进程通信


管道:基于文件级别的单向通信
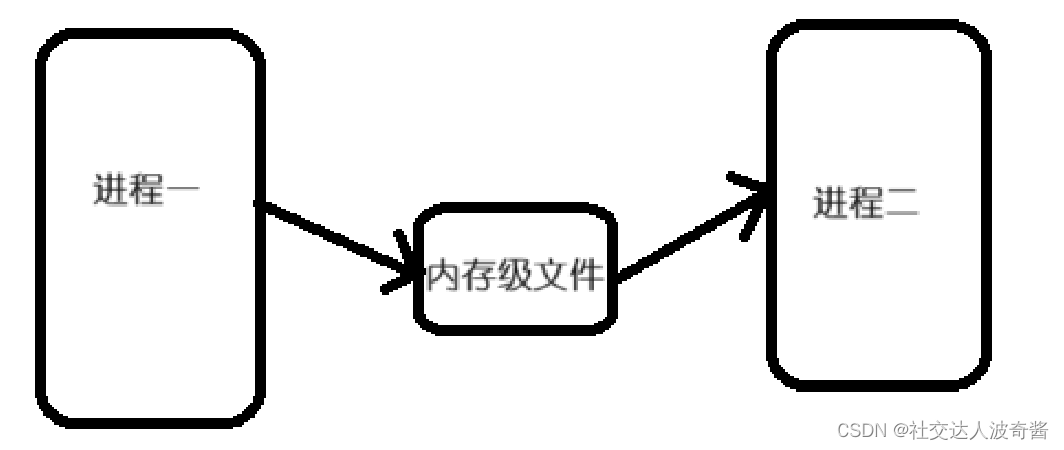
创建父子进程,使得进程的struct file*fd_array[]的文件描述符指向同一个struct file文件,这个文件是内存级文件。
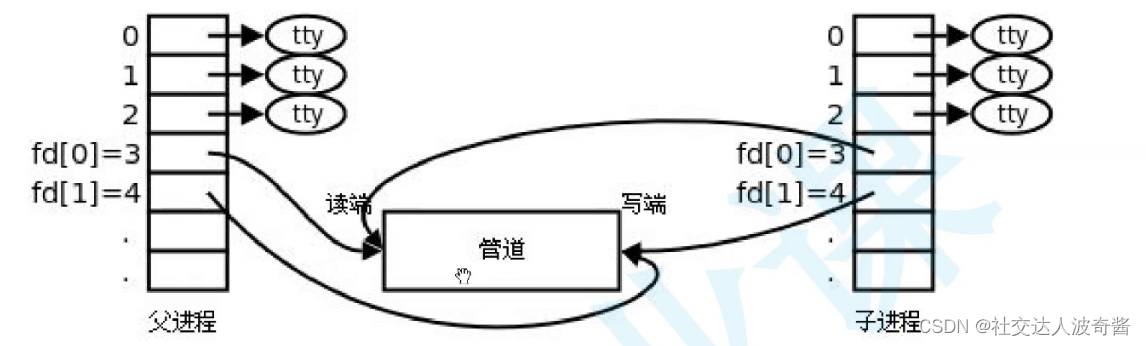
父进程关写端,子进程再关闭读端。实现单向通信
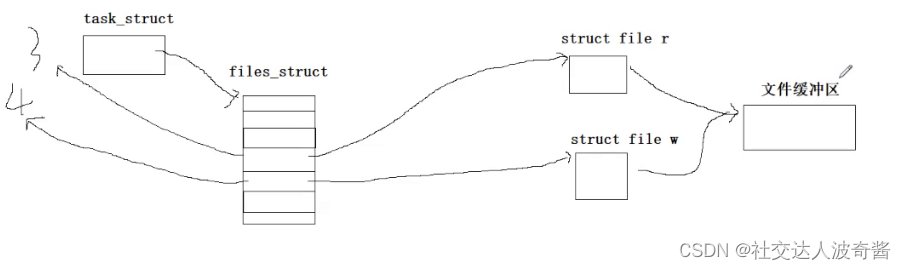
子进程写入,父进程读取。
如果进程不是父子关系,则无法利用管道,因此管道应用于父子或者兄弟进程
以上的管道叫做匿名管道。
创建管道:pipe
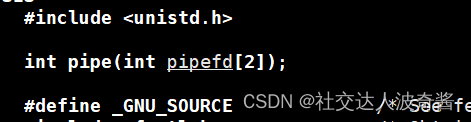
输出型参数
pipefd[0]读下标
pipefd[1]写下标
代码示例
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 2
#define NUM 1024
void Writer(int wfd)
{
string s="hello I am child";
pid_t self=getpid();
int number=0;
char buffer[NUM];
while(true)
{
buffer[0]=0; //字符串清空
//将字符串的内容放入buffer缓冲区中
snprintf(buffer,sizeof(buffer),"%s-%d-%d",s.c_str(),self,number++);
cout<<buffer<<endl;
// 发送给父进程
write(wfd,buffer,strlen(buffer));
sleep(1);
}
}
void Reader(int rfd)
{
char buffer[NUM];
while(true)
{
buffer[0]=0;
// n表示实际读到字节的大小
ssize_t n=read(rfd,buffer,sizeof(buffer));
if(n>0)
{
buffer[n]=0; //当成字符串加入"\0"
cout<<"father get a message["<<getpid()<<"]#"<<buffer<<endl;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int pipefd[]={0};
int n=pipe(pipefd);
if(n<0) return 1;
cout<<"pipefd[0]:"<<pipefd[0]<<", pipefd[1]: "<<pipefd[1]<<endl;
pid_t id=fork();
if(id<0) return 2;
if(id==0)
{
close(pipefd[0]);
//IPC code
Writer(pipefd[1]);
close(pipefd[1]);
exit(0);
}
close(pipefd[1]);
Reader(pipefd[0]);
