一.Object类
1.概述:
Object类:是java中所有的类共同的父类
1、观察包所属后发现,Object类属于java.lang包下的类,今后使用的时候,不需要进行导包
2.构造方法
Object() 无参构造方法
3.Object类的成员方法
(1)public int hashCode() 返回对象的哈希码值
(2)public final Class getClass() 获取一个类对应的Class对象
(3)public String toString() 输出一个对象,实际上输出的是对象调用的toString()方法
演示:
/*
Object类:是java中所有的类共同的父类
1、观察包所属后发现,Object类属于java.lang包下的类,今后使用的时候,不需要进行导包
构造方法:
Object() 无参构造方法
成员方法:
public int hashCode() 返回对象的哈希码值。
public final Class getClass() 获取一个类对应的Class对象
public String toString() 输出一个对象,实际上输出的是对象调用的toString()方法
一个标准类的最终写法:
1、成员变量私有化
2、构造方法(无参/所有参数)
3、getXxx()和setXxx()
4、toString()
*/
class Student {
//包含了继承自Object类的方法
String name;
int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override //toString()方法的重写
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
public class ObjectDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//public int hashCode() 返回对象的哈希码值。
Student s1 = new Student();
// System.out.println(s1.hashCode());
Student s2 = new Student();
// System.out.println(s2.hashCode());
// public final Class getClass() 获取一个类对应的Class对象
Class c1 = s1.getClass();
System.out.println(c1.hashCode()); //1163157884
System.out.println(c1); //class com.shujia.day10.Student
Class c2 = s2.getClass();
System.out.println(c2.hashCode()); //1163157884
System.out.println(c2); //class com.shujia.day10.Student
//public String toString() 输出一个对象,实际上输出的是对象调用的toString()方法
System.out.println(s1.toString()); //com.shujia.day10.Student@4554617c
/*
在Java中,所有的对象都是继承自Object,自然继承了toString方法,
在当使用System.out.println()里面为一个对象的引用时,自动调用toString方法将对象打印出来。
如果重写了tostring方法则调用重写的toString 方法。
*/
Student s3 = new Student("小花", 23);
System.out.println(s3);
}
}
由上述代码中toString()方法的重写,引出了一个标准类的最终写法(3.0):
( 在第五天中曾提到了1.0和2.0写法)
一个标准类的最终写法:
1、成员变量私有化
2、构造方法(无参/所有参数)4.
3、getXxx()和setXxx()
4、toString()
(4)public boolean equals(Object obj)
默认比较对象地址值(与==相同),若想比较对象中的具体值,可重写该方法(右键鼠标Generate自动生成)
演示:
/*
public boolean equals(Object obj)
*/
import java.util.Objects;
class Student2 {
public Student2() {
}
public Student2(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
String name;
int age;
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) { //equals()方法的重写
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student2 student2 = (Student2) o;
return age == student2.age && Objects.equals(name, student2.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
}
public class ObjectDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student2 s1 = new Student2("小明",12);
Student2 s2 = new Student2("小李",15);
//==比较引用数据类型的时候,比较的是地址值
System.out.println(s1==s2); //false
//Object类中的equals方法默认比较的是对象的地址值
/*源码:
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}
*/
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //false
/*
//要想比较两个对象中的成员变量值是否一样
//只需要自己对象所属类中重写equals方法,改写成比较成员变量值就可以了
//自动生成即可
*/
Student2 s3 = new Student2("小4",12);
Student2 s4 = new Student2("小4",12);
System.out.println(s3.equals(s4)); //true
//拓展内容:String类中的equals也是被重写的
String a = "hello";
String b = new String("hello");
System.out.println(a==b); //false 地址值不同
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(a)); //a的地址值 1163157884
