文章目录
- Struct
- redisDB
- dict
- dictType
- dictEntry
- 宏定义
- 散列函数
- 散列冲突
- dictEntry pointer bit tricks[指针位技巧]
- API implementation
- _dictReset
- _dictInit
- dictCreate
- dictGetHash
- dictSetKey
- dictSetVal
- dictSetNext
- dictGetNext
- dictGetVal
- dictGetKey
- _dictClear
- dictEmpty
- dictRelease
- 扩容
- dictResize|dictExpand|_dictExpand|_dictNextExp
- 扩容触发条件
- **dictAdd**
- **dictAddRaw**
- **dictFindPositionForInsert**
- **_dictExpandIfNeeded**
- **dictTypeExpandAllowed**
- **扩容策略**
- **扩容触发条件**
- **dictInsertAtPosition**
- 缩容
- dictDelete
- htNeedsResize
- 缩容条件
- 缩容策略
- 迁移
- 迁移时机
- 迁移步骤
- _dictRehashStep
- dictRehash
- redis服务器定时任务----迁移数据
- 旧版本中dict的结构
- 总结
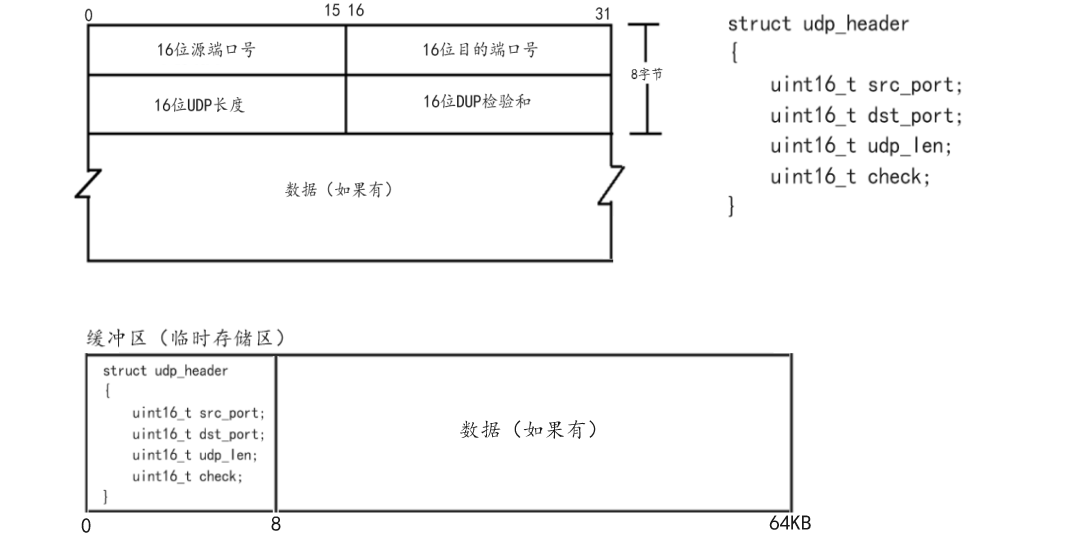
字典是Redis服务器中出现最为频繁的复合型数据结构,除了hash结构的数据会用到字典外,整个redis数据库的所有key和value也组成一个全局字典,还有带有过期时间的key集合也是一个字典。zet集合中存储value和score值的映射关系也是通过字典结构实现的。
先看一下redisDB的结构,它里面存储着数据字典和过期字典
Struct
redisDB
[redis-7.2.2\src\server.h]
redisDB
typedef struct redisDb {
//全局数据字典
dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */
//全局过期字典
dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */
dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP)*/
dict *blocking_keys_unblock_on_nokey; /* Keys with clients waiting for
* data, and should be unblocked if key is deleted (XREADEDGROUP).
* This is a subset of blocking_keys*/
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
//当前的数据库ID
int id; /* Database ID */
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
unsigned long expires_cursor; /* Cursor of the active expire cycle. */
list *defrag_later; /* List of key names to attempt to defrag one by one, gradually. */
clusterSlotToKeyMapping *slots_to_keys; /* Array of slots to keys. Only used in cluster mode (db 0). */
} redisDb;
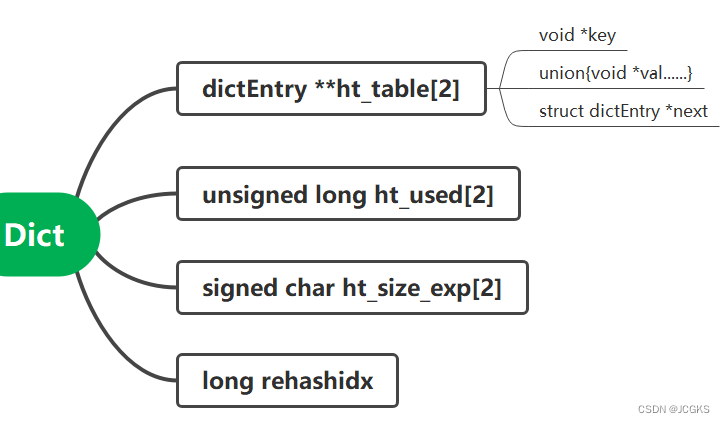
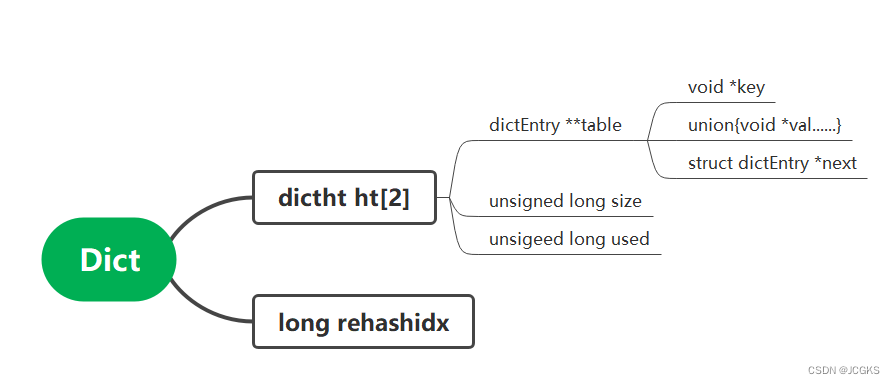
dict
struct dict {
//dictType是一个struct里面存储了各种与hashtable相关的function pointer,详细的见下面
dictType *type;
/*
正常情况下,使用ht_table[0]存储数据;
发生扩容或者缩容时,用ht_table[1]。
*/
dictEntry **ht_table[2];
/*
对应着两个ht_table的元素个数;
ht_used[0]表示ht_table[0]的对象总数;
ht_used[1]表示ht_table[1]的对象总数.