pid_t rid=waitpid(id,nullptr,0);
if(rid<0) return 3;
close(pipefd[0]);
return 0;
}然而多执行流会会出现访问冲突的问题--父进程访问的数据到一半时,旧数据被写端覆盖。
父子进程协同,保护管道文件数据安全
读写端正常,如果管道为空,读端阻塞
管道文件有大小,写满写端阻塞
读端正常读,写端关闭,写进程变成僵尸进程,读端就会读到0,表明读到文件结尾,而且不会阻塞
写端正常写,读端关闭,操作系统通过信号杀掉写入的进程。
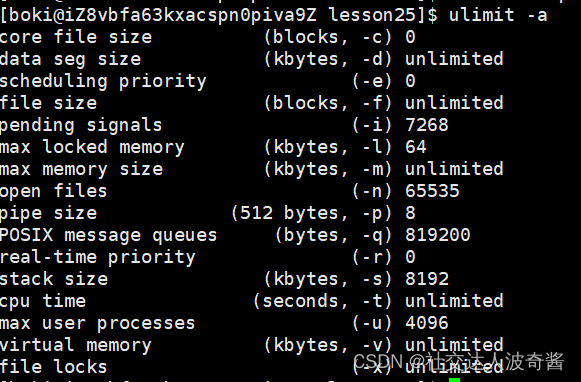
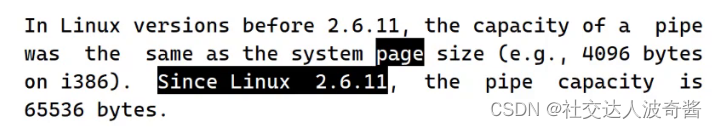
ulimit查看pipe size大小,但是不同内核可能有差别
管道面向字节流,一次性读完,有多少读多少,且将分割符看成一个普通字符,管道规范可以解决这个问题
管道是基于文件的,文件的生命周期是随进程的
管道的应用场景
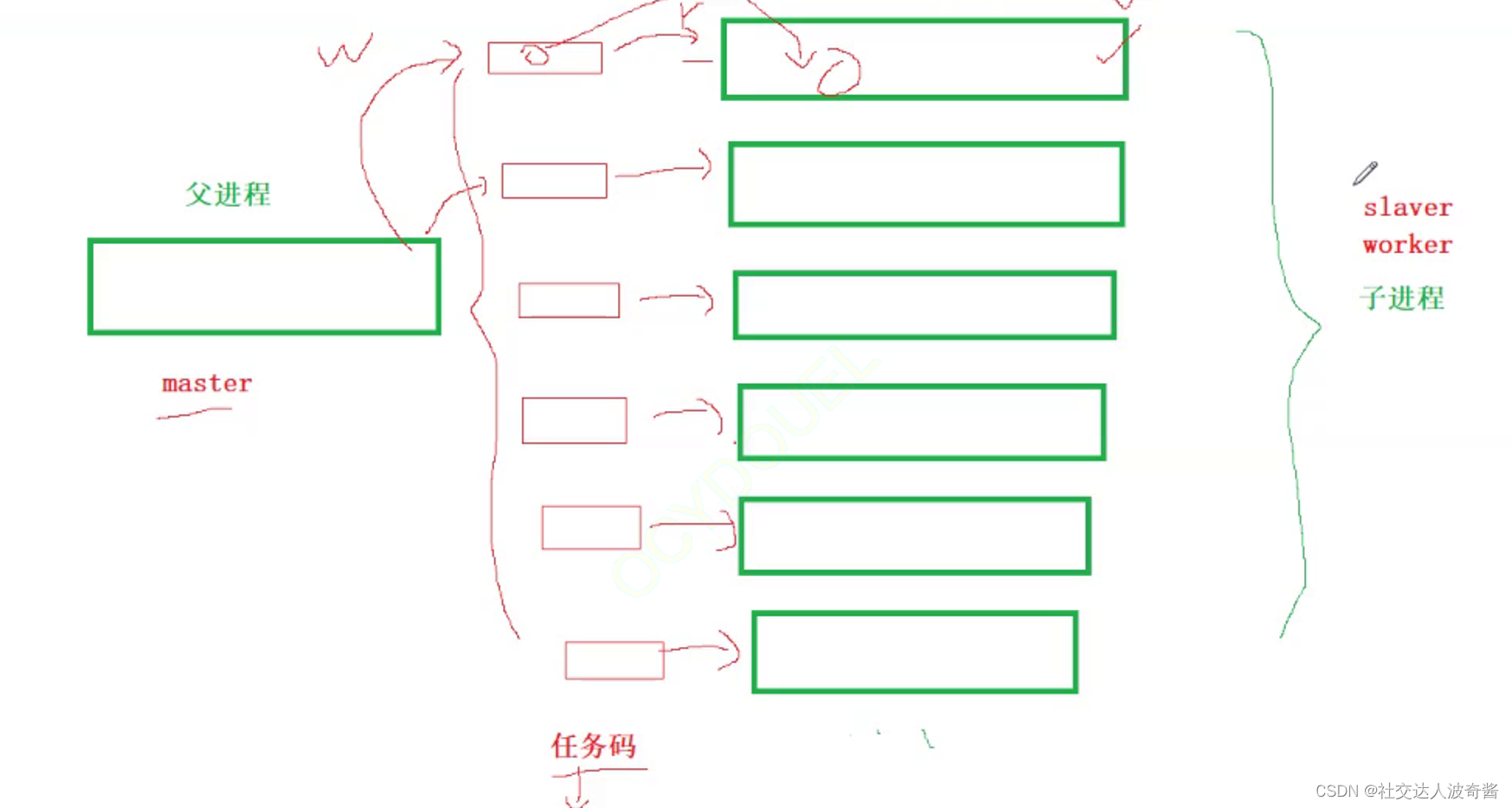
使用管道实现简易版本的进程池
Task.hpp
#pragma once
#include<cstdlib>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<string>
typedef void (*task_t)();
std::vector<task_t> tasks;
//任务是四个函数
void task1()
{
std::cout<<"task 1 call"<<std::endl;
}
void task2()
{
std::cout<<"task 2 call"<<std::endl;
}
void task3()
{
std::cout<<"task 3 call"<<std::endl;
}
void task4()
{
std::cout<<"task 4 call"<<std::endl;
}
// const & 输入 ->向函数内部输入
// * 输出
// & 输入 输出
void LoadTask(std::vector<task_t> *p_tasks)
{
p_tasks->push_back(&task1);
p_tasks->push_back(&task2);
p_tasks->push_back(&task3);
p_tasks->push_back(&task4);
}
ProcessPool.cc
#include "Task.hpp"
//对管道进行描述
#define processnum 10
class channel
{
public:
channel(int task_id,int pid,std::string processname)
:_cmdfd(task_id)
,_pid(pid)
,_processname(processname)
{}
public:
int _cmdfd;
int _pid;
std::string _processname;
