文章目录
- 一、200、岛屿数量
- 1.1 深度优先搜索DFS
- 1.2 广度优先搜索BFS
- 二、695、岛屿的最大面积
- 2.1 深度优先搜索DFS
- 2.2 广度优先搜索BFS
- 三、完整代码
所有的LeetCode题解索引,可以看这篇文章——【算法和数据结构】LeetCode题解。
一、200、岛屿数量
1.1 深度优先搜索DFS
思路分析:本题当中1代表的是陆地,0代表海洋,我们需要计算连接在一起的陆地(岛屿)数量,而上下左右这种才算连接在一起,对角线和反对角线上的元素不算。例如下图算三个岛屿:
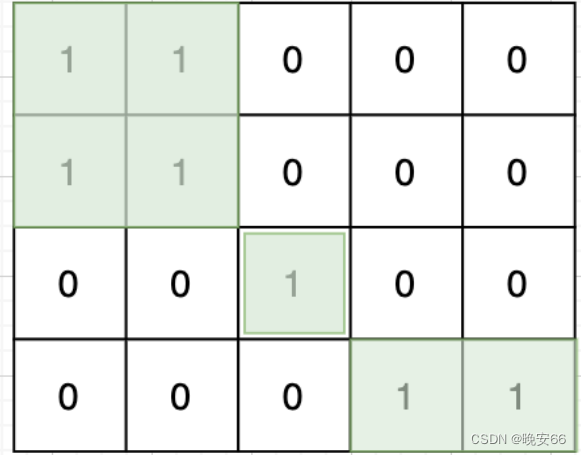
基本思路是遇到一个没有遍历过的陆地,计数器++,然后把该节点陆地连接的陆地全部标记上。遇到标记过的陆地节点和海洋节点全部跳过,最终计数器就是岛屿的数量。因为要标价节点是否遍历过,所以我们创建一个visited布尔数组,false代表未遍历过,true代表遍历过。遍历二维数组采用两个for循环。节点的连接节点遍历通过偏移量数组delta_x_y。终止条件和越界参数处理的if语句相同。
程序如下:
// 200、岛屿数量-深度优先搜索
class Solution {
private:
int result = 0;
vector<vector<int>> delta_x_y = { {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0} }; // 上下左右四个方向的偏移量
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) { // 1、递归输入参数
// 3、单层递归逻辑
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = x + delta_x_y[i][0];
int nexty = y + delta_x_y[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过 2、终止条件
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') { // 没有访问过的,同时是陆地的
visited[nextx][nexty] = true;
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);
}
}
}
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(grid.size(), vector<bool>(grid[0].size(), false)); // 遍历过的坐标
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) { // 遍历行
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++) { // 遍历列
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {
visited[i][j] = true; // 遍历的陆地标记改为true
result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,岛屿数量++
dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 深度优先搜索,将连接的陆地都标记上true
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( m × n ) O(m \times n) O(m×n),其中 m m m和 n n n分别是岛屿数组的行数和列数。
- 空间复杂度: O ( m × n ) O(m \times n) O(m×n),主要是栈的调用,最坏情况下,网格全是陆地,深度优先搜索的深度达到 m × n m \times n m×n。
1.2 广度优先搜索BFS
思路分析:广度优先搜索是一圈一圈的搜索过程,而模拟这样的搜索过程可以用队列来实现。每当我们将坐标加入队列时,就代表该左边已经遍历过了,将visited数组标记为true。
程序如下:
// 200、岛屿数量-广度优先搜索
class Solution2 {
private:
int result = 0;
vector<vector<int>> delta_x_y = { {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0} }; // 上下左右四个方向的偏移量
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>> que; // 定义队列,队列中的元素是对组 pair<int, int>
que.push({ x, y }); // 起始节点加入队列
visited[x][y] = true; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记为访问过的节点
while (!que.empty()) { // 开始遍历队列里的元素
pair<int, int> cur = que.front(); que.pop(); // 从队列取元素
int curx = cur.first;
int cury = cur.second; // 当前节点坐标
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 开始想当前节点的四个方向左右上下去遍历
int nextx = curx + delta_x_y[i][0];
int nexty = cury + delta_x_y[i][1]; // 获取周边四个方向的坐标
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 坐标越界了,直接跳过
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') { // 如果节点没被访问过
que.push({ nextx, nexty }); // 队列添加该节点为下一轮要遍历的节点
visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // 只要加入队列立刻标记,避免重复访问
}
}
}
}
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(grid.size(), vector<bool>(grid[0].size(), false)); // 遍历过的坐标
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) { // 遍历行
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++) { // 遍历列
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {
visited[i][j] = true; // 遍历的陆地标记改为true
result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,岛屿数量++
bfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 深度优先搜索,将连接的陆地都标记上true
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( m × n ) O(m \times n) O(m×n),其中 m m m和 n n n分别是岛屿数组的行数和列数。
- 空间复杂度: O ( m i n ( m , n ) ) O(min(m, n)) O(min(m,n)),在最坏情况下,整个网格均为陆地,队列的大小可以达到 m i n ( m , n ) min(m, n) min(m,n)。
二、695、岛屿的最大面积
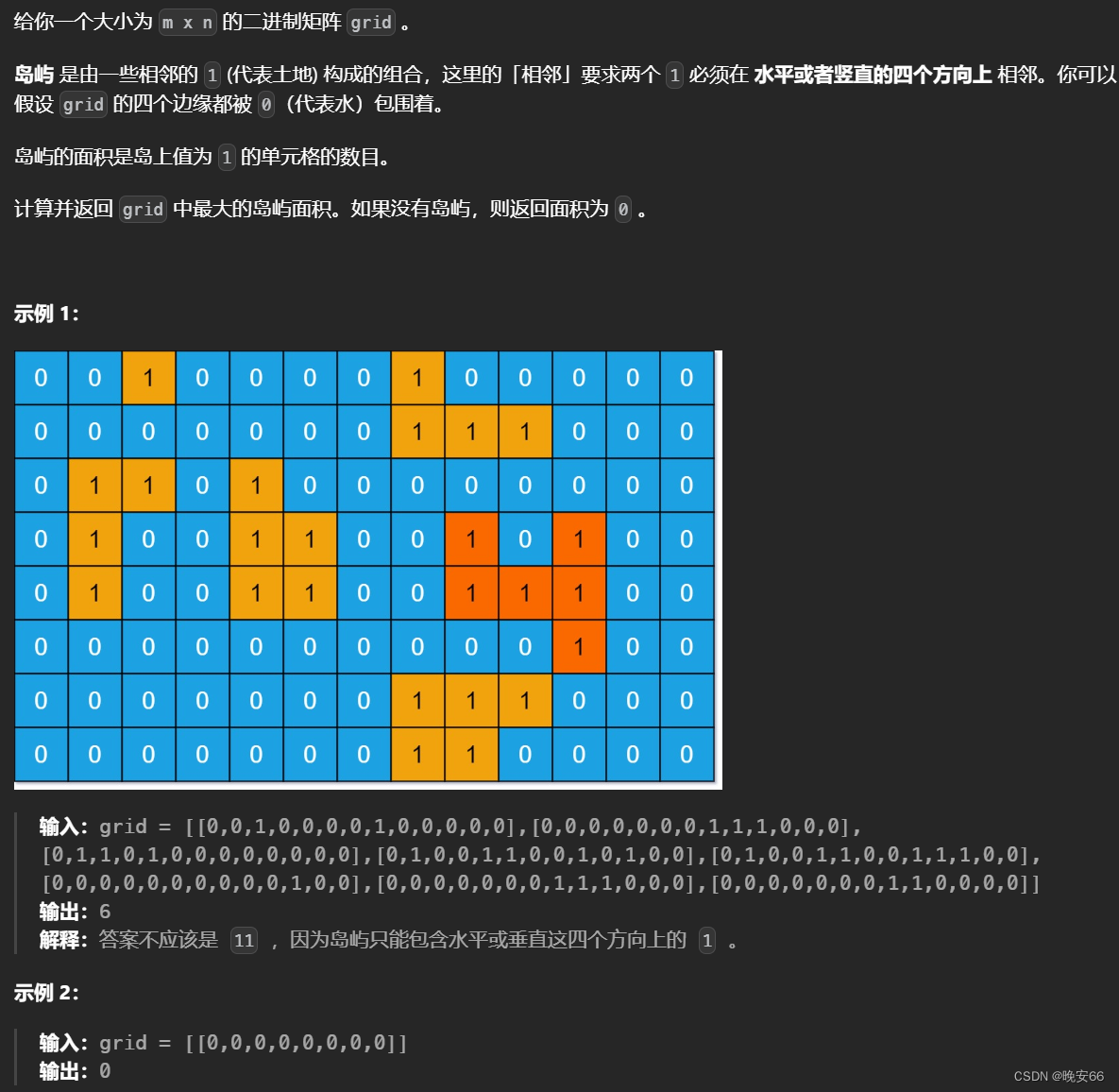
2.1 深度优先搜索DFS
思路分析:在200题岛屿数量的基础之上,题目要求我们求岛屿的最大面积,单块陆地的面积为1。思路很简单,每次遍历之后面积计数器++,然后在不同陆地的面积之中取最大值。
程序如下:
// 695、岛屿的最大面积-深度优先搜索
class Solution3 {
private:
int maxArea = 0;
int Area = 0;
vector<vector<int>> delta_x_y = { {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0} }; // 上下左右四个方向的偏移量
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) { // 1、递归输入参数
// 2、终止条件 访问过或者遇到海水
if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0) return;
visited[x][y] = true;
Area++;
// 3、单层递归逻辑
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = x + delta_x_y[i][0];
int nexty = y + delta_x_y[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);
}
}
public:
int maxAreaOfIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(grid.size(), vector<bool>(grid[0].size(), false)); // 遍历过的坐标
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) { // 遍历行
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++) { // 遍历列
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
Area = 0;
dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 深度优先搜索,将连接的陆地都标记上true
maxArea = max(Area, maxArea);
}
}
}
return maxArea;
}
};
- 时间复杂度: O ( m × n ) O(m \times n) O(m×n),其中 m m m和 n n n分别是岛屿数组的行数和列数。
- 空间复杂度: O ( m × n ) O(m \times n) O(m×n),主要是栈的调用,最坏情况下,网格全是陆地,深度优先搜索的深度达到 m × n m \times n m×n。
2.2 广度优先搜索BFS
思路分析:思路和深度优先搜索一样。
程序如下:
// 695、岛屿的最大面积-广度优先搜索
class Solution4 {
private:
int maxArea = 0;
int Area = 0;
vector<vector<int>> delta_x_y = { {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0} }; // 上下左右四个方向的偏移量
void bfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>> que; // 定义队列,队列中的元素是对组 pair<int, int>
que.push({ x, y }); // 起始节点加入队列
visited[x][y] = true; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记为访问过的节点
Area++;
while (!que.empty()) { // 开始遍历队列里的元素
pair<int, int> cur = que.front(); que.pop(); // 从队列取元素
int curx = cur.first;
int cury = cur.second; // 当前节点坐标
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 开始想当前节点的四个方向左右上下去遍历
int nextx = curx + delta_x_y[i][0];
int nexty = cury + delta_x_y[i][1]; // 获取周边四个方向的坐标
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 坐标越界了,直接跳过
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) { // 如果节点没被访问过
que.push({ nextx, nexty }); // 队列添加该节点为下一轮要遍历的节点
visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // 只要加入队列立刻标记,避免重复访问
Area++;
}
}
}
}
public:
int maxAreaOfIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(grid.size(), vector<bool>(grid[0].size(), false)); // 遍历过的坐标
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) { // 遍历行
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++) { // 遍历列
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
Area = 0;
bfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 深度优先搜索,将连接的陆地都标记上true
maxArea = max(Area, maxArea);
}
}
}
return maxArea;
}
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( m × n ) O(m \times n) O(m×n),其中 m m m和 n n n分别是岛屿数组的行数和列数。
- 空间复杂度: O ( m i n ( m , n ) ) O(min(m, n)) O(min(m,n)),在最坏情况下,整个网格均为陆地,队列的大小可以达到 m i n ( m , n ) min(m, n) min(m,n)。
三、完整代码
# include <iostream>
# include <vector>
# include <queue>
using namespace std;
// 200、岛屿数量-深度优先搜索
class Solution {
private:
int result = 0;
vector<vector<int>> delta_x_y = { {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0} }; // 上下左右四个方向的偏移量
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) { // 1、递归输入参数
// 3、单层递归逻辑
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = x + delta_x_y[i][0];
int nexty = y + delta_x_y[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过 2、终止条件
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') { // 没有访问过的,同时是陆地的
visited[nextx][nexty] = true;
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);
}
}
}
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(grid.size(), vector<bool>(grid[0].size(), false)); // 遍历过的坐标
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) { // 遍历行
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++) { // 遍历列
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {
visited[i][j] = true; // 遍历的陆地标记改为true
result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,岛屿数量++
dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 深度优先搜索,将连接的陆地都标记上true
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
// 200、岛屿数量-广度优先搜索
class Solution2 {
private:
int result = 0;
vector<vector<int>> delta_x_y = { {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0} }; // 上下左右四个方向的偏移量
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>> que; // 定义队列,队列中的元素是对组 pair<int, int>
que.push({ x, y }); // 起始节点加入队列
visited[x][y] = true; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记为访问过的节点
while (!que.empty()) { // 开始遍历队列里的元素
pair<int, int> cur = que.front(); que.pop(); // 从队列取元素
int curx = cur.first;
int cury = cur.second; // 当前节点坐标
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 开始想当前节点的四个方向左右上下去遍历
int nextx = curx + delta_x_y[i][0];
int nexty = cury + delta_x_y[i][1]; // 获取周边四个方向的坐标
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 坐标越界了,直接跳过
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') { // 如果节点没被访问过
que.push({ nextx, nexty }); // 队列添加该节点为下一轮要遍历的节点
visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // 只要加入队列立刻标记,避免重复访问
}
}
}
}
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(grid.size(), vector<bool>(grid[0].size(), false)); // 遍历过的坐标
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) { // 遍历行
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++) { // 遍历列
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {
visited[i][j] = true; // 遍历的陆地标记改为true
result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,岛屿数量++
bfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 深度优先搜索,将连接的陆地都标记上true
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
// 695、岛屿的最大面积-深度优先搜索
class Solution3 {
private:
int maxArea = 0;
int Area = 0;
