Signed Distance Field(有向距离场),简称SDF,这其实是图形学中非常常用的数学概念。数学上来说,是定义在空间中的一个标量场,标量值为空间一点到曲面的距离。曲面外的点为正值,曲面上的点为0,曲面内的点为负数。对于需要渲染的3d场景来说,我们需要计算它到场景中所有物体的最近距离,来生成distance field。对场景生成distance field和distance filed的表达存储本身也都是一个复杂的话题,比如如何处理非闭的网格(unclosed mesh)。
UE5基于这个做了好多东西,有兴趣的可以翻一番UE源码。至于其具体是什么,能干什么,有哪些优缺点,网上一大堆,大家自行查找吧,可以参照Games202 第五节有详细介绍。
其实网上资料虽然多,但是大都是介绍一个通识,我们今天就把他的生成过程和经典使用(SDFShadow)来详细说一下,至于DFAO等其实原理都一样。文章可参照:Erebus - Real-Time Ray Tracing SDFs; UE4/5 Style DFAO and Soft Shadows [HDRP/URP/BUILT-IN] 讲的比较好。

SDF全流程一般如下:
- CS生成一张3D Texture来记录SDF信息;
- 使用SDF Texture来实现算法;
至此,结束。
一、SDF生成
首先我们来看一下如何生成SDF数据,老规矩,上代码,大家直接看:
#define GROUP_SIZE 8
#define BVH_STACK_SIZE 32
cbuffer CSParams
{
float3 SDFLower;
int TriangleCount;
float3 SDFUpper;
int SignRayCount;
float3 SDFExtent;
int XBeg;
int XEnd;
}
struct Node
{
float minX;
float minY;
float minZ;
float maxX;
float maxY;
float maxZ;
uint childIndex;
uint childCount;
};
StructuredBuffer<Node> Nodes;
StructuredBuffer<float3> Vertices;
StructuredBuffer<float3> Normals;
RWTexture3D<float> SDF;
float dot2(float3 v)
{
return dot(v, v);
}
bool isLeaf(Node node)
{
return node.childCount != 0;
}
bool intersectSphereBox(float3 lower, float3 upper, float3 p, float radius2)
{
float3 q = clamp(p, lower, upper);
return dot(p - q, p - q) <= radius2;
}
//可参照 https://iquilezles.org/www/articles/distfunctions/distfunctions.htm具体实现
float udf2Triangle(float3 a, float3 b, float3 c, float3 p)
{
float3 ba = b - a;
float3 pa = p - a;
float3 cb = c - b;
float3 pb = p - b;
float3 ac = a - c;
float3 pc = p - c;
float3 nor = cross(ba, ac);
if (sign(dot(cross(ba, nor), pa)) +
sign(dot(cross(cb, nor), pb)) +
sign(dot(cross(ac, nor), pc)) < 2)
{
return min(min(
dot2(ba * clamp(dot(ba, pa) / dot2(ba), 0.0f, 1.0f) - pa),
dot2(cb * clamp(dot(cb, pb) / dot2(cb), 0.0f, 1.0f) - pb)),
dot2(ac * clamp(dot(ac, pc) / dot2(ac), 0.0f, 1.0f) - pc));
}
return dot(nor, pa) * dot(nor, pa) / dot2(nor);
}
bool intersectSphereTriangle(float3 a, float3 b, float3 c, float3 o, float r2)
{
return udf2Triangle(a, b, c, o) <= r2;
}
bool closestIntersectionWithTriangle(
float3 o,
float3 d,
float maxT,
float3 A,
float3 B_A,
float3 C_A,