};
std::vector<channel> channels;
void slaver()
{
while(true)
{
int tasknum=0;
ssize_t num=read(0,&tasknum,sizeof(int));//read block,等待输入
// tasknum=tasknum%tasks.size();
// (*tasks[tasknum])();
//std::cout<<"i and pid"<<i<<pid<<std::endl;
if (!num)break;
else
{
std::cout<<"child process "<<getpid()<<"pid: "<<"receive task_id: "<<tasknum<<std::endl;
(*tasks[tasknum])();
}
}
}
void InitProcessPool(std::vector<channel>* pchannels)
{
std::vector<int> oldfds;
for (int i=0;i<processnum;i++){
//create pipe
int pipefd[2];
int n=pipe(pipefd);
assert(!n); // n=0 success
pid_t pid=fork();
assert(pid!=-1); //pid =-1 fail
//child
//std::cout<<"i = "<<i;
if(pid==0)
{ std::cout<<"child process:"<<getpid()<<"have otherfds: ";
//only one write fd
for(auto oldfd:oldfds)
{
std::cout<<oldfd<<" ";
close(oldfd);
}
std::cout<<std::endl;
//build relationship
close(pipefd[1]);
// pipe read from fd=0 not fd=3;
dup2(pipefd[0],0);
close(pipefd[0]);
//
slaver();
exit(0);
}
close(pipefd[0]);
int status=0;
// ensure one by one ,block until child process finish
// pid_t result=waitpid(pid,&status,0);
// assert(result!=-1);
pchannels->push_back(channel(pipefd[1],pid,"process "+std::to_string(i)));
oldfds.push_back(pipefd[1]);
sleep(1);
}
}
void menu()
{
