文章目录
- 1.相对定位 relative
- 2.绝对定位 absolute
- 3.固定定位
- 4.display 转换元素
- 5.float浮动
- 6.float产生内容塌陷问题
- 7.overflow
CSS样式学习宝典,关注点赞加收藏,防止迷路哦
在CSS中关于定位的内容是:position:relative | absolute | static | fixed。static 没有特别的设定,遵循基本的定位规定,不能通过z-index进行层次分级。在文本流中,任何一个元素都被文本流所限制了自身的位置,但是通过CSS我们依然使得这些元素可以改变自己的位置,我们可以通过float来让元素浮动,我们也可以通过margin来让元素产生位置移动。
1.相对定位 relative
定位的种类,默认是static
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>定位:相对定位 relative</title>
<style>
.gg
{
width:200px;
height:200px;
border:solid 1px red;
}
.c1
{background:violet;}
.c2
{
background:tan;
position:relative;
top:10px;
left:100px;
z-index:2;
}
.c3
{background:blue;}
.c4
{background:green;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--
相对定位: 参考点是他自己本身,相对于原始的位置进行定位,本身原始位置指的是盒子设置好后,默认在浏览器的位置;
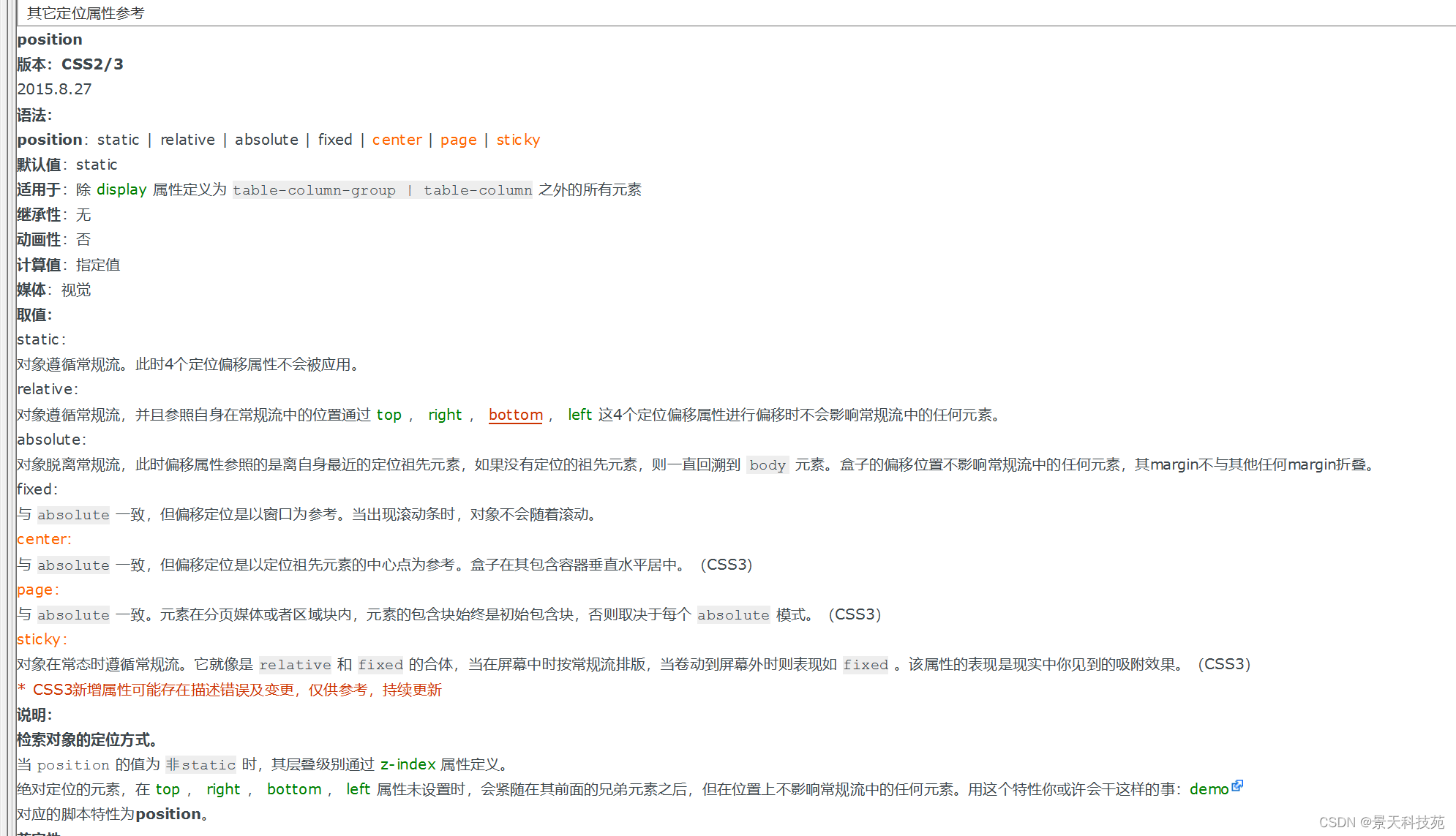
如果添加了定位:无论是添加(相对,绝对,固定)属性,添加之后会增加额外的其他属性:
z-index 控制层叠关系: 值越大越在上层,值越小越在下层
同一个层叠上下文中,层叠级别相同的两个元素,依据它们在HTML文档流中的顺序,写在后面的将会覆盖前面的。
不同层叠上下文中,元素的显示顺序依据祖先的层叠级别来决定,与自身的层叠级别无关。
