文章目录
- GAN的损失函数介绍
- 1.L1 losses
- 2.mse loss
- 3.smooth L1
- 4.charbonnier_loss
- 5.perceptual loss (content and style losses)
- 6.Gan损失
- 7.WeightedTVLoss
- 8.完整代码方便使用,含训练epoch代码。
GAN的损失函数介绍
1.L1 losses
pixel_opt:
type: L1Loss
loss_weight: 1.0
reduction: mean
相比于一般的l1 loss多了 loss weight, reduction, weight三个功能。
首先loss_util.py文件定义weight_loss
import functools
from torch.nn import functional as F
def reduce_loss(loss, reduction):
"""Reduce loss as specified.
Args:
loss (Tensor): Elementwise loss tensor.
reduction (str): Options are 'none', 'mean' and 'sum'.
Returns:
Tensor: Reduced loss tensor.
"""
reduction_enum = F._Reduction.get_enum(reduction)
# none: 0, elementwise_mean:1, sum: 2
if reduction_enum == 0:
return loss
elif reduction_enum == 1:
return loss.mean()
else:
return loss.sum()
def weight_reduce_loss(loss, weight=None, reduction='mean'):
"""Apply element-wise weight and reduce loss.
Args:
loss (Tensor): Element-wise loss.
weight (Tensor): Element-wise weights. Default: None.
reduction (str): Same as built-in losses of PyTorch. Options are
'none', 'mean' and 'sum'. Default: 'mean'.
Returns:
Tensor: Loss values.
"""
# if weight is specified, apply element-wise weight
if weight is not None:
assert weight.dim() == loss.dim()
assert weight.size(1) == 1 or weight.size(1) == loss.size(1)
loss = loss * weight
# if weight is not specified or reduction is sum, just reduce the loss
if weight is None or reduction == 'sum':
loss = reduce_loss(loss, reduction)
# if reduction is mean, then compute mean over weight region
elif reduction == 'mean':
if weight.size(1) > 1:
weight = weight.sum()
else:
weight = weight.sum() * loss.size(1)
loss = loss.sum() / weight
return loss
def weighted_loss(loss_func):
"""Create a weighted version of a given loss function.
To use this decorator, the loss function must have the signature like
`loss_func(pred, target, **kwargs)`. The function only needs to compute
element-wise loss without any reduction. This decorator will add weight
and reduction arguments to the function. The decorated function will have
the signature like `loss_func(pred, target, weight=None, reduction='mean',
**kwargs)`.
:Example:
>>> import torch
>>> @weighted_loss
>>> def l1_loss(pred, target):
>>> return (pred - target).abs()
>>> pred = torch.Tensor([0, 2, 3])
>>> target = torch.Tensor([1, 1, 1])
>>> weight = torch.Tensor([1, 0, 1])
>>> l1_loss(pred, target)
tensor(1.3333)
>>> l1_loss(pred, target, weight)
tensor(1.5000)
>>> l1_loss(pred, target, reduction='none')
tensor([1., 1., 2.])
>>> l1_loss(pred, target, weight, reduction='sum')
tensor(3.)
"""
@functools.wraps(loss_func)
def wrapper(pred, target, weight=None, reduction='mean', **kwargs):
# get element-wise loss
loss = loss_func(pred, target, **kwargs) # 这里 reduction='none'
loss = weight_reduce_loss(loss, weight, reduction)
return loss
return wrapper
接下来定义带weight的L1 loss
有什么用呢?主要是weight, weight和loss的shape是一致的,
比如 L1 loss : 图像a-图像b 的绝对值: N,c,h,w
那么weight的形状也是 N,c,h,w或者可以 广播到N,c,h,w
比如 N,1,h,w 和 N,c,1,1
import math
import torch
from torch import autograd as autograd
from torch import nn as nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
import numpy as np
@weighted_loss
def l1_loss(pred, target):
return F.l1_loss(pred, target, reduction='none')
class L1Loss(nn.Module):
"""L1 (mean absolute error, MAE) loss.
Args:
loss_weight (float): Loss weight for L1 loss. Default: 1.0.
reduction (str): Specifies the reduction to apply to the output.
Supported choices are 'none' | 'mean' | 'sum'. Default: 'mean'.
"""
def __init__(self, loss_weight=1.0, reduction='mean'):
super(L1Loss, self).__init__()
if reduction not in ['none', 'mean', 'sum']:
raise ValueError(f'Unsupported reduction mode: {reduction}. ' f'Supported ones are: {_reduction_modes}')
self.loss_weight = loss_weight
self.reduction = reduction
def forward(self, pred, target, weight=None, **kwargs):
"""
Args:
pred (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Predicted tensor.
target (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Ground truth tensor.
weight (Tensor, optional): of shape (N, C, H, W). Element-wise
weights. Default: None.
"""
return self.loss_weight * l1_loss(pred, target, weight, reduction=self.reduction)
2.mse loss
@weighted_loss
def mse_loss(pred, target):
return F.mse_loss(pred, target, reduction='none')
class MSELoss(nn.Module):
"""MSE (L2) loss.
Args:
loss_weight (float): Loss weight for MSE loss. Default: 1.0.
reduction (str): Specifies the reduction to apply to the output.
Supported choices are 'none' | 'mean' | 'sum'. Default: 'mean'.
"""
def __init__(self, loss_weight=1.0, reduction='mean'):
super(MSELoss, self).__init__()
if reduction not in ['none', 'mean', 'sum']:
raise ValueError(f'Unsupported reduction mode: {reduction}. ' f'Supported ones are: {_reduction_modes}')
self.loss_weight = loss_weight
self.reduction = reduction
def forward(self, pred, target, weight=None, **kwargs):
"""
Args:
pred (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Predicted tensor.
target (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Ground truth tensor.
weight (Tensor, optional): of shape (N, C, H, W). Element-wise
weights. Default: None.
