文章目录
- 流程梳理
- 1. 打开点云文件
- 2. 播放点云数据
- 3. SUMA部分的流程图说明
- 3.1 SUMA核心流程分析,其中也包含部分SUMA++
- 3.2 preprocess部分
- 3.3 updatePose部分
- 3.4 updateMap部分
- 4. SUMA++中有关语义模型rangenet++的部分
- 4.1 下面是解析模型引擎
- 4.2 下面这块是从配置文件中读取颜色以及标签还有一些参数的部分
- 4.3 这一块是执行语义模块并且将预测结果保存在一个语义容器当中,作为语义mask
- 未完待续:有人看就后面接着补充一些,先发布这么多,有关语义地图如何预处理修正还有里程计优化部分包括如何对动目标进行确定并且去除都还在看
首先拿到代码一定是先着重看一下结构,整体源代码分为三大块
- glow
- rangenet_lib
- semantic_suma。
其中rangenet_lib是语义相关的代码,而semantic_suma是核心代码,应该着重分析
流程梳理
一般来说,我们运行一个cpp项目文件,通常是要运行一个launch文件的,其中表明具体的运行节点以及对应的cpp。而这个SuMa++运行的时候是直接输入./visualizer,然后在可视化界面中打开对应的点云文件,并且播放的。所以我们刚开始的切入点就直接放在visualizer这个文件夹下面。
1. 打开点云文件
VisualizerWindow 43
// 该按钮对应的一个触发器,点一下就运行showOpenFileDialog()这个函数
connect(ui_.actionOpenLaserscan, SIGNAL(triggered()), this, SLOT(showOpenFileDialog()));
VisualizerWindow 202-211
void VisualizerWindow::showOpenFileDialog() {
play(false); // stop playback.
/*
*第一个参数 this,指代父窗口为当前组件,并在当前父窗口下弹出一个子框口对话框
*第二个参数Select laserscan file,用于指定弹出的对话框标题为"Select laserscan file"
*第三个参数lastDirectory_,指定对话框显示时默认打开的目录是lastDirectory_这个参数下存储的目录
*第四个参数过滤器,指筛选出来的文件格式
*/
QString retValue =
QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, "Select laserscan file", lastDirectory_,
"Laserscan files(*.bin *.pcap *.sim);;KITTI laserscans (*.bin);; PCAP "
"laserscans (*.pcap);; Simulation (*.sim)");
// 如果这个路径不为空,则打开该文件
if (!retValue.isNull()) openFile(retValue);
}
VisualizerWindow openFile()
void VisualizerWindow::openFile(const QString& filename) {
play(false); // stop playback.
// 设置窗口标题
if (!filename.isNull()) {
QString title = "Semantic SuMa";
title.append(" - ");
QStringList parts = filename.split("/");
title.append(QString::fromStdString(FileUtil::dirName(filename.toStdString())));
setWindowTitle(title);
std::shared_ptr<Model> model;
ui_.wCanvas->setRobotModel(model);
// 默认后缀为INVALID
std::string extension = "INVALID";
QFileInfo file_info(filename);
// 如果是目录,则以最多的文件后缀视作extension
if (file_info.isDir()) {
QDir directory(filename);
QStringList files = directory.entryList(QDir::NoFilter, QDir::Name);
std::map<std::string, int32_t> suffix_count;
for (int32_t i = 0; i < files.size(); ++i) {
QFileInfo info(directory.filePath(files[i]));
if (!info.isFile()) continue;
// 将文件后缀相同的数量存储在map suffix_count中,.suffix获取最后的文件后缀,toStdString转化为标准String
std::string ext = info.suffix().toStdString();
if (suffix_count.find(ext) == suffix_count.end()) suffix_count[ext] = 0;
suffix_count[ext] += 1;
}
if (suffix_count.size() > 0) {
int32_t maxCount = suffix_count.begin()->second;
extension = std::string(".") + suffix_count.begin()->first;
for (auto& entry : suffix_count) {
if (entry.second > maxCount) {
extension = std::string(".") + entry.first;
maxCount = entry.second;
}
}
std::cout << "Heuristically found '" << extension << "' as extension." << std::endl;
}
// 如果该文件只是一个,则将它的后缀作为extension
} else if (file_info.isFile()) {
extension = std::string(".") + file_info.suffix().toStdString();
}
if (extension == ".bin") {
delete reader_;
// 这个KITTIReader算是其中最重要的部分,读取了Kitti数据并且加入了语义信息
// 其中initScanFilenames(scan_filename);部分过滤了非".bin"格式的文件
// network = std::unique_ptr<Net>(new NetTensorRT(path));这个用TensorRT来读取已有的model
KITTIReader* reader_tmp = new KITTIReader(filename.toStdString(), params_, 50);
ui_.wCanvas->setColorMap(reader_tmp->getColorMap()); // get color map from rangenet
fusion_->setColorMap(reader_tmp->getColorMap());
reader_ = reader_tmp;
scanFrequency = 10.0f; // in Hz.