left
top
right
bottom
z-index
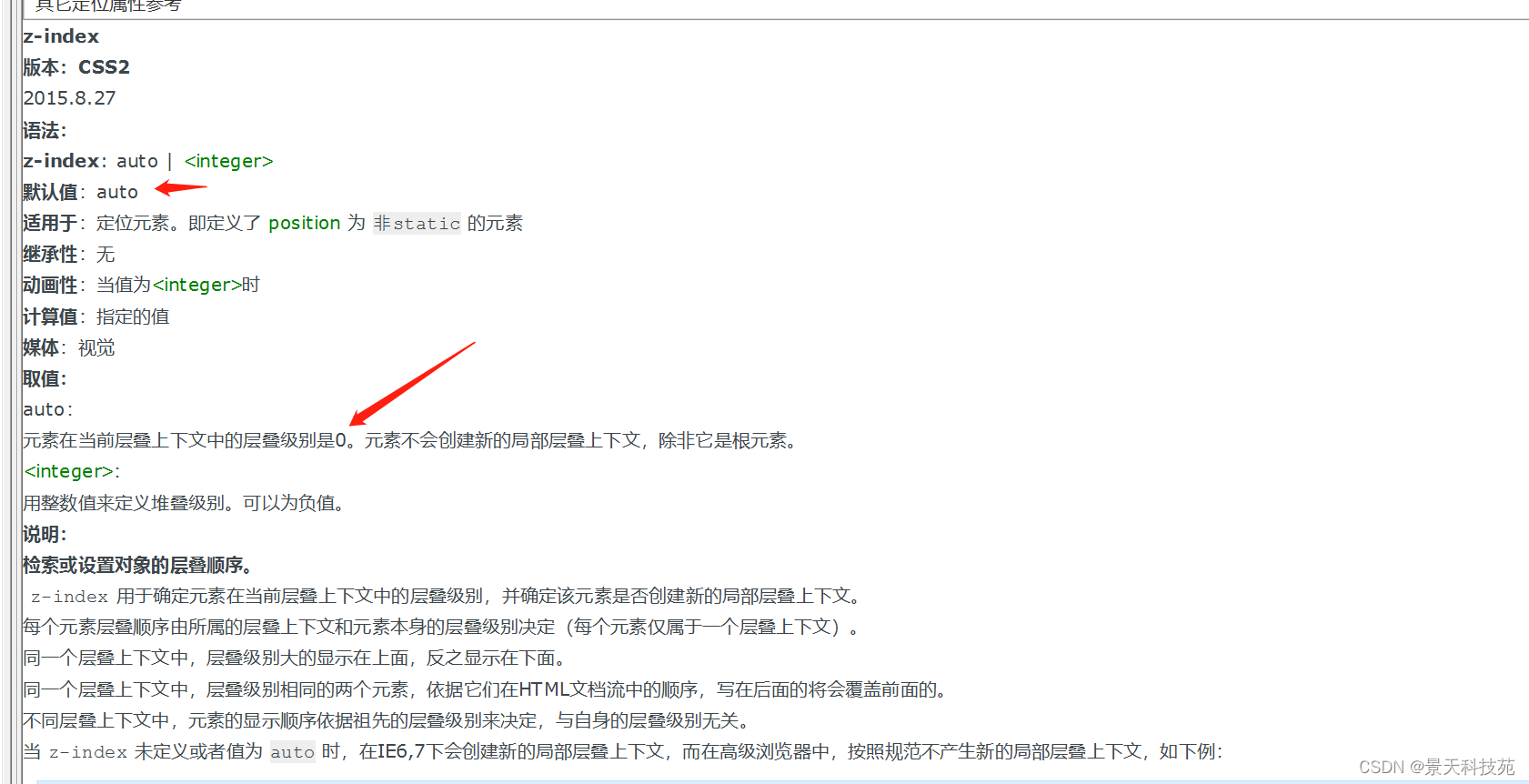
z-index 控制层叠关系: 值越大越在上层,值越小越在下层,默认是0
-->
<div class="c1 gg"></div>
<div class="c2 gg"></div>
<div class="c3 gg"></div>
<div class="c4 gg"></div>
</body>
</html>
2.绝对定位 absolute
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>定位:绝对定位 absolute</title>
<style>
.gg
{width:200px;height:200px;border:solid 1px red;}
.big
{
width:1000px;
height:1000px;
border:solid 1px red;
margin:100px 220px;
}
.c1
{
background:violet;
/* 无效 */
position: relative;
}
.c2
{
background:tan;
position: absolute;
top:0px;
left:0px;
/* bottom:0px;
right:0px; */
/* z-index:-1; */
}
.c3
{background:blue;}
.c4
{background:green;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--
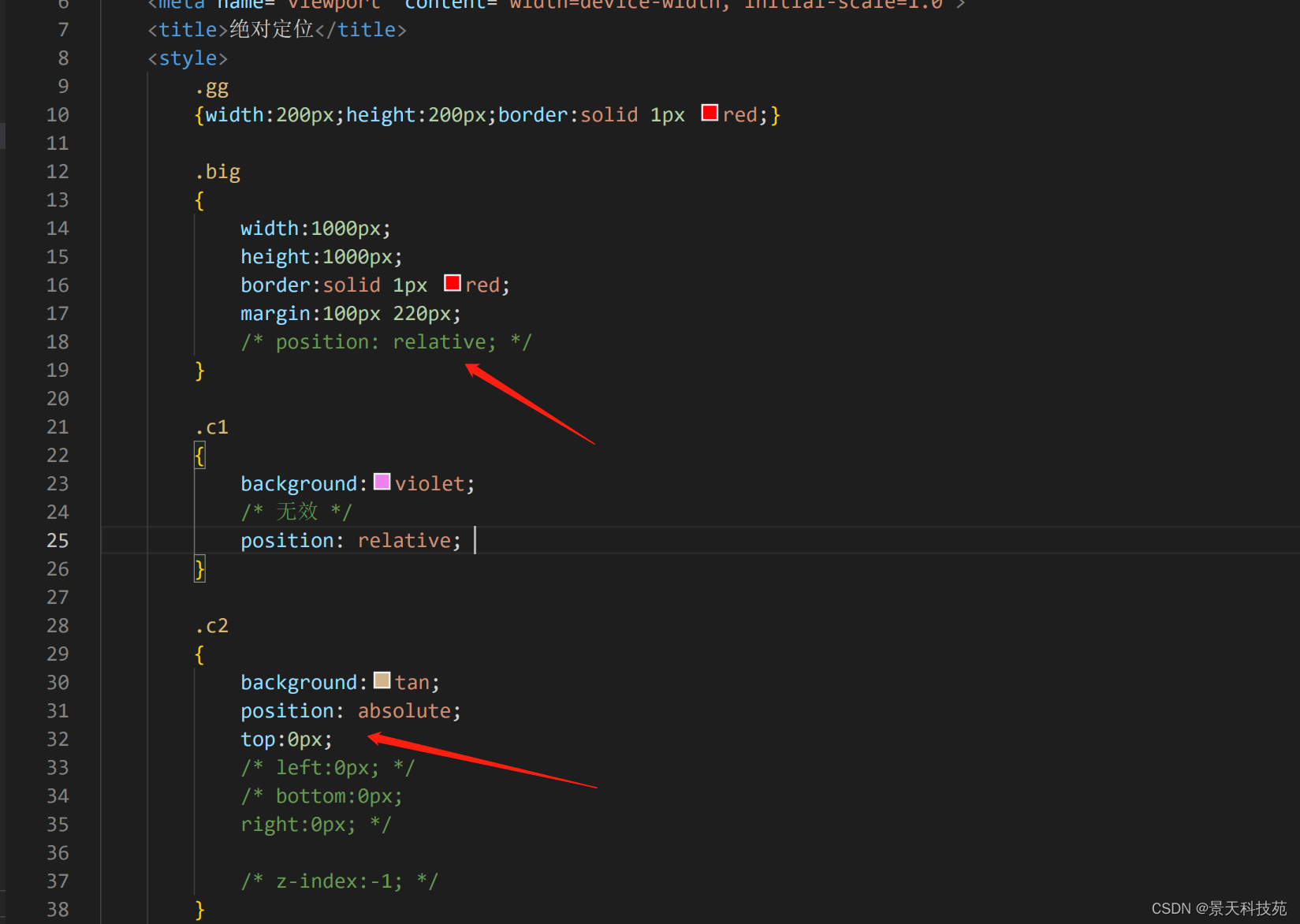
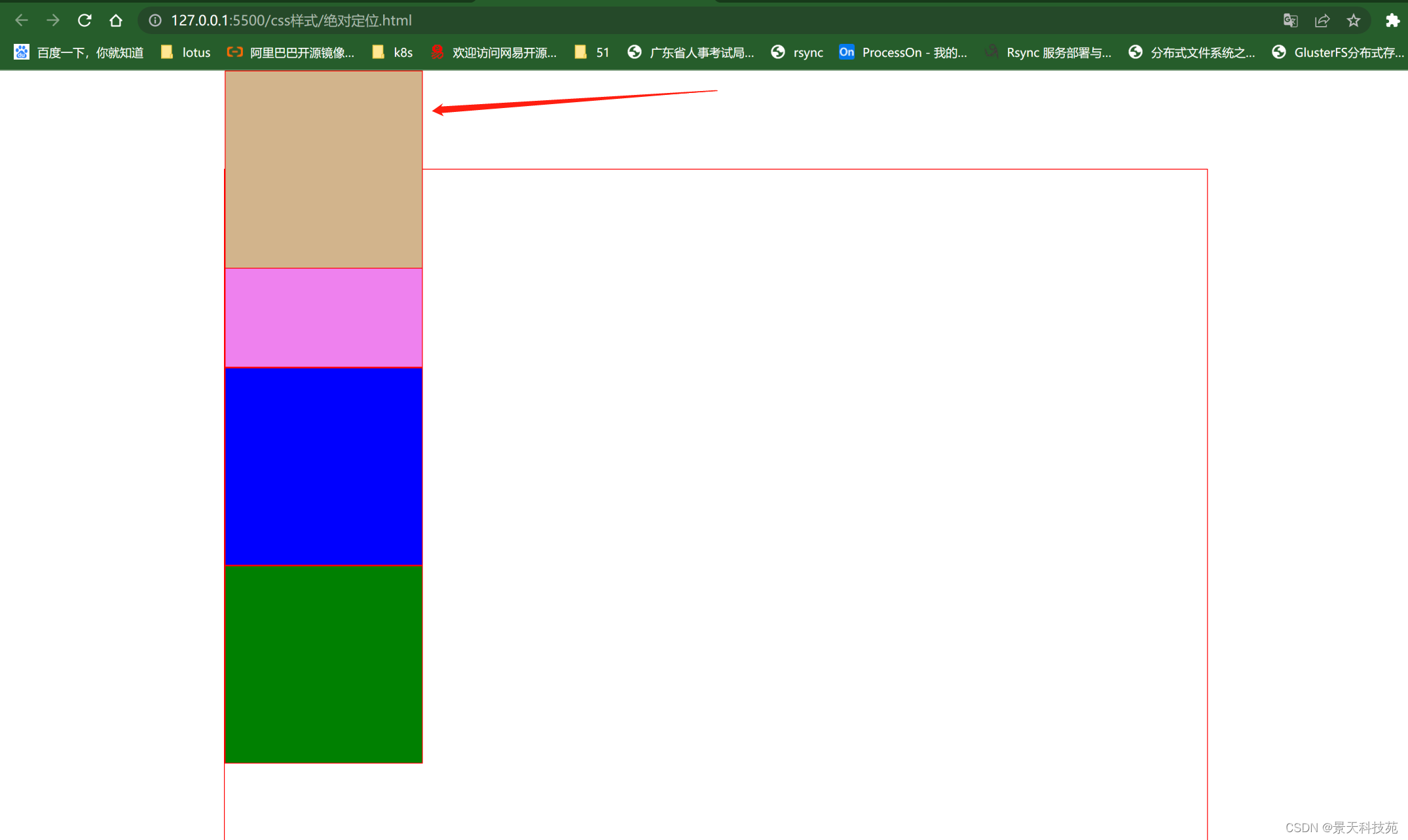
绝对定位:参考点默认参考的是body
效果:脱离文档流,后面的内容自动补位
使用:绝对定位会参照父级的相对定位进行移动,如果父级中没有relative,相对于body进行定位;
(1)把想要的父级元素变成relative
(2)把要定位的元素变成 absolute
-->
<div class="big">
<div class="c1 gg"></div>
<div class="c2 gg"></div>
<div class="c3 gg"></div>
<div class="c4 gg"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
父级没有relative,设置了absolute的元素会相对body进行定位
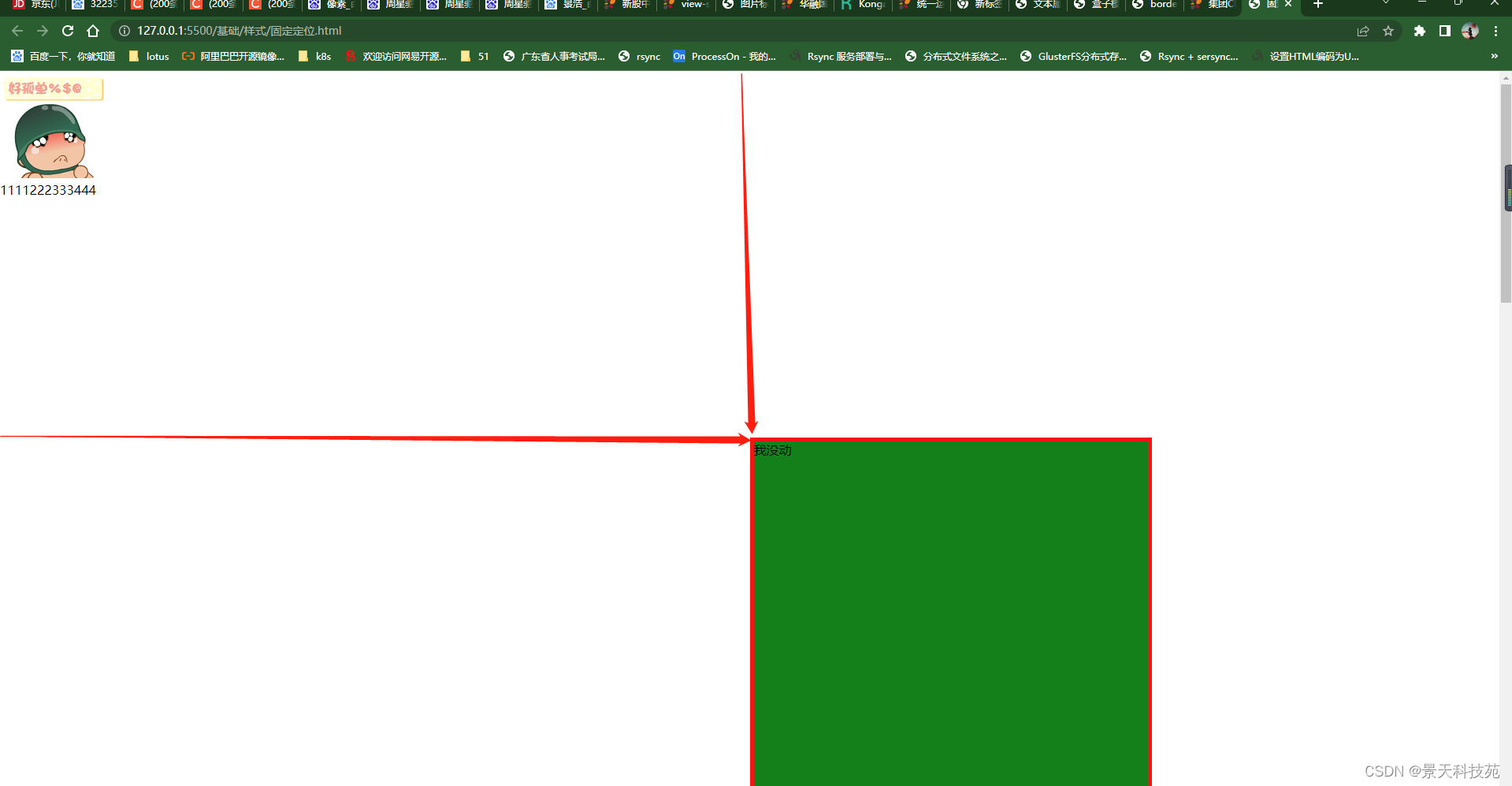
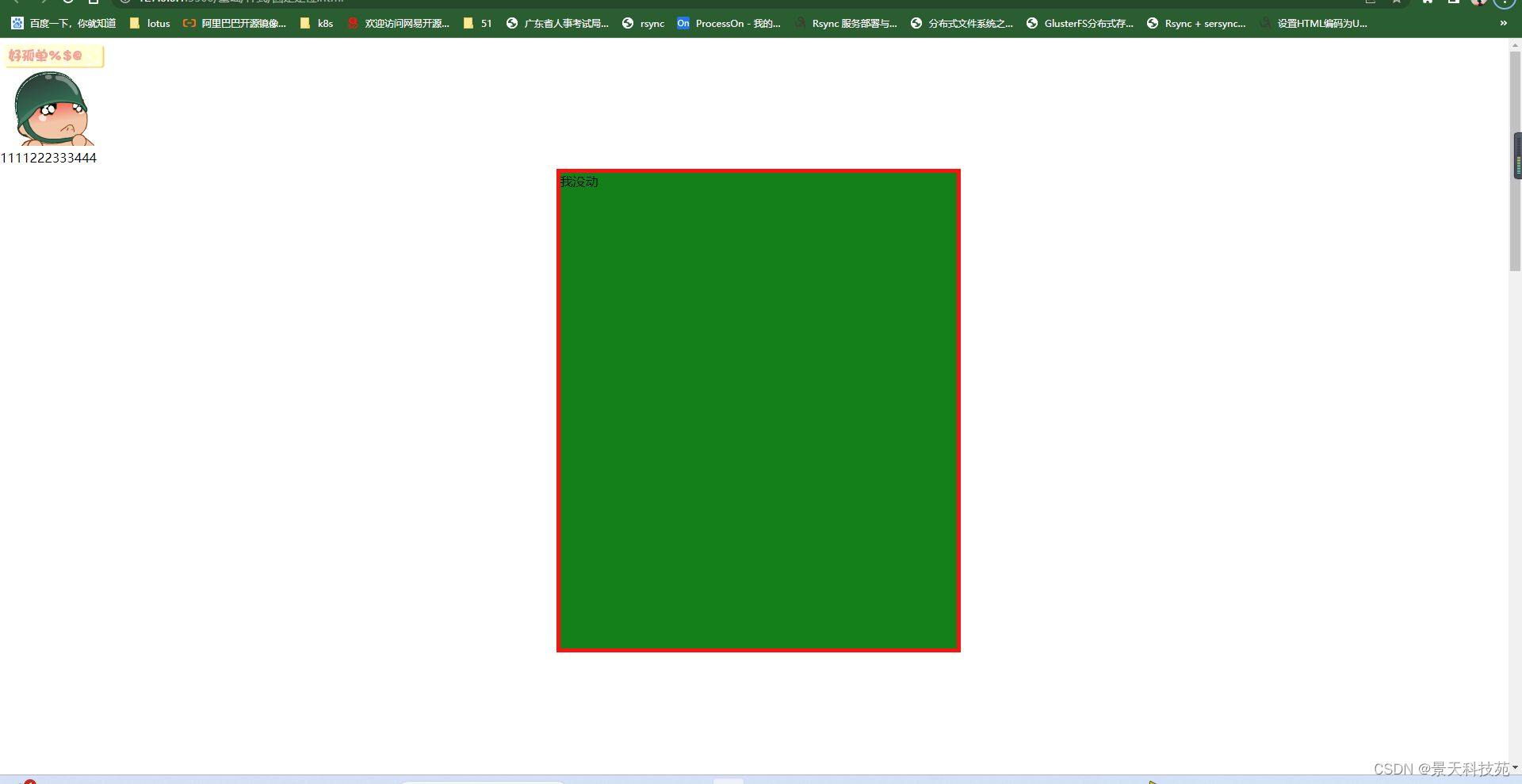
3.固定定位
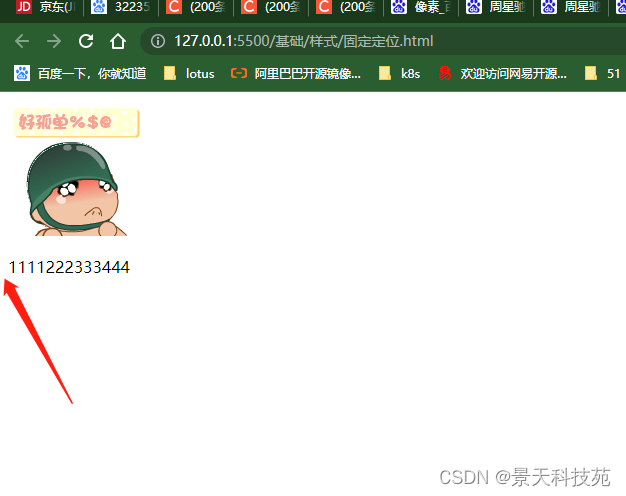
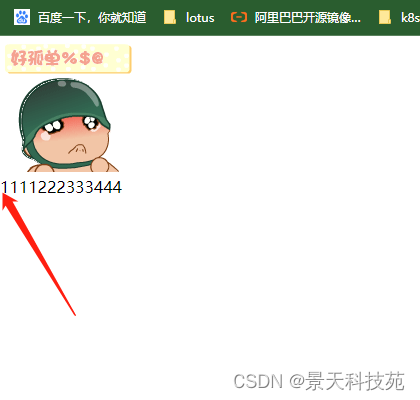
fixed固定页面,滑动页面该位置不动
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>定位:固定定位 fixed</title>
<style>
/* *号代表通配选择符,代表所有标签,默认标签中含有默认的间距,要在一开始的时候全部去掉; */
默认标签离左边栏有间距
*
{margin:0px;padding:0px;}
加上* 所有通配符设置间距为0,离左边栏不再有间距
body
{height:2000px;}
.c1
{
width:500px;
height: 600px;
border:solid 1px red;
background-color: green;
position: fixed;
/* 相对于左上角定点进行定位 */
left:50%;
margin-left:-250px;
top:50%;
margin-top:-300px;
}
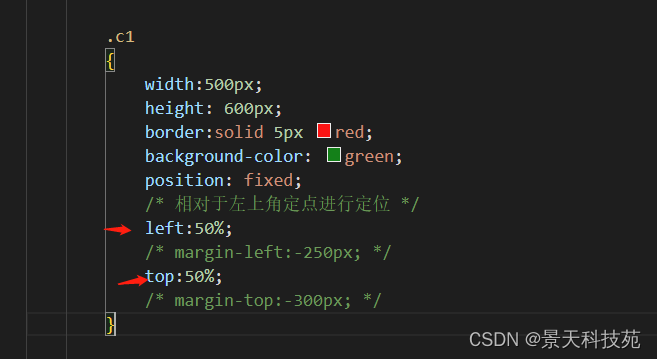
把多移动的移回来
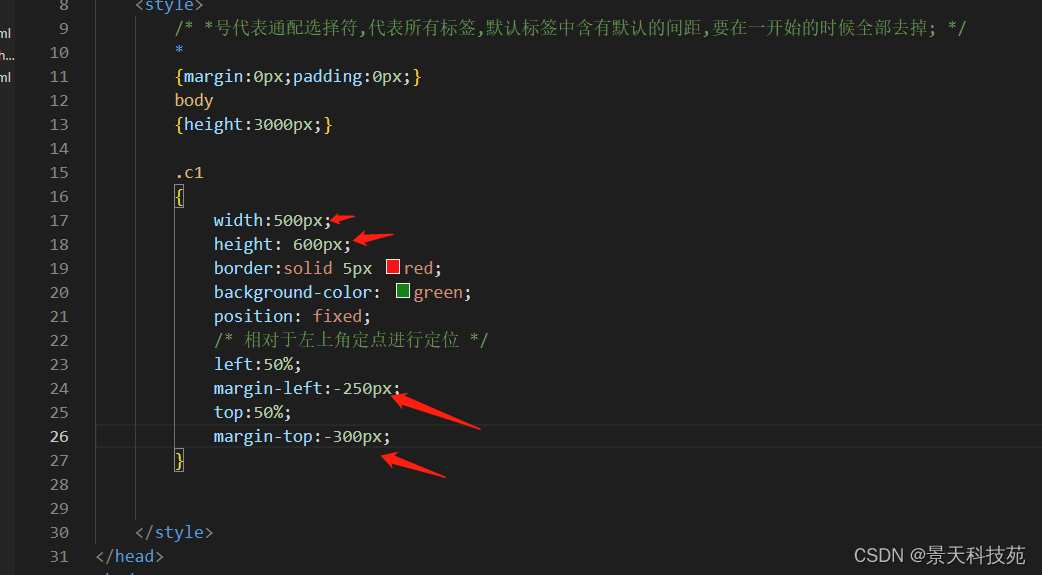
然后才能居中
过度属性
/*
<' transition-property '>: 检索或设置对象中的参与过渡的属性
<' transition-duration '>: 检索或设置对象过渡的持续时间
<' transition-timing-function '>: 检索或设置对象中过渡的动画类型
<' transition-delay '>: 检索或设置对象延迟过渡的时间
*/
img
{
position:fixed;
bottom:20px;
left:-100px;
transition: all 1s ease 0.1s;
}
img:hover
{
left:0px;
background-color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<img src="images/xiao.jpg"/>
<div class="c1">我没动</div>
<p>1111222333444</p>
</body>
</html>
4.display 转换元素
行内,块状,行内块状元素之间的转换
使用语法:
display : 要转换的元素类型(block inline inline-block)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>display 转换元素</title>
<style>
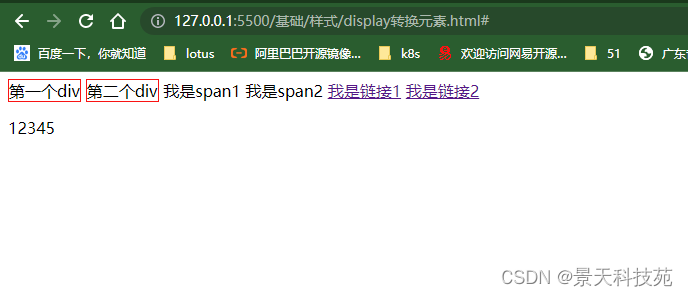
div
/* display:inline; 转换成行内元素 */
{display:inline;border:solid 1px red;width:1000px;height:20px;}
将块状元素设置成行内元素后,设置的高和宽已失效
span
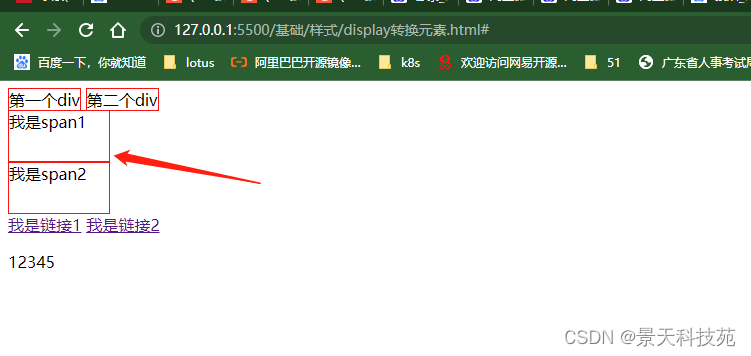
/* display:block; 转换成块状元素 */
{display:block;width:100px;height:50px;border:solid 1px red;}
行内元素转换成块状元素后,可以设置高和宽,并且独占一行
a
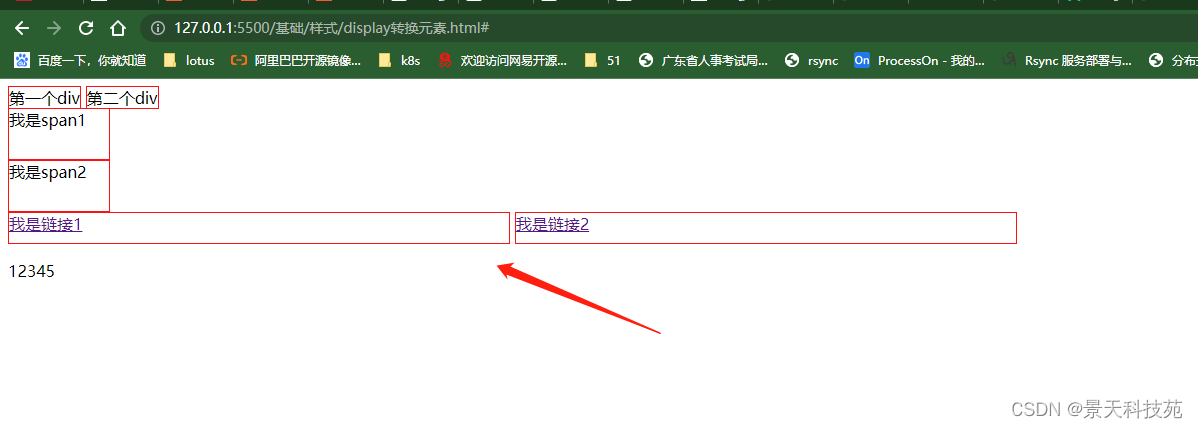
/* display:inline-block; 转换成行内块状元素 */
