1 前言
上一节《Modern C++ std::variant的实现原理》我们简单分析了std::variant的实现原理,其实要学好C++编程,除了看优秀的代码包括标准库实现,读文档也是很便捷且必须的一种办法。
本节我将逐条解析文档中的五个特性,解析的办法有两种:实现代码讲解、用例子举例。
2 文档
variant文档

3解析
以下所有实现代码都来自/usr/include/c++/11/variant。
3.1 类型安全
The class template std::variant represents a type-safe union.
An instance of std::variant at any given time either holds a value of one of its alternative types, or in the case of error - no value (this state is hard to achieve, see valueless_by_exception).
类型安全,且总会持有一种类型的值,但也有极小的可能无值(valueless)。
无值请参考文档, 我们重点说下类型安全。
咱们先说下union怎么类型不安全,比如下面的例子:
union Data {
int intValue;
double doubleValue;
};
Data d;
d.intValue = 10;
cout<<d.doubleValue; //类型不安全,存入int,取出double
但variant你做不到这样:
std::variant<int, double> v;
v = 1;
cout << get<1>(v)<<endl;
编译没问题,但运行报异常:
terminate called after throwing an instance of ‘std::bad_variant_access’
what(): std::get: wrong index for variant
这是因为当前存储了什么类型是被_M_index记了下来的,在我们的例子中存了int,故_M_index=0, 而double是下一个类型其_M_index=1. 实现代码如下:
1672 template<size_t _Np, typename... _Types>
1673 constexpr variant_alternative_t<_Np, variant<_Types...>>&
1674 get(variant<_Types...>& __v)
1675 {
1676 static_assert(_Np < sizeof...(_Types),
1677 "The index must be in [0, number of alternatives)");
1678 if (__v.index() != _Np) //index()返回_M_index
1679 __throw_bad_variant_access(__v.valueless_by_exception()); //本例触发异常
1680 return __detail::__variant::__get<_Np>(__v);
1681 }
当然,类型安全的代价就是需要比union多点内存存_M_index。它的类型可能是char, 也可能是short, 这取决于你的variant声明时要容纳的类型个数:
401 template <typename... _Types>
402 using __select_index =
403 typename __select_int::_Select_int_base<sizeof...(_Types),
404 unsigned char,
405 unsigned short>::type::value_type;
446 _Variadic_union<_Types...> _M_u;
447 using __index_type = __select_index<_Types...>;
448 __index_type _M_index;
449 };
3.2 默认持有第一个类型的值
