😎😎😎物体检测-系列教程 总目录
有任何问题欢迎在下面留言
本篇文章的代码运行界面均在Pycharm中进行
本篇文章配套的代码资源已经上传
点我下载源码
13、Focus模块
13.1 基本流程
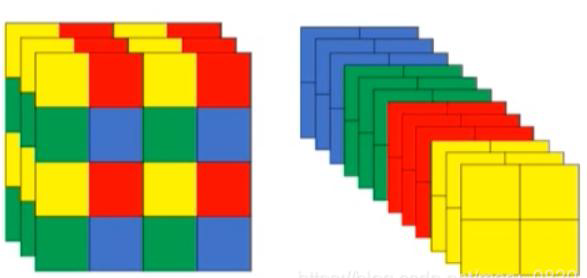
- 原始输入图像的格式为:tensor: float32[1,3,640,640]
- 如图所示,首先对于每个通道对应的图都将其平均分成A、B、C、D4块
- 再分别将A、B、C、D也平均分成更小4块
- 从A、B、C、D每个位置都各取一块拼接成一个大块
- 将大块在原图对应的通道位置进行通道的堆叠
- 最后得到4张图像,此时通道数变成了12
- 此时进行卷积的时候,长宽减小而通道输入增加了,有利于减少计算量,但是却不会减少AP值
- 此时数据的格式为:tensor: float32[1,320,320,12]
- focus模块也有自己的卷积,然后经过hardswish激活函数 H a r d s w i s h ( x ) = { 0 i f x < = − 3 , x i f x > = + 3 , x ∗ ( x + 3 ) / 6 o t h e r w i s e Hardswish(x)=\begin{cases} 0 & if x<=-3,\\ x & if x>=+3,\\ x*(x+3)/6 & otherwise \end{cases} Hardswish(x)=⎩ ⎨ ⎧0xx∗(x+3)/6ifx<=−3,ifx>=+3,otherwise
13.2 源码
Focus模块通过空间重组来增强通道信息
class Focus(nn.Module):
# Focus wh information into c-space
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super(Focus, self).__init__()
self.conv = Conv(c1 * 4, c2, k, s, p, g, act)
def forward(self, x): # x(b,c,w,h) -> y(b,4c,w/2,h/2)
return self.conv(torch.cat([x[..., ::2, ::2], x[..., 1::2, ::2], x[..., ::2, 1::2], x[..., 1::2, 1::2]], 1))
- 继承nn.module
- 构造函数,接受7个参数:c1输入通道、c2输出通道、k卷积核大小、s卷积步长、p填充、g卷积分组数、act激活函数
- 初始化
- 调用Conv类构造一个卷积层,这个类已经实现了批归一化、卷积、激活函数等
- 前向传播函数
- 将输入
x在空间维度上分割为四部分,然后在通道维度上拼接,通过卷积层处理后输出
14、Model类
14.1 构造函数
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfg='yolov5s.yaml', ch=3, nc=None): # model, input channels, number of classes
super(Model, self).__init__()
if isinstance(cfg, dict):
self.yaml = cfg # model dict
else: # is *.yaml
import yaml # for torch hub
self.yaml_file = Path(cfg).name
with open(cfg) as f:
self.yaml = yaml.load(f, Loader=yaml.FullLoader) # model dict
# Define model
if nc and nc != self.yaml['nc']:
print('Overriding %s nc=%g with nc=%g' % (cfg, self.yaml['nc'], nc))
self.yaml['nc'] = nc # override yaml value
self.model, self.save = parse_model(deepcopy(self.yaml), ch=[ch]) # model, savelist, ch_out
# print([x.shape for x in self.forward(torch.zeros(1, ch, 64, 64))])
# Build strides, anchors
m = self.model[-1] # Detect()
if isinstance(m, Detect):
s = 128 # 2x min stride
m.stride = torch.tensor([s / x.shape[-2] for x in self.forward(torch.zeros(1, ch, s, s))]) # forward
m.anchors /= m.stride.view(-1, 1, 1)
check_anchor_order(m)
self.stride = m.stride
self._initialize_biases() # only run once
# print('Strides: %s' % m.stride.tolist())
# Init weights, biases
initialize_weights(self)
self.info()
print('')
- 继承nn.Module
- 构造函数,传入3个参数,配置文件路径、输入通道数、类别数
- 初始化
- 配置信息是否为字典:
- 赋值给self.yaml
- 否则:
- 导入yaml工具包
- yaml_file ,获取文件名称
- 打开配置文件
- yaml ,加载配置文件
- 如果指定了类别数,并且与配置文件中的类别数不同
- 打印一条消息,说明正在覆盖YAML文件中的类别数
- 更新yaml字典中的类别数
- model,save ,调用parse_model函数,传入模型配置和输入通道数,返回模型的层和需要保存的层的列表
- m,获取模型的最后一层,通常是用于检测的层
- 最后一层是否是一个检测层
- s,设置一个基准步长大小
- m.stride,计算并设置检测层的步长。这是通过前向传播一个零张量(其尺寸基于s和输入通道数ch)并计算输出特征图的高度或宽度相对于s的比率来完成的
- m.anchors,调整锚点大小,使其适应步长的变化
- 调用check_anchor_order函数,检查锚点的顺序,并在需要时进行调整
- stride
- 调用**_initialize_biases函数**初始化模型的偏置参数,确保初始预测接近于均匀分布
- 调用initialize_weights函数来初始化模型中所有层的权重,以帮助模型训练时的收敛
- 调用info函数,打印模型的信息
- 打印一个换行,在输出中提供清晰的分隔,使得模型信息更容易阅读