"""
return self.loss_weight * mse_loss(pred, target, weight, reduction=self.reduction)
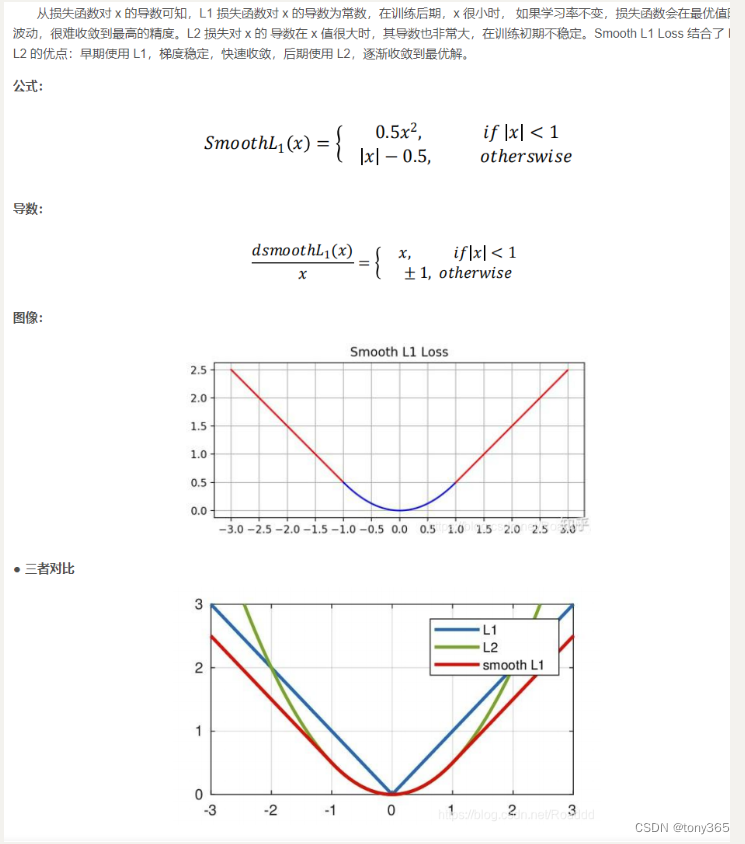
3.smooth L1
L1是 差异绝对值
L2(MSE)是差异的平方
使用L1结果会更容易稀疏(包含0),不太照顾离群点
使用L2结果会更平滑,对离群点压制比较厉害。
https://blog.csdn.net/Roaddd/article/details/114798798 这篇博客介绍的很好
torch.nn.functional.smooth_l1_loss(input, target, size_average=None, educe=None, reduction=‘mean’)
torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction=‘mean’)
@weighted_loss
def smooth_l1_loss(pred, target):
return F.smooth_l1_loss(pred, target, reduction='none')
class SmoothL1Loss(nn.Module):
"""MSE (L2) loss.
Args:
loss_weight (float): Loss weight for MSE loss. Default: 1.0.
reduction (str): Specifies the reduction to apply to the output.
Supported choices are 'none' | 'mean' | 'sum'. Default: 'mean'.
"""
def __init__(self, loss_weight=1.0, reduction='mean'):
super(MSELoss, self).__init__()
if reduction not in ['none', 'mean', 'sum']:
raise ValueError(f'Unsupported reduction mode: {reduction}. ' f'Supported ones are: {_reduction_modes}')
self.loss_weight = loss_weight
self.reduction = reduction
def forward(self, pred, target, weight=None, **kwargs):
"""
Args:
pred (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Predicted tensor.
target (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Ground truth tensor.
weight (Tensor, optional): of shape (N, C, H, W). Element-wise
weights. Default: None.
"""
return self.loss_weight * smooth_l1_loss(pred, target, weight, reduction=self.reduction)
4.charbonnier_loss
先平方,再开方是对L1的改进。
ϵ是一个很小的常数,用于保证在x=0时函数的可微性
@weighted_loss
def charbonnier_loss(pred, target, eps=1e-12):
return torch.sqrt((pred - target)**2 + eps)
class CharbonnierLoss(nn.Module):
"""Charbonnier loss (one variant of Robust L1Loss, a differentiable
variant of L1Loss).
Described in "Deep Laplacian Pyramid Networks for Fast and Accurate
Super-Resolution".
Args:
loss_weight (float): Loss weight for L1 loss. Default: 1.0.
reduction (str): Specifies the reduction to apply to the output.
Supported choices are 'none' | 'mean' | 'sum'. Default: 'mean'.
eps (float): A value used to control the curvature near zero.
Default: 1e-12.
"""
def __init__(self, loss_weight=1.0, reduction='mean', eps=1e-12):
super(CharbonnierLoss, self).__init__()
if reduction not in ['none', 'mean', 'sum']:
raise ValueError(f'Unsupported reduction mode: {reduction}. ' f'Supported ones are: {_reduction_modes}')
self.loss_weight = loss_weight
self.reduction = reduction
self.eps = eps
def forward(self, pred, target, weight=None, **kwargs):
"""
Args:
pred (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Predicted tensor.
target (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Ground truth tensor.
weight (Tensor, optional): of shape (N, C, H, W). Element-wise
weights. Default: None.
"""
return self.loss_weight * charbonnier_loss(pred, target, weight, eps=self.eps, reduction=self.reduction)
5.perceptual loss (content and style losses)
感知损失主要包括内容损失和风格损失。
vgg19下载地址:vgg19-dcbb9e9d.pth
perceptual loss需要用到训练好的vgg模型,这里以vgg19为例
首先修改 vgg model, 我们只提取特定层的feature。
import os
import torch
from collections import OrderedDict
from torch import nn as nn
from torchvision.models import vgg as vgg
from basicsr.utils.registry import ARCH_REGISTRY
VGG_PRETRAIN_PATH = 'experiments/pretrained_models/vgg19-dcbb9e9d.pth'
NAMES = {
'vgg11': [
'conv1_1', 'relu1_1', 'pool1', 'conv2_1', 'relu2_1', 'pool2', 'conv3_1', 'relu3_1', 'conv3_2', 'relu3_2',
'pool3', 'conv4_1', 'relu4_1', 'conv4_2', 'relu4_2', 'pool4', 'conv5_1', 'relu5_1', 'conv5_2', 'relu5_2',
'pool5'
],
'vgg13': [
'conv1_1', 'relu1_1', 'conv1_2', 'relu1_2', 'pool1', 'conv2_1', 'relu2_1', 'conv2_2', 'relu2_2', 'pool2',
'conv3_1', 'relu3_1', 'conv3_2', 'relu3_2', 'pool3', 'conv4_1', 'relu4_1', 'conv4_2', 'relu4_2', 'pool4',
'conv5_1', 'relu5_1', 'conv5_2', 'relu5_2', 'pool5'
],
'vgg16': [
'conv1_1', 'relu1_1', 'conv1_2', 'relu1_2', 'pool1', 'conv2_1', 'relu2_1', 'conv2_2', 'relu2_2', 'pool2',
'conv3_1', 'relu3_1', 'conv3_2', 'relu3_2', 'conv3_3', 'relu3_3', 'pool3', 'conv4_1', 'relu4_1', 'conv4_2',
'relu4_2', 'conv4_3', 'relu4_3', 'pool4', 'conv5_1', 'relu5_1', 'conv5_2', 'relu5_2', 'conv5_3', 'relu5_3',
'pool5'
],
'vgg19': [
'conv1_1', 'relu1_1', 'conv1_2', 'relu1_2', 'pool1', 'conv2_1', 'relu2_1', 'conv2_2', 'relu2_2', 'pool2',
'conv3_1', 'relu3_1', 'conv3_2', 'relu3_2', 'conv3_3', 'relu3_3', 'conv3_4', 'relu3_4', 'pool3', 'conv4_1',
'relu4_1', 'conv4_2', 'relu4_2', 'conv4_3', 'relu4_3', 'conv4_4', 'relu4_4', 'pool4', 'conv5_1', 'relu5_1',
'conv5_2', 'relu5_2', 'conv5_3', 'relu5_3', 'conv5_4', 'relu5_4', 'pool5'
]
}
def insert_bn(names):
"""Insert bn layer after each conv.
Args:
names (list): The list of layer names.
Returns:
list: The list of layer names with bn layers.
"""
names_bn = []
for name in names:
names_bn.append(name)
if 'conv' in name:
position = name.replace('conv', '')
names_bn.append('bn' + position)
return names_bn
@ARCH_REGISTRY.register()
class VGGFeatureExtractor(nn.Module):
"""VGG network for feature extraction.