*/
unsigned long ht_used[2];
/*
标记当前的hashtable是否处于rehash状态,如果rehashidx==-1则当前没有处于rehash状态,如果rehashidx>=0则表明当前处于rehash状态并且按照rehashidx指示的顺序进行迁移。
*/
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
/*
该值大于0表示rehash终止,小于0表示编码错误
*/
int16_t pauserehash;
/*
通过ht_size_exp可以计算出两个表的一维长度也即是槽的个数。
pow(2,ht_size_exp[0])表示ht_table[0]槽的个数;
pow(2,ht_size_exp[1])表示ht_table[1]槽的个数;
*/
signed char ht_size_exp[2];
/*
metadata是用于存储额外信息的字段,可以存储一些元数据
*/
void *metadata[];
};
dictType
typedef struct dictType {
uint64_t (*hashFunction)(const void *key);
void *(*keyDup)(dict *d, const void *key);
void *(*valDup)(dict *d, const void *obj);
int (*keyCompare)(dict *d, const void *key1, const void *key2);
void (*keyDestructor)(dict *d, void *key);
void (*valDestructor)(dict *d, void *obj);
int (*expandAllowed)(size_t moreMem, double usedRatio);
/*
如果设置了'no_value'标志,则表示没有使用值,即字典是一
个集合。设置此标志时,无法访问dictEntry的值,也无法使用
dicsetkey()。metadata也不能使用。
*/
unsigned int no_value:1;
/*
如果no_value =1并且所有的键都是奇数(LSB=1),那么设置
keys_are_odd =1可以实现另一个优化:在不分配dictEntry
的情况下存储键。
*/
unsigned int keys_are_odd:1;
size_t (*dictEntryMetadataBytes)(dict *d);
size_t (*dictMetadataBytes)(void);
void (*afterReplaceEntry)(dict *d, dictEntry *entry);
} dictType;
- set是一个集合,它的底层实现也是dict,但是对于集合来说只有key值没有value值;所以为了兼容set的实现,dictType中有一个标志性的字段"no_value",只要设置了该字段就表明这个dictEntry中只有key值没有value值,也就实现了set。
dictEntry
//dict中的entry
struct dictEntry {
void *key;//指向key
//union是指内存的同一个位置可以存储不同的数据类型,是为了兼容不同类型的value。
//当value是uint64_t、int64_t、double的数据类型的时候,
//可以直接内嵌在dictentry中,无需为此分配额外的内存,这样可以节省内存
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next; /* Next entry in the same hash bucket. 采用拉链法解决哈希冲突*/
void *metadata[]; //存储额外的信息
/*
一个任意数量的字节(从指针对齐的地址开始),大小由dictType
的dictEntryMetadataBytes()返回。
*/
};
当no_value=1时对应的结构是
//只有key没有value相当于set
typedef struct {
void *key;
dictEntry *next;
} dictEntryNoValue;
宏定义
[redis-7.2.2\src\dict.h]
//根据ht_size_exp计算dictht_size
#define DICTHT_SIZE(exp) ((exp) == -1 ? 0 : (unsigned long)1<<(exp))
//获取sizemask
#define DICTHT_SIZE_MASK(exp) ((exp) == -1 ? 0 : (DICTHT_SIZE(exp))-1)
//每一个hashtable的初始化大小
#define DICT_HT_INITIAL_EXP 2
#define DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE (1<<(DICT_HT_INITIAL_EXP))
#define dictFreeVal(d, entry) do { \
if ((d)->type->valDestructor) \
(d)->type->valDestructor((d), dictGetVal(entry)); \
} while(0)
#define dictFreeKey(d, entry) \
if ((d)->type->keyDestructor) \
(d)->type->keyDestructor((d), dictGetKey(entry))
#define dictCompareKeys(d, key1, key2) \
(((d)->type->keyCompare) ? \
(d)->type->keyCompare((d), key1, key2) : \
(key1) == (key2))
#define dictEntryMetadataSize(d) ((d)->type->dictEntryMetadataBytes \
? (d)->type->dictEntryMetadataBytes(d) : 0)
#define dictMetadataSize(d) ((d)->type->dictMetadataBytes \
? (d)->type->dictMetadataBytes() : 0)
//获取key的哈希值
#define dictHashKey(d, key) ((d)->type->hashFunction(key))
//获取两个dictht的总slot个数
#define dictSlots(d) (DICTHT_SIZE((d)->ht_size_exp[0])+DICTHT_SIZE((d)->ht_size_exp[1]))
//获取两个dictht的总对象个数
#define dictSize(d) ((d)->ht_used[0]+(d)->ht_used[1])
//判断当前是否处在rehash阶段
#define dictIsRehashing(d) ((d)->rehashidx != -1)
//终止rehash
#define dictPauseRehashing(d) ((d)->pauserehash++)
//重新开始rehash
#define dictResumeRehashing(d) ((d)->pauserehash--)
/* If our unsigned long type can store a 64 bit number, use a 64 bit PRNG. */
#if ULONG_MAX >= 0xffffffffffffffff
#define randomULong() ((unsigned long) genrand64_int64())
#else
#define randomULong() random()
#endif
散列函数
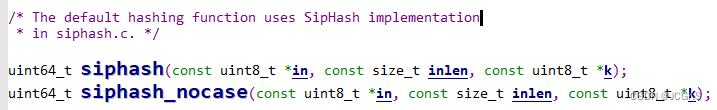
- redis的字典默认的哈希函数是siphash,siphash算法即使在key很小的情况下,也可以产生随机性特别好的输出,性能非常突出。
散列冲突
