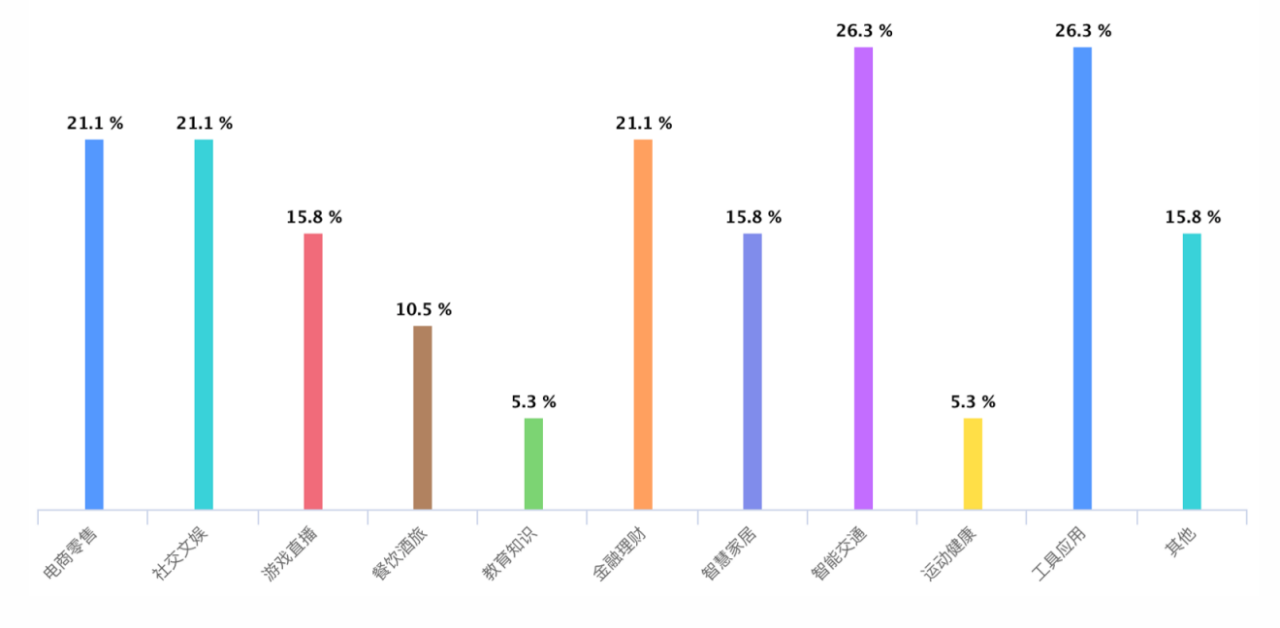
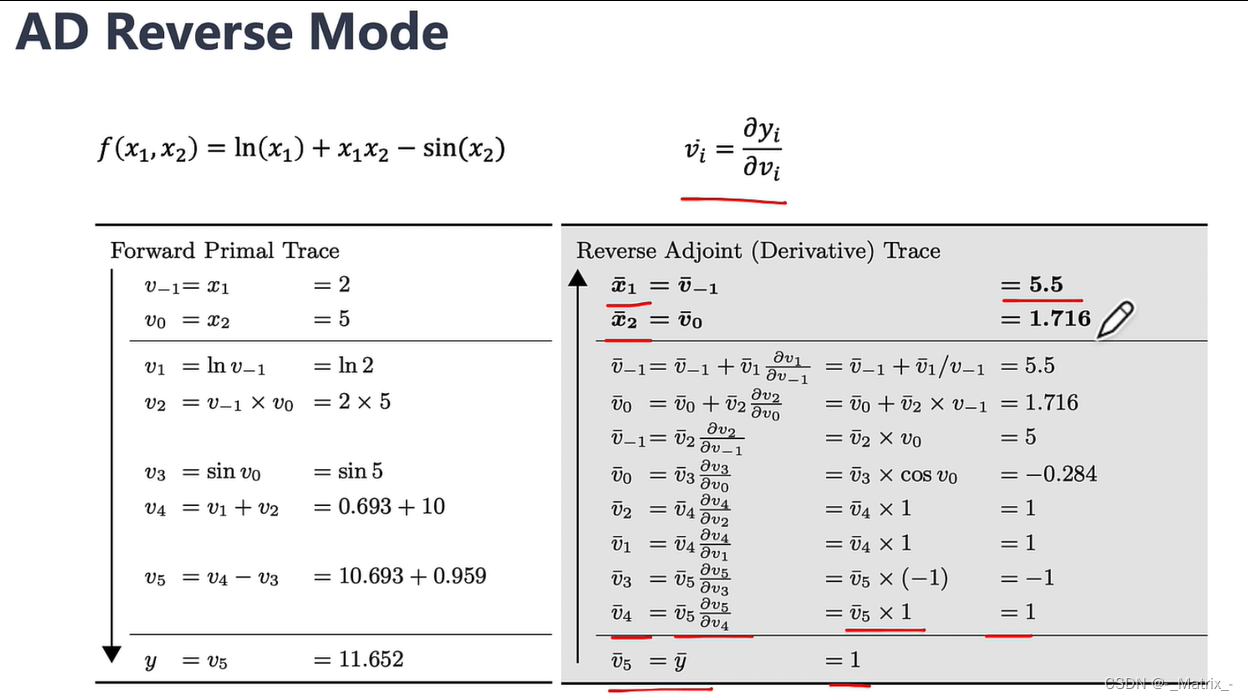
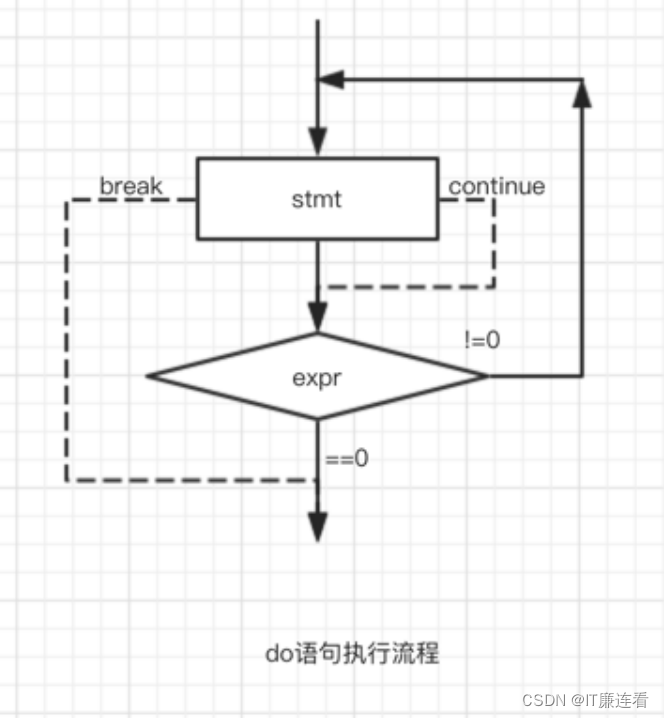
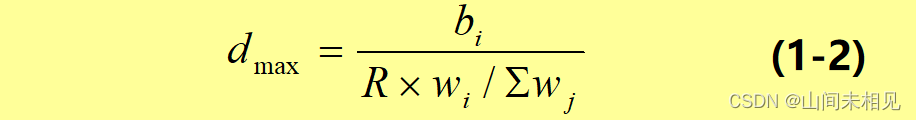文章目录
- 一、题目
- 二、解法
- 三、完整代码
所有的LeetCode题解索引,可以看这篇文章——【算法和数据结构】LeetCode题解。
一、题目

二、解法
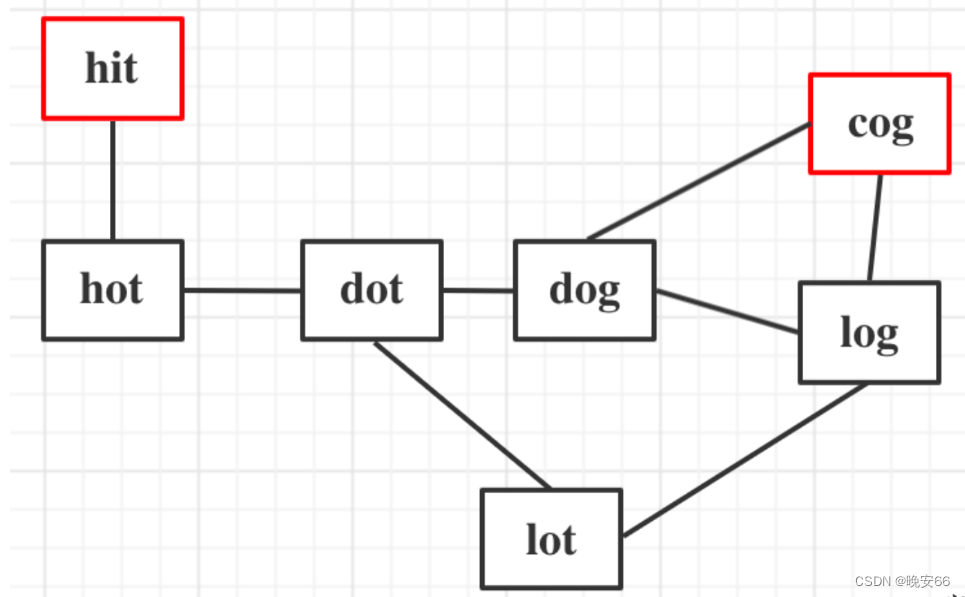
思路分析:示例1为例,hit到达cog的路线不止一条,如何找到最短是关键。广度优先搜索是一圈一圈的搜索过程,一旦找到了结果,一定是最短的。本题也只需要最短转换序列的数目而不需要具体的序列,因此不用去关心下图中线是如何连在一起的。因此最终选择广搜,只要差一个字符说明序列之间是连接的。
- 本题还是一个无向图,需要用到标记位,标记节点是否走过,否则会陷入死循环。为此我们引入一个unordered_map<string, int> visitMap类型的地图,记录word是否被访问过,key值为单词,value为beginWord到该单词的路径长度。
- 集合是数组类型的,提前转成集合set类型,查找更快。
根据单词的长度,每次替换其中一个单词,需要用到两个循环,一个循环选择单词中替换的字符位置,另一个用来选择26个字母中的其中一个。然后在单词集合中查找是否存在替换之后的新单词,如果找到将其加入visitMap中。如果新单词是endWord,那么直接放回path+1。path代表路径长度。
程序如下:
// 127、单词接龙-深度优先搜索
class Solution {
public:
int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
unordered_set<string> wordSet(wordList.begin(), wordList.end()); // 转成uset类型,查找更快
if (wordSet.find(endWord) == wordSet.end()) return 0; // endWord没有在单词集合中出现,直接返回0