In this implementation, we allow users to choose whether use normalization
in the input feature and the type of vgg network. Note that the pretrained
path must fit the vgg type.
Args:
layer_name_list (list[str]): Forward function returns the corresponding
features according to the layer_name_list.
Example: {'relu1_1', 'relu2_1', 'relu3_1'}.
vgg_type (str): Set the type of vgg network. Default: 'vgg19'.
use_input_norm (bool): If True, normalize the input image. Importantly,
the input feature must in the range [0, 1]. Default: True.
range_norm (bool): If True, norm images with range [-1, 1] to [0, 1].
Default: False.
requires_grad (bool): If true, the parameters of VGG network will be
optimized. Default: False.
remove_pooling (bool): If true, the max pooling operations in VGG net
will be removed. Default: False.
pooling_stride (int): The stride of max pooling operation. Default: 2.
"""
def __init__(self,
layer_name_list,
vgg_type='vgg19',
use_input_norm=True,
range_norm=False,
requires_grad=False,
remove_pooling=False,
pooling_stride=2):
super(VGGFeatureExtractor, self).__init__()
self.layer_name_list = layer_name_list
self.use_input_norm = use_input_norm
self.range_norm = range_norm
self.names = NAMES[vgg_type.replace('_bn', '')]
if 'bn' in vgg_type:
self.names = insert_bn(self.names)
# only borrow layers that will be used to avoid unused params
max_idx = 0
for v in layer_name_list:
idx = self.names.index(v)
if idx > max_idx:
max_idx = idx
if os.path.exists(VGG_PRETRAIN_PATH):
vgg_net = getattr(vgg, vgg_type)(pretrained=False)
state_dict = torch.load(VGG_PRETRAIN_PATH, map_location=lambda storage, loc: storage)
vgg_net.load_state_dict(state_dict)
else:
vgg_net = getattr(vgg, vgg_type)(pretrained=True)
features = vgg_net.features[:max_idx + 1]
modified_net = OrderedDict()
for k, v in zip(self.names, features):
if 'pool' in k:
# if remove_pooling is true, pooling operation will be removed
if remove_pooling:
continue
else:
# in some cases, we may want to change the default stride
modified_net[k] = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=pooling_stride)
else:
modified_net[k] = v
self.vgg_net = nn.Sequential(modified_net)
if not requires_grad:
self.vgg_net.eval()
for param in self.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
else:
self.vgg_net.train()
for param in self.parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
if self.use_input_norm:
# the mean is for image with range [0, 1]
self.register_buffer('mean', torch.Tensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).view(1, 3, 1, 1))
# the std is for image with range [0, 1]
self.register_buffer('std', torch.Tensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).view(1, 3, 1, 1))
def forward(self, x):
"""Forward function.
Args:
x (Tensor): Input tensor with shape (n, c, h, w).
Returns:
Tensor: Forward results.
"""
if self.range_norm:
x = (x + 1) / 2
if self.use_input_norm:
x = (x - self.mean) / self.std
output = {}
for key, layer in self.vgg_net._modules.items():
x = layer(x)
if key in self.layer_name_list:
output[key] = x.clone()
return output
perceptual loss:利用VGGFeatureExtractor 提取特定层的feature map
提取之后计算loss:
比如分别提取 gt 和 model output 的 vgg 特征图,然后计算差异:内容差异常用L1 loss, 风格差异常用 相似度
默认参数定义:
perceptual_opt:
type: PerceptualLoss
layer_weights:
# before relu
'conv1_2': 0.1
'conv2_2': 0.1
'conv3_4': 1
'conv4_4': 1
'conv5_4': 1
vgg_type: vgg19
use_input_norm: true
perceptual_weight: !!float 1
style_weight: 0
range_norm: false
criterion: l1
class PerceptualLoss(nn.Module):
"""Perceptual loss with commonly used style loss.
Args:
layer_weights (dict): The weight for each layer of vgg feature.
Here is an example: {'conv5_4': 1.}, which means the conv5_4
feature layer (before relu5_4) will be extracted with weight
1.0 in calculting losses.
vgg_type (str): The type of vgg network used as feature extractor.
Default: 'vgg19'.
use_input_norm (bool): If True, normalize the input image in vgg.
Default: True.
range_norm (bool): If True, norm images with range [-1, 1] to [0, 1].
Default: False.
perceptual_weight (float): If `perceptual_weight > 0`, the perceptual
loss will be calculated and the loss will multiplied by the
weight. Default: 1.0.
style_weight (float): If `style_weight > 0`, the style loss will be
calculated and the loss will multiplied by the weight.
Default: 0.
criterion (str): Criterion used for perceptual loss. Default: 'l1'.
"""
def __init__(self,
layer_weights,
vgg_type='vgg19',
use_input_norm=True,
range_norm=False,
perceptual_weight=1.0,
style_weight=0.,
criterion='l1'):
super(PerceptualLoss, self).__init__()
self.perceptual_weight = perceptual_weight
self.style_weight = style_weight
self.layer_weights = layer_weights
self.vgg = VGGFeatureExtractor(
layer_name_list=list(layer_weights.keys()),
vgg_type=vgg_type,
use_input_norm=use_input_norm,
range_norm=range_norm)
self.criterion_type = criterion
if self.criterion_type == 'l1':
self.criterion = torch.nn.L1Loss()
elif self.criterion_type == 'l2':
self.criterion = torch.nn.L2loss()
elif self.criterion_type == 'fro':
self.criterion = None
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f'{criterion} criterion has not been supported.')
def forward(self, x, gt):
"""Forward function.
Args:
x (Tensor): Input tensor with shape (n, c, h, w).
gt (Tensor): Ground-truth tensor with shape (n, c, h, w).
Returns:
Tensor: Forward results.
"""
# extract vgg features
x_features = self.vgg(x)
gt_features = self.vgg(gt.detach())
# calculate perceptual loss
if self.perceptual_weight > 0:
percep_loss = 0
for k in x_features.keys():
if self.criterion_type == 'fro':
percep_loss += torch.norm(x_features[k] - gt_features[k], p='fro') * self.layer_weights[k]
else:
percep_loss += self.criterion(x_features[k], gt_features[k]) * self.layer_weights[k]
percep_loss *= self.perceptual_weight
else:
percep_loss = None
# calculate style loss
if self.style_weight > 0:
style_loss = 0
for k in x_features.keys():
if self.criterion_type == 'fro':
style_loss += torch.norm(
self._gram_mat(x_features[k]) - self._gram_mat(gt_features[k]), p='fro') * self.layer_weights[k]
else:
style_loss += self.criterion(self._gram_mat(x_features[k]), self._gram_mat(gt_features[k])) * self.layer_weights[k]
style_loss *= self.style_weight
else:
style_loss = None
return percep_loss, style_loss
def _gram_mat(self, x): #其实计算的结果是c x c的矩阵,每个元素是各个通道的相关性,协方差矩阵
"""Calculate Gram matrix.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): Tensor with shape of (n, c, h, w).
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Gram matrix.
"""
n, c, h, w = x.size()
features = x.view(n, c, w * h)
features_t = features.transpose(1, 2)
gram = features.bmm(features_t) / (c * h * w) # bmm只能应用与维度为3的tensor
return gram
6.Gan损失
gan损失其实就是判别器的分类损失。
gan损失默认的一个参数设置如下:
# gan loss
gan_opt:
type: GANLoss
gan_type: vanilla
real_label_val: 1.0
fake_label_val: 0.0
loss_weight: !!float 1e-1
GANLoss 代码 和 MultiScaleGanLoss 代码如下
class GANLoss(nn.Module):
"""Define GAN loss.
Args:
gan_type (str): Support 'vanilla', 'lsgan', 'wgan', 'hinge'.
real_label_val (float): The value for real label. Default: 1.0.
fake_label_val (float): The value for fake label. Default: 0.0.
loss_weight (float): Loss weight. Default: 1.0.
Note that loss_weight is only for generators; and it is always 1.0
for discriminators.
"""
def __init__(self, gan_type, real_label_val=1.0, fake_label_val=0.0, loss_weight=1.0):
super(GANLoss, self).__init__()
self.gan_type = gan_type
self.loss_weight = loss_weight
self.real_label_val = real_label_val
self.fake_label_val = fake_label_val
if self.gan_type == 'vanilla':
self.loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
elif self.gan_type == 'lsgan':
self.loss = nn.MSELoss()
elif self.gan_type == 'wgan':
self.loss = self._wgan_loss
elif self.gan_type == 'wgan_softplus':
self.loss = self._wgan_softplus_loss
elif self.gan_type == 'hinge':
self.loss = nn.ReLU()
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f'GAN type {self.gan_type} is not implemented.')
def _wgan_loss(self, input, target):
"""wgan loss.
Args:
input (Tensor): Input tensor.
target (bool): Target label.
Returns:
Tensor: wgan loss.
"""
return -input.mean() if target else input.mean()
def _wgan_softplus_loss(self, input, target):
"""wgan loss with soft plus. softplus is a smooth approximation to the
ReLU function.
In StyleGAN2, it is called:
Logistic loss for discriminator;
Non-saturating loss for generator.
Args:
input (Tensor): Input tensor.
target (bool): Target label.
Returns:
Tensor: wgan loss.
"""
return F.softplus(-input).mean() if target else F.softplus(input).mean()
def get_target_label(self, input, target_is_real):
"""Get target label.
Args:
input (Tensor): Input tensor.
target_is_real (bool): Whether the target is real or fake.
Returns:
(bool | Tensor): Target tensor. Return bool for wgan, otherwise,
return Tensor.
"""
if self.gan_type in ['wgan', 'wgan_softplus']:
return target_is_real
target_val = (self.real_label_val if target_is_real else self.fake_label_val) #这里根据目标是real图还是生成图来 分别赋值 1和0, 挺多余的,转换来转换去,意思都一样。real就是1,fake就是0
return input.new_ones(input.size()) * target_val
def forward(self, input, target_is_real, is_disc=False):
"""
Args:
input (Tensor): The input for the loss module, i.e., the network
prediction.
target_is_real (bool): Whether the targe is real or fake.
is_disc (bool): Whether the loss for discriminators or not.
Default: False.
Returns:
Tensor: GAN loss value.
"""
target_label = self.get_target_label(input, target_is_real)
if self.gan_type == 'hinge':
if is_disc: # for discriminators in hinge-gan
input = -input if target_is_real else input
loss = self.loss(1 + input).mean()
else: # for generators in hinge-gan
loss = -input.mean()
else: # other gan types
loss = self.loss(input, target_label)
# loss_weight is always 1.0 for discriminators
return loss if is_disc else loss * self.loss_weight
"""
MultiScaleGANLoss 用于传进来的input是一个list,包含多个tensor的情况,这样对每个tensor分别计算ganloss,再求平均。
"""
class MultiScaleGANLoss(GANLoss):
"""
MultiScaleGANLoss accepts a list of predictions
"""
def __init__(self, gan_type, real_label_val=1.0, fake_label_val=0.0, loss_weight=1.0):
super(MultiScaleGANLoss, self).__init__(gan_type, real_label_val, fake_label_val, loss_weight)
def forward(self, input, target_is_real, is_disc=False):
"""
The input is a list of tensors, or a list of (a list of tensors)
"""
if isinstance(input, list):
loss = 0
for pred_i in input:
if isinstance(pred_i, list):
# Only compute GAN loss for the last layer
# in case of multiscale feature matching
pred_i = pred_i[-1]
# Safe operaton: 0-dim tensor calling self.mean() does nothing
loss_tensor = super().forward(pred_i, target_is_real, is_disc).mean()
loss += loss_tensor
return loss / len(input)
else:
return super().forward(input, target_is_real, is_disc)
7.WeightedTVLoss
这个损失很有意思,梯度损失?相邻像素的变化损失?。假如这个损失会更平滑,更连续吧
class WeightedTVLoss(L1Loss):
"""Weighted TV loss.
Args:
loss_weight (float): Loss weight. Default: 1.0.
"""
def __init__(self, loss_weight=1.0):
super(WeightedTVLoss, self).__init__(loss_weight=loss_weight)
def forward(self, pred, weight=None):
y_diff = super(WeightedTVLoss, self).forward(pred[:, :, :-1, :], pred[:, :, 1:, :], weight=weight[:, :, :-1, :])
x_diff = super(WeightedTVLoss, self).forward(pred[:, :, :, :-1], pred[:, :, :, 1:], weight=weight[:, :, :, :-1])
loss = x_diff + y_diff
return loss
在 3dlut生成中有类似的损失。
TV损失和mn是单调性损失
class TV_3D(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim=33):
super(TV_3D,self).__init__()
self.weight_r = torch.ones(3,dim,dim,dim-1, dtype=torch.float)
self.weight_r[:,:,:,(0,dim-2)] *= 2.0
self.weight_g = torch.ones(3,dim,dim-1,dim, dtype=torch.float)
self.weight_g[:,:,(0,dim-2),:] *= 2.0
self.weight_b = torch.ones(3,dim-1,dim,dim, dtype=torch.float)
self.weight_b[:,(0,dim-2),:,:] *= 2.0
self.relu = torch.nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, LUT):
dif_r = LUT.LUT[:,:,:,:-1] - LUT.LUT[:,:,:,1:]
dif_g = LUT.LUT[:,:,:-1,:] - LUT.LUT[:,:,1:,:]
dif_b = LUT.LUT[:,:-1,:,:] - LUT.LUT[:,1:,:,:]
tv = torch.mean(torch.mul((dif_r ** 2),self.weight_r)) + torch.mean(torch.mul((dif_g ** 2),self.weight_g)) + torch.mean(torch.mul((dif_b ** 2),self.weight_b))
# 3dlut 是不断递增的,因此希望后面的数比前面的数大, diff_r,diff_g,diff_b都是前面的减去后面的,因此希望为负 等价于 (加个relu使负的为0)
mn = torch.mean(self.relu(dif_r)) + torch.mean(self.relu(dif_g)) + torch.mean(self.relu(dif_b))
return tv, mn
8.完整代码方便使用,含训练epoch代码。
import functools
from torch.nn import functional as F
import math
import torch
from torch import autograd as autograd
from torch import nn as nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
import numpy as np
def reduce_loss(loss, reduction):
"""Reduce loss as specified.