out float r_t)
{
float3 s1 = cross(d, C_A);
float div = dot(s1, B_A);
float invDiv = 1 / div;
float3 o_A = o - A;
float alpha = dot(o_A, s1) * invDiv;
float3 s2 = cross(o_A, B_A);
float beta = dot(d, s2) * invDiv;
const float t = dot(C_A, s2) * invDiv;
if (t < 0 || t > maxT || alpha < 0 || beta < 0 || alpha + beta > 1)
return false;
r_t = t;
return true;
}
float max4(float x, float y, float z, float w)
{
return max(max(x, y), max(z, w));
}
float min4(float x, float y, float z, float w)
{
return min(min(x, y), min(z, w));
}
bool intersectRayBox(
float3 o, float3 invD, float t0, float t1, float3 lower, float3 upper)
{
float3 n = invD * (lower - o);
float3 f = invD * (upper - o);
float3 minnf = min(n, f);
float3 maxnf = max(n, f);
t0 = max4(t0, minnf.x, minnf.y, minnf.z);
t1 = min4(t1, maxnf.x, maxnf.y, maxnf.z);
return t0 <= t1;
}
bool containsTriangle(float3 o, float radius2, uint nodeIndex)
{
uint stack[BVH_STACK_SIZE];
stack[0] = nodeIndex;
int stackTop = 1;
while (stackTop)
{
uint ni = stack[--stackTop];
Node node = Nodes[ni];
if (!intersectSphereBox(
float3(node.minX, node.minY, node.minZ),
float3(node.maxX, node.maxY, node.maxY),
o, radius2))
continue;
if (isLeaf(node))
{
for (uint i = 0, j = 3 * node.childIndex;
i < node.childCount; ++i, j += 3)
{
if (intersectSphereTriangle(
Vertices[j], Vertices[j + 1], Vertices[j + 2], o, radius2))
return true;
}
return false;
}
stack[stackTop++] = node.childIndex;
stack[stackTop++] = node.childIndex + 1;
}
return false;
}
float estimateUpperBound(float3 p, int precison)
{
Node root = Nodes[0];
float3 lower = float3(root.minX, root.minY, root.minZ);
float3 upper = float3(root.maxX, root.maxY, root.maxZ);
float L = 0;
float R = distance(0.5 * (lower + upper), p) + distance(lower, upper);
for (int i = 0; i < precison; ++i)
{
float mid = 0.5 * (L + R);
if (containsTriangle(p, mid * mid, 0))
R = mid;
else
L = mid;
}
return R;
}
int traceTriangleIndex(float3 o, float3 d, float maxT)
{
float3 invD = 1.0f / d;
uint stack[BVH_STACK_SIZE];
stack[0] = 0;
int stackTop = 1;
int finalIdx = -1;
float finalT = maxT;
while (stackTop)
{
uint ni = stack[--stackTop];
Node node = Nodes[ni];
if (!intersectRayBox(
