
抽象类不能实例化(创建对象):
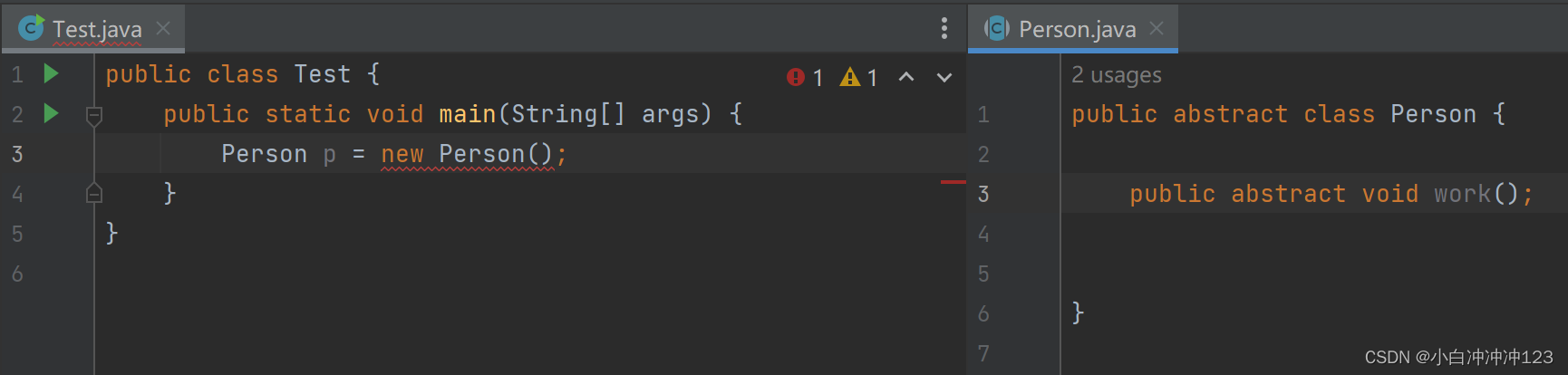
抽象类中不一定有抽象方法:
有抽象方法的类一定是抽象类: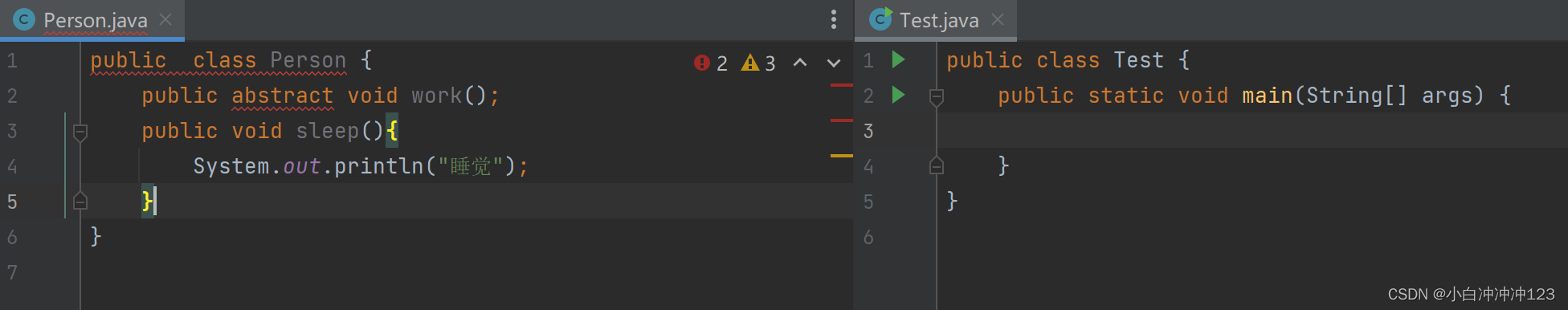
可以有构造方法:(作用:在创建子类对象时,给属性进行赋值的)
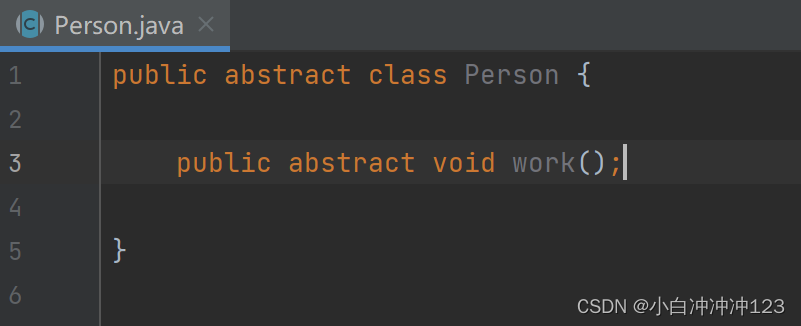
Person类:
public abstract class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public abstract void work();
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("睡觉");
}
}
Student类:
public class Student extends Person{
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void work() {