a default-constructed variant holds a value of its first alternative, unless that alternative is not default-constructible
我们先通过一个例子有个直观的认识:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <variant>
3 #include <string>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main() {
7 class Person{
8 public:
9 Person(){
10 char ch;
11 std::cout << "Enter a character: ";
12 std::cin.get(ch);
13 }
14 };
15 // Define a variant with 2 alternatives: Person, int
16 std::variant<Person,int> vpi; //并没有显示指明存入一个Person, 而实际却是存入了Person
我让程序卡在输入那(第12行),方便用GDB看下调用栈
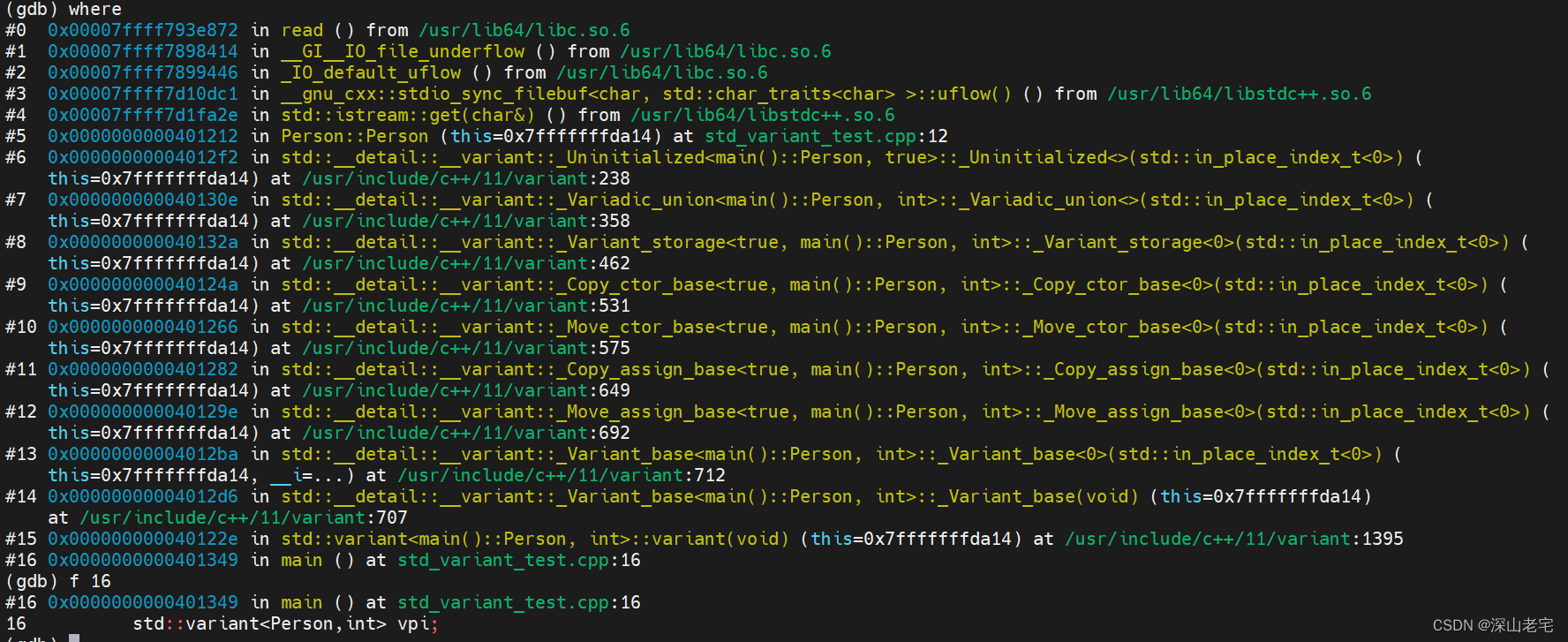
关键代码在栈第14、13层:
704 constexpr
705 _Variant_base()
706 noexcept(_Traits<_Types...>::_S_nothrow_default_ctor)
707 : _Variant_base(in_place_index<0>) { } //类型列表中的第一个类型即Person
**思考:**如果第一个类型没有默认构造函数哪?
答案也在文档中
unless that alternative is not default-constructible
把上面的默认构造函数置为delete, 编译出错:
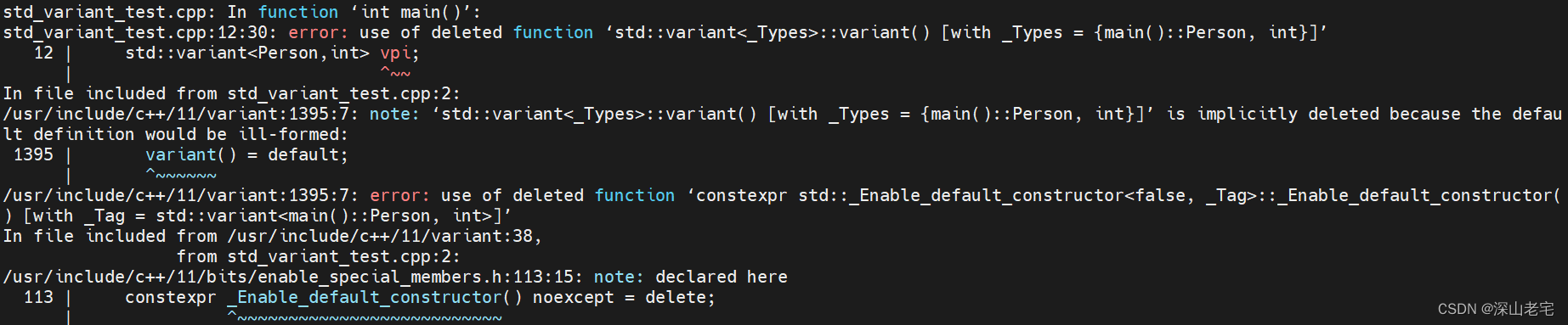
还记得上节preview的图吗?继承_Enable_default_constructor的原因也在这里(有机会再细讲)
3.3 内存开始即分配好,没有动态分配内存
As with unions, if a variant holds a value of some object type T, the object representation of T is allocated directly within the object representation of the variant itself. Variant is not allowed to allocate additional (dynamic) memory.
这一点我们上一节已经提到过,不在赘述。
3.4 不能存入引用,数组,void
A variant is not permitted to hold references, arrays, or the type void.
实现代码有如下片段:
1346 static_assert(sizeof...(_Types) > 0,
1347 "variant must have at least one alternative");
1348 static_assert(!(std::is_reference_v<_Types> || ...),
1349 "variant must have no reference alternative");
1350 static_assert(!(std::is_void_v<_Types> || ...),
1351 "variant must have no void alternative");
显然引用、void已经被禁。而原生数组不是完整类型,不能在标准库容器中被用于模板参数。
3.5 可以重复持有相同类型
A variant is permitted to hold the same type more than once, and to hold differently cv-qualified versions of the same type.