o, invD, 0, finalT,
float3(node.minX, node.minY, node.minZ),
float3(node.maxX, node.maxY, node.maxZ)))
continue;
if (isLeaf(node))
{
for (uint i = 0, j = 3 * node.childIndex;
i < node.childCount; ++i, j += 3)
{
float3 a = Vertices[j];
float3 b = Vertices[j + 1];
float3 c = Vertices[j + 2];
float newT;
if (closestIntersectionWithTriangle(
o, d, finalT, a, b - a, c - a, newT))
{
finalT = newT;
finalIdx = i + node.childIndex;
}
}
}
else
{
stack[stackTop++] = node.childIndex;
stack[stackTop++] = node.childIndex + 1;
}
}
return finalIdx;
}
struct UDF2Result
{
int triIdx;
float udf2;
};
int estimateSign(float3 o, float rn)
{
int rndTriIdx = int(rn * (TriangleCount - 1));
float3 a = Vertices[rndTriIdx * 3 + 0];
float3 b = Vertices[rndTriIdx * 3 + 1];
float3 c = Vertices[rndTriIdx * 3 + 2];
float3 d = 1.0f / 3 * (a + b + c) - o;
int triIdx = traceTriangleIndex(o, d, 1.0f / 0.0f);
if (triIdx < 0)
return 0;
float3 na = Normals[triIdx * 3 + 0];
float3 nb = Normals[triIdx * 3 + 1];
float3 nc = Normals[triIdx * 3 + 2];
return dot(d, na + nb + nc) < 0 ? 1 : -1;
}
UDF2Result udf2(float3 p, float u2, uint nodeIndex)
{
uint stack[BVH_STACK_SIZE];
stack[0] = nodeIndex;
int stackTop = 1;
int finalTriIdx = -1;
while (stackTop)
{
uint ni = stack[--stackTop];
Node node = Nodes[ni];
if (!intersectSphereBox(
float3(node.minX, node.minY, node.minZ),
float3(node.maxX, node.maxY, node.maxZ),
p, u2))
continue;
if (isLeaf(node))
{
for (uint i = 0, j = 3 * node.childIndex;
i < node.childCount; ++i, j += 3)
{
float newUDF2 = udf2Triangle(
Vertices[j], Vertices[j + 1], Vertices[j + 2], p);
if (newUDF2 < u2)
{
u2 = newUDF2;
finalTriIdx = int(i + node.childIndex);
}
}
}
else
{
stack[stackTop++] = node.childIndex;
stack[stackTop++] = node.childIndex + 1;
}
}
UDF2Result result;
result.triIdx = finalTriIdx;
result.udf2 = u2;
return result;
}
float sdf(float3 p, float upperBound)
{
if (upperBound <= 0)
upperBound = estimateUpperBound(p, 6);
UDF2Result udf2Result = udf2(p, upperBound * upperBound, 0);
float udfVal = sqrt(udf2Result.udf2);
int triIdx = udf2Result.triIdx;
int signEstimator = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < SignRayCount; ++i)
