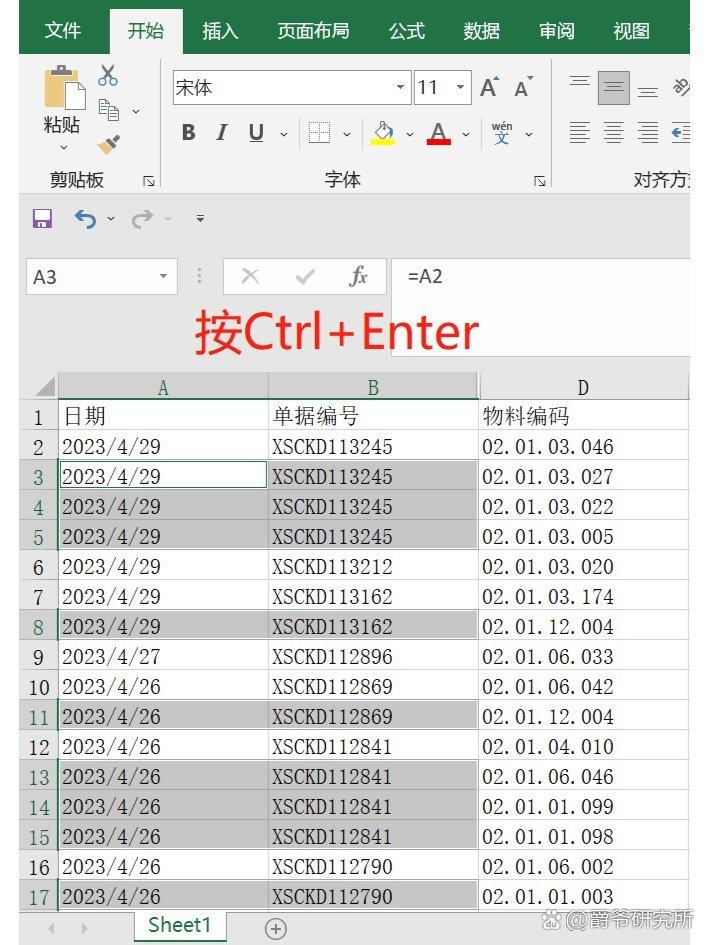
概述
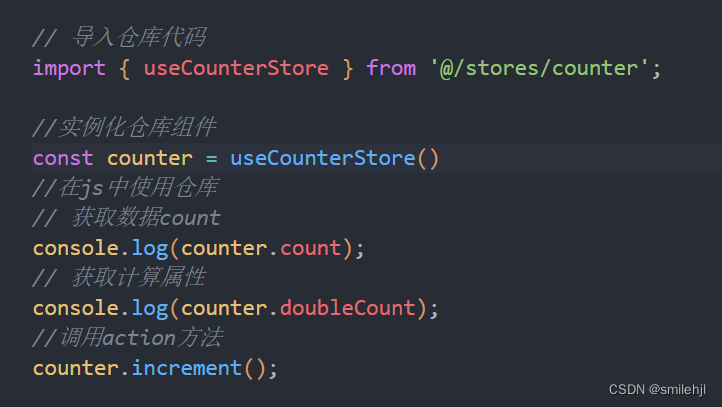
对象池的引入也是嵌入式开发的常用方法,也是内存预分配的一种,主要是用来隐藏全局对象的跟踪,通常预内存分配是通过数组来实现。
CMake配置
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5.1)
project(objpool)
add_executable(objpool objpool.cpp)
set(CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME Linux)
SET(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "--std=c++11")完整Demo
#include <iostream>
template<class T, size_t N>
class ObjectPool {
private:
T objects[N];
size_t available[N];
size_t top = 0;
public:
ObjectPool(): top(0) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++) {
available[i] = i;
}
}
T& get() {
if (top < N) {
size_t idx = available[top++];
return objects[idx];
} else {
throw std::runtime_error("All objects are in use");
}
}
void free(const T& obj) {
const T* ptr = &obj;
size_t idx = (ptr - objects) / sizeof(T);
if (idx < N) {
if (top) {
objects[idx].deinit();
top--;
available[top] = idx;
} else {
throw std::runtime_error("Some object was freed more than once");
}
} else {