System.out.println("学生的工作是学习");
}
}
Test类:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
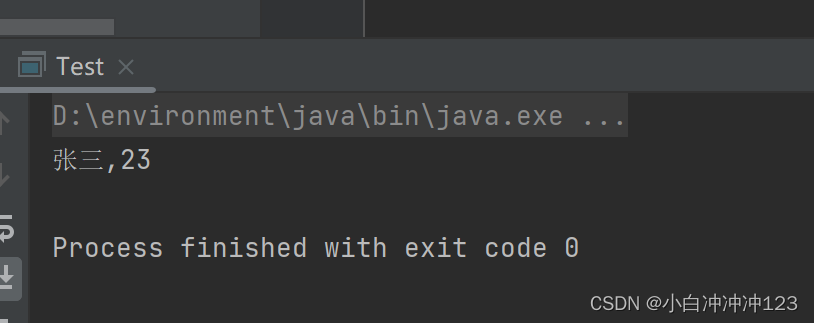
Student s = new Student ("张三",23);
System.out.println(s.getName()+","+s.getAge());
}
}代码运行结果:
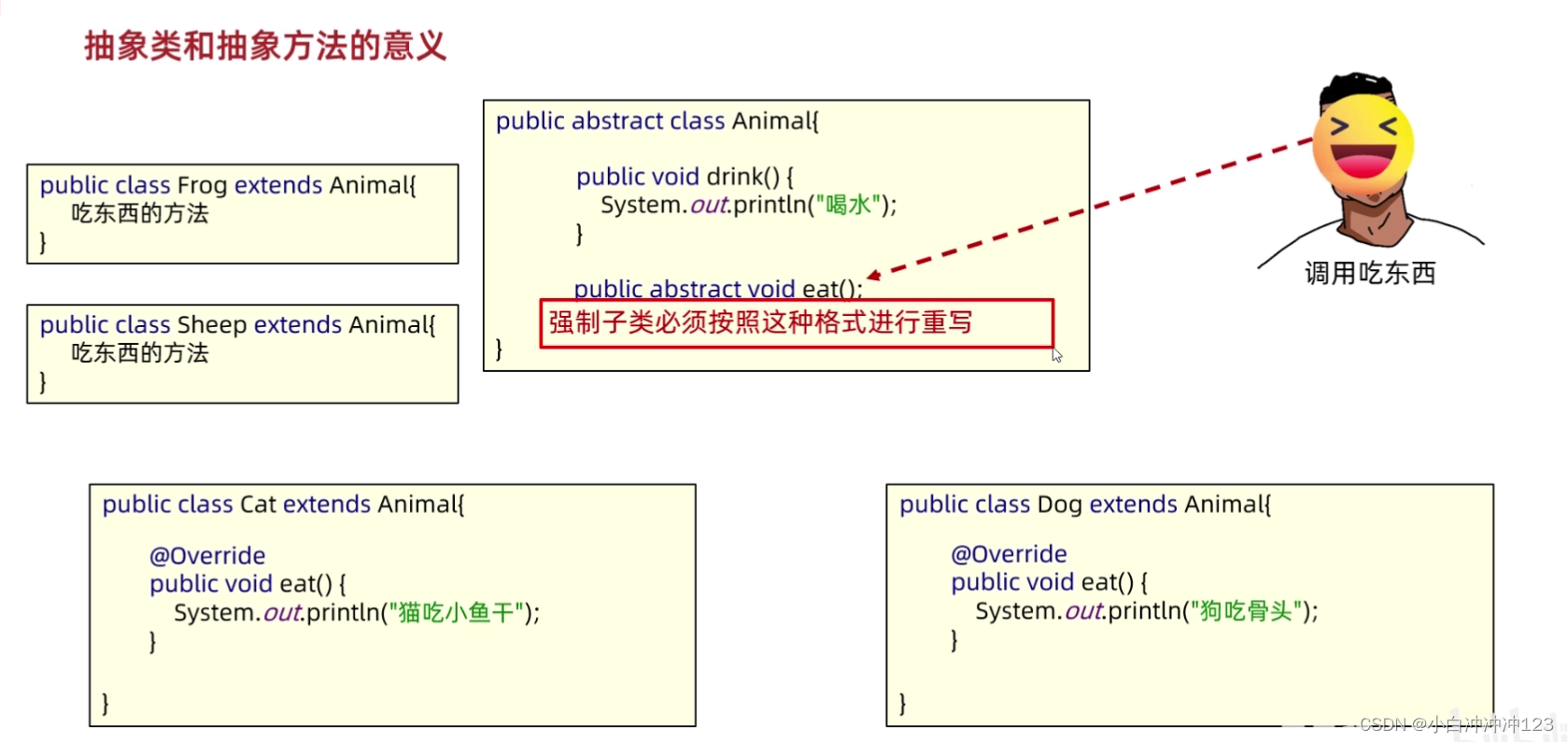
抽象类的子类:
有两种选择:1、重写所有抽象方法;2、子类也是抽象类(推荐第一种)
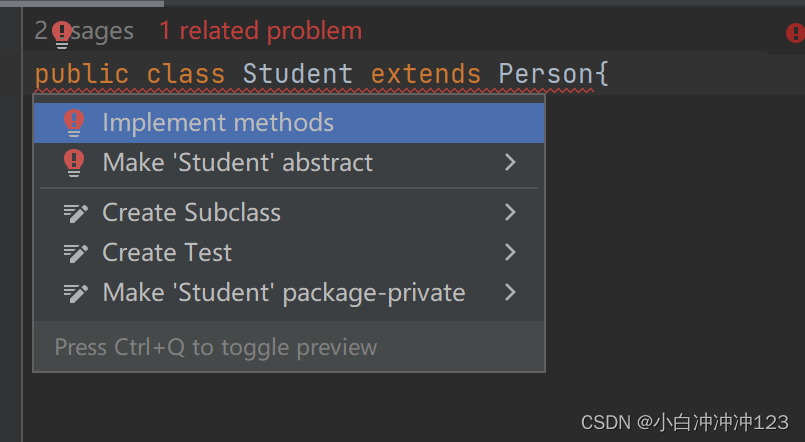
否则会报错: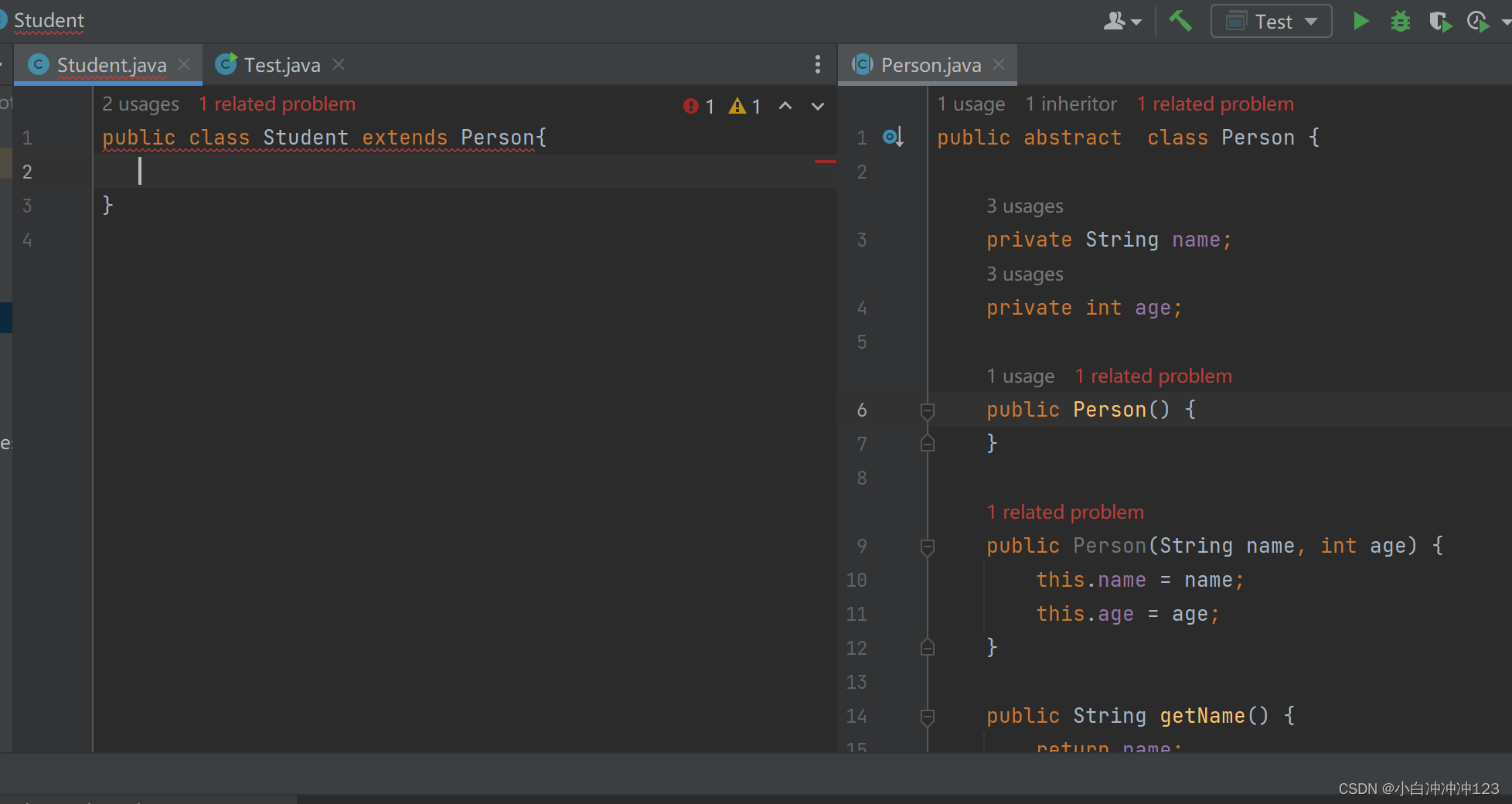
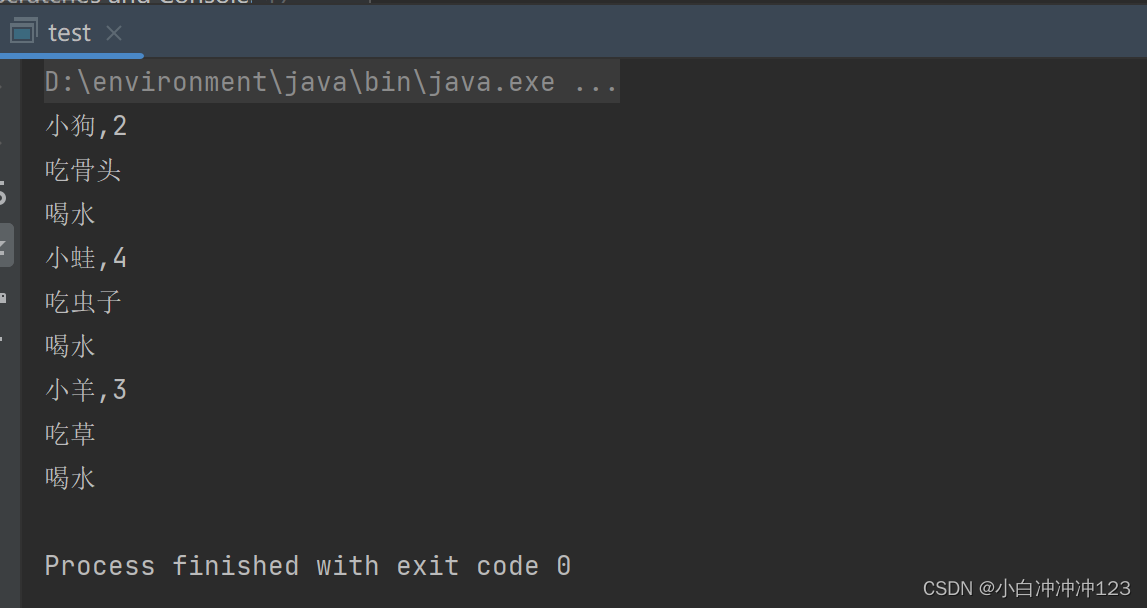
案例:
test类代码:
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d = new Dog("小狗",2);
frog f = new frog("小蛙",4);
Sheep s = new Sheep("小羊",3);
System.out.println(d.getName()+","+d.getAge());
d.eat();
d.drink();
System.out.println(f.getName()+","+f.getAge());
f.eat();
f.drink();
System.out.println(s.getName()+","+s.getAge());
s.eat();
s.drink();
}
}
Aniaml类代码:
public abstract class Animal {
private String name;
private int age;
public Animal() {
}
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void drink(){
System.out.println("喝水");
}
public abstract void eat();
}
frog类代码:
public class frog extends Animal{
public frog() {
}
public frog(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃虫子");
}
}
Dog类代码:
public class Dog extends Animal{
public Dog() {
}
public Dog(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃骨头");
}
}
Sheep类代码:
public class Sheep extends Animal{
public Sheep() {
}
public Sheep(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃草");
}
}
运行结果为: