1 sar 和sadf
1.1 简介
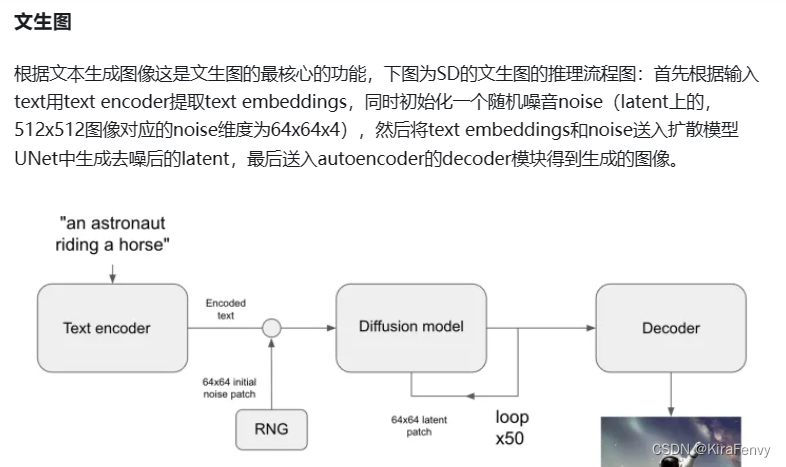
sar命令可以记录系统下的常见活动信息,例如CPU使用率、网络统计数据、Block I/O数据、内存使用情况 等。
sar命令的“-o [file_name]”参数可以将系统活动数据记录到file_name文件,然后通过sadf来解析,sadf命令的“-g”参数可以生成各种图表。
下面1.2节,以cpu的utilization为例,演示如何通过sar 和 sadf生成图表。