- 通过dictEntry的结构中包含"struct entry *next 指向同一个slot的下一个next entry"可以得出,dict采用"拉链法"解决"散列冲突"。
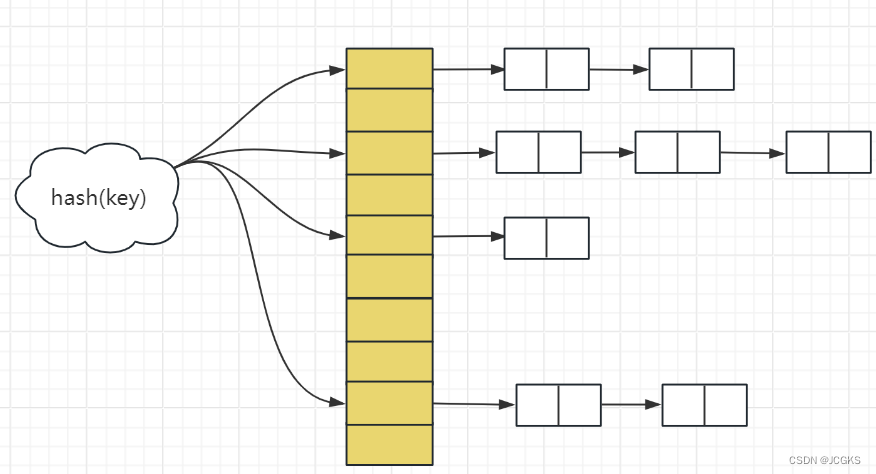
dictEntry pointer bit tricks[指针位技巧]
/*
指向dictEntry的指针中的最低3位决定了该指针实际指向的是什么。如果最小的位被设置,它就是一个键值。否则,最少的3位有效位标记条目的类型。
*/
#define ENTRY_PTR_MASK 7 /* 111 与Mask相与获取数据的低三bit位*/
#define ENTRY_PTR_NORMAL 0 /* 000 已分配的entry并且带有value值*/
#define ENTRY_PTR_NO_VALUE 2 /* 010 已分配的entry但是不带有value值*/
/*
返回1:entry pointer指向一个key值,而不是已经分配好的entry。
其它情况返回0.
*/
static inline int entryIsKey(const dictEntry *de) {
//最低位设置了就是key
return (uintptr_t)(void *)de & 1;
}
/*
entry pointer指向的是一个dictentry struct返回1
否则返回0
*/
static inline int entryIsNormal(const dictEntry *de) {
return ((uintptr_t)(void *)de & ENTRY_PTR_MASK) == ENTRY_PTR_NORMAL;
}
/*
entry 指向的是一个不带value值得 dictentry struct返回1
否则返回0
*/
static inline int entryIsNoValue(const dictEntry *de) {
return ((uintptr_t)(void *)de & ENTRY_PTR_MASK) == ENTRY_PTR_NO_VALUE;
}
/* Creates an entry without a value field. */
static inline dictEntry *createEntryNoValue(void *key, dictEntry *next) {
dictEntryNoValue *entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry));
entry->key = key;
entry->next = next;
//设置标记位ENTRY_PTR_NO_VALUE
/*
void*是普通指针相互转换的桥梁
uintptr_t可以与void*相互转换
uintptr_t可以参与指针计算
*/
return (dictEntry *)(void *)((uintptr_t)(void *)entry | ENTRY_PTR_NO_VALUE);
}
//编码,设置标志位
static inline dictEntry *encodeMaskedPtr(const void *ptr, unsigned int bits) {
assert(((uintptr_t)ptr & ENTRY_PTR_MASK) == 0);
return (dictEntry *)(void *)((uintptr_t)ptr | bits);
}
//解码,消除标志位
static inline void *decodeMaskedPtr(const dictEntry *de) {
//非key才进行获取标志位操作
assert(!entryIsKey(de));
//"~"的优先级高于"&",先进行取反操作后进行按位与操作
//&~操作消除左操作数中与右操作数对应位置的1
return (void *)((uintptr_t)(void *)de & ~ENTRY_PTR_MASK);
}
//使用该函数之前确保dictEntry没有value,可以使用
//static inline int entryIsNoValue(const dictEntry *de) 进行判断
static inline dictEntryNoValue *decodeEntryNoValue(const dictEntry *de) {
return decodeMaskedPtr(de);
}
//如果entry有一个value值,也就是正常的ENTRY_PTR_NORMAL,返回1
static inline int entryHasValue(const dictEntry *de) {
return entryIsNormal(de);
}
API implementation
_dictReset
/* Reset hash table parameters already initialized with _dictInit()*/
static void _dictReset(dict *d, int htidx)
{
d->ht_table[htidx] = NULL;
d->ht_size_exp[htidx] = -1;
d->ht_used[htidx] = 0;
}
_dictInit
/* Initialize the hash table */
int _dictInit(dict *d, dictType *type)
{
_dictReset(d, 0);
_dictReset(d, 1);
d->type = type;
d->rehashidx = -1;
d->pauserehash = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
dictCreate
//创建一个新的hashtable
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type)
{
size_t metasize = type->dictMetadataBytes ? type->dictMetadataBytes() : 0;
dict *d = zmalloc(sizeof(*d) + metasize);
if (metasize) {
memset(dictMetadata(d), 0, metasize);
}
_dictInit(d,type);
return d;
}
dictGetHash
uint64_t dictGetHash(dict *d, const void *key) {
return dictHashKey(d, key);
}
dictSetKey
void dictSetKey(dict *d, dictEntry* de, void *key) {
//如果dictEntry设置了no_value标识,则不能使用该函数
assert(!d->type->no_value);
if (d->type->keyDup)
de->key = d->type->keyDup(d, key);
else
de->key = key;
}
dictSetVal
void dictSetVal(dict *d, dictEntry *de, void *val) {
//entry有value值才可以设置
assert(entryHasValue(de));
//前面分析过,de->v是一个union
de->v.val = d->type->valDup ? d->type->valDup(d, val) : val;
}
dictSetNext
static void dictSetNext(dictEntry *de, dictEntry *next) {
//分配好的entry struct才可以设置next
assert(!entryIsKey(de));
if (entryIsNoValue(de)) {
dictEntryNoValue *entry = decodeEntryNoValue(de);
entry->next = next;
} else {
de->next = next;
}
}
dictGetNext
/* Returns the 'next' field of the entry or
NULL if the entry doesn't have a'next' field.