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(b)); //b的地址值 1956725890
System.out.println(a.equals(b)); //true 比较的是具体值,说明String类中重写了String方法
}
}
(5)protected void finalize()
用于垃圾回收
(6)protected Object clone()
克隆/拷贝 而且是浅拷贝
演示:
/*
protected Object clone() 拷贝
浅拷贝 √ 元素的地址值未被拷贝,指向本身元素的地址
深拷贝
首先,如果此对象的类不实现接口Cloneable ,则抛出CloneNotSupportedException 。
Cloneable中什么成员都没有,这样的接口,在java中称之为标记接口
*/
class Demo {
int a = 20;
}
class Student3 implements Cloneable {
String name;
int age;
Demo demo;
public Student3() {
}
public Student3(String name, int age, Demo demo) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.demo = demo;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student3{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", demo=" + demo +
'}';
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
public class ObjerctDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Demo demo = new Demo();
Student3 s3 = new Student3("许嵩", 18, demo);
Object o = s3.clone();
Student3 o1 =(Student3)o; //由于拷贝的对象是Object类,无法获取Student3中的成员变量demo,因此向下转型
//获取s3和克隆对象中成员变量demo的地址值,如果相同则说明该克隆为浅拷贝,不同则为深拷贝
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s3.demo)); //1163157884
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(o1.demo)); //1163157884
//也可以直接获取
System.out.println(s3.demo); //com.shujia.day10.Demo@4554617c
System.out.println(o1.demo); //com.shujia.day10.Demo@4554617c
}
}
二.Scanner类概述及其构造方法
1.概述:
JDK5以后用于获取用户的键盘输入
2.构造方法:
public Scanner(InputStream source)
3.常用方法
public int nextXxx() //Xxx可以是Int,Double等
public String nextLine()
演示:
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
Scanner: 其中有一个作用是获取键盘上的符号
构造方法:
Scanner(InputStream source) 构造一个新的 Scanner ,产生从指定输入流扫描的值。
InputStream 字节流
next() 获取字符串
public String nextLine() 获取字符串 可以接收换行符
nextInt() 获取整数
public boolean hasNextInt() 判断管道中的下一个数据是否是整数
*/
public class ScannerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入一个整数:");
int s1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入一个数字:");
// int s2 = sc.nextInt();
String s2 = sc.nextLine(); //可以接收换行符
System.out.println("=========================================");
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s1);
}
}
三.String类概述及其构造方法
1.String类概述
字符串是由多个字符组成的一串数据(字符序列)
字符串可以看成是字符数组
2.特点
1、一旦被创建,就不能被改变
2、Java程序中的所有字符串文字(例如"abc" )都被实现为此类的实例
3、因为String对象是不可变的,它们可以被共享(常量池)
4、字符串可以被看作一个字符数组
演示:
/*
String: 字符串 由若干个字符组成的字符序列,整体叫做字符串
特点:
1、一旦被创建,就不能被改变
2、Java程序中的所有字符串文字(例如"abc" )都被实现为此类的实例。
3、因为String对象是不可变的,它们可以被共享(常量池)
4、字符串可以被看作一个字符数组
*/
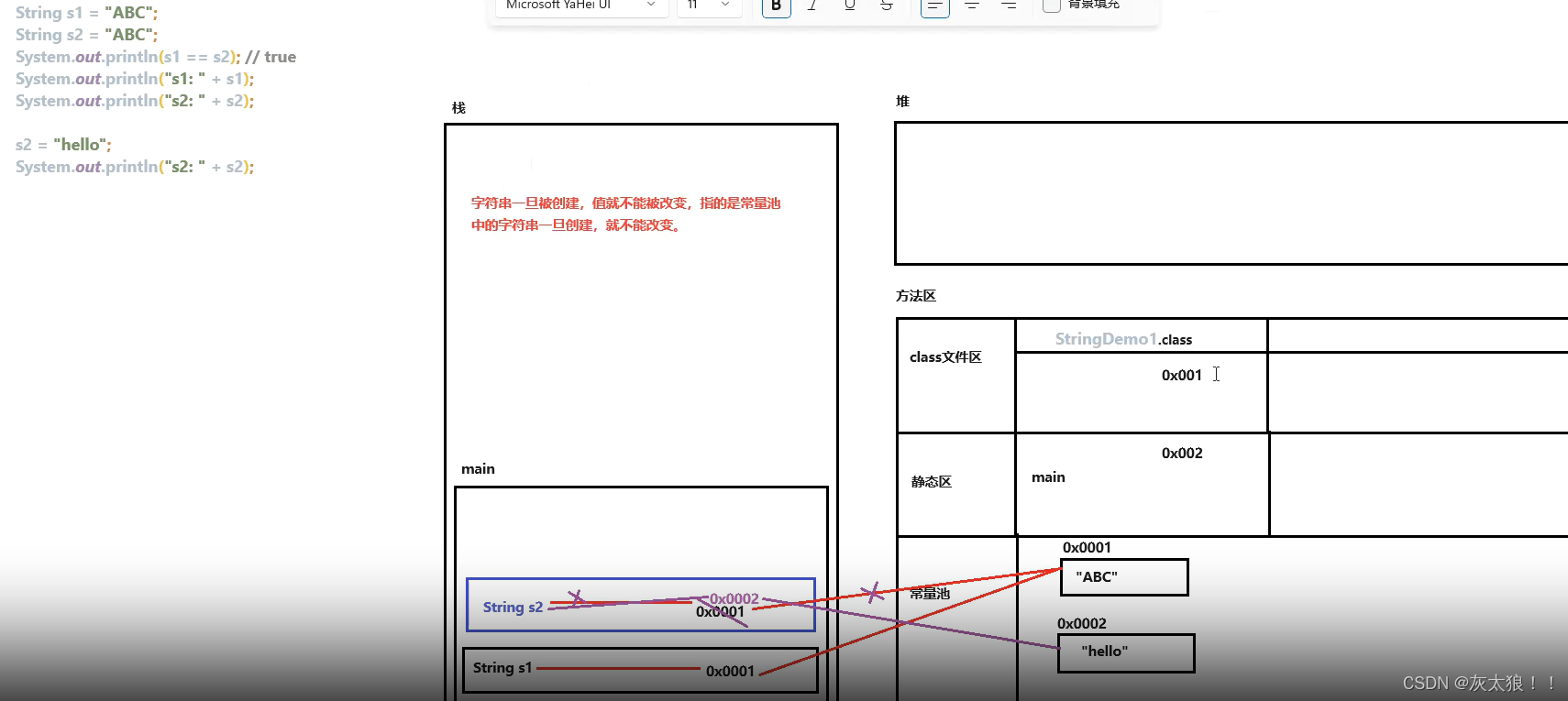
public class StringDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "ABC";
String s2 = "ABC";
System.out.println(s1 == s2); //true 地址值相同,因为String对象是不可变的,它们可以被共享(常量池)
System.out.println("s1:"+s1); //ABC
System.out.println("s2:"+s2); //ABC
System.out.println("=====================");
s1="hello";
System.out.println("s1:"+s1); //hello
System.out.println("s2:"+s2); //ABC
System.out.println(s1==s2); //false
}
}
内存图解:
3.String类的构造方法
public String()
public String(String original)
public String(byte[] bytes) 将字节数组转化成字符串