{
signEstimator += estimateSign(
p, lerp(0.0f, 1.0f, (i + 0.5f) / SignRayCount));
}
if (signEstimator > 0)
return udfVal;
if (signEstimator < 0)
return -udfVal;
float3 a = Vertices[triIdx * 3 + 0];
float3 b = Vertices[triIdx * 3 + 1];
float3 c = Vertices[triIdx * 3 + 2];
float3 na = Normals[triIdx * 3 + 0];
float3 nb = Normals[triIdx * 3 + 1];
float3 nc = Normals[triIdx * 3 + 2];
int ja = dot(p - a, na) >= 0 ? 1 : -1;
int jb = dot(p - b, nb) >= 0 ? 1 : -1;
int jc = dot(p - c, nc) >= 0 ? 1 : -1;
return ja + jb + jc > 0 ? udfVal : -udfVal;
}
[numthreads(1, GROUP_SIZE, GROUP_SIZE)]
void CSMain(int3 threadIdx : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
int width, height, depth;
SDF.GetDimensions(width, height, depth);
if (threadIdx.y >= height || threadIdx.z >= depth)
return;
float dx = 1.05f * SDFExtent.x / width;
float zf = lerp(SDFLower.z, SDFUpper.z, (threadIdx.z + 0.5f) / depth);
float yf = lerp(SDFLower.y, SDFUpper.y, (threadIdx.y + 0.5f) / height);
float lastUDF = -100 * dx;
for (int x = XBeg; x < XEnd; ++x)
{
float xf = lerp(SDFLower.x, SDFUpper.x, (x + 0.5f) / width);
float upperBound = lastUDF + dx;
float newSDF = sdf(float3(xf, yf, zf), upperBound);
lastUDF = abs(newSDF);
SDF[int3(x, threadIdx.yz)] = newSDF;
}
}
上边代码看似有点复杂,其实大致原理很简单:
通过将模型在应用程序构建树型结构(一般采用BVH),然后将整体包围盒信息、模型数据、bvh节点传入CS,之后根据其大小和存储的3DTexture尺寸切片保存到3D纹理中即可,具体Shader间上边的内容就行。
需要注意的是,在应用程序端需要对存储的数据做好调用规划,之后循环调用即可填充SDF纹理,至于纹理多大就看你自己项目要求了:
constexpr int GROUP_SIZE = 8;
const int groupCountY = (res.y + GROUP_SIZE - 1) / GROUP_SIZE;
const int groupCountZ = (res.z + GROUP_SIZE - 1) / GROUP_SIZE;
constexpr int X_SLICE_SIZE = 32;
for(int xBeg = 0; xBeg < res.x; xBeg += X_SLICE_SIZE)
{
csParams.update({
lower, static_cast<int>(triangleCount),
upper, signRayCount_,
upper - lower, xBeg,
(std::min)(res.x, xBeg + X_SLICE_SIZE),
0, 0, 0
});
deviceContext.dispatch(1, groupCountY, groupCountZ);
}
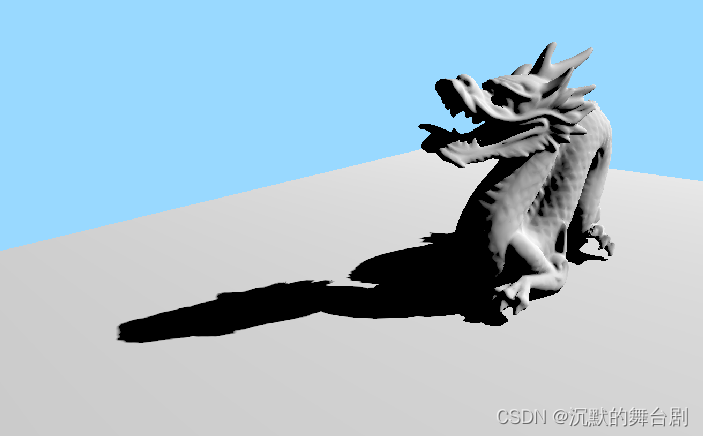
基于上述CS可以生成如下可视化数据:
其实就是一张3D纹理贴图、里边记录了每个位置的距离场信息,具体执行过程看Shader吧,不再赘述了。
二、SDF可视化
struct VSOutput
{
float4 position : SV_POSITION;
float2 texCoord : TEXCOORD;
};
VSOutput VSMain(uint vertexID : SV_VertexID)
{
VSOutput output;