*/
static dictEntry *dictGetNext(const dictEntry *de) {
if (entryIsKey(de)) return NULL; /* there's no next */
if (entryIsNoValue(de)) return decodeEntryNoValue(de)->next;
return de->next;
}
dictGetVal
void *dictGetVal(const dictEntry *de) {
assert(entryHasValue(de));
return de->v.val;
}
dictGetKey
void *dictGetKey(const dictEntry *de) {
if (entryIsKey(de)) return (void*)de;
if (entryIsNoValue(de)) return decodeEntryNoValue(de)->key;
return de->key;
}
_dictClear
/* Destroy an entire dictionary */
//销毁一个完整的字典
//callback回调函数,传入参数是dict*传出参数是void
int _dictClear(dict *d, int htidx, void(callback)(dict*)) {
unsigned long i;
//释放所有的元素
for (i = 0; i < DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[htidx]) && d->ht_used[htidx] > 0; i++) {
dictEntry *he, *nextHe;
if (callback && (i & 65535) == 0) callback(d);
if ((he = d->ht_table[htidx][i]) == NULL) continue;
while(he) {
nextHe = dictGetNext(he);
//释放key
dictFreeKey(d, he);
//释放val
dictFreeVal(d, he);
//如果entry he不是一个key,释放entry struct
if (!entryIsKey(he)) zfree(decodeMaskedPtr(he));
//元素个数减一
d->ht_used[htidx]--;
he = nextHe;
}
}
/* Free the table and the allocated cache structure */
//释放整个表
zfree(d->ht_table[htidx]);
/* Re-initialize the table */
//初始化d[htidx]
_dictReset(d, htidx);
return DICT_OK; /* never fails */
}
dictEmpty
void dictEmpty(dict *d, void(callback)(dict*)) {
//清除第一个表dictht[0]
_dictClear(d,0,callback);
//清除第二个表dictht[1]
_dictClear(d,1,callback);
//重置rehashidx和pauserehash
d->rehashidx = -1;
d->pauserehash = 0;
}
dictRelease
/* Clear & Release the hash table */
void dictRelease(dict *d)
{
//清除第一个表dictht[0]
_dictClear(d,0,NULL);
//清除第二个表dictht[1]
_dictClear(d,1,NULL);
//释放字典
zfree(d);
}
扩容
dictResize|dictExpand|_dictExpand|_dictNextExp
这个函数是用来重新设置dictht的大小。在达到扩容条件或者缩容条件的时候,进行内存重新分配的时候就会用到此函数计算出正确的内存大小。
typedef enum {
DICT_RESIZE_ENABLE,
DICT_RESIZE_AVOID,
DICT_RESIZE_FORBID,
} dictResizeEnable;
static dictResizeEnable dict_can_resize = DICT_RESIZE_ENABLE;
/*
将表的大小调整为包含所有元素的最小大小,并且还要保证负载因子"used(表中的元素个数)/size(表的长度)"<=1;
*/
int dictResize(dict *d)
{
unsigned long minimal;
//如果当前的hashtable处于不能resize或者正在rehash的状态,则不能进行扩容或者缩容
if (dict_can_resize != DICT_RESIZE_ENABLE || dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_ERR;
//获取旧表的元素个数
minimal = d->ht_used[0];
//#define DICT_HT_INITIAL_EXP 2
//#define DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE (1<<(DICT_HT_INITIAL_EXP))
if (minimal < DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE)
minimal = DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE;
return dictExpand(d, minimal);
}
- 第一步先矫正minimal。
- 之后调用dictExpand,先根据_dictNextExp计算新表的容量之后重新分配内存。
/* return DICT_ERR if expand was not performed */
int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size) {
return _dictExpand(d, size, NULL);
}
辅助函数dictNextExp
//返回大于等于size的第一个pow(2,exp)中的exp
static signed char _dictNextExp(unsigned long size)
{
//#define DICT_HT_INITIAL_EXP 2
unsigned char e = DICT_HT_INITIAL_EXP;//2
if (size >= LONG_MAX) return (8*sizeof(long)-1);
while(1) {
if (((unsigned long)1<<e) >= size)
return e;
e++;
}
}
/*
成功分配返回DICT_OK,否则返回DICT_ERR
*/
int _dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size, int* malloc_failed)
{
//清空指针
if (malloc_failed) *malloc_failed = 0;
//正处于rehashing阶段或者申请内存小于当前元素个数[发生这种可能是刚刚迁移完数据,新表替代旧表]
if (dictIsRehashing(d) || d->ht_used[0] > size)
return DICT_ERR;
// new hashtable
dictEntry **new_ht_table;
// the use of the new hashtable
unsigned long new_ht_used;
//根据size[旧表容量]计算出新表的容量
//作用是返回第一次大于等于size的pow(2,exp)的exp
signed char new_ht_size_exp = _dictNextExp(size);
//检测是否溢出
size_t newsize = 1ul<<new_ht_size_exp;
if (newsize < size || newsize * sizeof(dictEntry*) < newsize)
return DICT_ERR;
//新表的大小等于旧表的大小
if (new_ht_size_exp == d->ht_size_exp[0]) return DICT_ERR;
/* Allocate the new hash table and initialize all pointers to NULL */
//malloc_failed记录是否分配成功
if (malloc_failed) {
