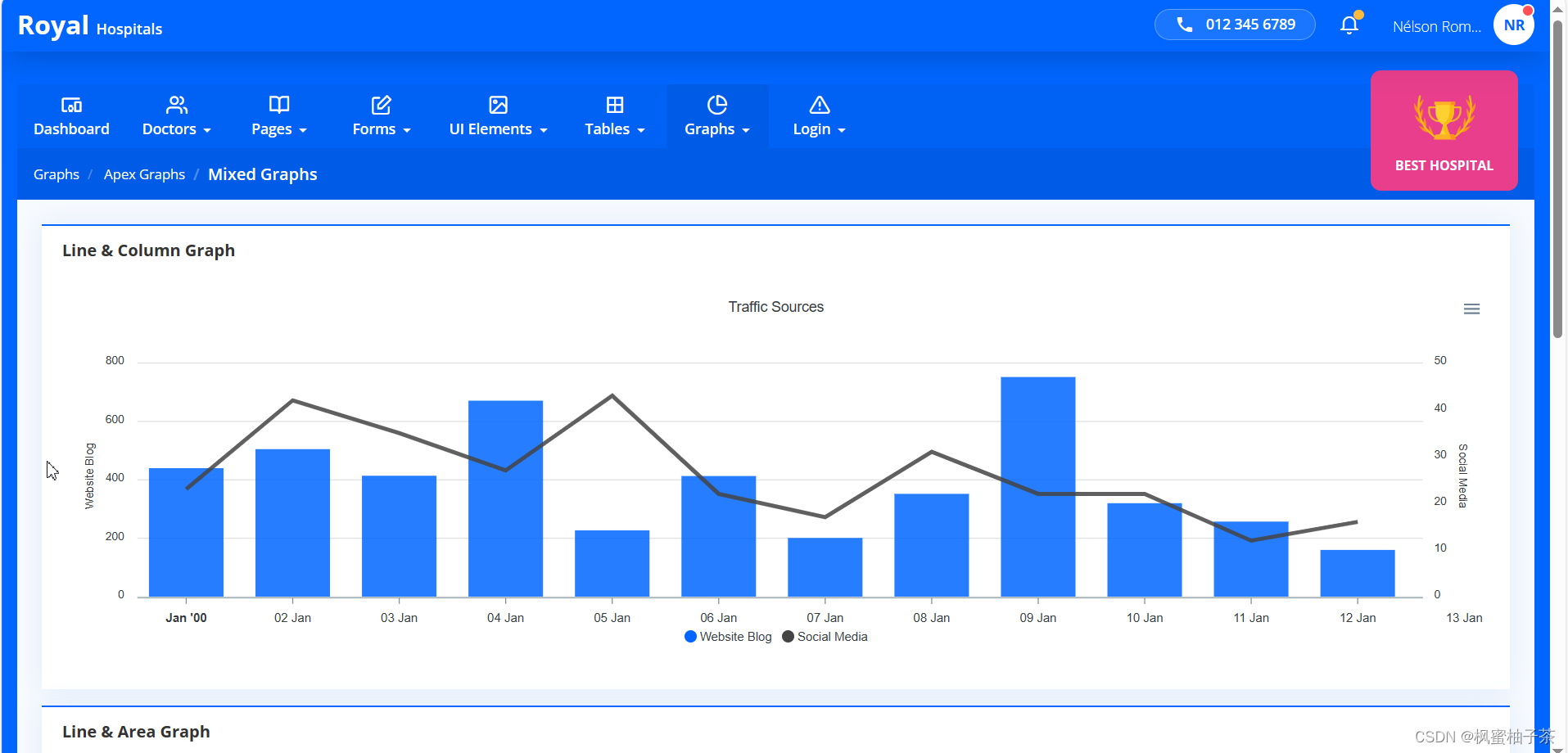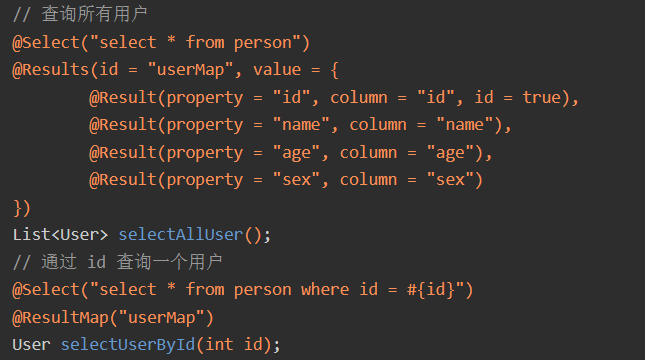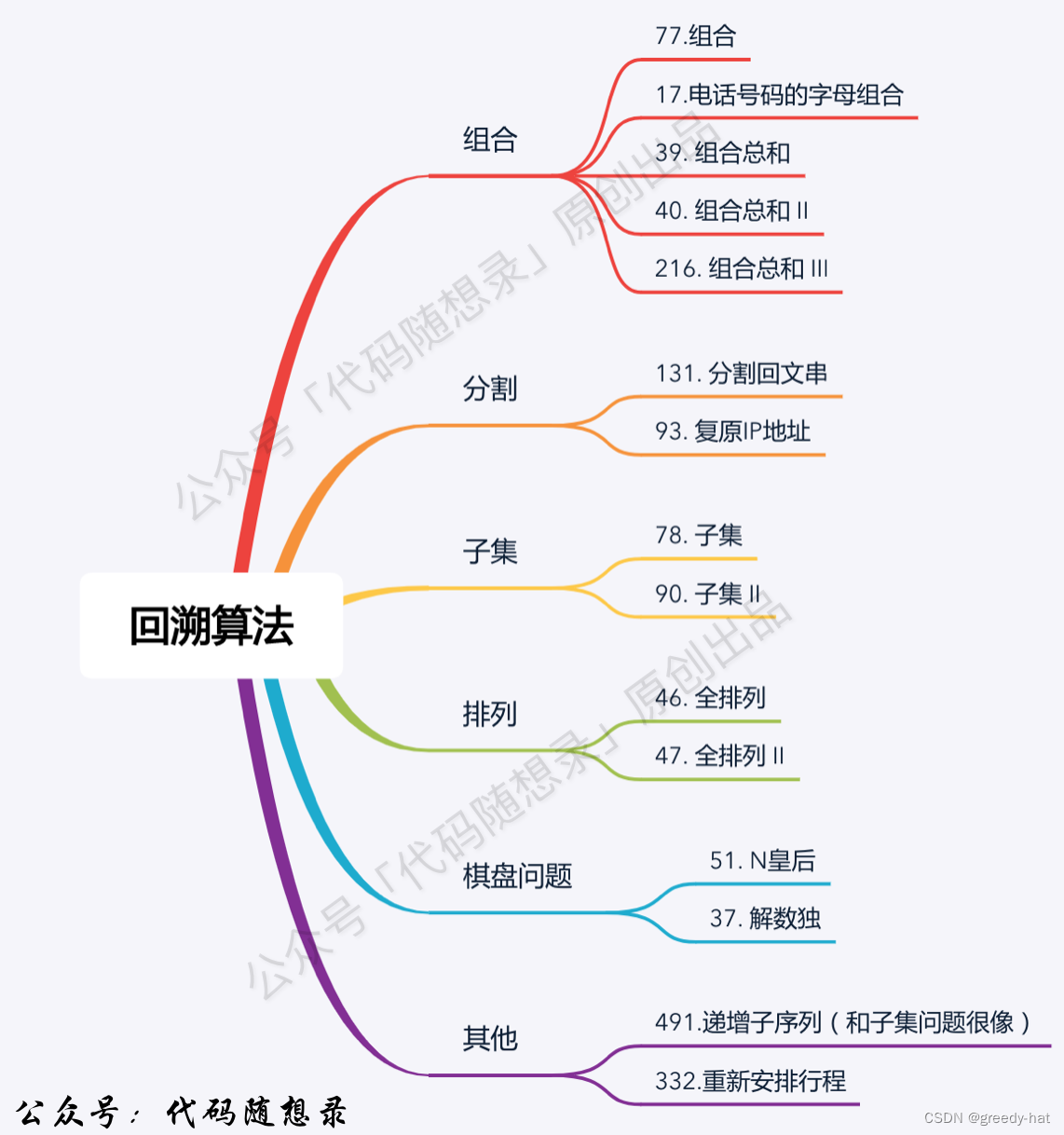
- 组合
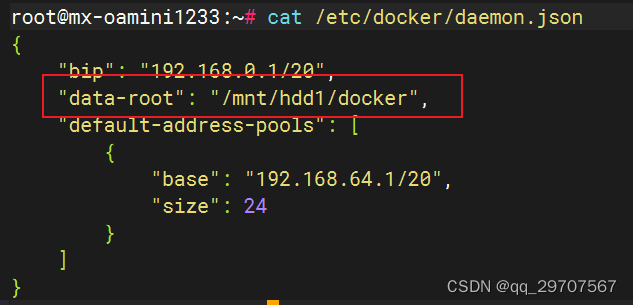
//未剪枝
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
backtracking(n, k, 1);
return ans;
}
public void backtracking(int n, int k, int startIndex) {
if (path.size() == k) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {
path.add(i);
backtracking(n, k, i + 1);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
//剪枝
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
backtracking(n, k, 1);
return ans;
}
public void backtracking(int n, int k, int startIndex) {
if (path.size() == k) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i <= n - (k - path.size()) + 1; i++) {
path.add(i);
backtracking(n, k, i + 1);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
- 组合总和 III
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
backtracking(k, n, 0, 1);
return ans;
}
public void backtracking(int k, int targetSum, int sum, int startIndex) {
if (path.size() == k) {
if (sum == targetSum) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i <= 9; i++) {
sum += i;
path.add(i);
backtracking(k, targetSum, sum, i + 1);
sum -= i;
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
- 电话号码的字母组合
class Solution {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder();
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
if (digits == null || digits.length() == 0) {
return ans;
}
String[] numString = { "", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz" };
backTracking(digits, numString, 0);
return ans;
}
public void backTracking(String digits, String[] numString, int len) {
if (len == digits.length()) {
ans.add(temp.toString());
return;
}
String str = numString[digits.charAt(len) - '0'];
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
temp.append(str.charAt(i));
backTracking(digits, numString, len + 1);
temp.deleteCharAt(temp.length() - 1);
}
}
}
- 组合总和
//未剪枝
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
bacaktracking(candidates, target, 0, 0);
return ans;
}
public void bacaktracking(int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex) {
if (sum > target) {
return;
}
if (sum == target) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {
sum += candidates[i];
path.add(candidates[i]);
bacaktracking(candidates, target, sum, i);
sum -= candidates[i];
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
在求和问题中,排序之后加剪枝是常见的套路!