output.texCoord = float2((vertexID << 1) & 2, vertexID & 2);
output.position = float4(output.texCoord * float2(2, -2) + float2(-1, 1), 0.5, 1);
return output;
}
//视口与物体包围盒信息
cbuffer PSParams
{
float3 FrustumA; int MaxTraceSteps;
float3 FrustumB; float AbsThreshold;
float3 FrustumC;
float3 FrustumD;
float3 Eye;
float3 SDFLower;
float3 SDFUpper;
float3 SDFExtent;
}
Texture3D<float> SDF;
SamplerState SDFSampler;
float max3(float x, float y, float z)
{
return max(x, max(y, z));
}
float min3(float x, float y, float z)
{
return min(x, min(y, z));
}
//射线与盒子求交
float2 intersectRayBox(float3 o, float3 d)
{
float3 invD = 1 / d;
float3 n = invD * (SDFLower - o);
float3 f = invD * (SDFUpper - o);
float3 minnf = min(n, f);
float3 maxnf = max(n, f);
float t0 = max3(minnf.x, minnf.y, minnf.z);
float t1 = min3(maxnf.x, maxnf.y, maxnf.z);
return float2(max(0.0f, t0), t1);
}
float4 PSMain(VSOutput input) : SV_TARGET
{
float3 o = Eye;
float3 d = normalize(lerp(
lerp(FrustumA, FrustumB, input.texCoord.x),
lerp(FrustumC, FrustumD, input.texCoord.x), input.texCoord.y));
float2 incts = intersectRayBox(o, d);
if(incts.x >= incts.y)
return float4(0, 0, 0, 1);
float t = incts.x + 0.01;
int i = 0;
//3D纹理可视化
for(; i < MaxTraceSteps; ++i)
{
float3 p = o + t * d;
float3 uvw = (p - SDFLower) / SDFExtent;
if(any(saturate(uvw) != uvw))
break;
float sdf = SDF.SampleLevel(SDFSampler, uvw, 0);
float udf = abs(sdf);
if(udf <= AbsThreshold)
break;
t += udf;
}
float color = float(i) / (MaxTraceSteps - 1);
color = pow(color, 1 / 2.2);
return float4(color.xxx*float3(1,1,0), 1);
}
上述代码其实就是一个很简单的采样三维纹理的过程,其中有一点需要注意的就是屏幕采样点生成射线并求交,其余的没啥,这过程在计算Shadow的时候也是这样,只是具体视点和采样方向是具体的采样点和光源数据而已,具体的流程看Shader吧。

三、SDF阴影
cbuffer VSTransform
{
float4x4 WorldToClip;
}
struct VSInput
{
float3 position : POSITION;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
float3 color : COLOR;
};
struct VSOutput
{
float4 position : SV_POSITION;
float3 worldPosition : WORLD_POSITION;
float3 worldNormal : WORLD_NORMAL;
float3 color : COLOR;
};
VSOutput VSMain(VSInput input)
{
VSOutput output;
output.position = mul(float4(input.position, 1), WorldToClip);
output.worldPosition = input.position;