1.2 CPU的utilization图表
1.2.1 采集数据
执行以下命令
sar -P ALL 1 -o tmp2上面的脚本运行起来后,执行以下命令来产生一定的负载,使得系统负载数据产生波动,便于观察
perf bench sched pipe -T 4 -l 100000001.2.2 生成图表
执行以下命令,生成图表文件test2.svg。
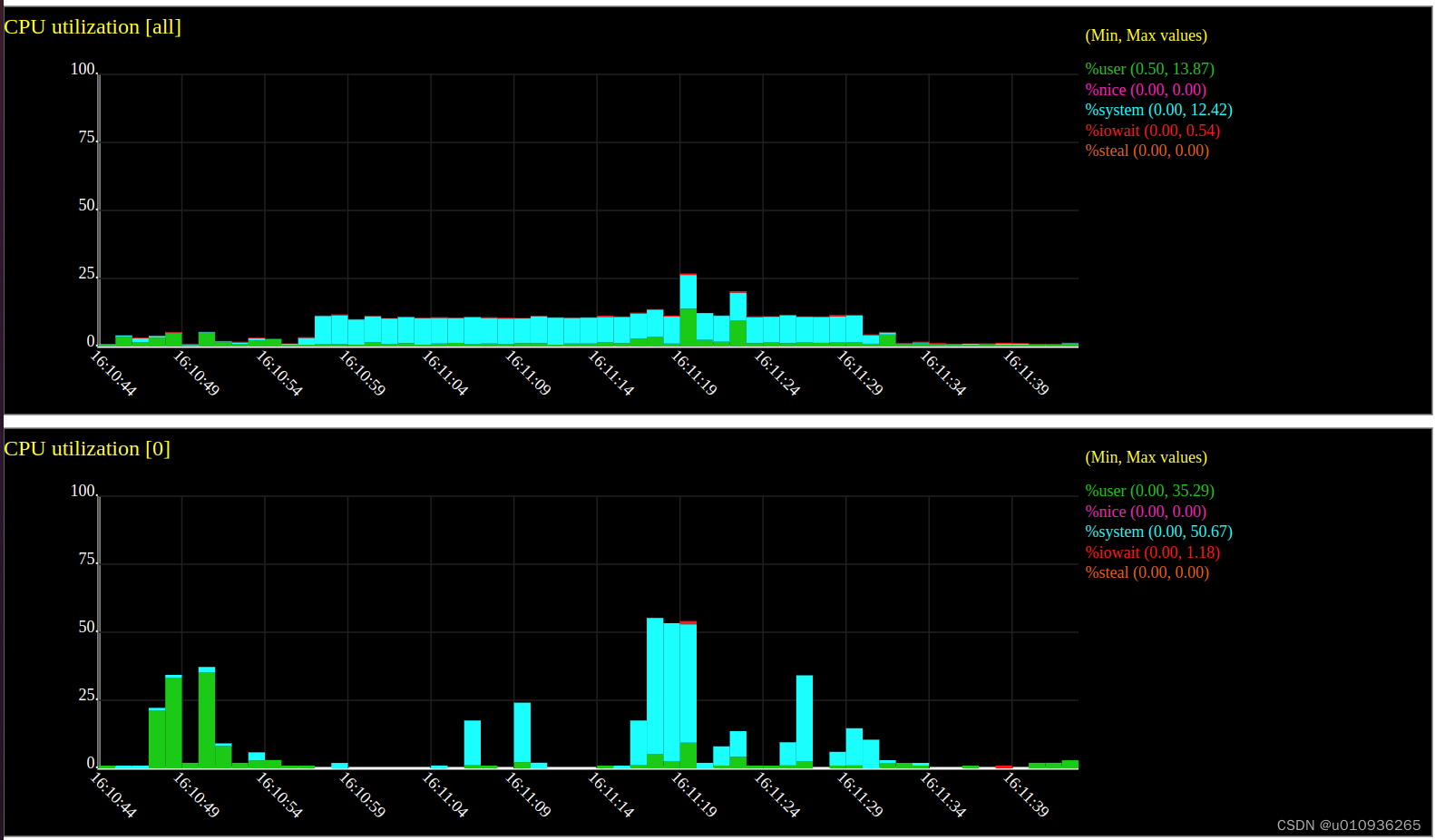