Args:
loss (Tensor): Elementwise loss tensor.
reduction (str): Options are 'none', 'mean' and 'sum'.
Returns:
Tensor: Reduced loss tensor.
"""
reduction_enum = F._Reduction.get_enum(reduction)
# none: 0, elementwise_mean:1, sum: 2
if reduction_enum == 0:
return loss
elif reduction_enum == 1:
return loss.mean()
else:
return loss.sum()
def weight_reduce_loss(loss, weight=None, reduction='mean'):
"""Apply element-wise weight and reduce loss.
Args:
loss (Tensor): Element-wise loss.
weight (Tensor): Element-wise weights. Default: None.
reduction (str): Same as built-in losses of PyTorch. Options are
'none', 'mean' and 'sum'. Default: 'mean'.
Returns:
Tensor: Loss values.
"""
# if weight is specified, apply element-wise weight
if weight is not None:
assert weight.dim() == loss.dim()
assert weight.size(1) == 1 or weight.size(1) == loss.size(1)
loss = loss * weight
# if weight is not specified or reduction is sum, just reduce the loss
if weight is None or reduction == 'sum':
loss = reduce_loss(loss, reduction)
# if reduction is mean, then compute mean over weight region
elif reduction == 'mean':
if weight.size(1) > 1:
weight = weight.sum()
else:
weight = weight.sum() * loss.size(1)
loss = loss.sum() / weight
return loss
def weighted_loss(loss_func):
"""Create a weighted version of a given loss function.
To use this decorator, the loss function must have the signature like
`loss_func(pred, target, **kwargs)`. The function only needs to compute
element-wise loss without any reduction. This decorator will add weight
and reduction arguments to the function. The decorated function will have
the signature like `loss_func(pred, target, weight=None, reduction='mean',
**kwargs)`.
:Example:
>>> import torch
>>> @weighted_loss
>>> def l1_loss(pred, target):
>>> return (pred - target).abs()
>>> pred = torch.Tensor([0, 2, 3])
>>> target = torch.Tensor([1, 1, 1])
>>> weight = torch.Tensor([1, 0, 1])
>>> l1_loss(pred, target)
tensor(1.3333)
>>> l1_loss(pred, target, weight)
tensor(1.5000)
>>> l1_loss(pred, target, reduction='none')
tensor([1., 1., 2.])
>>> l1_loss(pred, target, weight, reduction='sum')
tensor(3.)
"""
@functools.wraps(loss_func)
def wrapper(pred, target, weight=None, reduction='mean', **kwargs):
# get element-wise loss
loss = loss_func(pred, target, **kwargs) # 这里 reduction='none'
loss = weight_reduce_loss(loss, weight, reduction)
return loss
return wrapper
###############################################################################################
"""
pixel_opt:
type: L1Loss
loss_weight: 1.0
reduction: mean
"""
@weighted_loss
def l1_loss(pred, target):
return F.l1_loss(pred, target, reduction='none')
class L1Loss(nn.Module):
"""L1 (mean absolute error, MAE) loss.
Args:
loss_weight (float): Loss weight for L1 loss. Default: 1.0.
reduction (str): Specifies the reduction to apply to the output.
Supported choices are 'none' | 'mean' | 'sum'. Default: 'mean'.
"""
def __init__(self, loss_weight=1.0, reduction='mean'):
super(L1Loss, self).__init__()
if reduction not in ['none', 'mean', 'sum']:
raise ValueError(f'Unsupported reduction mode: {reduction}. ' f'Supported ones are: {_reduction_modes}')
self.loss_weight = loss_weight
self.reduction = reduction
def forward(self, pred, target, weight=None, **kwargs):
"""
Args:
pred (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Predicted tensor.
target (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Ground truth tensor.
weight (Tensor, optional): of shape (N, C, H, W). Element-wise
weights. Default: None.
"""
return self.loss_weight * l1_loss(pred, target, weight, reduction=self.reduction)
@weighted_loss
def mse_loss(pred, target):
return F.mse_loss(pred, target, reduction='none')
class MSELoss(nn.Module):
"""MSE (L2) loss.
Args:
loss_weight (float): Loss weight for MSE loss. Default: 1.0.
reduction (str): Specifies the reduction to apply to the output.
Supported choices are 'none' | 'mean' | 'sum'. Default: 'mean'.
"""
def __init__(self, loss_weight=1.0, reduction='mean'):
super(MSELoss, self).__init__()
if reduction not in ['none', 'mean', 'sum']:
raise ValueError(f'Unsupported reduction mode: {reduction}. ' f'Supported ones are: {_reduction_modes}')
self.loss_weight = loss_weight
self.reduction = reduction
def forward(self, pred, target, weight=None, **kwargs):
"""
Args:
pred (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Predicted tensor.
target (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Ground truth tensor.
weight (Tensor, optional): of shape (N, C, H, W). Element-wise
weights. Default: None.
"""
return self.loss_weight * mse_loss(pred, target, weight, reduction=self.reduction)
@weighted_loss
def smooth_l1_loss(pred, target):
return F.smooth_l1_loss(pred, target, reduction='none')
class SmoothL1Loss(nn.Module):
"""MSE (L2) loss.
Args:
loss_weight (float): Loss weight for MSE loss. Default: 1.0.
reduction (str): Specifies the reduction to apply to the output.
Supported choices are 'none' | 'mean' | 'sum'. Default: 'mean'.
"""
def __init__(self, loss_weight=1.0, reduction='mean'):
super(MSELoss, self).__init__()
if reduction not in ['none', 'mean', 'sum']:
raise ValueError(f'Unsupported reduction mode: {reduction}. ' f'Supported ones are: {_reduction_modes}')
self.loss_weight = loss_weight
self.reduction = reduction
def forward(self, pred, target, weight=None, **kwargs):
"""
Args:
pred (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Predicted tensor.
target (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Ground truth tensor.
weight (Tensor, optional): of shape (N, C, H, W). Element-wise
weights. Default: None.
"""
return self.loss_weight * smooth_l1_loss(pred, target, weight, reduction=self.reduction)
@weighted_loss
def charbonnier_loss(pred, target, eps=1e-12):
return torch.sqrt((pred - target)**2 + eps)
class CharbonnierLoss(nn.Module):
"""Charbonnier loss (one variant of Robust L1Loss, a differentiable
variant of L1Loss).
Described in "Deep Laplacian Pyramid Networks for Fast and Accurate
Super-Resolution".
Args:
loss_weight (float): Loss weight for L1 loss. Default: 1.0.
reduction (str): Specifies the reduction to apply to the output.
Supported choices are 'none' | 'mean' | 'sum'. Default: 'mean'.
eps (float): A value used to control the curvature near zero.
Default: 1e-12.