std::cout<<"*********************"<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"******1.task one*****"<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"******2.task two*****"<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"******3.task three***"<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"******4.task four****"<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"******0.quit*********"<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"*********************"<<std::endl;
}
void ctrlSlaver()
{
int which=0;
while(true)
{
menu();
int enter=0;
std::cout<<"enter number:";
std::cin>>enter;
std::cout<<std::endl;
if (enter==0){
std::cout<<"quit software"<<std::endl;
//ssize_t n=write(0,&enter,0); 不用写入,直接退出就好了
//assert(n!=-1);
break;
}
ssize_t n=write(channels[which]._cmdfd,&enter,sizeof(int));
assert(n!=-1);
std::cout<<"parent send a task_num "<<enter<<" to process "<<channels[which]._processname<<std::endl;
which++;
which=which%processnum;
}
}
void quitProcess(std::vector<channel>& pchannels)
{
for(auto channel:channels)
{
std::cout<<"close process"<<channel._pid<<std::endl;
//关闭读端,进程关闭
close(channel._cmdfd);
wait(NULL);
}
}
void PrintTask(const std::vector<task_t> tasks)
{
for(auto task:tasks)
{
(*task)();
}
}
int main()
{
// load the task
LoadTask(&tasks);
//PrintTask(tasks);
InitProcessPool(&channels);
ctrlSlaver();
quitProcess(channels);
return 0;
}