timer_.setInterval(10); // 1./10. second = 100 msecs.
if (fusion_ != nullptr) fusion_->reset();
ui_.wCanvas->reset();
uint32_t N = reader_->count();
precomputed_.resize(N);
oldPoses_.resize(N);
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
precomputed_[i] = false;
}
if (oldPoses_.size() > 0) oldPoses_[0] = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity();
calib_.clear();
groundtruth_.clear();
// 校准文件读取
if (parts.size() > 2) {
std::string calibration_file;
for (int32_t i = 0; i < parts.size() - 2; ++i) {
calibration_file += parts[i].toStdString();
calibration_file += "/";
}
calibration_file += "calib.txt";
std::cout << "calibration filename: " << calibration_file << "..." << std::flush;
if (rv::FileUtil::exists(calibration_file)) {
calib_.initialize(calibration_file);
std::cout << "loaded." << std::endl;
ui_.wCanvas->setCalibration(calib_);
fusion_->setCalibration(calib_);
} else {
std::cout << "not found." << std::endl;
}
}
// 如果有矫正矩阵数据,则地面数据读取时存入为矫正后的数据
// 如果没有矫正数据,则直接存入地面真值数据
if (parts.size() > 3 && calib_.exists("Tr")) {
std::string sequence = parts[parts.size() - 3].toStdString();
Eigen::Matrix4f Tr = calib_["Tr"];
Eigen::Matrix4f Tr_inv = Tr.inverse();
// find ground truth poses.
std::string poses_file;
for (int32_t i = 0; i < parts.size() - 4; ++i) {
poses_file += parts[i].toStdString();
poses_file += "/";
}
poses_file += "poses/" + sequence + ".txt";
std::cout << "ground truth filename: " << poses_file << std::endl;
if (rv::FileUtil::exists(poses_file)) {
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4f> poses = KITTI::Odometry::loadPoses(poses_file);
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < poses.size(); ++i) {
Eigen::Matrix4f pose = poses[i];
groundtruth_.push_back(Tr_inv * pose * Tr);
}
std::cout << groundtruth_.size() << " poses read." << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "not found." << std::endl;
}
} else {
std::string sequence = parts[parts.size() - 3].toStdString();
// find ground truth poses.
std::string poses_file;
for (int32_t i = 0; i < parts.size() - 4; ++i) {
poses_file += parts[i].toStdString();
poses_file += "/";
}
poses_file += "poses/" + sequence + ".txt";
std::cout << "ground truth filename: " << poses_file << std::endl;
if (rv::FileUtil::exists(poses_file)) {
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4f> poses = KITTI::Odometry::loadPoses(poses_file);
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < poses.size(); ++i) {
Eigen::Matrix4f pose = poses[i];
groundtruth_.push_back(pose);
}
std::cout << groundtruth_.size() << " poses read." << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "not found." << std::endl;
}
}
// load the car model.
// 读取小汽车模型并且设定位姿
initilizeKITTIrobot();
ui_.wCanvas->setGroundtruth(groundtruth_);
ui_.sldTimeline->setEnabled(reader_->isSeekable());
ui_.sldTimeline->setMaximum(reader_->count() - 1);
if (ui_.sldTimeline->value() == 0) setScan(0); // triggers update of scan.
ui_.sldTimeline->setValue(0);
}
else {
std::cerr << "SuMa++ will fail because of wrong format of input LiDAR scans" << std::endl;
}
}
if (reader_ != nullptr) {
ui_.wCanvas->setScanCount(reader_->count());
}
}
2. 播放点云数据
VisualizerWindow.cpp 46
connect(ui_.btnPlay, SIGNAL(toggled(bool)), this, SLOT(play(bool)));
void VisualizerWindow::play(bool start) {
if (start) {
timer_.start();
ui_.btnPlay->setChecked(true);
} else {
timer_.stop();
ui_.btnPlay->setChecked(false);
}
updatePlaybackControls();
}
void VisualizerWindow::updatePlaybackControls() {
if (reader_ != nullptr) {
// 播放按钮的功能
ui_.btnPlay->setEnabled(true);
// 重新回到开始
ui_.btnReset->setEnabled(true);
// maybe better to define separate up/down icons.
if (ui_.btnPlay->isChecked())
ui_.btnPlay->setIcon(QIcon::fromTheme("media-playback-pause"));
else
ui_.btnPlay->setIcon(QIcon::fromTheme("media-playback-start"));
if (currentScanIdx_ < reader_->count() - 1)
// 如果当前帧不为最后一帧
ui_.btnNext->setEnabled(true);
else
ui_.btnNext->setEnabled(false);
} else {
ui_.btnPlay->setEnabled(false);
ui_.btnNext->setEnabled(false);
ui_.btnReset->setEnabled(false);
}
}
所以从这部分播放的代码可以看出,在可视化界面中的播放只是播放出结果,但是主要的处理过程是在打开点云的时候就执行完了。
3. SUMA部分的流程图说明
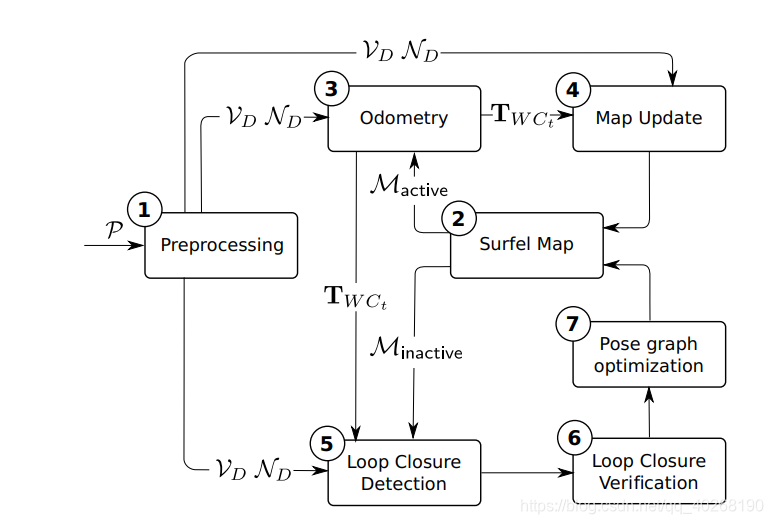
3.1 SUMA核心流程分析,其中也包含部分SUMA++
VisualizerWindow.cpp 515
if (ui_.sldTimeline->value() == 0) setScan(0); // triggers update of scan.
ui_.sldTimeline->setValue(0);
void VisualizerWindow::setScan(int idx) {
if (reader_ == nullptr) return;
if (static_cast<uint32_t>(idx) >= reader_->count()) return; // ignore invalid calls.
if (!reader_->isSeekable() && ((uint32_t)idx < currentScanIdx_)) return;
uint32_t lastScanIdx = currentScanIdx_;
currentScanIdx_ = idx;
// 这一部分的代码在我的Vscode里面ctrl+左键跳转出现问题,跳转到SimulationReader.cpp,其实应当在KITTIReader.cpp,因为是继承的KITTIReader
// 将要找的帧在缓存中查找,如果确定在缓存中,则继续。否则,只要缓存的容量充足,将当前帧和要查找的帧之间的帧进行缓存。
if (reader_->isSeekable()) reader_->seek(idx);
/*在KITTIReader::read(uint32_t scan_idx, Laserscan& scan)函数中有一个doProjection(scan, num_points)函数,
这部分代码对应于点云图到顶点图之间的转换
// get angles
float yaw = -std::atan2(y, x);
float pitch = std::asin(z / range);
// get projections in image coords
float proj_x = 0.5 * (yaw / M_PI + 1.0); // in [0.0, 1.0]
float proj_y = 1.0 - (pitch + std::abs(fov_down)) / fov; // in [0.0, 1.0]
// scale to image size using angular resolution
proj_x *= _img_w; // in [0.0, W]
proj_y *= _img_h; // in [0.0, H]
*/
/*生成二维距离图
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < inputs.size(); ++i) {
range_image[int(sorted_proj_ys[i] * _img_w + sorted_proj_xs[i])] = inputs[i];
}
...
...
// 将最终处理过的的range图(这里的range图已经是存储的推理后的数据)转换到semantic_scan(反投影)中保存,用作后续的语义标签
semantic_scan.push_back(range_image[proj_ys[i] * _img_w + proj_xs[i]]);
...
// 这一部分是从生成的语义数组中确认,每个点应当是哪个对应的语义类别,即从20个类中选最大的那个值作为该点的语义类,并且保存对应的语义标签
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < num_points; ++i) {
labels[i] = 0;
labels_prob[i] = 0;
for (uint32_t j = 0; j < 20; ++j)
{
if (labels_prob[i] <= color_mask[i*20+j])
{
labels[i] = label_map_[j];
labels_prob[i] = color_mask[i*20+j];
}
}
}
*/
reader_->read(currentLaserscan_);
if (lastScanIdx > currentScanIdx_) {
acc_->clear();
}
if (parameterUpdateNeeded_) {
fusion_->setParameters(params_);
// 如果参数需要更新,则重新设置一遍参数,并且对loop相关的几个参数更新阈值
// update timeseries thresholds.
// GraphWidget::Timeseries::Ptr ts = ui_.wGraph->getTimeseries("loop_relative_error_inlier");
// ts->removeAllThresholds();
// ts->addThreshold(params_["loop-residual-thresh"]);
GraphWidget::Timeseries::Ptr ts = ui_.wGraph->getTimeseries("loop_relative_error_all");
ts->removeAllThresholds();
ts->addThreshold(params_["loop-residual-threshold"]);
ts = ui_.wGraph->getTimeseries("loop_outlier_ratio");
ts->removeAllThresholds();
ts->addThreshold(params_["loop-outlier-threshold"]);
ts = ui_.wGraph->getTimeseries("loop_valid_ratio");
ts->removeAllThresholds();
ts->addThreshold(params_["loop-valid-threshold"]);
parameterUpdateNeeded_ = false;
}
// for (rv::ParameterList::const_iterator pit = params_.begin(); pit != params_.end(); ++pit) {
// std::cout << "pit: " << *pit << std::endl;
// }
if (fusion_ != nullptr) {
if (precomputed_[currentScanIdx_]) {
// 如果之前该帧处理过了
fusion_->setCurrentPose(oldPoses_[currentScanIdx_]);
fusion_->initialize(currentLaserscan_);
fusion_->preprocess();
fusion_->getCurrentFrame()->pose = oldPoses_[currentScanIdx_];
} else {
// 这帧是第一次处理
// 记录时间戳
int32_t timestamp = fusion_->timestamp();
// 本文后面有解析
fusion_->processScan(currentLaserscan_);
oldPoses_[currentScanIdx_] = fusion_->getCurrentPose().cast<float>();
precomputed_[currentScanIdx_] = true;
if (currentScanIdx_ % history_stride_ == 0) {
std::vector<rv::Point3f> pts = currentLaserscan_.points();
if (currentLaserscan_.hasRemission()) {
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < pts.size(); ++i) {
pts[i].vec[3] = currentLaserscan_.remission(i);
}
}
acc_->insert(timestamp, fusion_->getCurrentPose().cast<float>(), pts);
}
SurfelMapping::Stats stats = fusion_->getStatistics();
statistics.push_back(stats);
ui_.wGraph->getTimeseries("runtime")->insert(timestamp, stats["complete-time"]);
ui_.wGraph->getTimeseries("loop_outlier_ratio")->insert(timestamp, stats["loop_outlier_ratio"]);
ui_.wGraph->getTimeseries("loop_relative_error_all")->insert(timestamp, stats["loop_relative_error_all"]);
// ui_.wGraph->getTimeseries("num_iterations")->insert(timestamp, stats["num_iterations"]);
ui_.wGraph->getTimeseries("loop_valid_ratio")->insert(timestamp, stats["valid_ratio"]);
ui_.wGraph->getTimeseries("loop_outlier_ratio")->insert(timestamp, stats["outlier_ratio"]);
ui_.wGraph->getTimeseries("increment_difference")->insert(timestamp, stats["increment_difference"]);
// ui_.wGraph->getTimeseries("icp_percentage")->insert(timestamp, stats["icp_percentage"]);
if (fusion_->useLoopClosureCandidate()) ui_.wGraph->insertMarker(timestamp, Qt::green);
ui_.wCanvas->setResidualMap(fusion_->getCurrentFrame()->residual_map);
}
ui_.wCanvas->setCurrentFrame(currentScanIdx_, *fusion_->getCurrentFrame());
ui_.wCanvas->setOldSurfelFrame(*fusion_->getOldSurfelMap());
ui_.wCanvas->setNewSurfelFrame(*fusion_->getNewSurfelMap());
ui_.wCanvas->setModelFrame(*fusion_->getCurrentModelFrame());
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4d> optimizedPoses = fusion_->getOptimizedPoses();
ui_.wCanvas->setOptimizedPoses(optimizedPoses);
ui_.wCanvas->setLoopClosurePose(fusion_->foundLoopClosureCandidate(), fusion_->useLoopClosureCandidate(),
fusion_->getLoopClosurePoses(), fusion_->getNewMapPose(), fusion_->getOldMapPose());
// update poses in accumulator.
std::vector<int32_t>& timestamps = acc_->getTimestamps();
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4f>& acc_poses = acc_->getPoses();
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < timestamps.size(); ++i) {
if (timestamps[i] > -1) {
acc_poses[i] = optimizedPoses[timestamps[i]].cast<float>();
}
}
ui_.wGraph->setTimestamp(currentScanIdx_);
}
// triggers redraw:
ui_.wCanvas->setLaserscan(currentLaserscan_);
updatePlaybackControls();
ui_.txtScanNumber->setText(QString::number(currentScanIdx_));
ui_.wCanvas->setOdomPoses(fusion_->getIntermediateOdometryPoses());
if (recording_) {
std::string out_filename = outputDirectory_;
out_filename += QString("/%1.png").arg((int)currentScanIdx_, 5, 10, (QChar)'0').toStdString();
ui_.wCanvas->grabFrameBuffer().save(QString::fromStdString(out_filename));
std::cout << "Writing to " << out_filename << std::endl;
}
#ifdef QUERY_MEMORY_NV
GLint totalMemory = 0, availableMemory = 0;
glGetIntegerv(GL_GPU_MEM_INFO_TOTAL_AVAILABLE_MEM_NVX, &totalMemory);
glGetIntegerv(GL_GPU_MEM_INFO_CURRENT_AVAILABLE_MEM_NVX, &availableMemory);
CheckGlError();
ui_.pbGpuMemory->setValue(100 * float(availableMemory) / float(totalMemory));
#endif
}
void SurfelMapping::processScan(const rv::Laserscan& scan) {
// 时间tictak
Stopwatch::tic();
// check if optimization ready, copy poses, reinitialize loop closure count.
// 将之前进行回环处理的位姿变换进行更新,回环数量进行调整,减去之前的回环
/* void SurfelMapping::integrateLoopClosures(){
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < poses_opt.size(); ++i) {
// 优化后的位姿图位姿直接插入新的位姿数组
casted_poses.push_back(poses_opt[i].cast<float>());
posegraph_->setInitial(i, poses_opt[i]);
}
loopCount_ -= beforeLoopCount_;
// 新的回环产生的位姿变换
Eigen::Matrix4d difference = poses_opt[beforeID_] * beforeOptimizationPose_.inverse();
for (uint32_t i = poses_opt.size(); i < poses_before.size(); ++i) {
// 更新原先存储的位姿
poses_before[i] = difference * poses_before[i];
casted_poses.push_back(poses_before[i].cast<float>());
posegraph_->setInitial(i, poses_before[i]);
}
...
}
*/
if (makeLoopClosures_ && performMapping_) integrateLoopClosures();
Stopwatch::tic();
// 初始化雷达数据,将雷达数据表示成xyz(为啥不用点云库?),复制给current_pts_
initialize(scan);
statistics_["initialize-time"] = Stopwatch::toc();
Stopwatch::tic();
// 用OpenGL根据处理过的点云创建vertex map和normal map
// SuMa++引入了一种洪泛算法来消除错误标签。洪泛算法以语义mask和顶点图为输入,输出修正之后的语义mask
preprocess();
statistics_["preprocessing-time"] = Stopwatch::toc();
// double icpTime = 0.0;
if (timestamp_ > 0) {
Stopwatch::tic();
// 更新当前帧的位姿,并且更新位姿图,同时保存位姿变化距离存入轨迹距离栈,采用最后一个姿态增量进行初始化。
// 帧间ICP的优化最小距离,odometry部分
updatePose();
statistics_["icp-time"] = Stopwatch::toc();
Stopwatch::tic();
/*
//Verifying and adding constraints.
// 渲染静态图
map_->render_inactive(pose_old, getConfidenceThreshold());
// adjust increment.