可以持有多个相同类型,比如两个int
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <variant>
3 #include <string>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main() {
7 std::variant<int,int> v2i;
8 v2i.emplace<0>(1);
9 //cout<<get<1>(v2i)<<endl; //虽然类型相同,但依然不能按第二个int取值
10 v2i.emplace<1>(2);
11 cout<<get<1>(v2i)<<endl;
3.6 get by type
这一条在get部分
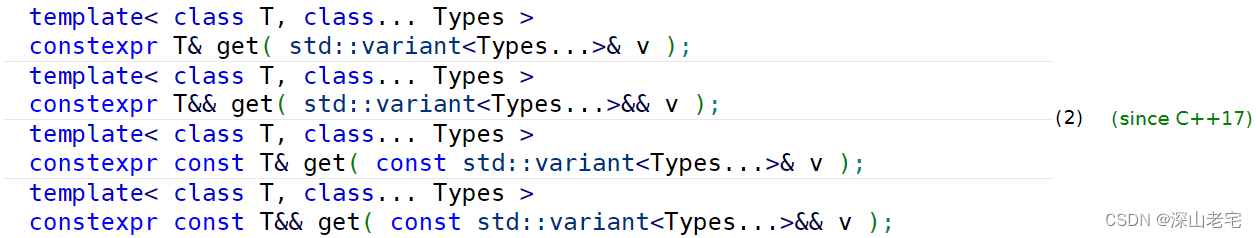
获得数据不仅仅能用下标,还能用类型,比如
std::variant<int, double> v;
v = 1;
cout << get<double>(v)<<endl;
后台还是找到double的下标取得数据。如何转的哪?先不要急,让我们先看看3.4中提到的例子
7 std::variant<int,int> v2i;
8 v2i.emplace<0>(1);
9 //cout<<get<1>(v2i)<<endl; //虽然类型相同,但依然不能按第二个int取值
10 v2i.emplace<1>(2);
11 cout<<get<int>(v2i)<<endl; //get<n> 改为get<int>
这会导致编译出错,
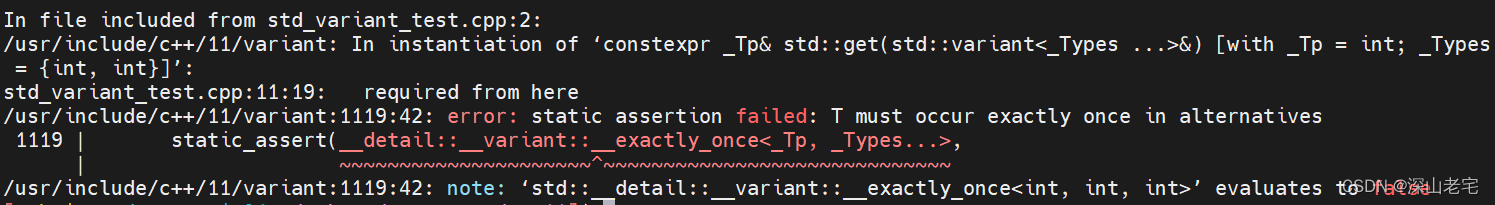
显然它区分不出来你要去第几个int, 它也不允许这么用:
1116 template<typename _Tp, typename... _Types>
1117 constexpr _Tp& get(variant<_Types...>& __v)
1118 {
1119 static_assert(__detail::__variant::__exactly_once<_Tp, _Types...>,
1120 "T must occur exactly once in alternatives");
1121 static_assert(!is_void_v<_Tp>, "_Tp must not be void");
1122 return std::get<__detail::__variant::__index_of_v<_Tp, _Types...>>(__v);
1123 }
我们例子中_Tp=int, _Types={int,int}, _Tp在_Types中出现了两次,导致__exactly_once是false, 所以报了1119行的T must occur exactly once in alternatives
__exactly_once的实现又是一个递归哈。
721 // For how many times does _Tp appear in _Tuple?
722 template<typename _Tp, typename _Tuple>
723 struct __tuple_count;
724
725 template<typename _Tp, typename _Tuple>
726 inline constexpr size_t __tuple_count_v =
727 __tuple_count<_Tp, _Tuple>::value;
728
729 template<typename _Tp, typename... _Types>
730 struct __tuple_count<_Tp, tuple<_Types...>>
731 : integral_constant<size_t, 0> { };
732
733 template<typename _Tp, typename _First, typename... _Rest>
734 struct __tuple_count<_Tp, tuple<_First, _Rest...>>
735 : integral_constant<
736 size_t,
737 __tuple_count_v<_Tp, tuple<_Rest...>> + is_same_v<_Tp, _First>> { };
738
739 // TODO: Reuse this in <tuple> ?
740 template<typename _Tp, typename... _Types>
741 inline constexpr bool **__exactly_once** =
742 __tuple_count_v<_Tp, tuple<_Types...>> == 1;
回到正常,如果1119行不报错,则来到
1122 return std::get<__detail::__variant::__index_of_v<_Tp, _Types...>>(__v);
查找_Tp在_Types中的下标,其实现也是递归,又是递归啊:
167 // Returns the first appearance of _Tp in _Types.
168 // Returns sizeof...(_Types) if _Tp is not in _Types.
169 template<typename _Tp, typename... _Types>
170 struct __index_of : std::integral_constant<size_t, 0> {};
171
172 template<typename _Tp, typename... _Types>
173 inline constexpr size_t __index_of_v = __index_of<_Tp, _Types...>::value;
174
175 template<typename _Tp, typename _First, typename... _Rest>
176 struct __index_of<_Tp, _First, _Rest...> :
177 std::integral_constant<size_t, is_same_v<_Tp, _First>
178 ? 0 : __index_of_v<_Tp, _Rest...> + 1> {};