{display:inline-block;width:500px;height:30px;border:solid 1px red;}
行内元素转换成行内块状元素,可以设置高和宽
p
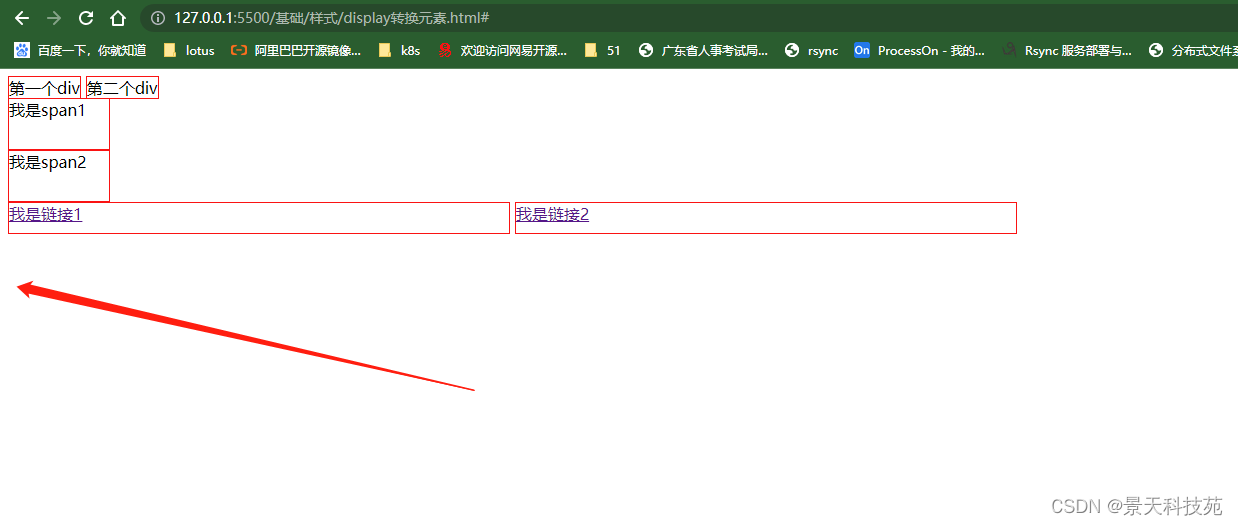
/* display:none 隐藏元素 */
{display:none;}
p元素隐藏了
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 元素的分类:
块状元素 : block
行内元素 : inline
行内块状元素 : inline-block
-->
<div>第一个div</div>
<div>第二个div</div>
<span>我是span1</span>
<span>我是span2</span>
<a href="#">我是链接1</a>
<a href="#">我是链接2</a>
<p>12345</p>
</body>
</html>
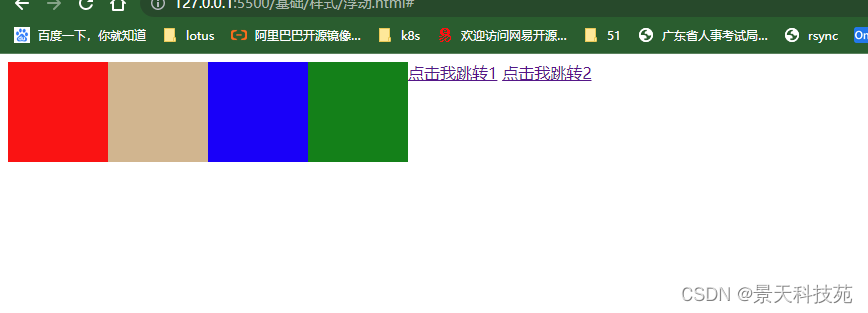
5.float浮动
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>float 浮动</title>
<style>
.content
{width:700px;clear:both;}
.content .c1
{background: red;width:100px;height:100px;float:left;}
.content .c2
{background: tan;width:100px;height:100px;float:left;}
.content .c3
{background:blue;width:100px;height:100px;float:left;}
.content .c4
{background:green;width:100px;height:100px;float:left;}
div默认是从上到下,垂直排列,使用float之后,从左向右横向排列
是设置了float下面的元素脱离文档流,压在了设置float元素的下面
.content2