new_ht_table = ztrycalloc(newsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));
*malloc_failed = new_ht_table == NULL;
if (*malloc_failed)
return DICT_ERR;
} else
new_ht_table = zcalloc(newsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));
new_ht_used = 0;//重置新表的元素个数
//d->ht_table[0]==NULL表明是第一次插入数据,此时d->ht_table被初始化默认的大小4
if (d->ht_table[0] == NULL) {
d->ht_size_exp[0] = new_ht_size_exp;
d->ht_used[0] = new_ht_used;
d->ht_table[0] = new_ht_table;
return DICT_OK;
}
/* Prepare a second hash table for incremental rehashing */
//为rehashing做准备,设置ht_table[1]
d->ht_size_exp[1] = new_ht_size_exp;
d->ht_used[1] = new_ht_used;
d->ht_table[1] = new_ht_table;
d->rehashidx = 0;//从0号索引开始迁移
//此时只是为rehashing做了准备阶段,并没有真正的开启迁移数据
return DICT_OK;
}
扩容触发条件
- 随着数据量的不断增大,哈希碰撞产生的可能性越来越大,同一个槽内的链表越来越长,为了保持查找,删除,添加的效率,需要进行扩容。所以我们从dictAdd函数下手。
dictAdd
/* Add an element to the target hash table */
int dictAdd(dict *d, void *key, void *val)
{
//dictAddRaw找出key合适的插入位置并插入,如果已经存在返回NULL
dictEntry *entry = dictAddRaw(d,key,NULL);
//key已经存在
if (!entry) return DICT_ERR;
//没有设置no_value标识,设置相应的value值
if (!d->type->no_value) dictSetVal(d, entry, val);
return DICT_OK;
}
dictAddRaw
/*
*/
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key, dictEntry **existing)
{
//寻找key的插入位置,如果key已经存在返回NULL
void *position = dictFindPositionForInsert(d, key, existing);
//key已经存在
if (!position) return NULL;
/* Dup the key if necessary. */
if (d->type->keyDup) key = d->type->keyDup(d, key);
//在合适的位置插入key,此时不设置对应的key,是为了满足用户根据自己的意愿设置或者不设置value值。
return dictInsertAtPosition(d, key, position);
}
dictFindPositionForInsert
//寻找目标key的插入位置,如果key已经存在返回NULL
void *dictFindPositionForInsert(dict *d, const void *key, dictEntry **existing) {
unsigned long idx, table;
dictEntry *he;
//获取key对应的hash值
uint64_t hash = dictHashKey(d, key);
if (existing) *existing = NULL;
/*
如果当前处于rehash的状态[rehashidx!=-1],进行数据的迁移操作。
这也是数据迁移触发的条件之一
针对迁移的详细分析在下面。
*/
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
/* Expand the hash table if needed */
if (_dictExpandIfNeeded(d) == DICT_ERR)
return NULL;
//开始查找
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
//哈希值与MASK相与,得出寻找的目标key在dictht的位置下标
idx = hash & DICTHT_SIZE_MASK(d->ht_size_exp[table]);
//获取下标所在位置的第一个dictEntry
he = d->ht_table[table][idx];
//像遍历链表那样,依次寻找目标key
while(he) {
//获取dictEntry的key值
void *he_key = dictGetKey(he);
if (key == he_key || dictCompareKeys(d, key, he_key)) {
//key存在,返回NULL;并将目标key存储在existing中
if (existing) *existing = he;
return NULL;
}
//继续寻找下一个entry
he = dictGetNext(he);
}
//没有rehash,说明ht[1]没有,故不需要在ht[1]中寻找,直接退出外层循环。
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break;
}
//走到这一步说明在ht中没有找到目标key,返回插入位置为插入操作做准备
//如果正处于rehash,插入位置在ht[1]中,否则插入在ht[0]中。[头插法]
dictEntry **bucket = &d->ht_table[dictIsRehashing(d) ? 1 : 0][idx];
return bucket;
}
_dictExpandIfNeeded
/* Expand the hash table if needed */
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d)
{
//如果正在rehashing就直接返回
//迁移数据的阶段不需要扩容
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_OK;
//第一插入数据,将ht[0]扩大为初始的大小
if (DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0]) == 0) return dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE);
/*
检验是否允许expand,详细代码如下
不允许的话,直接返回。
*/
if (!dictTypeExpandAllowed(d))
return DICT_OK;
//以下是扩容触发的条件
if ((dict_can_resize == DICT_RESIZE_ENABLE &&
d->ht_used[0] >= DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0])) ||
(dict_can_resize != DICT_RESIZE_FORBID &&
d->ht_used[0] / DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0]) > dict_force_resize_ratio))
{
return dictExpand(d, d->ht_used[0] + 1);
}
return DICT_OK;
}
/* Using dictEnableResize() / dictDisableResize() we make possible to
* enable/disable resizing of the hash table as needed. This is very important
* for Redis, as we use copy-on-write and don't want to move too much memory
* around when there is a child performing saving operations.
