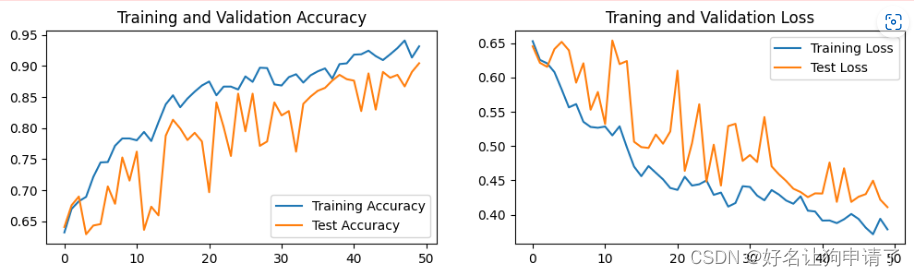
Transformer Encoder的结构如上图所示,代码也基本和上图描述的一致,不过代码中在Multi-Head Attention和Feed Forward之后都存在一个Dropout操作。(可以认为每层网络之后都会接一个Dropout层,是作为网络模块的一部分)
可以将Transformer Encoder过程表述为:
(1)MultiheadAttention + Dropout + 残差连接 + LayerNorm
(2)FeedForword(Linear + RELU + Dropout + Linear + Dropout) + 残差连接 + LayerNorm;Transformer默认的隐含层激活函数是RELU;
可以将 Bert Encoder过程表述为:
(1)BertSelfAttention: MultiheadAttention + Dropout
(2)BertSelfOutput:Linear+ Dropout + 残差连接 + LayerNorm; 注意:这里的残差连接是作用在BertSelfAttention的输入上,不是Linear的输入。
(3)BertIntermediate:Linear + GELU激活
(4)BertOutput:Linear + Dropout + 残差连接 + LayerNorm;注意:这里的残差连接是作用在BertIntermediate的输入上,不是Linear的输入;
进一步,把(1)(2)合并,(3)(4)合并:
(1)MultiheadAttention + Dropout + Linear + Dropout + 残差连接 + LayerNorm
(2)FeedForword(Linear + GELU激活 + Linear + Dropout) + 残差连接 + LayerNorm;Bert默认的隐含层激活函数是GELU;
所以,Bert Encoder和Transformer Encoder最大的区别是,Bert Encoder在做完Attention计算后,还会用一个线性层去提取特征,然后才进行残差连接。其次,是FeedForword中的默认激活函数不同。Bert Encoder图结构如下:
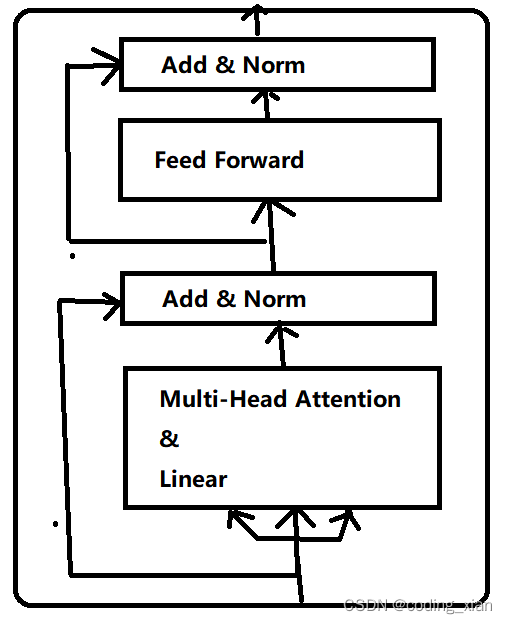
Bert 为什么要这么做?或许是多一个线性层,特征提取能力更强,模型表征能力更好。
GELU和RELU:GELU是RELU的改进版,效果更好。
Reference
- GeLU、ReLU函数学习_gelu和relu-CSDN博客