{width:700px;height:500px;border:solid 1px red;clear:both;}
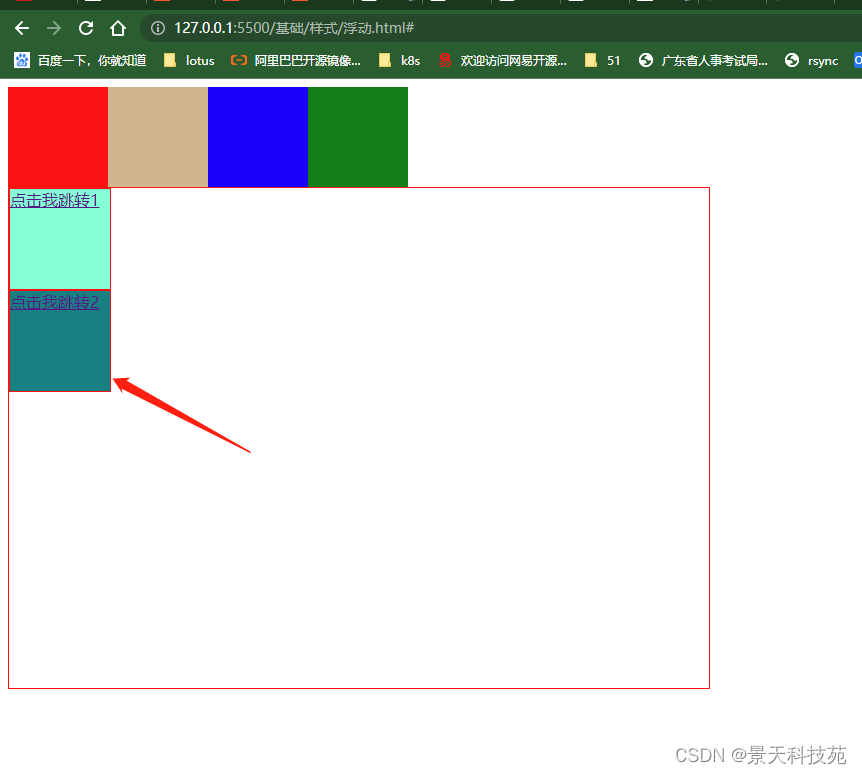
#a1
{float:left;width:100px;height:100px;border:solid 1px red;}
#a2
{display:block;width:100px;height:100px;border:solid 1px red;background: teal;clear: both;}
不加clear:both,a2设置的属性没显示出来
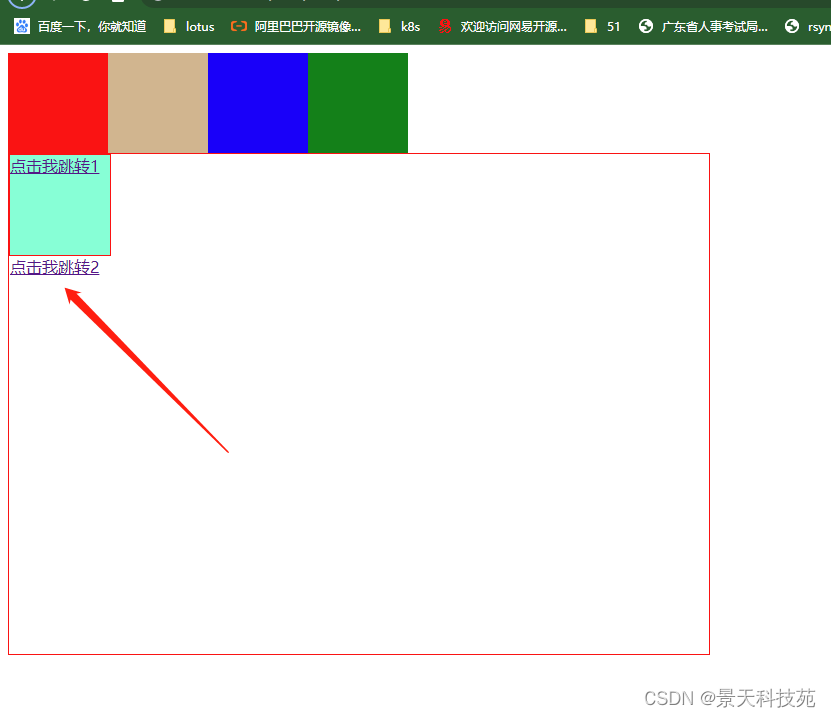
加了clear:both。显示正常
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--
# ###块状元素浮动:
float:left 向左浮动 ,元素脱离原始文档流,后面的内容自动补齐;
float:right 向右浮动 ,元素脱离原始文档流,后面的内容自动补齐;
目的: 让块状元素在一排显示
clear:both; 清除两边的浮动 在不需要浮动的地方加
-->
<div class="content">
<div class="c1"></div>
<div class="c2"></div>
<div class="c3"></div>
<div class="c4"></div>
</div>
<!--
# ###行内元素浮动:
如果对行内元素进行浮动:
默认会把行内元素升级成行内块状元素,可以设置宽和高
消除浮动产生的影响:clear:both;
-->
<div class="content2">
<a href="#" id="a1">点击我跳转1</a>
<a href="#" id="a2">点击我跳转2</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
6.float产生内容塌陷问题
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>float 会产生内容塌陷问题</title>
<style>