unordered_map<string, int> visitMap; // 记录word是否被访问过,key值为单词,value为beginWord到该单词的路径长度
queue<string> que;
visitMap.insert(pair<string, int>(beginWord, 1));
que.push(beginWord);
while (!que.empty()) {
string word = que.front();
que.pop();
int path = visitMap[word]; // 路径长度
for (int i = 0; i < word.size(); i++) {
string newWord = word; // 用一个新单词替换word,每次置换一个字母
for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) {
newWord[i] = j + 'a';
if (newWord == endWord) return path + 1; // 找到end
if (wordSet.find(newWord) != wordSet.end() && visitMap.find(newWord) == visitMap.end()) { // newWord出现在wordSet中,且没有访问过
visitMap.insert(pair<string, int>(newWord, path + 1));
que.push(newWord);
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度: O ( N × C ) O(N \times C) O(N×C),N为wordList长度,C为单词长度。字符串数组转化成umap字符串类型需要 O ( N ) O(N) O(N)。最坏情况下,遍历到wordList最后一个元素才会找到endWord,while循环中的一些操作(如visitMap插入元素和que队列插入、弹出元素复杂度)为 O ( N ) O(N) O(N)。两个for循环的复杂度为 O ( 26 × C ) O(26 \times C) O(26×C)。因此最终的复杂度为 O ( N × C ) O(N \times C) O(N×C)。
-
空间复杂度: O ( N × C ) O(N \times C) O(N×C)。
三、完整代码
// 127、单词接龙-深度优先搜索
class Solution {
public:
int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
unordered_set<string> wordSet(wordList.begin(), wordList.end()); // 转成uset类型,查找更快
if (wordSet.find(endWord) == wordSet.end()) return 0; // endWord没有在单词集合中出现,直接返回0
unordered_map<string, int> visitMap; // 记录word是否被访问过,key值为单词,value为beginWord到该单词的路径长度
queue<string> que;
visitMap.insert(pair<string, int>(beginWord, 1));
que.push(beginWord);
while (!que.empty()) {
string word = que.front();
que.pop();
int path = visitMap[word]; // 路径长度
for (int i = 0; i < word.size(); i++) {
string newWord = word; // 用一个新单词替换word,每次置换一个字母
for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) {
newWord[i] = j + 'a';
if (newWord == endWord) return path + 1; // 找到end
if (wordSet.find(newWord) != wordSet.end() && visitMap.find(newWord) == visitMap.end()) { // newWord出现在wordSet中,且没有访问过
visitMap.insert(pair<string, int>(newWord, path + 1));
que.push(newWord);
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
};
end