// 确认当前帧和上一帧的增量是否更大,如果距离更近,则选用当前帧作为候选回环帧
objective_->setData(currentFrame_, map_->oldMapFrame());
gn_->minimize(*objective_, lastIncrement_);
// 根据上述产生的候选回环帧和当前帧制作虚拟帧,也就是这里的composed地图
map_->render_composed(pose_old, currentPose_new_.cast<float>(), getConfidenceThreshold());
// 根据上述产生的虚拟帧进行回环检测,如果满足回环的标准,作为回环候选
// 当有三个以上回环候选时,对每个回环候选,用三个参数计算帧间残差,取出变化最小的那个
gn_->minimize(*objective_, initializations[i]);
// 如果最小的残差满足标准,则作为预备回环,加入unverifiedLoopClosures_
*/
if (makeLoopClosures_ && performMapping_) checkLoopClosure();
statistics_["loop-time"] = Stopwatch::toc();
}
Stopwatch::tic();
// 创建面元,并且更新先前的地图中关联的面元,对原先活动子图中的坐标进行更新
if (performMapping_) updateMap();
statistics_["mapping-time"] = Stopwatch::toc();
float completeTime = Stopwatch::toc();
statistics_["complete-time"] = completeTime;
statistics_["icp_percentage"] = statistics_["opt-time"] / completeTime;
timestamp_ += 1;
}
3.2 preprocess部分
3.3 updatePose部分
3.4 updateMap部分
4. SUMA++中有关语义模型rangenet++的部分
// initialize the rangenet
net = std::shared_ptr<RangenetAPI> (new RangenetAPI(params_));
// 这里的标签地图指的是顺序排列的序号(0-19)对应的相应类标签的索引(值)
label_map_ = net->getLabelMap();
// 这里的颜色地图是以标签序号作为下标的,存储的值为对应的颜色
color_map_ = net->getColorMap();
4.1 下面是解析模型引擎
NetTensorRT::NetTensorRT(const std::string& model_path)
: Net(model_path), _engine(0), _context(0) {
// set default verbosity level
verbosity(_verbose);
// Try to open the model
std::cout << "Trying to open model" << std::endl;
// generate trt path form model path
std::string engine_path = model_path + "/model.trt";
// try to deserialize the engine
try {
// 判断文件是否存在
// file_ifstream(engine_path.c_str());
// 将模型读取到缓冲区中
// gieModelStream << file_ifstream.rdbuf();
// 对其进行反序列化以获得引擎:
// _engine = infer->deserializeCudaEngine(modelMem, modelSize);
deserializeEngine(engine_path);
} catch (std::exception e) {
std::cout << "Could not deserialize TensorRT engine. " << std::endl
<< "Generating from sratch... This may take a while..."
<< std::endl;
// destroy crap from engine
// if (_engine) _engine->destroy();
if (_engine) delete _engine;
} catch (...) {
throw std::runtime_error("Unknown TensorRT exception. Giving up.");
}
// 下面这段理论上在SUMA++里面是不执行的
// if there is no engine, try to generate one from onnx
if (!_engine) {
// generate path
std::string onnx_path = model_path + "/model.onnx";
// generate engine
generateEngine(onnx_path);
// save engine
serializeEngine(engine_path);
}
// prepare buffers for io :)
prepareBuffer();
CUDA_CHECK(cudaStreamCreate(&_cudaStream));
} // namespace segmentation
4.2 下面这块是从配置文件中读取颜色以及标签还有一些参数的部分
Net::Net(const std::string& model_path)
: _model_path(model_path), _verbose(true) {
// set default verbosity level
verbosity(_verbose);
// Try to get the config file as well
// 配置参数路径
std::string arch_cfg_path = _model_path + "/arch_cfg.yaml";
try {
// 读取有关模型的一些配置参数
arch_cfg = YAML::LoadFile(arch_cfg_path);
} catch (YAML::Exception& ex) {
throw std::runtime_error("Can't open cfg.yaml from " + arch_cfg_path);
}
// Assign fov_up and fov_down from arch_cfg
_fov_up = arch_cfg["dataset"]["sensor"]["fov_up"].as
<double>();
_fov_down = arch_cfg["dataset"]["sensor"]["fov_down"].as
<double>();
// kitti数据集的标签文件路径
std::string data_cfg_path = _model_path + "/data_cfg.yaml";
try {
// 读取相关标签及颜色配置文件
data_cfg = YAML::LoadFile(data_cfg_path);
} catch (YAML::Exception& ex) {
throw std::runtime_error("Can't open cfg.yaml from " + data_cfg_path);
}