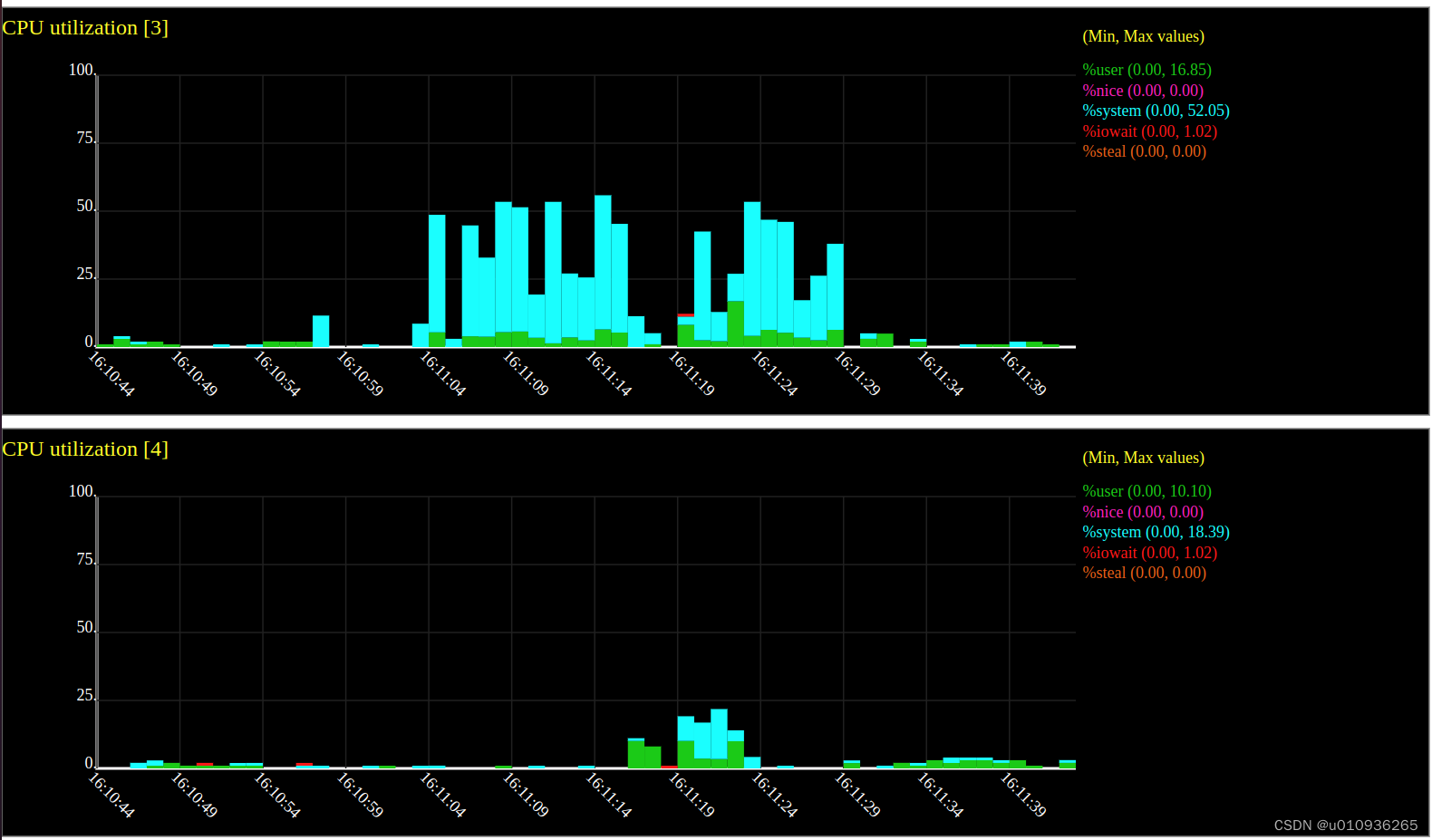
sadf -T -O height=400 -g ./tmp2 -- -P 0 > test2.svg然后用浏览器打开test2.svg。以下是一个8核CPU生成的图表。


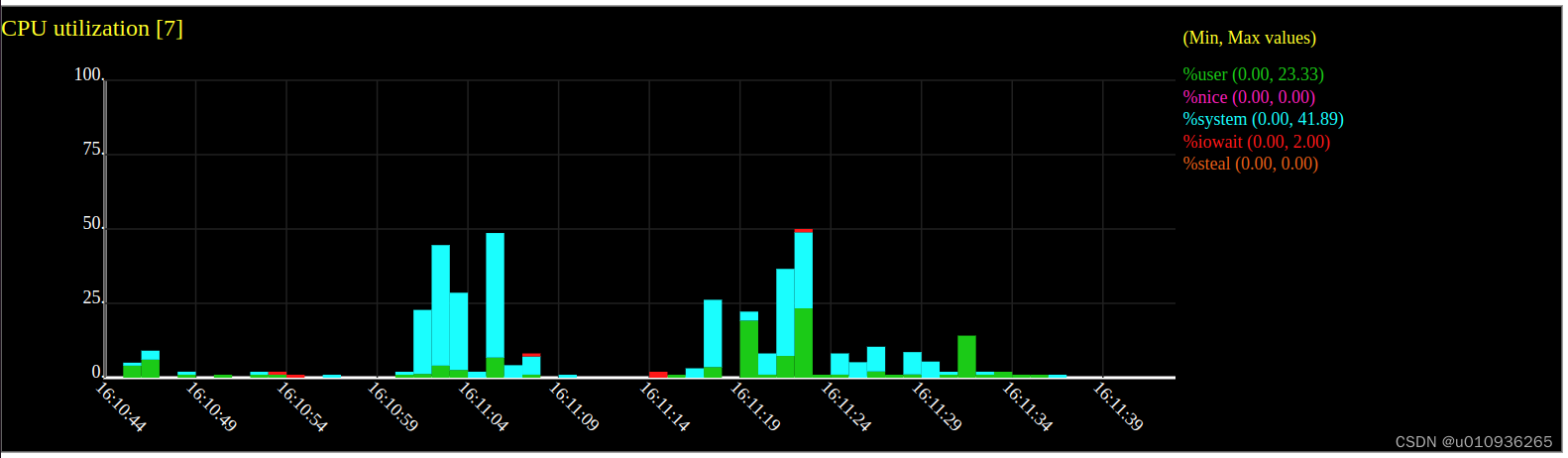
2 cpuplayer(用来生成三元图)
2.1 简介
Performance Data Visualization of Multiprocessor Systems.