throw std::runtime_error("Freeing object that does not belong to the pool");
}
}
size_t requested() const { return top; }
};
struct Point {
int x, y;
void deinit() { std::cout << "Hello " << x << ", " << y << "\n"; }
};
int main() {
ObjectPool<Point, 10> points;
Point& a = points.get();
a.x = 10; a.y=20;
std::cout << "Point a (" << a.x << ", " << a.y << ") initialized, requested " <<
points.requested() << std::endl;
Point& b = points.get();
std::cout << "Point b (" << b.x << ", " << b.y << ") not initialized, requested " <<
points.requested() << std::endl;
points.free(a);
std::cout << "Point a(" << a.x << ", " << a.y << ") returned, requested " <<
points.requested() << std::endl;
Point& c = points.get();
std::cout << "Point c(" << c.x << ", " << c.y << ") not intialized, requested " <<
points.requested() << std::endl;
Point local;
try {
points.free(local);
} catch (std::runtime_error e) {
std::cout << "Exception caught: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
}
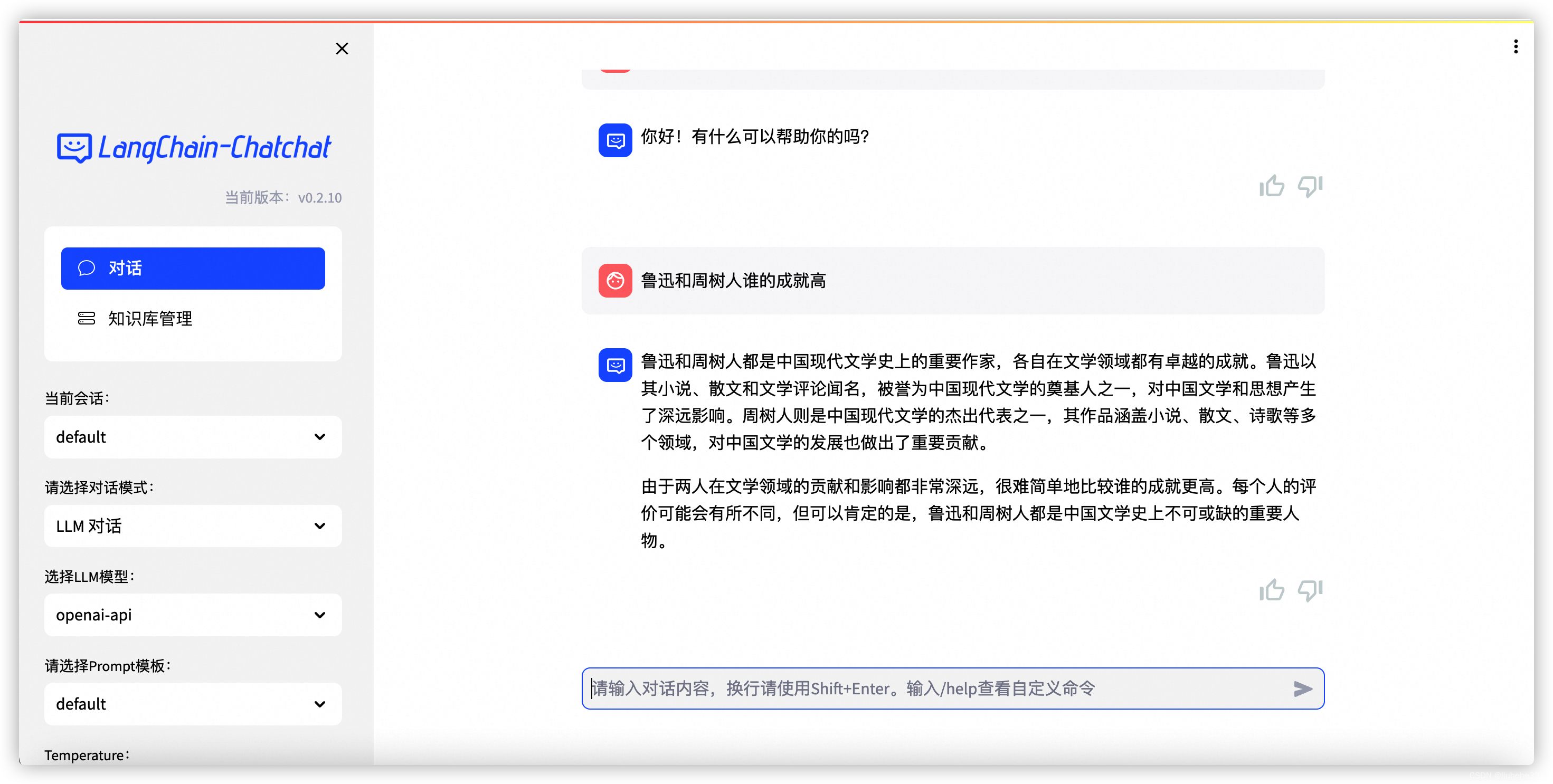
运行结果

我公司承接各类技术服务,主要聚焦于:stm32、单片机、嵌入式、QT应用开发、Web+Python+Django应用开发。欢迎合作。