专栏介绍:YOLOv9改进系列 | 包含深度学习最新创新,主力高效涨点!!!
一、本文介绍
本文只有代码及注意力模块简介,YOLOv9中的添加教程:可以看这篇文章。
YOLOv9有效提点|加入SE、CBAM、ECA、SimAM等几十种注意力机制(一)
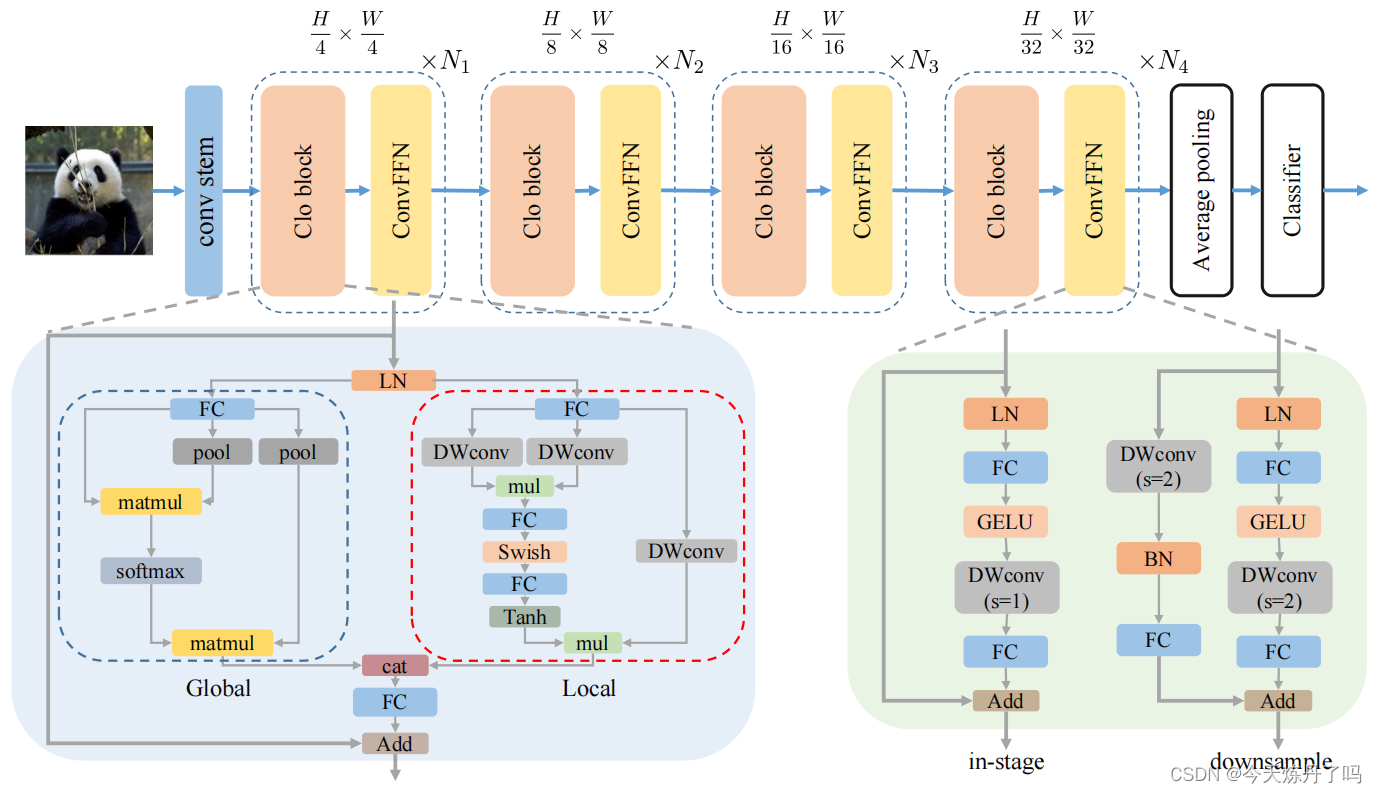
CloFormer:《Rethinking Local Perception in Lightweight Vision Transformer》
CloFormer是一种轻量级视觉转换器,它通过利用上下文感知的本地增强,提高了在图像分类、目标检测和语义分割等任务上的性能。CloFormer通过引入一种名为AttnConv的卷积操作,结合共享权重和上下文感知权重,有效地捕捉了高频率的本地信息。实验结果表明,CloFormer在各种视觉任务中具有显著优势。
class AttnMap(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim):
super().__init__()
self.act_block = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 1, 1, 0),
MemoryEfficientSwish(),
nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 1, 1, 0)
#nn.Identity()
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.act_block(x)
class EfficientAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, group_split: List[int], kernel_sizes: List[int], window_size=7,
attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0., qkv_bias=True):
super().__init__()
assert sum(group_split) == num_heads
assert len(kernel_sizes) + 1 == len(group_split)
self.dim = dim
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.dim_head = dim // num_heads
self.scalor = self.dim_head ** -0.5
self.kernel_sizes = kernel_sizes
self.window_size = window_size
self.group_split = group_split
convs = []
act_blocks = []
qkvs = []
#projs = []
for i in range(len(kernel_sizes)):
kernel_size = kernel_sizes[i]
group_head = group_split[i]
if group_head == 0:
continue
convs.append(nn.Conv2d(3*self.dim_head*group_head, 3*self.dim_head*group_head, kernel_size,
1, kernel_size//2, groups=3*self.dim_head*group_head))
act_blocks.append(AttnMap(self.dim_head*group_head))
qkvs.append(nn.Conv2d(dim, 3*group_head*self.dim_head, 1, 1, 0, bias=qkv_bias))
#projs.append(nn.Linear(group_head*self.dim_head, group_head*self.dim_head, bias=qkv_bias))
if group_split[-1] != 0:
self.global_q = nn.Conv2d(dim, group_split[-1]*self.dim_head, 1, 1, 0, bias=qkv_bias)
self.global_kv = nn.Conv2d(dim, group_split[-1]*self.dim_head*2, 1, 1, 0, bias=qkv_bias)
#self.global_proj = nn.Linear(group_split[-1]*self.dim_head, group_split[-1]*self.dim_head, bias=qkv_bias)
self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(window_size, window_size) if window_size!=1 else nn.Identity()
self.convs = nn.ModuleList(convs)
self.act_blocks = nn.ModuleList(act_blocks)
self.qkvs = nn.ModuleList(qkvs)
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 1, 1, 0, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
def high_fre_attntion(self, x: torch.Tensor, to_qkv: nn.Module, mixer: nn.Module, attn_block: nn.Module):
'''
x: (b c h w)
'''
b, c, h, w = x.size()
qkv = to_qkv(x) #(b (3 m d) h w)
qkv = mixer(qkv).reshape(b, 3, -1, h, w).transpose(0, 1).contiguous() #(3 b (m d) h w)
q, k, v = qkv #(b (m d) h w)
attn = attn_block(q.mul(k)).mul(self.scalor)
attn = self.attn_drop(torch.tanh(attn))
res = attn.mul(v) #(b (m d) h w)
return res
def low_fre_attention(self, x : torch.Tensor, to_q: nn.Module, to_kv: nn.Module, avgpool: nn.Module):
'''
x: (b c h w)
'''
b, c, h, w = x.size()
q = to_q(x).reshape(b, -1, self.dim_head, h*w).transpose(-1, -2).contiguous() #(b m (h w) d)
kv = avgpool(x) #(b c h w)
kv = to_kv(kv).view(b, 2, -1, self.dim_head, (h*w)//(self.window_size**2)).permute(1, 0, 2, 4, 3).contiguous() #(2 b m (H W) d)
k, v = kv #(b m (H W) d)
attn = self.scalor * q @ k.transpose(-1, -2) #(b m (h w) (H W))
attn = self.attn_drop(attn.softmax(dim=-1))
res = attn @ v #(b m (h w) d)
res = res.transpose(2, 3).reshape(b, -1, h, w).contiguous()
return res
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):
'''
x: (b c h w)
'''
res = []
for i in range(len(self.kernel_sizes)):
if self.group_split[i] == 0:
continue
res.append(self.high_fre_attntion(x, self.qkvs[i], self.convs[i], self.act_blocks[i]))
if self.group_split[-1] != 0:
res.append(self.low_fre_attention(x, self.global_q, self.global_kv, self.avgpool))
return self.proj_drop(self.proj(torch.cat(res, dim=1)))
《Reversible Column Networks》
Reversible Column Networks一种新的神经网络设计范式——可逆列网络(RevCol)。RevCol主要由多个子网络(称为“列”)的副本组成,这些子网络之间使用了多级可逆连接。这种架构方案使得RevCol的行为与传统的网络非常不同:在正向传播过程中,当特征通过每个列时,它们被逐渐解开,同时保持总信息量,而不是像其他网络那样进行压缩或丢弃。
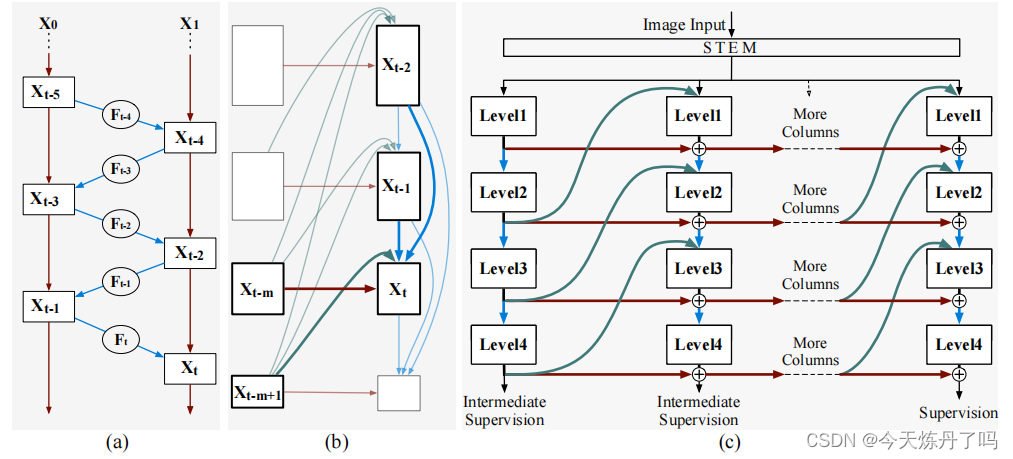
这个暂时没调试,代码地址:RevCol/models/revcol.py at main · megvii-research/RevCol (github.com)![]() https://github.com/megvii-research/RevCol/blob/main/models/revcol.py
https://github.com/megvii-research/RevCol/blob/main/models/revcol.py
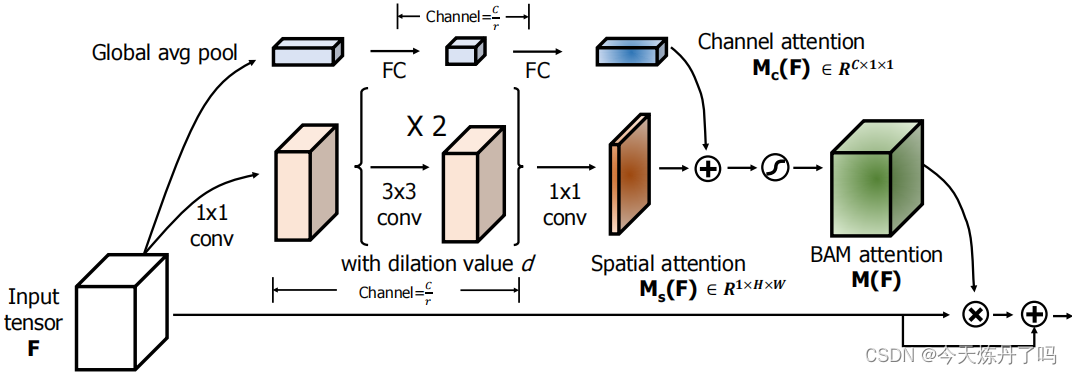
《BAM: Bottleneck Attention Module》
瓶颈注意模块(BAM)关注深度神经网络中注意力机制的影响,提出了一个简单而有效的注意力模块,即瓶颈注意模块(BAM),可以与任何前馈卷积神经网络集成,沿着两个不同的路径(通道和空间)推断注意力映射。 将模块放在模型的每个瓶颈处(特征映射产生降采样),构建一个具有多个参数的分层注意,可以与任何前馈模型以端到端方式进行训练。
def autopad(k, p=None, d=1): # kernel, padding, dilation
"""Pad to 'same' shape outputs."""
if d > 1:
k = d * (k - 1) + 1 if isinstance(k, int) else [d * (x - 1) + 1 for x in k] # actual kernel-size
if p is None:
p = k // 2 if isinstance(k, int) else [x // 2 for x in k] # auto-pad
return p
class Flatten(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16, num_layers=3):
super().__init__()
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
gate_channels = [channel]
gate_channels += [channel // reduction] * num_layers
gate_channels += [channel]
self.ca = nn.Sequential()
self.ca.add_module('flatten', Flatten())
for i in range(len(gate_channels) - 2):
self.ca.add_module('fc%d' % i, nn.Linear(gate_channels[i], gate_channels[i + 1]))
self.ca.add_module('bn%d' % i, nn.BatchNorm1d(gate_channels[i + 1]))
self.ca.add_module('relu%d' % i, nn.ReLU())
self.ca.add_module('last_fc', nn.Linear(gate_channels[-2], gate_channels[-1]))
def forward(self, x):
res = self.avgpool(x)
res = self.ca(res)
res = res.unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1).expand_as(x)
return res
class SpatialAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16, num_layers=3, dia_val=2):
super().__init__()
self.sa = nn.Sequential()
self.sa.add_module('conv_reduce1',
nn.Conv2d(kernel_size=1, in_channels=channel, out_channels=channel // reduction))
self.sa.add_module('bn_reduce1', nn.BatchNorm2d(channel // reduction))
self.sa.add_module('relu_reduce1', nn.ReLU())
for i in range(num_layers):
self.sa.add_module('conv_%d' % i, nn.Conv2d(kernel_size=3, in_channels=channel // reduction,
out_channels=channel // reduction, padding=autopad(3, None, dia_val), dilation=dia_val))
self.sa.add_module('bn_%d' % i, nn.BatchNorm2d(channel // reduction))
self.sa.add_module('relu_%d' % i, nn.ReLU())
self.sa.add_module('last_conv', nn.Conv2d(channel // reduction, 1, kernel_size=1))
def forward(self, x):
res = self.sa(x)
res = res.expand_as(x)
return res
class BAMBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel=512, reduction=16, dia_val=2):
super().__init__()
self.ca = ChannelAttention(channel=channel, reduction=reduction)
self.sa = SpatialAttention(channel=channel, reduction=reduction, dia_val=dia_val)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def init_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001)
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
sa_out = self.sa(x)
ca_out = self.ca(x)
weight = self.sigmoid(sa_out + ca_out)
out = (1 + weight) * x
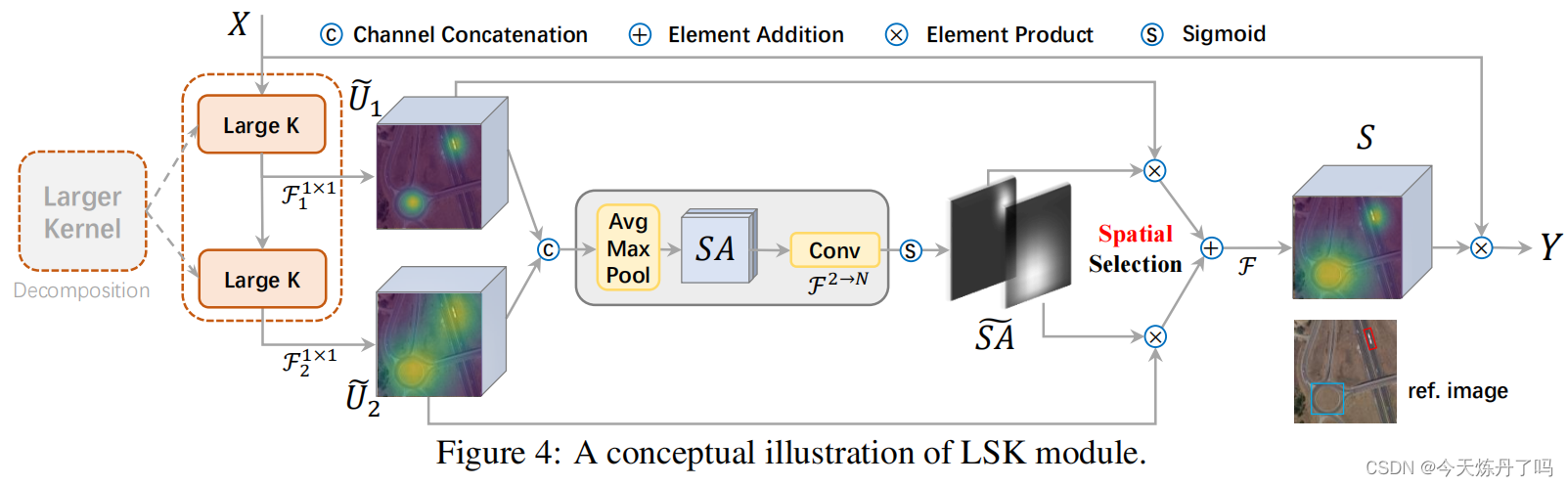
return out《Large Selective Kernel Network for Remote Sensing Object Detection》
LSKnet是一种用于遥感目标检测的大规模选择性核网络,改论文提出了远程感应目标检测新方法LSKNet,这种网络可以动态地调整其大的空间感受野,以更好地模拟远程感应场景中不同物体的范围上下文。文章中提到,这是首次在远程感应目标检测领域探索大型和选择性核机制。
class LSKblock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim):
super().__init__()
self.conv0 = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 5, padding=2, groups=dim)
self.conv_spatial = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 7, stride=1, padding=9, groups=dim, dilation=3)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim//2, 1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim//2, 1)
self.conv_squeeze = nn.Conv2d(2, 2, 7, padding=3)
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(dim//2, dim, 1)
def forward(self, x):
attn1 = self.conv0(x)
attn2 = self.conv_spatial(attn1)
attn1 = self.conv1(attn1)
attn2 = self.conv2(attn2)
attn = torch.cat([attn1, attn2], dim=1)
avg_attn = torch.mean(attn, dim=1, keepdim=True)
max_attn, _ = torch.max(attn, dim=1, keepdim=True)
agg = torch.cat([avg_attn, max_attn], dim=1)
sig = self.conv_squeeze(agg).sigmoid()
attn = attn1 * sig[:,0,:,:].unsqueeze(1) + attn2 * sig[:,1,:,:].unsqueeze(1)
attn = self.conv(attn)
return x * attn