cpuplayer可以同时显示单个处理器核的%user、%sys 和 %idle。
cpuplayer可以解析的数据格式如下:
1263821686:3:8:47:45
1263821686:17:7:43:49
1263821686:2:9:44:47
1263821686:1:8:47:45
1263821686:18:8:42:50
1263821686:0:10:45:45
1263821686:16:7:45:48
1263821686:19:7:44:49每一列的数据含义是:
- timestamp: UNIX time
- cpuid: the CPU id
- User cpu percent utilization 0-100
- System cpu percent utilization 0-100
- Idle state cpu percent utilization 0-100
2.2 获取cpuplayer源码 和 编译
获取源码:git clone https://github.com/sparvu/cpuplayer.git
编译:安装源码目录的README.md文件里的说明进行编译。
2.3 生成图表
2.3.1 采集数据
export S_TIME_FORMAT=ISO //使得mpstat输出的时间格式为hh:mm:ss,便于后面awk处理
mpstat -P ALL 1 > tmp
将tmp⽂件最后“平均时间”⼏⾏⼿动删除
awk 'NR>2&&$2!="CPU"&&$2!="all"&&NF>0 {print $1" "$2" "$3" "$5" "$12}' tmp > tmp2 //过滤⽆关的⾏并提取时间、核编号、%usr、%sys和%idle
awk 'gsub(/:/," ",$0){a=strftime("%Y %m %d"); b=a" "$1" "$2" "$3; c=mktime(b); print c":"$4":"$5":"$6":"$7}' tmp2 > trace.txt //将时间转换为unix时间戳2.3.2 生成图表
执行命令:./cpuplayer trace.txt
将会生成一个动态变化的画面,每秒变化一次,大致如下:

3 gnuplot
3.1 简介
gnuplot是一个非常强大的图表生成工具,可以生成各种图表,下面以网卡8个队列的中断计数为数据,演示如何在linux系统下生成折线图。
3.2 生成网卡8个队列中断计数增长的折线图
3.2.1 采集数据
从/proc/interrupts文件中采集数据
while true
do
cat /proc/interrupts | grep iwlwifi:queue_1 | awk '{a=$2+$3+$4+$5+$6+$7+$8+$9;b=systime(); print b" "a}' >> trace_irq_1.txt
cat /proc/interrupts | grep iwlwifi:queue_2 | awk '{a=$2+$3+$4+$5+$6+$7+$8+$9;b=systime(); print b" "a}' >> trace_irq_2.txt
cat /proc/interrupts | grep iwlwifi:queue_3 | awk '{a=$2+$3+$4+$5+$6+$7+$8+$9;b=systime(); print b" "a}' >> trace_irq_3.txt
cat /proc/interrupts | grep iwlwifi:queue_4 | awk '{a=$2+$3+$4+$5+$6+$7+$8+$9;b=systime(); print b" "a}' >> trace_irq_4.txt
cat /proc/interrupts | grep iwlwifi:queue_5 | awk '{a=$2+$3+$4+$5+$6+$7+$8+$9;b=systime(); print b" "a}' >> trace_irq_5.txt
cat /proc/interrupts | grep iwlwifi:queue_6 | awk '{a=$2+$3+$4+$5+$6+$7+$8+$9;b=systime(); print b" "a}' >> trace_irq_6.txt