"""
def __init__(self, loss_weight=1.0, reduction='mean', eps=1e-12):
super(CharbonnierLoss, self).__init__()
if reduction not in ['none', 'mean', 'sum']:
raise ValueError(f'Unsupported reduction mode: {reduction}. ' f'Supported ones are: {_reduction_modes}')
self.loss_weight = loss_weight
self.reduction = reduction
self.eps = eps
def forward(self, pred, target, weight=None, **kwargs):
"""
Args:
pred (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Predicted tensor.
target (Tensor): of shape (N, C, H, W). Ground truth tensor.
weight (Tensor, optional): of shape (N, C, H, W). Element-wise
weights. Default: None.
"""
return self.loss_weight * charbonnier_loss(pred, target, weight, eps=self.eps, reduction=self.reduction)
##############################################################################################################################
# perceptual loss
"""
perceptual_opt:
type: PerceptualLoss
layer_weights:
# before relu
'conv1_2': 0.1
'conv2_2': 0.1
'conv3_4': 1
'conv4_4': 1
'conv5_4': 1
vgg_type: vgg19
use_input_norm: true
perceptual_weight: !!float 1
style_weight: 0
range_norm: false
criterion: l1
"""
import os
import torch
from collections import OrderedDict
from torch import nn as nn
from torchvision.models import vgg as vgg
#from basicsr.utils.registry import ARCH_REGISTRY
VGG_PRETRAIN_PATH = 'experiments/pretrained_models/vgg19-dcbb9e9d.pth'
NAMES = {
'vgg11': [
'conv1_1', 'relu1_1', 'pool1', 'conv2_1', 'relu2_1', 'pool2', 'conv3_1', 'relu3_1', 'conv3_2', 'relu3_2',
'pool3', 'conv4_1', 'relu4_1', 'conv4_2', 'relu4_2', 'pool4', 'conv5_1', 'relu5_1', 'conv5_2', 'relu5_2',
'pool5'
],
'vgg13': [
'conv1_1', 'relu1_1', 'conv1_2', 'relu1_2', 'pool1', 'conv2_1', 'relu2_1', 'conv2_2', 'relu2_2', 'pool2',
'conv3_1', 'relu3_1', 'conv3_2', 'relu3_2', 'pool3', 'conv4_1', 'relu4_1', 'conv4_2', 'relu4_2', 'pool4',
'conv5_1', 'relu5_1', 'conv5_2', 'relu5_2', 'pool5'
],
'vgg16': [
'conv1_1', 'relu1_1', 'conv1_2', 'relu1_2', 'pool1', 'conv2_1', 'relu2_1', 'conv2_2', 'relu2_2', 'pool2',
'conv3_1', 'relu3_1', 'conv3_2', 'relu3_2', 'conv3_3', 'relu3_3', 'pool3', 'conv4_1', 'relu4_1', 'conv4_2',
'relu4_2', 'conv4_3', 'relu4_3', 'pool4', 'conv5_1', 'relu5_1', 'conv5_2', 'relu5_2', 'conv5_3', 'relu5_3',
'pool5'
],
'vgg19': [
'conv1_1', 'relu1_1', 'conv1_2', 'relu1_2', 'pool1', 'conv2_1', 'relu2_1', 'conv2_2', 'relu2_2', 'pool2',
'conv3_1', 'relu3_1', 'conv3_2', 'relu3_2', 'conv3_3', 'relu3_3', 'conv3_4', 'relu3_4', 'pool3', 'conv4_1',
'relu4_1', 'conv4_2', 'relu4_2', 'conv4_3', 'relu4_3', 'conv4_4', 'relu4_4', 'pool4', 'conv5_1', 'relu5_1',
'conv5_2', 'relu5_2', 'conv5_3', 'relu5_3', 'conv5_4', 'relu5_4', 'pool5'
]
}
def insert_bn(names):
"""Insert bn layer after each conv.
Args:
names (list): The list of layer names.
Returns:
list: The list of layer names with bn layers.
"""
names_bn = []
for name in names:
names_bn.append(name)
if 'conv' in name:
position = name.replace('conv', '')
names_bn.append('bn' + position)
return names_bn
class VGGFeatureExtractor(nn.Module):
"""VGG network for feature extraction.
In this implementation, we allow users to choose whether use normalization
in the input feature and the type of vgg network. Note that the pretrained
path must fit the vgg type.
Args:
layer_name_list (list[str]): Forward function returns the corresponding
features according to the layer_name_list.
Example: {'relu1_1', 'relu2_1', 'relu3_1'}.
vgg_type (str): Set the type of vgg network. Default: 'vgg19'.
use_input_norm (bool): If True, normalize the input image. Importantly,
the input feature must in the range [0, 1]. Default: True.
range_norm (bool): If True, norm images with range [-1, 1] to [0, 1].
Default: False.
requires_grad (bool): If true, the parameters of VGG network will be
optimized. Default: False.
remove_pooling (bool): If true, the max pooling operations in VGG net
will be removed. Default: False.
pooling_stride (int): The stride of max pooling operation. Default: 2.
"""
def __init__(self,
layer_name_list,
vgg_type='vgg19',
use_input_norm=True,
range_norm=False,
requires_grad=False,
remove_pooling=False,
pooling_stride=2):
super(VGGFeatureExtractor, self).__init__()
self.layer_name_list = layer_name_list
self.use_input_norm = use_input_norm
self.range_norm = range_norm
self.names = NAMES[vgg_type.replace('_bn', '')]
if 'bn' in vgg_type:
self.names = insert_bn(self.names)
# only borrow layers that will be used to avoid unused params
max_idx = 0
for v in layer_name_list:
idx = self.names.index(v)
if idx > max_idx:
max_idx = idx
if os.path.exists(VGG_PRETRAIN_PATH):
vgg_net = getattr(vgg, vgg_type)(pretrained=False)
state_dict = torch.load(VGG_PRETRAIN_PATH, map_location=lambda storage, loc: storage)
vgg_net.load_state_dict(state_dict)
else:
vgg_net = getattr(vgg, vgg_type)(pretrained=True)
features = vgg_net.features[:max_idx + 1]
modified_net = OrderedDict()
for k, v in zip(self.names, features):
if 'pool' in k:
# if remove_pooling is true, pooling operation will be removed
if remove_pooling:
continue
else:
# in some cases, we may want to change the default stride
modified_net[k] = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=pooling_stride)
else:
modified_net[k] = v
self.vgg_net = nn.Sequential(modified_net)
if not requires_grad:
self.vgg_net.eval()
for param in self.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
else:
self.vgg_net.train()
for param in self.parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
if self.use_input_norm:
# the mean is for image with range [0, 1]
self.register_buffer('mean', torch.Tensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).view(1, 3, 1, 1))
# the std is for image with range [0, 1]
self.register_buffer('std', torch.Tensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).view(1, 3, 1, 1))
def forward(self, x):
"""Forward function.
Args:
x (Tensor): Input tensor with shape (n, c, h, w).
Returns:
Tensor: Forward results.
"""
if self.range_norm:
x = (x + 1) / 2
if self.use_input_norm:
x = (x - self.mean) / self.std
output = {}
for key, layer in self.vgg_net._modules.items():
x = layer(x)
if key in self.layer_name_list:
output[key] = x.clone()
return output
class PerceptualLoss(nn.Module):
"""Perceptual loss with commonly used style loss.
Args:
layer_weights (dict): The weight for each layer of vgg feature.