vector<vector<int>> delta_x_y = { {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0} }; // 上下左右四个方向的偏移量
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) { // 1、递归输入参数
// 2、终止条件 访问过或者遇到海水
if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0) return;
visited[x][y] = true;
Area++;
// 3、单层递归逻辑
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = x + delta_x_y[i][0];
int nexty = y + delta_x_y[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);
}
}
public:
int maxAreaOfIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(grid.size(), vector<bool>(grid[0].size(), false)); // 遍历过的坐标
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) { // 遍历行
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++) { // 遍历列
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
Area = 0;
dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 深度优先搜索,将连接的陆地都标记上true
maxArea = max(Area, maxArea);
}
}
}
return maxArea;
}
};
// 695、岛屿的最大面积-广度优先搜索
class Solution4 {
private:
int maxArea = 0;
int Area = 0;
vector<vector<int>> delta_x_y = { {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0} }; // 上下左右四个方向的偏移量
void bfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>> que; // 定义队列,队列中的元素是对组 pair<int, int>
que.push({ x, y }); // 起始节点加入队列
visited[x][y] = true; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记为访问过的节点
Area++;
while (!que.empty()) { // 开始遍历队列里的元素
pair<int, int> cur = que.front(); que.pop(); // 从队列取元素
int curx = cur.first;
int cury = cur.second; // 当前节点坐标
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 开始想当前节点的四个方向左右上下去遍历
int nextx = curx + delta_x_y[i][0];
int nexty = cury + delta_x_y[i][1]; // 获取周边四个方向的坐标
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 坐标越界了,直接跳过
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) { // 如果节点没被访问过
que.push({ nextx, nexty }); // 队列添加该节点为下一轮要遍历的节点
visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // 只要加入队列立刻标记,避免重复访问
Area++;
}
}
}
}
public:
int maxAreaOfIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(grid.size(), vector<bool>(grid[0].size(), false)); // 遍历过的坐标
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) { // 遍历行
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++) { // 遍历列
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
Area = 0;
bfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 深度优先搜索,将连接的陆地都标记上true
maxArea = max(Area, maxArea);
}
}
}
return maxArea;
}
};
int main() {
// // 200、岛屿数量测试案例
//vector<vector<char>> grid = { {'1', '1', '1', '1', '0'} ,{'1', '1', '0', '1', '0'}, {'1', '1', '0', '0', '0'}, {'0', '0', '0', '0', '0'} };
//Solution s1;
//int result = s1.numIslands(grid);
// 695、岛屿的最大面积测试案例
vector<vector<int>> grid = { {0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 }, { 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
Solution4 s1;
int result = s1.maxAreaOfIsland(grid);
cout << result << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
end

![[ Python+OpenCV+Mediapipe ] 实现对象识别](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/79f2f3c81f544bb1a1646cf73992f926.png)





![[ 2024春节 Flink打卡 ] -- Paimon](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/3c84841d55964805bf010c22ea80b83e.png)