cat /proc/interrupts | grep iwlwifi:queue_7 | awk '{a=$2+$3+$4+$5+$6+$7+$8+$9;b=systime(); print b" "a}' >> trace_irq_7.txt
cat /proc/interrupts | grep iwlwifi:queue_8 | awk '{a=$2+$3+$4+$5+$6+$7+$8+$9;b=systime(); print b" "a}' >> trace_irq_8.txt
sleep 1
done因为时间戳数据太大,图表中显示有问题,所以对时间戳进行处理,使得时间戳从0开始,便于图表中显示。1708659315是数据中最早的时间戳。
awk '{a=$1-1708659315; print a" "$2}' trace_irq_1.txt > irq_1.txt
awk '{a=$1-1708659315; print a" "$2}' trace_irq_2.txt > irq_2.txt
awk '{a=$1-1708659315; print a" "$2}' trace_irq_3.txt > irq_3.txt
awk '{a=$1-1708659315; print a" "$2}' trace_irq_4.txt > irq_4.txt
awk '{a=$1-1708659315; print a" "$2}' trace_irq_5.txt > irq_5.txt
awk '{a=$1-1708659315; print a" "$2}' trace_irq_6.txt > irq_6.txt
awk '{a=$1-1708659315; print a" "$2}' trace_irq_7.txt > irq_7.txt
awk '{a=$1-1708659315; print a" "$2}' trace_irq_8.txt > irq_8.txt3.2.2 生成折线图
编写gnuplot脚本——irq.demo
set title 'irq count'
set ylabel 'count'
set xlabel 'second'
set grid
p "irq_1.txt" t "queue_1" lt 7 lc 0 w lp, \
"irq_2.txt" t "queue_2" lt 7 lc 1 w lp, \
"irq_3.txt" t "queue_3" lt 7 lc 2 w lp, \
"irq_4.txt" t "queue_4" lt 7 lc 3 w lp, \
"irq_5.txt" t "queue_5" lt 7 lc 4 w lp, \
"irq_6.txt" t "queue_6" lt 7 lc 5 w lp, \
"irq_7.txt" t "queue_7" lt 7 lc 6 w lp, \
"irq_8.txt" t "queue_8" lt 7 lc 7 w lp运行命令: gnuplot
在gnuplot命令行中加载 irq.demo
gnuplot> load "irq.demo"生成折线图如下:

4 Heat Map
4.1 简介
Heat maps allow three dimensions of data to be visualized, similar to weather radar maps where color is used as a dimension. As data is quantized into buckets, they are practical for handling large datasets, such as performance monitoring metrics across thousands of servers.
4.2 生成热力图的脚本
git clone https://github.com/brendangregg/HeatMap.git
4.3 Latency Heat Maps
4.3.1 采集数据