Here is an example: {'conv5_4': 1.}, which means the conv5_4
feature layer (before relu5_4) will be extracted with weight
1.0 in calculting losses.
vgg_type (str): The type of vgg network used as feature extractor.
Default: 'vgg19'.
use_input_norm (bool): If True, normalize the input image in vgg.
Default: True.
range_norm (bool): If True, norm images with range [-1, 1] to [0, 1].
Default: False.
perceptual_weight (float): If `perceptual_weight > 0`, the perceptual
loss will be calculated and the loss will multiplied by the
weight. Default: 1.0.
style_weight (float): If `style_weight > 0`, the style loss will be
calculated and the loss will multiplied by the weight.
Default: 0.
criterion (str): Criterion used for perceptual loss. Default: 'l1'.
"""
def __init__(self,
layer_weights,
vgg_type='vgg19',
use_input_norm=True,
range_norm=False,
perceptual_weight=1.0,
style_weight=0.,
criterion='l1'):
super(PerceptualLoss, self).__init__()
self.perceptual_weight = perceptual_weight
self.style_weight = style_weight
self.layer_weights = layer_weights
self.vgg = VGGFeatureExtractor(
layer_name_list=list(layer_weights.keys()),
vgg_type=vgg_type,
use_input_norm=use_input_norm,
range_norm=range_norm)
self.criterion_type = criterion
if self.criterion_type == 'l1':
self.criterion = torch.nn.L1Loss()
elif self.criterion_type == 'l2':
self.criterion = torch.nn.L2loss()
elif self.criterion_type == 'fro':
self.criterion = None
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f'{criterion} criterion has not been supported.')
def forward(self, x, gt):
"""Forward function.
Args:
x (Tensor): Input tensor with shape (n, c, h, w).
gt (Tensor): Ground-truth tensor with shape (n, c, h, w).
Returns:
Tensor: Forward results.
"""
# extract vgg features
x_features = self.vgg(x)
gt_features = self.vgg(gt.detach())
# calculate perceptual loss
if self.perceptual_weight > 0:
percep_loss = 0
for k in x_features.keys():
if self.criterion_type == 'fro':
percep_loss += torch.norm(x_features[k] - gt_features[k], p='fro') * self.layer_weights[k]
else:
percep_loss += self.criterion(x_features[k], gt_features[k]) * self.layer_weights[k]
percep_loss *= self.perceptual_weight
else:
percep_loss = None
# calculate style loss
if self.style_weight > 0:
style_loss = 0
for k in x_features.keys():
if self.criterion_type == 'fro':
style_loss += torch.norm(
self._gram_mat(x_features[k]) - self._gram_mat(gt_features[k]), p='fro') * self.layer_weights[k]
else:
style_loss += self.criterion(self._gram_mat(x_features[k]), self._gram_mat(gt_features[k])) * self.layer_weights[k]
style_loss *= self.style_weight
else:
style_loss = None
return percep_loss, style_loss
def _gram_mat(self, x): #其实计算的结果是c x c的矩阵,每个元素是各个通道的相关性,协方差矩阵
"""Calculate Gram matrix.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): Tensor with shape of (n, c, h, w).
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Gram matrix.
"""
n, c, h, w = x.size()
features = x.view(n, c, w * h)
features_t = features.transpose(1, 2)
gram = features.bmm(features_t) / (c * h * w) # bmm只能应用与维度为3的tensor
return gram
#################################################################################################
# gan loss
# 默认设置参数
"""
gan_opt:
type: GANLoss
gan_type: vanilla
real_label_val: 1.0
fake_label_val: 0.0
loss_weight: !!float 1e-1
"""
class GANLoss(nn.Module):
"""Define GAN loss.
Args:
gan_type (str): Support 'vanilla', 'lsgan', 'wgan', 'hinge'.
real_label_val (float): The value for real label. Default: 1.0.
fake_label_val (float): The value for fake label. Default: 0.0.
loss_weight (float): Loss weight. Default: 1.0.
Note that loss_weight is only for generators; and it is always 1.0
for discriminators.
"""
def __init__(self, gan_type, real_label_val=1.0, fake_label_val=0.0, loss_weight=1.0):
super(GANLoss, self).__init__()
self.gan_type = gan_type
self.loss_weight = loss_weight
self.real_label_val = real_label_val
self.fake_label_val = fake_label_val
if self.gan_type == 'vanilla':
self.loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
elif self.gan_type == 'lsgan':
self.loss = nn.MSELoss()
elif self.gan_type == 'wgan':
self.loss = self._wgan_loss
elif self.gan_type == 'wgan_softplus':
self.loss = self._wgan_softplus_loss
elif self.gan_type == 'hinge':
self.loss = nn.ReLU()
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f'GAN type {self.gan_type} is not implemented.')
def _wgan_loss(self, input, target):
"""wgan loss.
Args:
input (Tensor): Input tensor.
target (bool): Target label.
Returns:
Tensor: wgan loss.
"""
return -input.mean() if target else input.mean()
def _wgan_softplus_loss(self, input, target):
"""wgan loss with soft plus. softplus is a smooth approximation to the
ReLU function.
In StyleGAN2, it is called:
Logistic loss for discriminator;
Non-saturating loss for generator.
Args:
input (Tensor): Input tensor.
target (bool): Target label.
Returns:
Tensor: wgan loss.
"""
return F.softplus(-input).mean() if target else F.softplus(input).mean()
def get_target_label(self, input, target_is_real):
"""Get target label.
Args:
input (Tensor): Input tensor.
target_is_real (bool): Whether the target is real or fake.
Returns:
(bool | Tensor): Target tensor. Return bool for wgan, otherwise,
return Tensor.
"""
if self.gan_type in ['wgan', 'wgan_softplus']:
return target_is_real
target_val = (self.real_label_val if target_is_real else self.fake_label_val) #这里根据目标是real图还是生成图来 分别赋值 1和0, 挺多余的,转换来转换去,意思都一样。real就是1,fake就是0
return input.new_ones(input.size()) * target_val
def forward(self, input, target_is_real, is_disc=False):
"""
Args:
input (Tensor): The input for the loss module, i.e., the network
prediction.
target_is_real (bool): Whether the targe is real or fake.
is_disc (bool): Whether the loss for discriminators or not.
Default: False.
Returns:
Tensor: GAN loss value.
"""
target_label = self.get_target_label(input, target_is_real)
if self.gan_type == 'hinge':
if is_disc: # for discriminators in hinge-gan
input = -input if target_is_real else input
loss = self.loss(1 + input).mean()
else: # for generators in hinge-gan
loss = -input.mean()
else: # other gan types
loss = self.loss(input, target_label)
# loss_weight is always 1.0 for discriminators
return loss if is_disc else loss * self.loss_weight
"""
MultiScaleGANLoss 用于传进来的input是一个list,包含多个tensor的情况,这样对每个tensor分别计算ganloss,再求平均。
"""
class MultiScaleGANLoss(GANLoss):
"""
MultiScaleGANLoss accepts a list of predictions
"""
def __init__(self, gan_type, real_label_val=1.0, fake_label_val=0.0, loss_weight=1.0):
super(MultiScaleGANLoss, self).__init__(gan_type, real_label_val, fake_label_val, loss_weight)
def forward(self, input, target_is_real, is_disc=False):
"""
The input is a list of tensors, or a list of (a list of tensors)
"""
if isinstance(input, list):
loss = 0
for pred_i in input:
if isinstance(pred_i, list):
# Only compute GAN loss for the last layer
# in case of multiscale feature matching
pred_i = pred_i[-1]
# Safe operaton: 0-dim tensor calling self.mean() does nothing
loss_tensor = super().forward(pred_i, target_is_real, is_disc).mean()
loss += loss_tensor
return loss / len(input)
else:
return super().forward(input, target_is_real, is_disc)
#################################################################################################
class WeightedTVLoss(L1Loss):
"""Weighted TV loss.