// Get label dictionary from yaml cfg
YAML::Node color_map;
try {
// 读取其中的颜色
color_map = data_cfg["color_map"];
} catch (YAML::Exception& ex) {
std::cerr << "Can't open one the label dictionary from cfg in " + data_cfg_path
<< std::endl;
throw ex;
}
// Generate string map from xentropy indexes (that we'll get from argmax)
YAML::const_iterator it;
for (it = color_map.begin(); it != color_map.end(); ++it) {
// Get label and key
// 取出前面对应的序号
int key = it->first.as<int>(); // <- key
Net::color color = std::make_tuple(
// 取出对应的颜色,分别为bgr三色
static_cast<u_char>(color_map[key][0].as<unsigned int>()),
static_cast<u_char>(color_map[key][1].as<unsigned int>()),
static_cast<u_char>(color_map[key][2].as<unsigned int>()));
_color_map[key] = color;
}
// Get learning class labels from yaml cfg
YAML::Node learning_class;
try {
// 取出顺序排列的所有19种标签对应的类(其中已经有一部分标签被整合,例如moving-bicyclist和bicyclist以及moving-person和person)
// 这一步表明其实语义可以筛选出来动目标,但是显然作者在使用的过程中,并未以此作为动静目标的划分优化,而是选择将他们看成一个类。
learning_class = data_cfg["learning_map_inv"];
} catch (YAML::Exception& ex) {
std::cerr << "Can't open one the label dictionary from cfg in " + data_cfg_path
<< std::endl;
throw ex;
}
// get the number of classes
_n_classes = learning_class.size();
// remapping the colormap lookup table
// 存储颜色信息到_argmax_to_rgb[key]数组中,相当于按顺序存储,并且通过_lable_map索引对应的类标签序号
_lable_map.resize(_n_classes);
for (it = learning_class.begin(); it != learning_class.end(); ++it) {
int key = it->first.as<int>(); // <- key
_argmax_to_rgb[key] = _color_map[learning_class[key].as<unsigned int>()];
_lable_map[key] = learning_class[key].as<unsigned int>();
}
// 后面都是从arch_cfg中读取数据,存入对应的参数中
// get image size
_img_h = arch_cfg["dataset"]["sensor"]["img_prop"]["height"].as<int>();
_img_w = arch_cfg["dataset"]["sensor"]["img_prop"]["width"].as<int>();
_img_d = 5; // range, x, y, z, remission
// get normalization parameters
YAML::Node img_means, img_stds;
try {
img_means = arch_cfg["dataset"]["sensor"]["img_means"];
img_stds = arch_cfg["dataset"]["sensor"]["img_stds"];
} catch (YAML::Exception& ex) {
std::cerr << "Can't open one the mean or std dictionary from cfg"
<< std::endl;
throw ex;
}
// fill in means from yaml node
for (it = img_means.begin(); it != img_means.end(); ++it) {
// Get value
float mean = it->as<float>();
// Put in indexing vector
_img_means.push_back(mean);
}
// fill in stds from yaml node
for (it = img_stds.begin(); it != img_stds.end(); ++it) {
// Get value
float std = it->as<float>();
// Put in indexing vector
_img_stds.push_back(std);
}
}
4.3 这一块是执行语义模块并且将预测结果保存在一个语义容器当中,作为语义mask
std::vector<std::vector<float>> NetTensorRT::infer(const std::vector<float>& scan, const uint32_t& num_points) {
// check if engine is valid
// 引擎是否是可行的
if (!_engine) {
throw std::runtime_error("Invaild engine on inference.");
}
// start inference
// 开始推理运算的计时
if (_verbose) {
tic();
std::cout << "Inferring with TensorRT" << std::endl;
tic();
}
// project point clouds into range image
// 将三维点云数据(x,y,z,w)投影为二维数据(u,v),方便进行后续的推理,其中保存的键为(u,v),也就是sorted_proj_ys[i] * _img_w + sorted_proj_xs[i]),值则是 inputs[i],即input = {ranges[idx], xs[idx], ys[idx], zs[idx], intensitys[idx]}
std::vector<std::vector<float>> projected_data = doProjection(scan, num_points);
// 三维投影二维的时间
if (_verbose) {
std::cout << "Time for projection: "
<< toc() * 1000
<< "ms" << std::endl;
tic();
}
// put in buffer using position
// 后续取出推理后结果的参数
int channel_offset = _img_h * _img_w;