public String(byte[] bytes,int offset,int length) 将字节数组的一部分转成字符串
public String(char[] value) 将字符数组转成字符串
public String(char[] value,int offset,int count) 将字符数组的一部分转成字符串
演示:
/*
String类的构造方法:
public String()
public String(byte[] bytes)
public String(byte[] bytes,int offset,int length)
public String(char[] value)
public String(char[] value,int offset,int count)
public String(String original)
*/
public class StringDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//public String()
String s1 = new String(); // 相当于创建一个空的字符串
System.out.println("s1" + s1); // 结果为空,说明String类重写了toString()方法
//public String(byte[] bytes) 将字节数组转化成字符串
byte[] arr2 = {65, 66, 67, 68, 69};
String s2 = new String(arr2);
System.out.println(s2); //ABCDE
//public String(byte[] bytes,int index,int length) 将字节数组的一部分转成字符串
String s3 = new String(arr2, 1, 2);
System.out.println(s3); //B,C
//public String(char[] value) 将字符数组转成字符串
char[] arr3 = {'断', '桥', '残', '雪'};
String c1 = new String(arr3);
System.out.println(c1); //断桥残雪
//public String(char[] value,int index,int count) 将字符数组的一部分转成字符串
String c2 = new String(arr3, 1, 2);
System.out.println(c2); //桥残
//public String(String original)
String c3 ="hello"; //也是在创建对象(常量池)
System.out.println(c3);
String c4 = new String("hello"); //在堆内存创建对象,指向常量池中的"hello"
System.out.println(c4); //hello
}
}
4.String类中的判断功能
boolean equals(Object obj) 判断两个字符串内容是否相同
boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str) 判断两个字符串内容是否相同,忽略大小写比较
boolean contains(String str) 判断一个字符串中是否包含另一个字符串
boolean startsWith(String str) 判断字符串是否以某个字符串开头
boolean endsWith(String str) 判断字符串是否以某个字符串结尾
boolean isEmpty() 判断字符串是否为空字符串
演示:
/*String类中的判断功能:
boolean equals(Object obj)
boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str)
boolean contains(String str)
boolean startsWith(String str)
boolean endsWith(String str)
boolean isEmpty()
*/
public class StringDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "Duan QIao";
String s2 = "duan qiao";
//boolean equals(Object obj) 判断两个字符串内容是否相同
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //false
//boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str) 判断两个字符串内容是否相同,忽略大小写比较
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)); //true
//boolean contains(String str) 判断一个字符串中是否包含另一个字符串
String s3 = "hello wOrlD";
String s4 = "hell";
System.out.println(s3.contains(s4)); //true
//boolean startsWith(String str) 判断字符串是否以某个字符串开头
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("Du")); //true
//boolean endsWith(String str) 判断字符串是否以某个字符串结尾
System.out.println(s2.endsWith("ao")); //true
//boolean isEmpty() 判断字符串是否为空字符串
System.out.println(s3.isEmpty()); //false
System.out.println("".isEmpty()); //true
}
}
5.String类的获取功能
(1) int length()
获取字符串中的字符个数
(2) char charAt(int index)
根据索引获取索引对应的字符
(3) int indexOf(int ch)
获取字符的位置
(4) int indexOf(String str)
获取小字符串在大字符串中第一次出现的位置,返回小字符串第一个字符的位置索引
(5) int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex)
从fromIndex位置开始找该字符,如果找到返回该字符在大字符串中的位置索引
(6) int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex)
从fromIndex位置开始找该字符串,如果找到返回该字符在大字符串中的位置索引
(7) String substring(int start)