* * Note that even when dict_can_resize is set to 0, not all resizes are
* prevented: a hash table is still allowed to grow if the ratio between
* the number of elements and the buckets > dict_force_resize_ratio. */
static unsigned int dict_force_resize_ratio = 5;
- 翻译一下上述的那段英文。在进行copy-on-write[写时复制,执行bgsave或者aofrewrite的时候会发生cop],为了避免过多的内存从child中分离,此时不希望进行扩容操作。
- 如果装载因子超过安全值,不论当前有没有发生写时复制都会执行扩容操作。
dictTypeExpandAllowed
/*
扩容的时候,因为要一次性分配足够大的内存,所以需要根据成员函数"expandAlloewd"判断是否能够完成本次分配。
*/
static int dictTypeExpandAllowed(dict *d) {
if (d->type->expandAllowed == NULL) return 1;
return d->type->expandAllowed(
DICTHT_SIZE(_dictNextExp(d->ht_used[0] + 1)) * sizeof(dictEntry*),
(double)d->ht_used[0] / DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0]));
}
- expandAllowed的第一个参数是计算扩容之后新的容量,也即是第一次大于等于(d->ht_used[0]+1)的pow(2,exp)[这里的d->ht_used[0]加1是因为,需要先判断是否需要扩容,接着才会把新的key加入;所以计算的时候,新key还没有加入表中但是要计算的时候要将其包括在内。]
- expandAllowed的第二个参数是,哈希表的装载因子
扩容策略

- 插入一个新的key之前,先判断是否需要扩容,如果需要扩容的话,先申请新的更大的空间,之后再将新的key插入新的表中。
- 扩容的原则就是"在满足能够包含所有元素[包括新插入的key]的基础上,保证新表的大小是最小的pow(2,exp)"。
扩容触发条件

- 扩容的触发条件1。装载因子大于等于1并且当前没有进行写时复制[bgsave,aofrewrite]
- 扩容的触发条件2。装载因子大于5.
dictInsertAtPosition
通过"dictFindPositionForInsert"找到目标key的插入位置,[key已经存在返回NULL此时不需要插入]。通过"dictInsertAtPosition"插入目标key。
dictEntry *dictInsertAtPosition(dict *d, void *key, void *position) {
dictEntry **bucket = position; /* It's a bucket, but the API hides that. */
dictEntry *entry;
//判断插入位置position是否适当合理
int htidx = dictIsRehashing(d) ? 1 : 0;
assert(bucket >= &d->ht_table[htidx][0] &&
bucket <= &d->ht_table[htidx][DICTHT_SIZE_MASK(d->ht_size_exp[htidx])]);
size_t metasize = dictEntryMetadataSize(d);
//如果设置了no_value标识
if (d->type->no_value) {
//不能使用metadata
assert(!metasize); /* Entry metadata + no value not supported. */
if (d->type->keys_are_odd && !*bucket) {
/* We can store the key directly in the destination bucket without the
* allocated entry.
*
* TODO: Add a flag 'keys_are_even' and if set, we can use this
* optimization for these dicts too. We can set the LSB bit when
* stored as a dict entry and clear it again when we need the key
* back. */
entry = key;
assert(entryIsKey(entry));
} else {
/* Allocate an entry without value. */
entry = createEntryNoValue(key, *bucket);
}
} else {
entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry) + metasize);
assert(entryIsNormal(entry)); /* Check alignment of allocation */
if (metasize > 0) {
memset(dictEntryMetadata(entry), 0, metasize);
}
//link newentry
entry->key = key;
entry->next = *bucket;
}
*bucket = entry;
d->ht_used[htidx]++;
return entry;
}
- 通过代码可以发现,插入的操作很简单就是头插法
缩容
- 随着删除操作的不断执行,表中的数据越来越少,为了节约内存空间,需要把当前的表在满足装下所有元素的基础上进行缩小。所以从"Delete操作"入手。
[redis-7.2.2\src\t_hash.c]

dictDelete
//成功删除返回DICT_OK,否则返回DICT_ERR
int dictDelete(dict *ht, const void *key) {
return dictGenericDelete(ht,key,0) ? DICT_OK : DICT_ERR;
}
//找到目标key并删除
static dictEntry *dictGenericDelete(dict *d, const void *key, int nofree) {
uint64_t h, idx;
dictEntry *he, *prevHe;
int table;
/* dict is empty */
if (dictSize(d) == 0) return NULL;
//此时正处于rehash阶段,先进行数据的迁移工作
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
//获取目标key的哈希值
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
//获取目标key在ht中的位置下标
idx = h & DICTHT_SIZE_MASK(d->ht_size_exp[table]);
//获取下标所在的bucket
he = d->ht_table[table][idx];
prevHe = NULL;
//遍历链表
while(he) {
//获取entry指向的key
void *he_key = dictGetKey(he);
//找到目标key
if (key == he_key || dictCompareKeys(d, key, he_key)) {
//目标key处在中间位置
if (prevHe)
dictSetNext(prevHe, dictGetNext(he));
else
//当前目标节点是bucket中的第一个节点
d->ht_table[table][idx] = dictGetNext(he);
if (!nofree) {
//释放节点
dictFreeUnlinkedEntry(d, he);
}
//元素个数减一
d->ht_used[table]--;
return he;
}
//保存prevhe,继续检测下一个entry
prevHe = he;
he = dictGetNext(he);
}
//没有rehash无需寻找ht[1]
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break;