//剪枝
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
bacaktracking(candidates, target, 0, 0);
return ans;
}
public void bacaktracking(int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex) {
if (sum == target) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {
sum += candidates[i];
if (sum > target) {
break;
}
path.add(candidates[i]);
bacaktracking(candidates, target, sum, i);
sum -= candidates[i];
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
- 组合总和 II
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0);
return ans;
}
public void backtracking(int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex) {
if (sum == target) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (i > startIndex && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
sum += candidates[i];
if (sum > target) {
break;
}
path.add(candidates[i]);
backtracking(candidates, target, sum, i + 1);
sum -= candidates[i];
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
- 分割回文串
class Solution {
List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<String> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
backtracking(s, 0);
return ans;
}
public void backtracking(String s, int startIndex) {
if (startIndex >= s.length()) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (isPalindrome(s, startIndex, i)) {
String str = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1);
path.add(str);
} else {
continue;
}
backtracking(s, i + 1);
path.removeLast();
}
}
public boolean isPalindrome(String s, int start, int end) {
for (int i = startIndex, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {
if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
- 复原 IP 地址
class Solution {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder currentIP = new StringBuilder();
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
if (s.length() > 12)
return ans;
backtracking(s, 0, 0);
return ans;
}
private void backtracking(String s, int startIndex, int pointNum) {
if (pointNum == 3) {
if (isValid(s, startIndex, s.length() - 1)) {
currentIP.append(s.substring(startIndex));
ans.add(currentIP.toString());
}
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (isValid(s, startIndex, i)) {
int len = currentIP.length();
currentIP.append(s.substring(startIndex, i + 1));
if (pointNum < 3) {
currentIP.append(".");
}
backtracking(s, i + 1, pointNum + 1);
currentIP.setLength(len);
} else {
break;
}
}
}
private Boolean isValid(String s, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) {
return false;
}
if (s.charAt(start) == '0' && start != end) { // 0开头的数字不合法
return false;
}
int num = 0;
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) > '9' || s.charAt(i) < '0') { // 遇到非数字字符不合法
return false;
}
num = num * 10 + (s.charAt(i) - '0');
if (num > 255) { // 如果大于255了不合法
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
class Solution {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder currentIP = new StringBuilder();
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
if (s.length() > 12)
return ans;
backtracking(s, 0, 0);
return ans;
}
private void backtracking(String s, int startIndex, int pointNum) {
if (pointNum == 3) {
if (isValid(s, startIndex, s.length() - 1)) {
currentIP.append(s.substring(startIndex));
ans.add(currentIP.toString());
}
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (isValid(s, startIndex, i)) {
int len = currentIP.length();
currentIP.append(s.substring(startIndex, i + 1));
if (pointNum < 3) {
currentIP.append(".");
}
backtracking(s, i + 1, pointNum + 1);
currentIP.setLength(len);
} else {
break;
}
}
}
private Boolean isValid(String s, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) {
return false;
}
if (s.charAt(start) == '0' && start != end) {
return false;
}
if (Integer.parseInt(s.substring(start, end + 1)) < 0 || Integer.parseInt(s.substring(start, end + 1)) > 255) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
- 子集
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
backtracking(nums, 0);
return ans;
}
public void backtracking(int[] nums, int startIndex) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
if (startIndex >= nums.length) {
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {
path.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(nums, i + 1);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
- 子集 II
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
backtracking(nums, 0);
return ans;
}
public void backtracking(int[] nums, int startIndex) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (i > startIndex && nums[i - 1] == nums[i]) {
continue;
}
path.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(nums, i + 1);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
- 非递减子序列
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) {
backtacking(nums, 0);
return ans;
}
public void backtacking(int[] nums, int startIndex) {
if (path.size() >= 2) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (!path.isEmpty() && path.peekLast() > nums[i] || set.contains(nums[i])) {
continue;
}
set.add(nums[i]);
path.add(nums[i]);
backtacking(nums, i + 1);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
- 全排列
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) {
return ans;
}
backtracking(nums, path);
return ans;
}
public void backtracking(int[] nums, Deque<Integer> path) {
if (path.size() == nums.length) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (path.contains(nums[i])) {
continue;
}
path.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(nums, path);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}