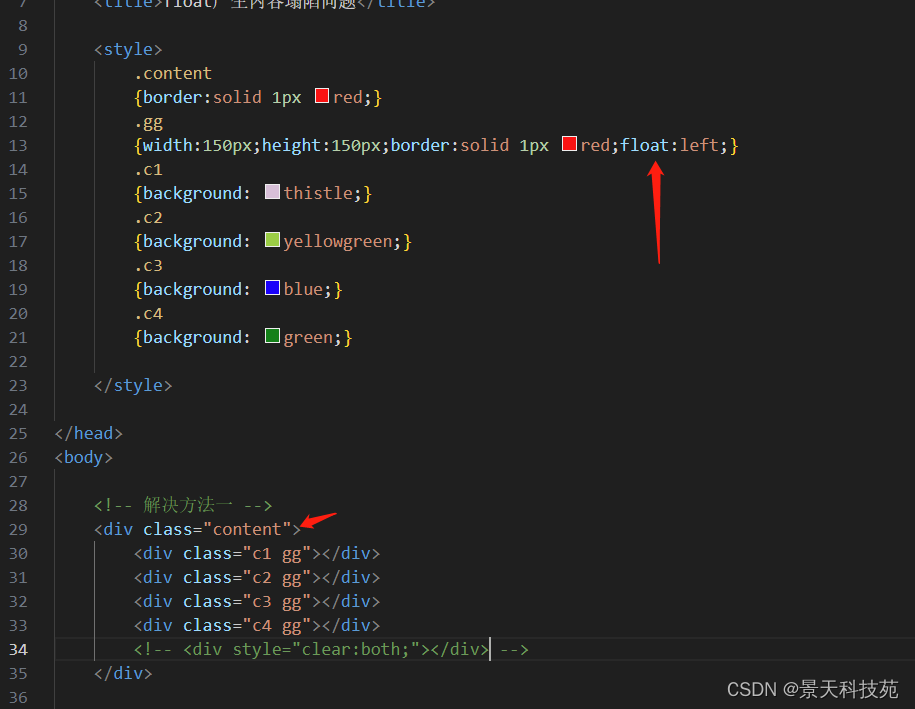
.content
{border:solid 1px red;}
.gg
{width:150px;height:150px;border:solid 1px red;float:left;}
.c1
{background: thistle;}
.c2
{background: yellowgreen;}
.c3
{background: blue;}
.c4
{background: green;}
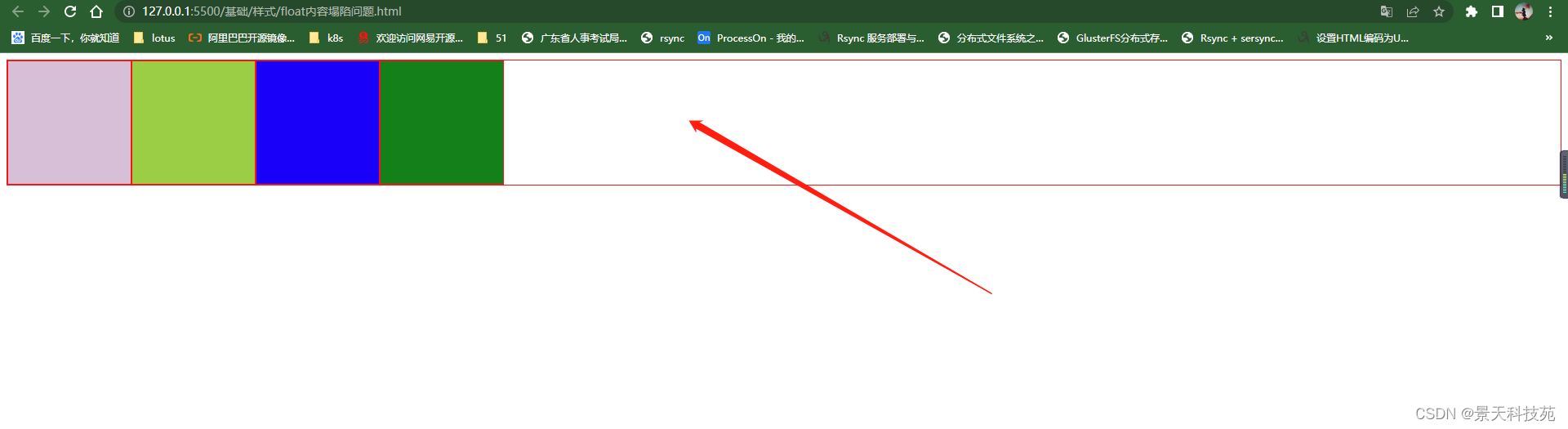
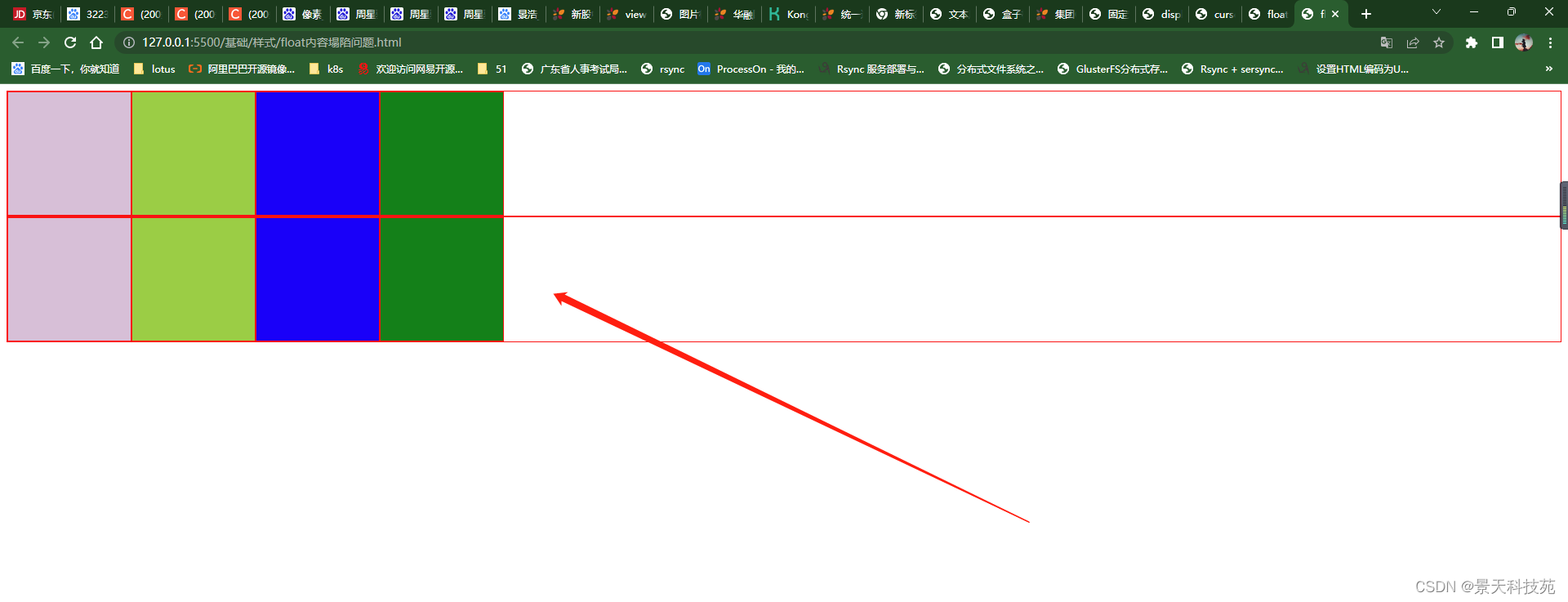
大div里面几个小div浮动,导致大盒子没撑开
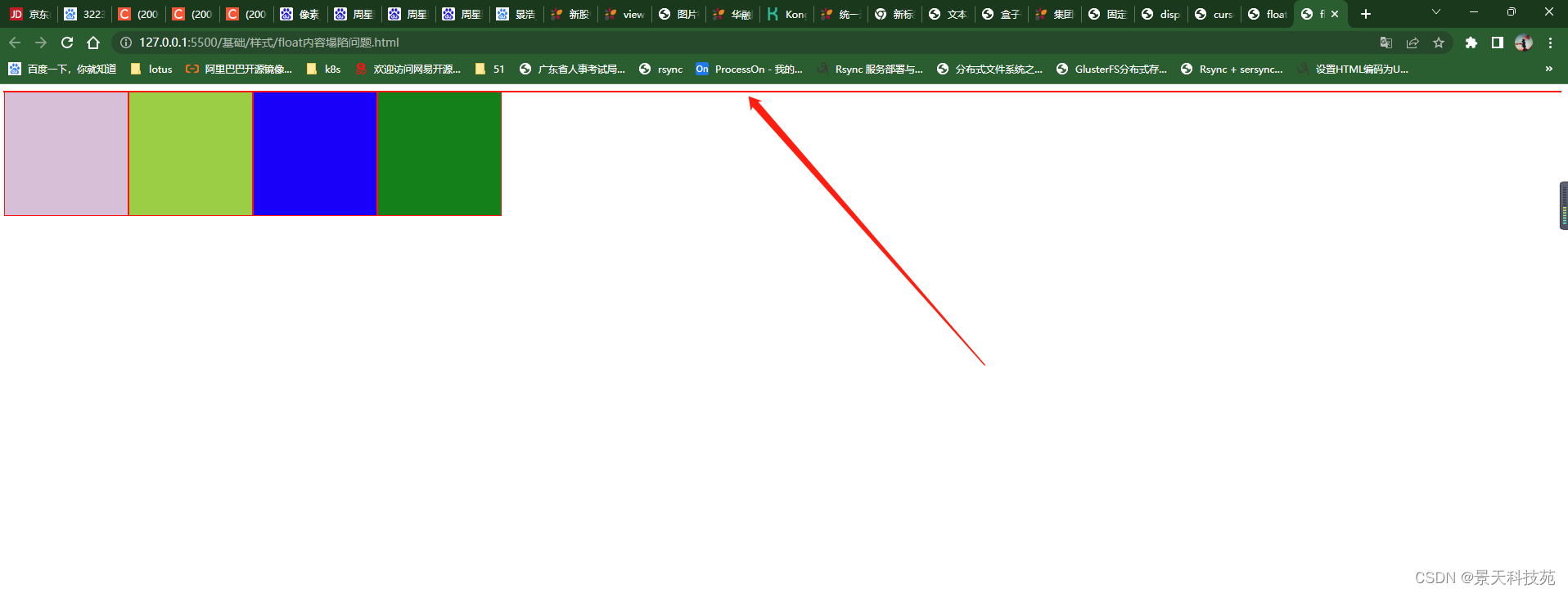
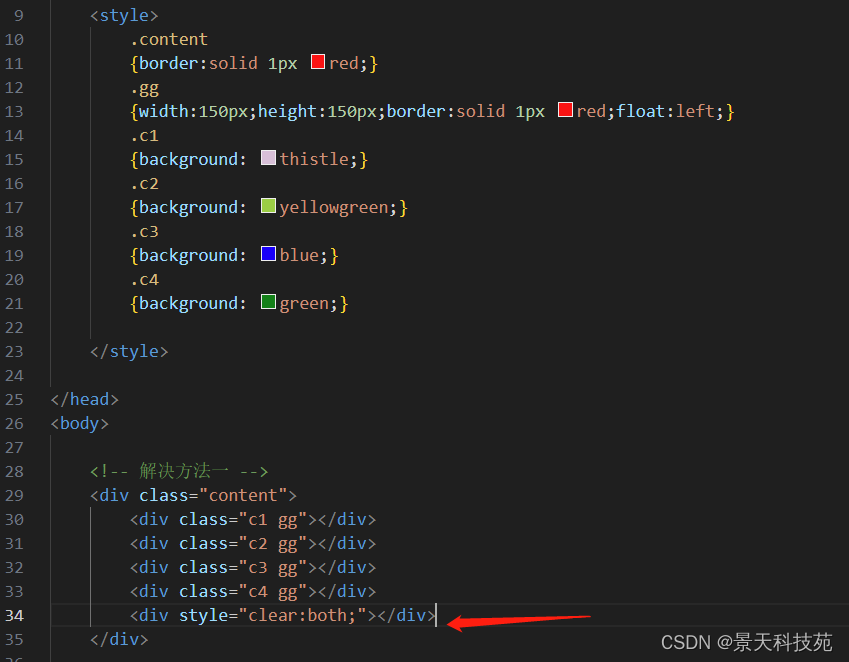
解决办法一:在html里面解决
在小div里面增加一个div 只设置style clear:both
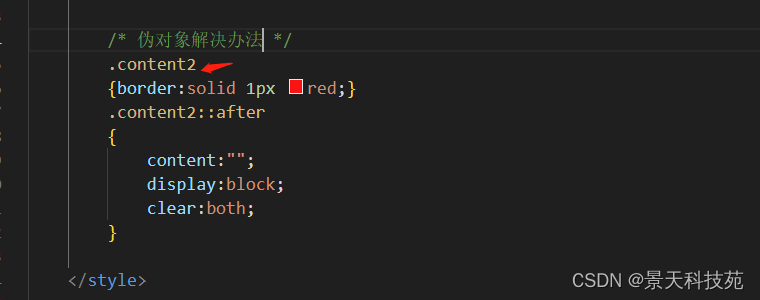
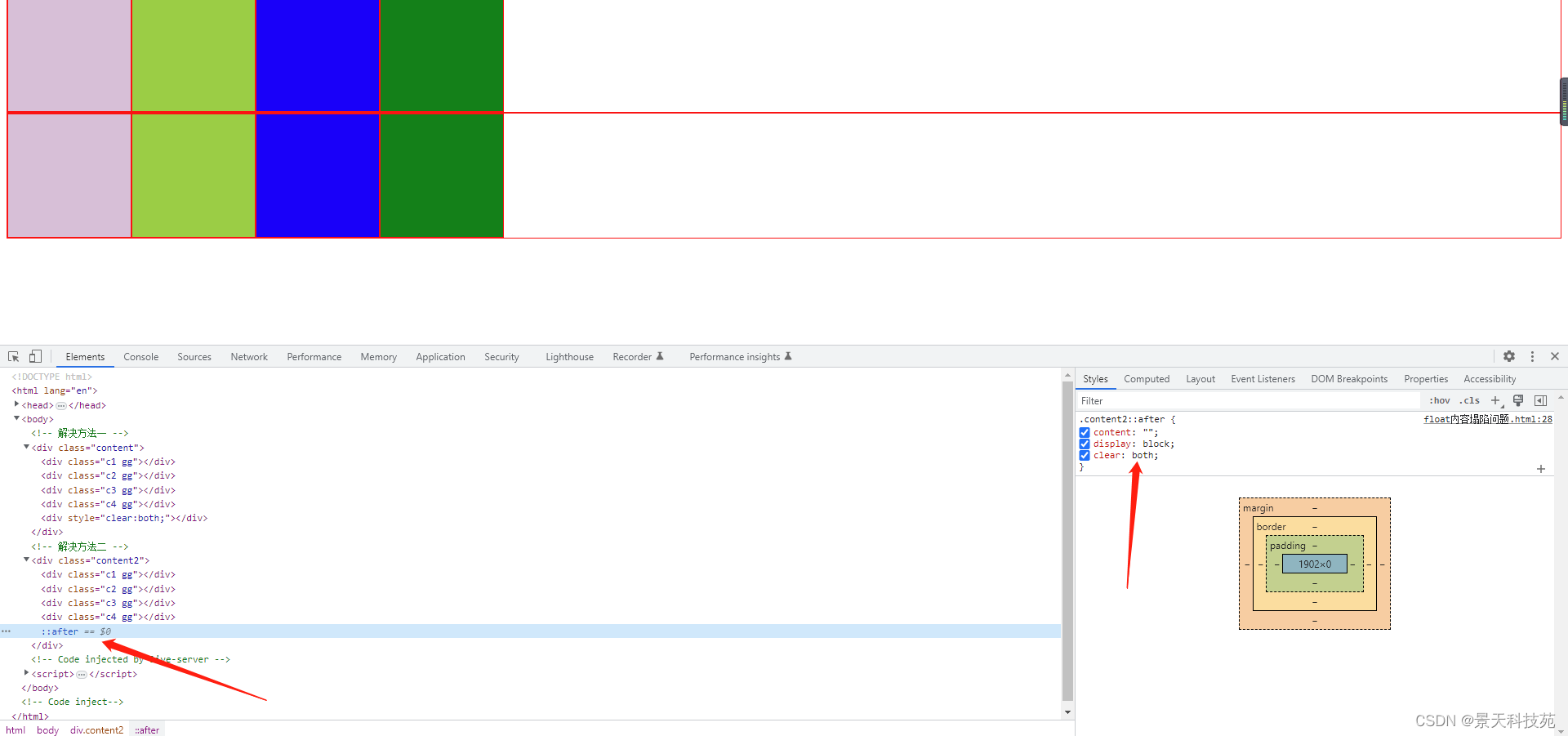
.content2
{border:solid 1px red;}
.content2::after
{
content:"";
display:block;
clear:both;
}
解决方法二:在CSS里面通过伪对象来解决
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 解决方法一 -->
<div class="content">
<div class="c1 gg"></div>
<div class="c2 gg"></div>
<div class="c3 gg"></div>
<div class="c4 gg"></div>
<div style="clear:both;"></div>
</div>
<!-- 解决方法二 -->
<div class="content2">
<div class="c1 gg"></div>