}
return NULL; /* not found */
}
htNeedsResize
int htNeedsResize(dict *dict) {
long long size, used;
//获取dict中两个ht的buckets长度之和
size = dictSlots(dict);
//获取dict中两个ht的元素总个数
used = dictSize(dict);
//#define HASHTABLE_MIN_FILL 10 /* Minimal hash table fill 10% */
return (size > DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE &&
(used*100/size < HASHTABLE_MIN_FILL));
}
缩容条件

- 缩容条件:装载因子小于0.1
缩容策略
if (htNeedsResize(o->ptr)) dictResize(o->ptr);
- dictResize前面分析过:获取并修正旧表ht[0]的元素个数,以此为基础进行扩容,扩大[缩小为]为
大于等于used的第一个pow(2,exp)
迁移
迁移时机
扩容只是第一步,接下来需要逐步,以增量的方式迁移数据,将旧表中的数据迁移到新表,然后用新表替代旧表,将新表重置待下次扩容[缩容]时使用。
通过以上"扩容,缩容的分析",我们可以发现,迁移触发的时机有以下两个

- 在hashtable中寻找新key的目标位置的时候,如果当前正处在rehash阶段,会先rehash进行数据的迁移,[如果不处于rehash阶段,会先判断是否需要扩容,先扩容],然后会遍历key所在的槽判断key是否已经存在,不存在返回应该插入的位置,已经存在返回NULL。

- 删除一个key的时候,如果当前处于rehash阶段,会先进行rehash数据的迁移,之后遍历寻找目标key,找到之后删除key。
总结一下,就是在执行写操作的时候会触发数据的迁移rehash。可是也存在一个问题,如果线上客户端都不在执行删除,修改,插入这些写操作,那永远都不会触发迁移,那旧表中的数据该如何安置。其实redis服务器会有定时任务进行数据的迁移,即使线上没有写操作的执行也会进行数据的迁移。定时任务在后面介绍
接下俩看看,迁移的流程
迁移步骤
_dictRehashStep
/*
该函数由字典中的常见查找或更新操作调用,以便哈希表在活跃使用时自动从H1迁移到H2。也就是所查找和更新操作会触发rehash而且每次只rehash一个位置处[rehashidx指向的位置]的key链表
*/
static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) {
//如果rehash没有被终止,就进行数据的迁移
if (d->pauserehash == 0) dictRehash(d,1);
}
dictRehash
/*
执行N步增量散列。如果仍有键需要从old-hashtable迁移到new-hashtable则返回1,否则返回0;
一个rehash步骤在于移动一个bucket[包括产生hash冲突的key即一个槽内所有的key]从old-hashtable到new-hashtable;
由于hashtable的一部分可能由空白空间组成,因此不能保证此函数会rehash整个单个bucket,因为最多可以访问N*10个empty bucket,超过将会停止当前轮的rehash,该函数会阻塞很长时间
*/
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
int empty_visits = n*10; //最多能够访问N*10个empty bucket
//hashatable[0]的size
unsigned long s0 = DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0]);
//hashatable[1]的size
unsigned long s1 = DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[1]);
//如果当前的状态处于禁止rehash或者,没有设置rehashidx直接返回
if (dict_can_resize == DICT_RESIZE_FORBID || !dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
if (dict_can_resize == DICT_RESIZE_AVOID &&
((s1 > s0 && s1 / s0 < dict_force_resize_ratio) ||
(s1 < s0 && s0 / s1 < dict_force_resize_ratio)))
{
return 0;
}
//开始进行迁移,n表示迁移的步数
//如果过hashtable[0]没有元素则表示迁移结束
while(n-- && d->ht_used[0] != 0) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
/*
确保rehashidx没有超出范围
*/
assert(DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0]) > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);
//从rehashidx开始,寻找一个非空的bucket,最多只能有n*10个empty bucket
while(d->ht_table[0][d->rehashidx] == NULL) {
d->rehashidx++;//遍历下一个bucket
if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1;
}
//获取rehashidx指向槽的第一个Entry
de = d->ht_table[0][d->rehashidx];
//相当于遍历单链表
while(de) {
uint64_t h;
//获取下一个dictentry
nextde = dictGetNext(de);
//从de中找出key
void *key = dictGetKey(de);
//扩容状态,获取entry在新表中的位置
if (d->ht_size_exp[1] > d->ht_size_exp[0]) {
//重新计算哈希值
h = dictHashKey(d, key) & DICTHT_SIZE_MASK(d->ht_size_exp[1]);
} else {
//处在缩容阶段
h = d->rehashidx & DICTHT_SIZE_MASK(d->ht_size_exp[1]);
}
//设置了no_value标识
if (d->type->no_value) {
if (d->type->keys_are_odd && !d->ht_table[1][h]) {
assert(entryIsKey(key));
if (!entryIsKey(de)) zfree(decodeMaskedPtr(de));
de = key;
} else if (entryIsKey(de)) {
/* We don't have an allocated entry but we need one. */
de = createEntryNoValue(key, d->ht_table[1][h]);
} else {
/* Just move the existing entry to the destination table and
* update the 'next' field. */
assert(entryIsNoValue(de));
dictSetNext(de, d->ht_table[1][h]);
}
} else {
//将de插入newhashtable对应的位置处
dictSetNext(de, d->ht_table[1][h]);
}
//修改槽的位置
d->ht_table[1][h] = de;
//ht[0]的元素个数减1
d->ht_used[0]--;
//ht[1]的元素个数加1
d->ht_used[1]++;
//继续迁移槽内的下一个entry
de = nextde;
}
//ht[0]rehashidx指向的bucket已经全部迁移到ht[1]中,将其置为空
d->ht_table[0][d->rehashidx] = NULL;
d->rehashidx++;//为下一次rehash做准备
}
/* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */
//rehash完成,释放hashtable[0];
//hashatable[1]成为hashtable[0]
if (d->ht_used[0] == 0) {
//释放ht[0]
zfree(d->ht_table[0]);
/* Copy the new ht onto the old one */
d->ht_table[0] = d->ht_table[1];
d->ht_used[0] = d->ht_used[1];
d->ht_size_exp[0] = d->ht_size_exp[1];
//重置ht1
_dictReset(d, 1);
//关闭rehash标识
d->rehashidx = -1;
//迁移全部完成返回0
return 0;
}
/* More to rehash... */
return 1;
}
迁移的顺序
- 通过源码分析,可以得出迁移的顺序是按照"rehashidx"进行的,并且每次只迁移一个非空的bucket,寻找非空的bucket时最多只能扫描到n*10个 empty bucket。[这里的n表示每次进行几次迁移操作,每次只迁移一次]
迁移何时停止,或者说如何判断迁移是否完成
- 分析源码可以发现,ht_used[0]==0表示数据迁移全部完成。即是否迁移完成是根据旧表是否还有元素来进行判断的。
redis服务器定时任务----迁移数据
为了防止,线上的客户端不再执行写操作(hset,hdel等指令),导致迁移操作无法继续进行。redis会在定时任务对字典进行主动搬迁。
[redis-7.2.2\src\server.c]
void databasesCron(void) {
//通过随机采样删除过期key,从节点不需要主动删除
//通过主节点同步del语句即可
if (server.active_expire_enabled) {
if (iAmMaster()) {
activeExpireCycle(ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW);
} else {
expireSlaveKeys();
}
}
/* Defrag keys gradually. */
activeDefragCycle();
/*
如果需要,执行散列表重新散列,但只有在没有其他进程在磁盘上保存DB时才执行。
否则,重新散列是不好的,因为会导致大量的写时复制内存页。
*/
if (!hasActiveChildProcess()) {
static unsigned int resize_db = 0;
static unsigned int rehash_db = 0;
//#define CRON_DBS_PER_CALL 16
int dbs_per_call = CRON_DBS_PER_CALL;
int j;
/* Don't test more DBs than we have. */
if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum) dbs_per_call = server.dbnum;
/* Resize */
for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call; j++) {
tryResizeHashTables(resize_db % server.dbnum);
resize_db++;
}
/* Rehash */
if (server.activerehashing) {
for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call; j++) {
int work_done = incrementallyRehash(rehash_db);
if (work_done) {
/* If the function did some work, stop here, we'll do
* more at the next cron loop. */
break;
} else {
/* If this db didn't need rehash, we'll try the next one. */
rehash_db++;
rehash_db %= server.dbnum;
}
}
}
}
}
/* If the percentage of used slots in the HT reaches HASHTABLE_MIN_FILL
* we resize the hash table to save memory */
void tryResizeHashTables(int dbid) {
if (htNeedsResize(server.db[dbid].dict))
dictResize(server.db[dbid].dict);
if (htNeedsResize(server.db[dbid].expires))
dictResize(server.db[dbid].expires);
}
/*
我们的哈希表实现在我们从哈希表中写入/读取时执行增量的重新哈希。但是,如果服务器空闲,哈希表将长时间使用两个表。因此,我们尝试在每次调用该函数时使用1毫秒的CPU时间来执行一些重新散列。
如果执行了一些散列,该函数返回1,否则返回0。
*/
int incrementallyRehash(int dbid) {
/* Keys dictionary */
if (dictIsRehashing(server.db[dbid].dict)) {
dictRehashMilliseconds(server.db[dbid].dict,1);
return 1; /* already used our millisecond for this loop... */
}
/* Expires */
if (dictIsRehashing(server.db[dbid].expires)) {
dictRehashMilliseconds(server.db[dbid].expires,1);
return 1; /* already used our millisecond for this loop... */
}
return 0;
}
旧版本中dict的结构
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
dictht ht[2];
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */
} dict;
/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we
* implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;
unsigned long size;
unsigned long sizemask;
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
//Union允许在同一内存位置存储不同的数据类型,而Enum用于定义一组相关常量并赋予它们有意义的名称。
总结
负载因子ratio=used/buckets[表中的元素数量/哈希表一维数组长度]
扩容时机
- ratio>=1并且不发生aofwrite,bgsave,这样做是为了防止更多的内存分离
- ratio>5,强制进行扩容
缩容时机
- ratio<0.1强制缩容,为了节省内存空间
扩容策略
- 新表的大小为第一次大于原表uesd+1的2的次幂[redis3.2.100版本是原表used*2]
缩容策略
- 容纳所有元素的最小大小;新表的大小为第一次大于原表uesd的2的次幂[redis3.2.100版本是原表used]
迁移的实现
- 迁移的时机。在"dictFindPositionForInsert"和"dictGenericDelete"这两个函数中会发生数据的迁移dictRehash,也就是线上执行写操作的时候会触发rehash。为了防止客户端下线不再执行写操作,dict长时间占用着两个表,redis后台线程会专门维护一个定时任务用来进行数据的迁移。
- 迁移的顺序。按照rehashidx指向的顺序进行数据的迁移,而且每次只迁移一个bucket。
- 迁移完成。如果旧表中的元素个数变为0则表明迁移完成。(通过源码可以发现,最外层循环是通过判断旧表中的元素个数是否为0,不为0的话进入循环内会继续判断rehashidx是否超过旧表数组的一维长度,所以我认为判断迁移是否完成是通过used和rehashidx共同完成的。)