output.worldNormal = input.normal;
output.color = input.color;
return output;
}
cbuffer PSParams
{
float3 LightDirection; float ShadowRayOffset;
float3 LightRadiance; float ShadowK;
float3 SDFLower; int MaxTraceSteps;
float3 SDFUpper; float AbsThreshold;
float3 SDFExtent;
}
Texture3D<float> SDF;
SamplerState SDFSampler;
float max3(float x, float y, float z)
{
return max(x, max(y, z));
}
float min3(float x, float y, float z)
{
return min(x, min(y, z));
}
float2 intersectRayBox(float3 o, float3 d)
{
float3 invD = 1 / d;
float3 n = invD * (SDFLower - o);
float3 f = invD * (SDFUpper - o);
float3 minnf = min(n, f);
float3 maxnf = max(n, f);
float t0 = max3(minnf.x, minnf.y, minnf.z);
float t1 = min3(maxnf.x, maxnf.y, maxnf.z);
return float2(max(0.0f, t0), t1);
}
// 参照大神的文章实现 https://www.iquilezles.org/www/articles/rmshadows/rmshadows.htm
float shadowFactor(float3 o, float3 d)
{
float2 incts = intersectRayBox(o, d);
if(incts.x >= incts.y)
return 1;
float result = 1;
float ph = 1e20;
float t = incts.x;
for(int i = 0; i < MaxTraceSteps; ++i)
{
float3 p = o + t * d;
float3 uvw = (p - SDFLower) / SDFExtent;
float sdf = SDF.SampleLevel(SDFSampler, uvw, 0);
float udf = abs(sdf);
float y = udf * udf / (2.0 * ph);
float m = sqrt(udf * udf - y * y);
result = min(result, ShadowK * m / max(0.0f, t - y));
ph = udf;
//result = min(result, ShadowK * udf / t);
if(udf < AbsThreshold)
return 0;
t += udf;
if(t >= incts.y)
break;
}
return result;
}
float4 PSMain(VSOutput input) : SV_TARGET
{
float3 d = -LightDirection;
float3 o = input.worldPosition + ShadowRayOffset * input.worldNormal;
float shadow = shadowFactor(o, d) ;
float cosFac = max(0.0f, dot(input.worldNormal, -LightDirection));
float3 result = LightRadiance * cosFac * shadow;
return float4(pow(result, 1 / 2.2f), 1);
}
这个其实就是针对具体采样点与光照方向来Tracing阴影的软硬因子,具体采用的近似方式都是一样,可参照闫大神的文章介绍

具体过程其实和采样3D纹理一样,结合实际采样点与方向即可;
具体的算法性能和效果其实和raytracingcount等有很大关系,但是比CSM等方法速度和效果好很多,前提是你生成SDF Texture的数据你能够处理好。
-
K=1
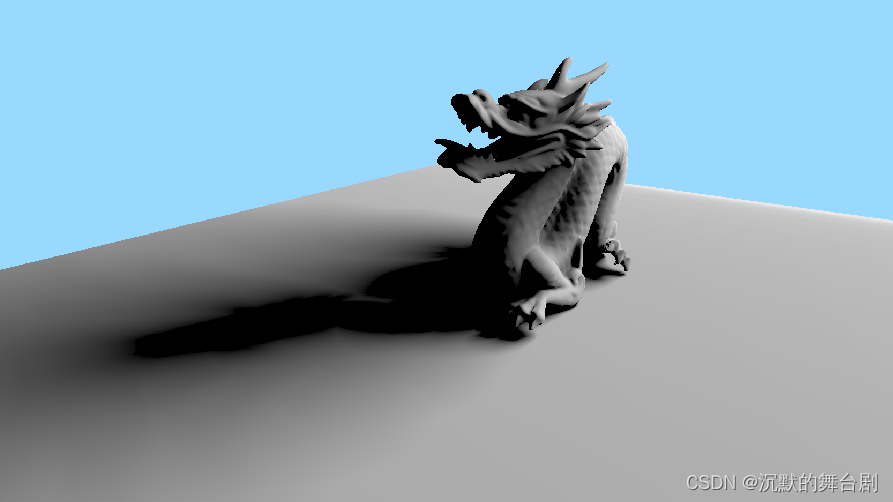
-
K=2

-
K=8
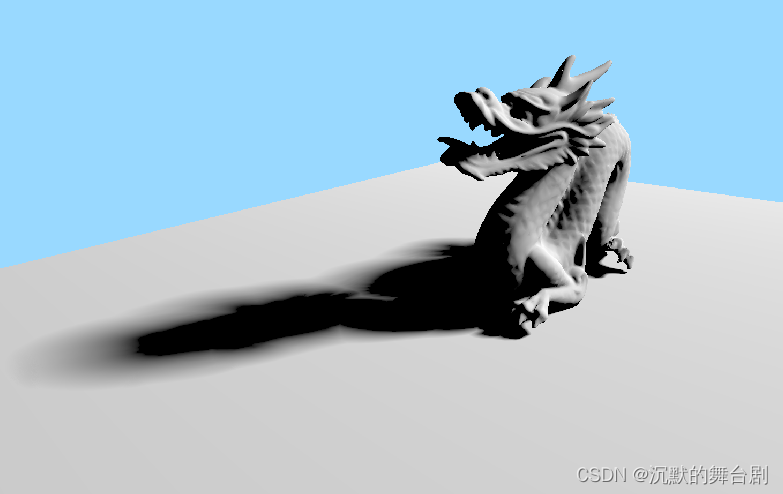
-
K=32
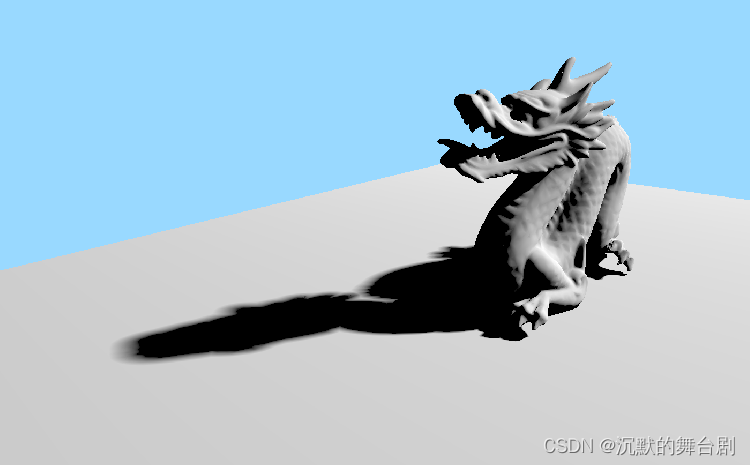

-
K=128
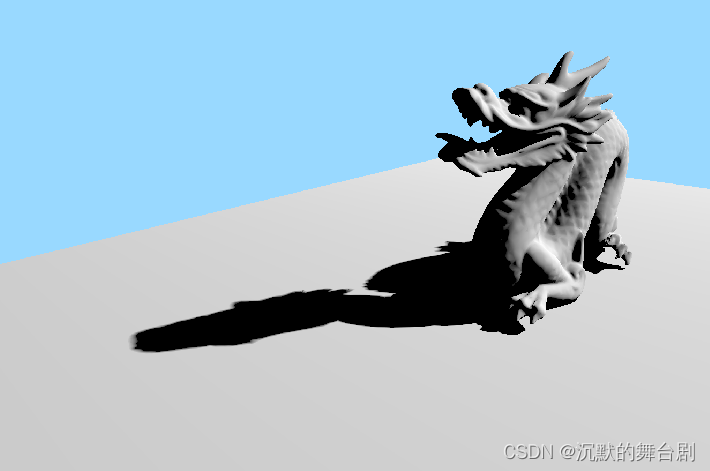
-
K=256