bool all_zeros = false;
std::vector<int> invalid_idxs;
for (uint32_t pixel_id = 0; pixel_id < projected_data.size(); pixel_id++){
// 检查数据是否合理
// check if the pixel is invalid
all_zeros = std::all_of(projected_data[pixel_id].begin(), projected_data[pixel_id].end(), [](int i) { return i==0.0f; });
if (all_zeros) {
invalid_idxs.push_back(pixel_id);
}
for (int i = 0; i < _img_d; i++) {
// normalize the data
// 预处理数据,将数据进行规范化以方便后续进行推理
if (!all_zeros) {
projected_data[pixel_id][i] = (projected_data[pixel_id][i] - this->_img_means[i]) / this->_img_stds[i];
}
int buffer_idx = channel_offset * i + pixel_id;
// 送入host缓冲当中进行推理
((float*)_hostBuffers[_inBindIdx])[buffer_idx] = projected_data[pixel_id][i];
}
}
// clock now
// 前期的预处理所消耗的时间
if (_verbose) {
std::cout << "Time for preprocessing: "
<< toc() * 1000
<< "ms" << std::endl;
tic();
}
// execute inference
// 推理部分,采用CUDA,我只当是黑盒(不关心怎么跑,反正知道结果长什么样子就行)
CUDA_CHECK(
cudaMemcpyAsync(_deviceBuffers[_inBindIdx], _hostBuffers[_inBindIdx],
getBufferSize(_engine->getBindingDimensions(_inBindIdx),
_engine->getBindingDataType(_inBindIdx)),
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, _cudaStream));
if (_verbose) {
CUDA_CHECK(cudaStreamSynchronize(_cudaStream));
std::cout << "Time for copy in: "
<< toc() * 1000
<< "ms" << std::endl;
tic();
}
// _context->enqueue(1, &_deviceBuffers[_inBindIdx], _cudaStream, nullptr);
_context->enqueueV2(&_deviceBuffers[_inBindIdx], _cudaStream, nullptr);
// 推理完毕,计时
if (_verbose) {
CUDA_CHECK(cudaStreamSynchronize(_cudaStream));
std::cout << "Time for inferring: "
<< toc() * 1000
<< "ms" << std::endl;
tic();
}
// 推理后的数据进行复制
CUDA_CHECK(
cudaMemcpyAsync(_hostBuffers[_outBindIdx], _deviceBuffers[_outBindIdx],
getBufferSize(_engine->getBindingDimensions(_outBindIdx),
_engine->getBindingDataType(_outBindIdx)),
cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, _cudaStream));
CUDA_CHECK(cudaStreamSynchronize(_cudaStream));
// 复制用时
if (_verbose) {
std::cout << "Time for copy back: "
<< toc() * 1000
<< "ms" << std::endl;
tic();
}
// take the data out
// 将推理后的结果保存到一个二维range图上
std::vector<std::vector<float>> range_image(channel_offset);
// 可以看出第一维度的数据还是没有变,但是输出的第二个维度,从原来的(range,x,y,z,intensity)变成了(classes0,classes1,...,classesn)应当是0-19一共20个种类
for (int pixel_id = 0; pixel_id < channel_offset; pixel_id++){
for (int i = 0; i < _n_classes; i++) {
int buffer_idx = channel_offset * i + pixel_id;
range_image[pixel_id].push_back(((float*)_hostBuffers[_outBindIdx])[buffer_idx]);
}
}
// 保存消耗的时间
if (_verbose) {
std::cout << "Time for taking the data out: "
<< toc() * 1000
<< "ms" << std::endl;
tic();
}
// 之前检查出来的无效点云,也进行保存
// set invalid pixels
for (int idx : invalid_idxs) {
range_image[idx] = invalid_output;
}
// 将所有处理后的二维语义信息,反投影回一个三维的容器semantic_scan当中,作为语义mask来进行后续的处理
// unprojection, labelling raw point clouds
std::vector<std::vector<float>> semantic_scan;
for (uint32_t i = 0 ; i < num_points; i++) {
semantic_scan.push_back(range_image[proj_ys[i] * _img_w + proj_xs[i]]);
}
if (_verbose) {
std::cout << "Time for unprojection: "
<< toc() * 1000
<< "ms" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Time for the whole: "
<< toc() * 1000
<< "ms" << std::endl;
}
// 返回的该数据格式应当是(_img_h * _img_w,20),这20个数据表明每一种类别的概率
return semantic_scan;
}







![[Flutter]TextButton自定义样式](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/9be4fa5a7ede494d8ccf28542ddc61e8.png)