Args:
loss_weight (float): Loss weight. Default: 1.0.
"""
def __init__(self, loss_weight=1.0):
super(WeightedTVLoss, self).__init__(loss_weight=loss_weight)
def forward(self, pred, weight=None):
y_diff = super(WeightedTVLoss, self).forward(pred[:, :, :-1, :], pred[:, :, 1:, :], weight=weight[:, :, :-1, :])
x_diff = super(WeightedTVLoss, self).forward(pred[:, :, :, :-1], pred[:, :, :, 1:], weight=weight[:, :, :, :-1])
loss = x_diff + y_diff
return loss
class TV_3D(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim=33):
super(TV_3D,self).__init__()
self.weight_r = torch.ones(3,dim,dim,dim-1, dtype=torch.float)
self.weight_r[:,:,:,(0,dim-2)] *= 2.0
self.weight_g = torch.ones(3,dim,dim-1,dim, dtype=torch.float)
self.weight_g[:,:,(0,dim-2),:] *= 2.0
self.weight_b = torch.ones(3,dim-1,dim,dim, dtype=torch.float)
self.weight_b[:,(0,dim-2),:,:] *= 2.0
self.relu = torch.nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, LUT):
dif_r = LUT.LUT[:,:,:,:-1] - LUT.LUT[:,:,:,1:]
dif_g = LUT.LUT[:,:,:-1,:] - LUT.LUT[:,:,1:,:]
dif_b = LUT.LUT[:,:-1,:,:] - LUT.LUT[:,1:,:,:]
tv = torch.mean(torch.mul((dif_r ** 2),self.weight_r)) + torch.mean(torch.mul((dif_g ** 2),self.weight_g)) + torch.mean(torch.mul((dif_b ** 2),self.weight_b))
# 3dlut 是不断递增的,因此希望后面的数比前面的数大, diff_r,diff_g,diff_b都是前面的减去后面的,因此希望为负 等价于 (加个relu使负的为0)
mn = torch.mean(self.relu(dif_r)) + torch.mean(self.relu(dif_g)) + torch.mean(self.relu(dif_b))
return tv, mn
# type: L1Loss
# loss_weight: 1.0
# reduction: mean
# type: PerceptualLoss
# layer_weights:
# # before relu
# 'conv1_2': 0.1
# 'conv2_2': 0.1
# 'conv3_4': 1
# 'conv4_4': 1
# 'conv5_4': 1
# vgg_type: vgg19
# use_input_norm: true
# perceptual_weight: !!float 1
# style_weight: 0
# range_norm: false
# criterion: l1
# type: GANLoss
# gan_type: vanilla
# real_label_val: 1.0
# fake_label_val: 0.0
# loss_weight: !!float 1e-1
def gan_loss_opti(net_g, net_d, input, gt, optimizer_g, optimizer_d, epoch, net_d_init_iters=100, net_d_iters=1):
# 0. loss define
cri_pix = L1Loss(loss_weight = 1.0, reduction='mean')
cri_perceptual = PerceptualLoss(layer_weights={ 'conv1_2': 0.1,
'conv2_2': 0.1,
'conv3_4': 1,
'conv4_4': 1,
'conv5_4': 1},
vgg_type='vgg19',
use_input_norm=True,
range_norm=False,
perceptual_weight=1.0,
style_weight=0.,
criterion='l1')
cri_gan = GANLoss(gan_type='vanilla', real_label_val=1.0, fake_label_val=0.0, loss_weight=0.1)
# 一次迭代步骤的优化。优化一次生成器,接着优化一次判别器。
# optimize net_g
# 1. 首先优化 生成网络net_g, net_d判别网络不更新weight
for p in net_d.parameters():
p.requires_grad = False
# 2. 梯度归0
optimizer_g.zero_grad()
# 3. 前向生成网络,输入的是一个低质图像
output = net_g(input)
# 4. 计算训练生成网络的损失
# 主要包括 pixel loss 重建损失 self.cri_pix(self.output, self.gt)
# 图像内容和风格感知损失 self.cri_perceptual(self.output, self.gt)
# gan损失,使预测迷惑判别器 self.cri_gan(fake_g_pred, True, is_disc=False)
l_g_total = 0
loss_dict = OrderedDict()
# 首先在epoch小于net_d_init_iters的情况下只训练 net_d, 不训练net_g
if (epoch % net_d_iters == 0 and epoch > net_d_init_iters):
# pixel loss
if cri_pix:
l_pix = cri_pix(output, gt)
l_g_total += l_pix
loss_dict['l_pix'] = l_pix
# perceptual loss
if cri_perceptual:
l_percep, l_style = cri_perceptual(output, gt)
if l_percep is not None:
l_g_total += l_percep
loss_dict['l_percep'] = l_percep
if l_style is not None:
l_g_total += l_style
loss_dict['l_style'] = l_style
# gan loss
fake_g_pred = net_d(output)
l_g_gan = cri_gan(fake_g_pred, True, is_disc=False)
l_g_total += l_g_gan
loss_dict['l_g_gan'] = l_g_gan
# 5. 计算梯度和优化
l_g_total.backward()
optimizer_g.step()
# optimize net_d
# 6. 优化判别器网络,首先requires_grad设为ture,可训练
for p in net_d.parameters():
p.requires_grad = True
# 7. 梯度归0
optimizer_d.zero_grad()
# real
# 8. 计算gt进入判别器的损失,使gt 尽量为 1
real_d_pred = net_d(gt)
l_d_real = cri_gan(real_d_pred, True, is_disc=True)
loss_dict['l_d_real'] = l_d_real
loss_dict['out_d_real'] = torch.mean(real_d_pred.detach())
l_d_real.backward()
# fake
# 9. 计算gt进入判别器的损失,使predict output 尽量为 0
fake_d_pred = net_d(output.detach())
l_d_fake = cri_gan(fake_d_pred, False, is_disc=True)
loss_dict['l_d_fake'] = l_d_fake
loss_dict['out_d_fake'] = torch.mean(fake_d_pred.detach())
# 10. 梯度计算和优化
l_d_fake.backward()
optimizer_d.step()
# 11. for log
log_dict = OrderedDict()
for name, value in loss_dict.items():
log_dict[name] = value.mean().item()
#print(log_dict)
return output, log_dict




![[技术杂谈]解决右键没有vscode打开选项的问题](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/21d765c91ecd425085ca2484945cf4db.png)