字符串截取 从start索引位置截取,一直到末尾
(8) String substring(int start,int end)
子串开始于指定beginIndex并延伸到字符索引endIndex-1
演示:
/*
String类中的获取功能:
int length()
char charAt(int index)
int indexOf(int ch)
int indexOf(String str)
int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex)
int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex)
String substring(int start)
String substring(int start,int end)
*/
public class StringDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "duan qiao er";
//int length() 获取字符串中的字符个数
System.out.println(s1.length()); //9
//char charAt(int index) 根据索引获取索引对应的字符
System.out.println(s1.charAt(3)); //n
//int indexOf(int ch) 获取字符的位置
System.out.println(s1.indexOf("a")); //2
//101--ASCII码:e
//判断'e'第一次出现在字符串中的位置索引
System.out.println(s1.indexOf(101)); //10
System.out.println(s1.indexOf("c")); //-1 找不到会 返回结果-1
//int indexOf(String str) 获取小字符串在大字符串中第一次出现的位置,返回小字符串第一个字符的位置索引
String s2= "can xuedjsquedase";
String s3= "u";
String s4= "y";
System.out.println(s2.indexOf(s3)); //5
System.out.println(s2.indexOf(s4)); //-1 找不到返回-1
//int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex) //从fromIndex位置开始找该字符,如果找到返回该字符在大字符串中的位置索引
System.out.println(s2.indexOf(s3,7)); //11
//int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex) //从fromIndex位置开始找该字符串,如果找到返回该字符在大字符串中的位置索引
System.out.println(s2.indexOf(s3,1)); //5
//String substring(int start) 字符串截取 从start索引位置截取,一直到末尾
System.out.println(s2.substring(4)); //xuedjsquedase
//String substring(int start,int end) 子串开始于指定beginIndex并延伸到字符索引endIndex-1
//[start,end)
System.out.println(s2.substring(4,8)); //xued
}
}
6.String类的转换功能
byte[] getBytes() 将字符串转换成字节数组
char[] toCharArray() 将字符串转换成字符数组
static String valueOf(char[] chs) 将字符数组转成字符串
static String valueOf(int i) 将数值转成字符串 100-->"100"
String toLowerCase() 转小写
String toUpperCase() 转大写
String concat(String str) 字符串拼接
演示:
/*
字符串的转换功能:
byte[] getBytes()
char[] toCharArray()
static String valueOf(char[] chs)
static String valueOf(int i)
String toLowerCase()
String toUpperCase()
String concat(String str)
*/
public class StringDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "万里长城";
//byte[] getBytes() 将字符串转换成字节数组
byte [] arr1 = s1.getBytes();
System.out.println(s1); //万里长城
System.out.println(arr1); //[B@4554617c
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr1[i]); //-28-72-121-23-121-116-23-107-65-27-97-114
}
// char[] toCharArray() 将字符串转换成字符数组
char [] arr2=s1.toCharArray();
System.out.println(arr2); //[B@4554617c
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr2[i]);
}
//static String valueOf(char[] chs) //将字符数组转成字符串
String sv1 = String.valueOf(arr2);
System.out.println(sv1); //万里长城
//static String valueOf(int i) 将数值转成字符串 100-->"100"
String sv2 = String.valueOf(100);
System.out.println(sv2); //100
//String toLowerCase() 转小写
String s2= "Hua Wei";
System.out.println(s2.toLowerCase()); //hua wei
//String toUpperCase() 转大写
System.out.println(s2.toUpperCase()); //HUA WEI
//String concat(String str) 字符串拼接
String s3 = "xu song";
String s4 = "daun qiao can xue";
System.out.println(s3.concat(" ").concat(s4)); //xu song daun qiao can xue
}
}
7.String类的其他功能
替换功能
String replace(char old,char new)
String replace(String old,String new)
去除字符串两空格
String trim()
按字典顺序比较两个字符串
int compareTo(String str)
int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
演示:
/*
替换功能
String replace(char old,char new)
String replace(String old,String new)
去除字符串两空格
String trim()
按字典顺序比较两个字符串
int compareTo(String str)
int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
*/
public class StringDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "www.张伟是混蛋.com";
//String replace(char old,char new) 使用新字符替换旧字符
System.out.println(s1.replace('混', '好')); //www.张伟是好蛋.com
//String replace(String old,String new) 使用字符串替换旧字符串
System.out.println(s1.replace("混蛋", "好人")); //www.张伟是好人.com
//String trim() 去除字符串两边的空格
String s2 = " www.张伟是混蛋.com ";
System.out.println(s2.trim()); // www.张伟是混蛋.com
//比较两个字符串内容是否相同,在java中有两种方法可以实现
//boolean equals(String s)
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2.trim())); //true
//int compareTo(String str)
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); //87
/**
* //compareTo源码:
*
* class String{
*
* public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
* // value -- "hello"
* // anotherString -- "hel"
* int len1 = value.length;
* int len2 = anotherString.value.length;
* int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);
* char v1[] = value;
* char v2[] = anotherString.value;
*
* int k = 0;
* while (k < lim) {
* char c1 = v1[k]; // 'h' 'e' 'l'
* char c2 = v2[k]; // 'h' 'e' 'l'
* if (c1 != c2) {
* return c1 - c2; // 104-119 = -15
* }
* k++; // 1 2 3
* }
* return len1 - len2; // 2
* }
* }
*/
}
}
8.练习
(1)把数组中的数据按照指定个格式拼接成一个字符串
举例:int[] arr = {1,2,3}; 输出结果:[1, 2, 3]
public class StringTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
String str = "[";
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (i == arr.length - 1) {
str = str.concat(arr[i]+"]");
}else {
str = str.concat(arr[i]+",");
}
}
System.out.println(str);
}
}
(2)字符串反转
举例:键盘录入”abc” 输出结果:”cba”
public class StringTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "我爱中国";
//方案1:字符串拼接
String res = "";
for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0 ;i--){
res = res.concat(String.valueOf(s.charAt(i)));
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
(3) 统计大串中小串出现的次数
举例:在字符串” woaijavawozhenaijavawozhendeaijavawozhendehenaijavaxinbuxinwoaijavagun”中java出现了5次
/*
统计大串中小串出现的次数
举例:在字符串” woaijavawozhenaijavawozhendeaijavawozhendehenaijavaxinbuxinwoaijavagun”中java出现了5次
分析:
1、可以使用indexOf()方法获取小串第一次出现的位置
2、使用subString()截取每次java的后续剩余字符串,继续查找
3、因为不知道次数,使用while循环
*/
public class StringTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "gdkenandsuahduisagdy usakenanhdiuyehaiuhkenangdasyugdyusagdkenanhdsajk";
String s2 = "kenan";
int count = 0;
int i = s1.indexOf(s2); //2 从索引7开始截取
while (i != -1) {
count++;
s1 = s1.substring(i + s2.length());
i=s1.indexOf(s2);
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
四.StringBuffer类概述及其构造方法
1.StringBuffer类概述
我们如果对字符串进行拼接操作,每次拼接,都会构建一个新的String对象,既耗时又浪费空间,而StringBuffer就可以解决这个问题
2.构造方法
public StringBuffer() 创建一个空的StringBuffer容器
public StringBuffer(int capacity) 创建指定大小容量的容器
public StringBuffer(String str) 创建StringBuffer的同时,内部就包含了一个初始字符串
演示:
public class StringBufferDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// public StringBuffer() 创建一个空的StringBuffer容器
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer();
// public int capacity() 返回当前容量
System.out.println(sb1.capacity());
//public int length() 返回长度(字符数)。
System.out.println(sb1.length());
System.out.println("sb1:"+sb1);// StringBuffer重写了toString()
//
// //public StringBuffer(int capacity) 创建指定大小容量的容器
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer(30);
System.out.println(sb2.capacity());
System.out.println(sb2.length());
//
// //public StringBuffer(String str) 创建StringBuffer的同时,内部就包含了一个初始字符串
StringBuffer sb3 = new StringBuffer("xusong");
System.out.println(sb3); //xusong
System.out.println(sb3.capacity()); // 22
System.out.println(sb3.length()); // 6
}
}
3.StringBuffer类的成员方法
添加功能
public StringBuffer append(String str)
public StringBuffer insert(int offset,String str)
删除功能
public StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index)
public StringBuffer delete(int start,int end)
替换功能
public StringBuffer replace(int start,int end,String str)
反转功能
public StringBuffer reverse()
演示:
/*
添加功能
public StringBuffer append(String str)
public StringBuffer insert(int offset,String str)
删除功能
public StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index)
public StringBuffer delete(int start,int end)
替换功能
public StringBuffer replace(int start,int end,String str)
反转功能
public StringBuffer reverse()
*/
public class StringBufferDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//public StringBuffer append(String str) 追加
//无论添加的是什么类型的元素值,只要进入到StringBuffer中,它就是一个一个的普通字符
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer("xia");
String s2="xue";
System.out.println(sb1.append(" ").append(s2)); //xia xue
//public StringBuffer insert(int index,String str) 在StringBuffer容器中指定位置添加字符串
System.out.println(sb1.insert(0, "ming tian ")); //ming tian xia xue
//public StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index) 删除指定位置索引上的字符
StringBuffer sb3 = new StringBuffer("你 好 啊");
sb3.deleteCharAt(2);
System.out.println(sb3); //你 啊
//public StringBuffer delete(int start,int end) [start,end)
System.out.println(sb3.delete(2, 5)); //你
//public StringBuffer replace(int start,int end,String str) [start,end)
System.out.println(sb3.replace(1,5,"太棒l")); //你太棒l
//public StringBuffer reverse() //反转
System.out.println(sb3.reverse()); //l棒太你
}
}
截取功能
public String substring(int start)
public String substring(int start,int end)
截取功能和前面几个功能的不同:返回值类型是String类型,本身没有发生改变
演示:
/*
截取功能
public String substring(int start)
public String substring(int start,int end)
*/
public class StringBufferDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// public String substring(int start)
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer("xusong");
System.out.println(sb1.substring(1)); //usong
// String s1 = "xusong";
// System.out.println(s1.substring(1)); //usong
//public String substring(int start,int end)
System.out.println(sb1.substring(1,3)); //us
}
}