<div class="c2 gg"></div>
<div class="c3 gg"></div>
<div class="c4 gg"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
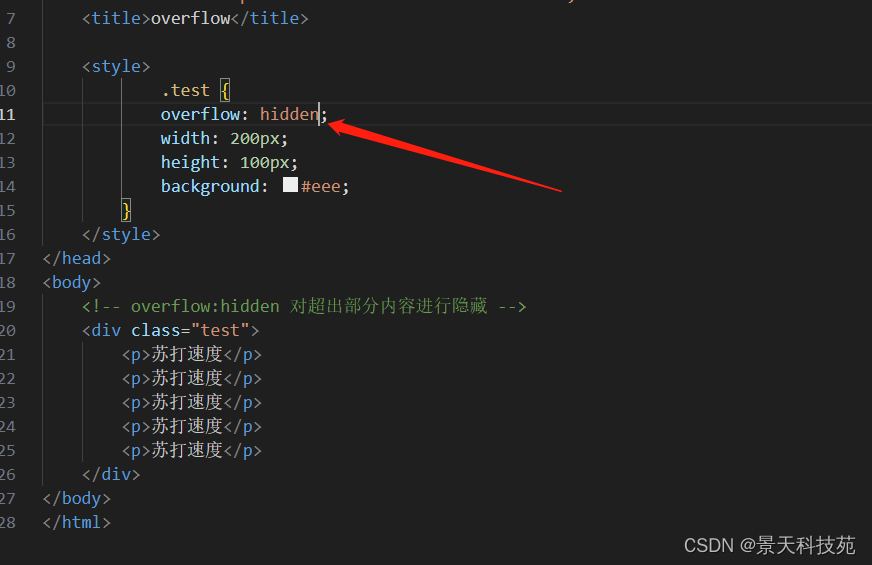
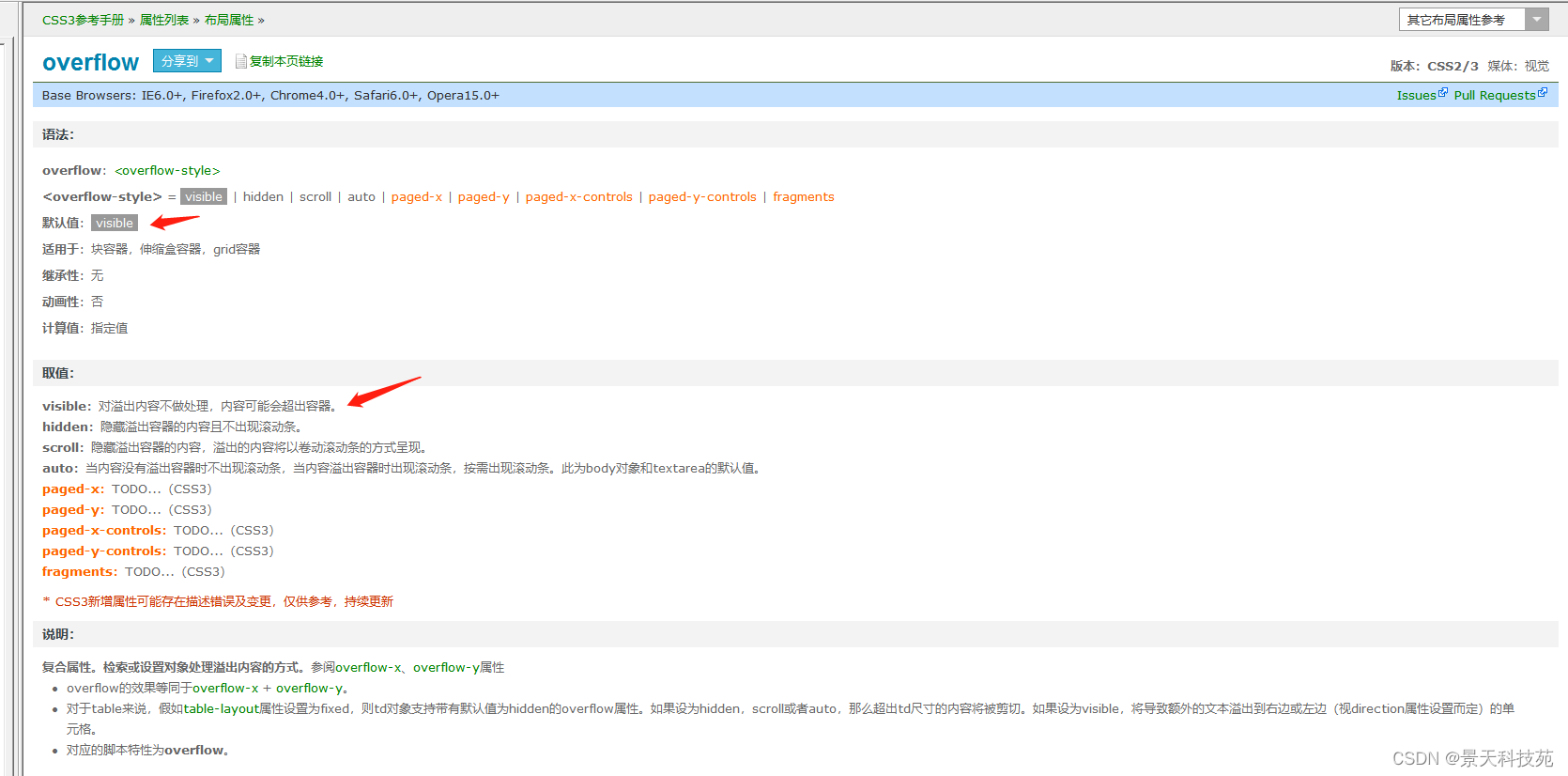
7.overflow
对超出部分内容的处理
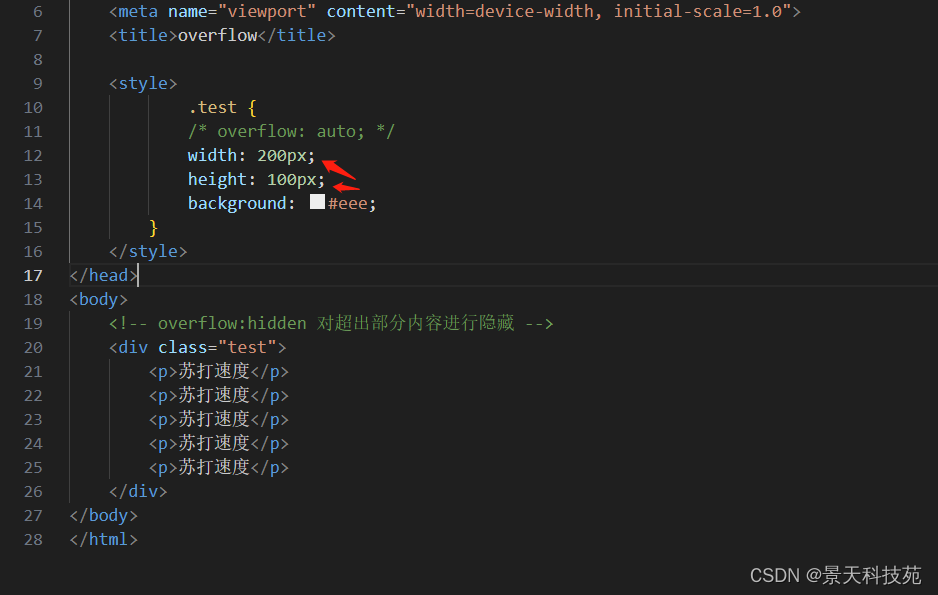
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<style>
.test {
overflow: hidden;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background: #eee;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
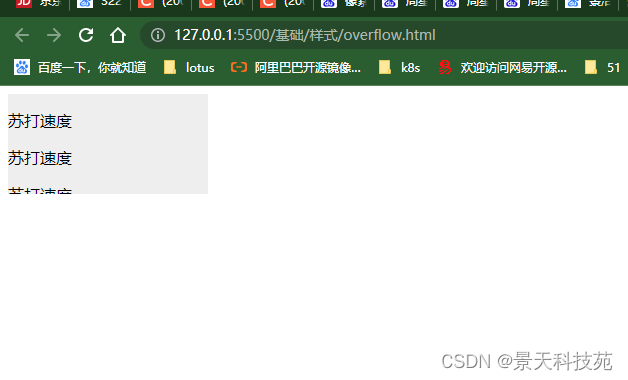
<!-- overflow:hidden 对超出部分内容进行隐藏 -->
<div class="test">
<p>苏打速度</p>
<p>苏打速度</p>
<p>苏打速度</p>
<p>苏打速度</p>
<p>苏打速度</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
对于超过边界的内容,默认是visible 对超出边框的内容不做处理,显示出来。这样很不美观
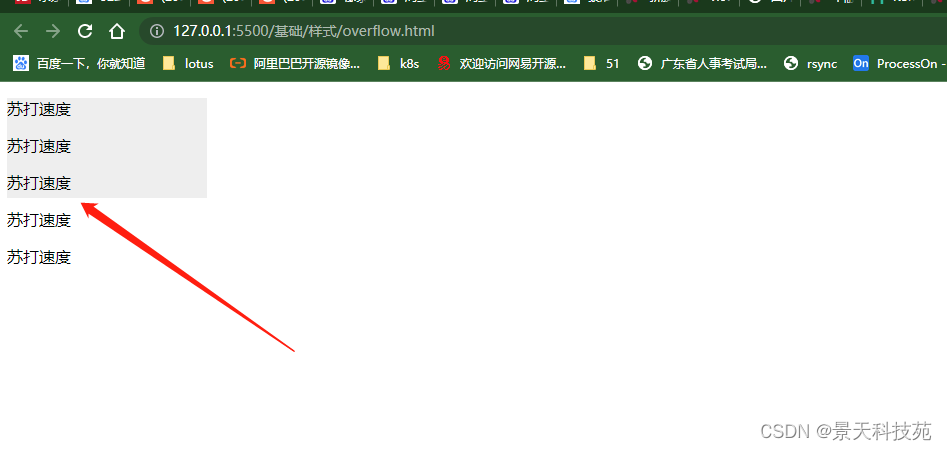
对超出的内容可以设置隐藏,或者滚动条显示auto:当内容没有溢出容器时不出现滚动条,当内容溢出容器时出现滚动条,按需出现滚动条。此为body对象和textarea的默认值。
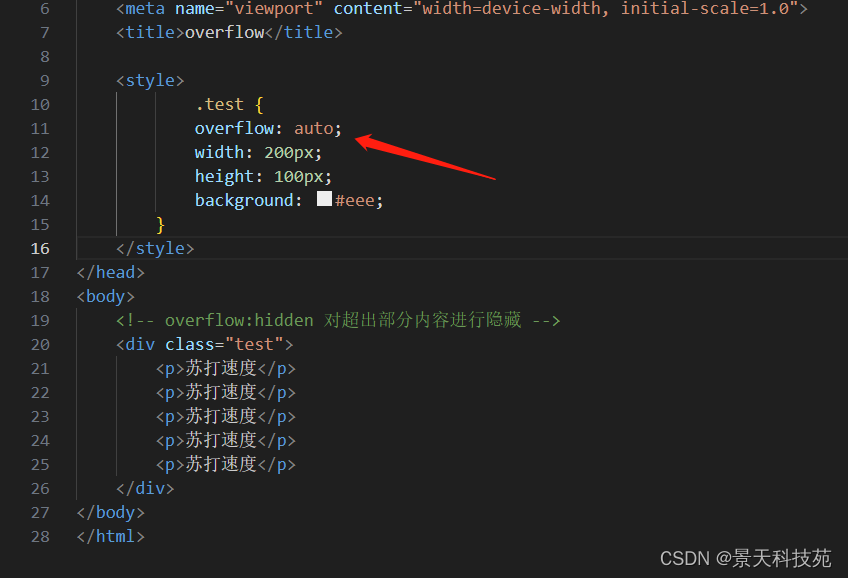
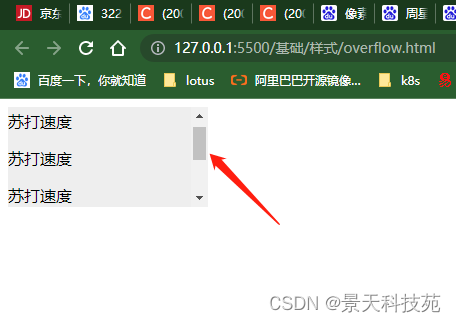
hidden:隐藏溢出的内容