使用perf-tools命令集中的iosnoop命令来获取Block I/O操作的延迟数据
./perf-tools/iosnoop -s > data
awk 'NR>2&&$1!=""&&$1!="Ending"{ print $1 " " $8}' data > trace2.txt4.3.2 生成热力图
执行命令:./trace2heatmap.pl --unitstime=s --unitslabel=ms --grid trace2.txt > heatmap3.svg
生成热力图片如下:

4.4 Utilization Heat Map
4.4.1 采集数据
export S_TIME_FORMAT=ISO //让mpstat输出信息中的时间戳格式为hh:mm:ss
mpstat -P ALL 1 >tmp
vim tmp //将tmp⽂件最后“平均时间”⼏⾏⼿动删除
awk 'NR>2&&$2!="CPU"&&$2!="all"&&NF>0 {print $1" "$12}' tmp > tmp2 //过滤⽆关的⾏并提取时间和空闲率(%idle)信息,保存到tmp2
awk 'gsub(/:/," ",$0){a=strftime("%Y %m %d"); b=a" "$1" "$2" "$3; c=mktime(b); d=100-$4; print c" "d}' tmp2 > trace3.txt //将tmp2中的数据转换成
trace2heatmap.pl识别的格式4.4.2 生成热力图
执行命令:./trace2heatmap.pl --unitstime=s --unitslabel="%util" --maxlat=100 --title="Utilization Heat Map" --grid trace3.txt > heatmap2.svg

4.5 FlameScope
该⼯具可以将性能分析结果展⽰为按秒聚合的热⼒图,以便可以按时间⽚段分析⽕焰图。
参考资料:
Heat Maps
Utilization Heat Maps
5 perf timechart
5.1 简介
perf-timechart - Tool to visualize total system behavior during a workload
5.2 生成图表
5.2.1 采集数据
编写测试程序,测试程序会周期性的运行1秒,然后睡眠1秒。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
time_t timestamp, timestamp_old = time(NULL);
while(1){
while(1){
timestamp = time(NULL);
if(timestamp_old+1 < timestamp){
timestamp_old = timestamp;
sleep(1);
}
else{
for(j = 0; j < 1000000; j++)
k++;
}
}
printf("%ld\n",timestamp);
sleep(1);
}
}编译测试程序生成可执行文件a.out
采集数据,执行:perf timechart record ./a.out
运行一段时间后,Ctrl + c退出。
5.2.2 生成图表
执行命令:perf timechart -p 4200 //4200是a.out的pid
上面的命令会默认生成output.svg文件,用浏览器 或者 inkscape 打开此文件,生成的图表如下:
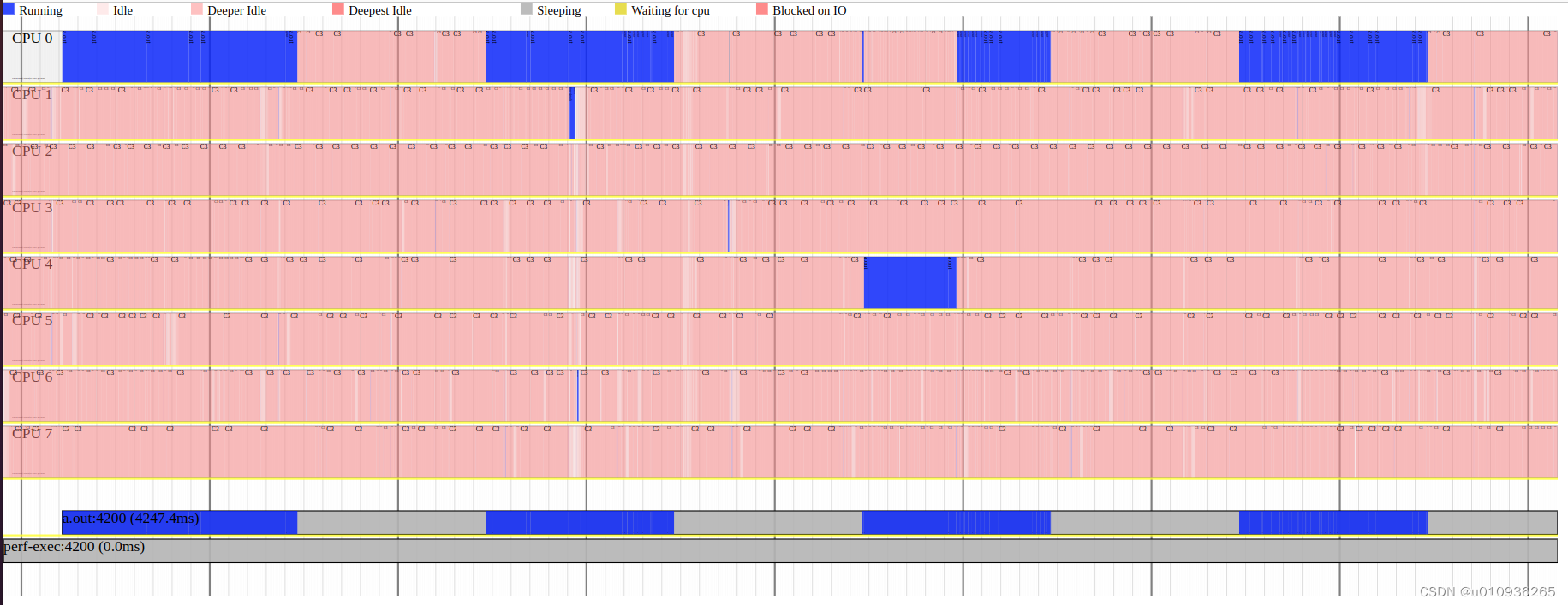
上面的图显示当前CPU的8个核基本处于空闲状态。
5.3 小技巧
上面图片里的某些任务运行时间很短,看上去只有很窄的一条细线,可以在inkscape软件中选中细线所在区域进行大比例放大。
5.4 遇到的问题
在繁忙的系统上,perf timechart record命令会采集到大量的数据(几秒就会产生上百兆),用这些数据生成的output.svg也很庞大,在用浏览器 或者 inkscape打开output.svg时,浏览器 和 inkscape 会直接卡死。
6 火焰图
网上资料很多。