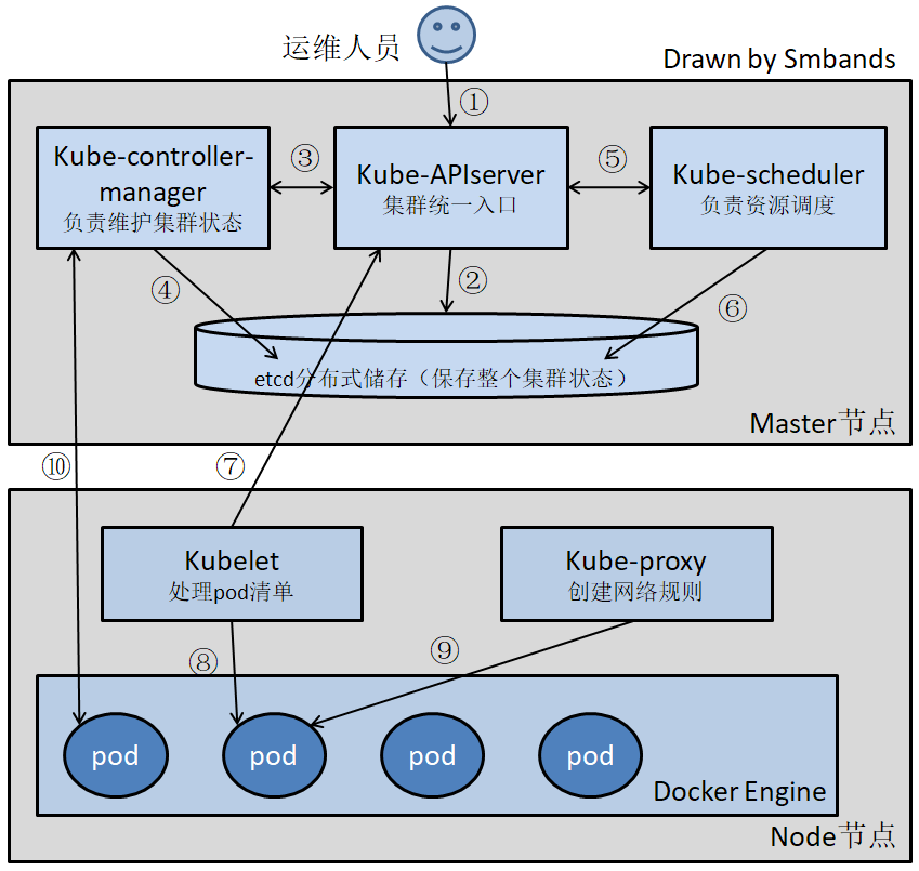
接前一篇文章:
上回书重点解析了virtio_pci_modern_probe函数。再来回顾一下其中相关的数据结构:
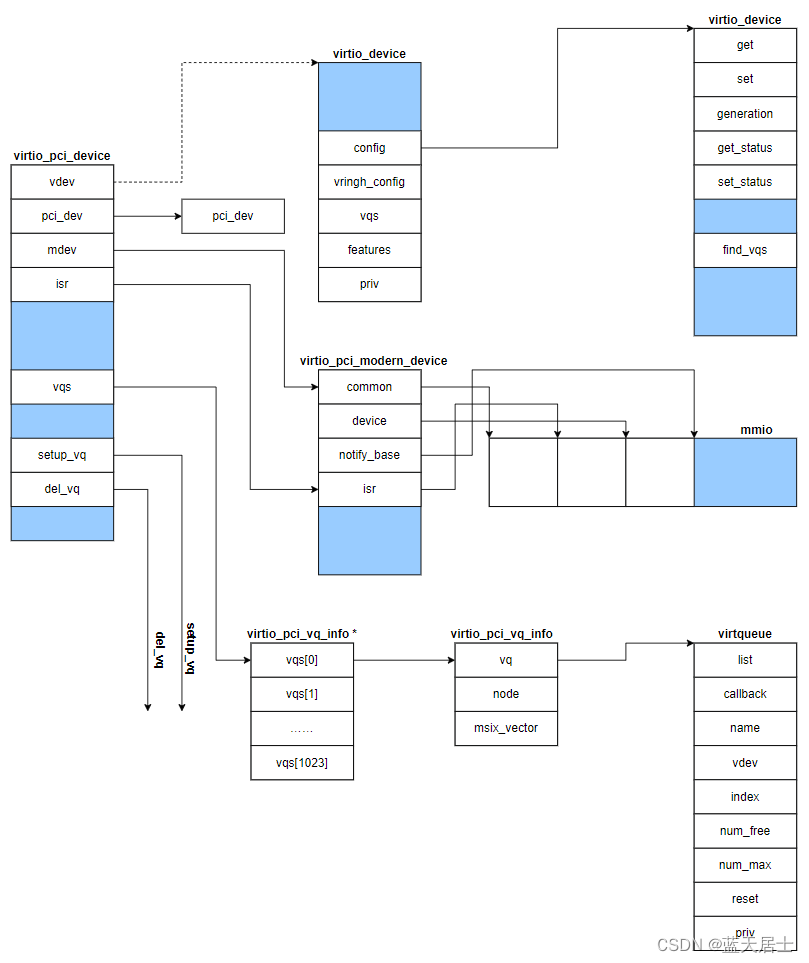
- struct virtio_pci_device
struct virtio_pci_device的定义在Linux内核源码/drivers/virtio/virtio_pci_common.h中,如下:
/* Our device structure */
struct virtio_pci_device {
struct virtio_device vdev;
struct pci_dev *pci_dev;
union {
struct virtio_pci_legacy_device ldev;
struct virtio_pci_modern_device mdev;
};
bool is_legacy;
/* Where to read and clear interrupt */
u8 __iomem *isr;
/* a list of queues so we can dispatch IRQs */
spinlock_t lock;
struct list_head virtqueues;
/* array of all queues for house-keeping */
struct virtio_pci_vq_info **vqs;
/* MSI-X support */
int msix_enabled;
int intx_enabled;
cpumask_var_t *msix_affinity_masks;
/* Name strings for interrupts. This size should be enough,
* and I'm too lazy to allocate each name separately. */
char (*msix_names)[256];
/* Number of available vectors */
unsigned int msix_vectors;
/* Vectors allocated, excluding per-vq vectors if any */
unsigned int msix_used_vectors;
/* Whether we have vector per vq */
bool per_vq_vectors;
struct virtqueue *(*setup_vq)(struct virtio_pci_device *vp_dev,
struct virtio_pci_vq_info *info,
unsigned int idx,
void (*callback)(struct virtqueue *vq),
const char *name,
bool ctx,
u16 msix_vec);
void (*del_vq)(struct virtio_pci_vq_info *info);
u16 (*config_vector)(struct virtio_pci_device *vp_dev, u16 vector);
};virtio_pci_modern_probe执行完成后,相关数据结构如下图所示:
回到virtio_pci_probe函数。在Linux内核源码/drivers/virtio/virtio_pci_common.c中,代码如下:
static int virtio_pci_probe(struct pci_dev *pci_dev,
const struct pci_device_id *id)
{
struct virtio_pci_device *vp_dev, *reg_dev = NULL;
int rc;
/* allocate our structure and fill it out */
vp_dev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct virtio_pci_device), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!vp_dev)
return -ENOMEM;
pci_set_drvdata(pci_dev, vp_dev);
vp_dev->vdev.dev.parent = &pci_dev->dev;
vp_dev->vdev.dev.release = virtio_pci_release_dev;
vp_dev->pci_dev = pci_dev;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&vp_dev->virtqueues);
spin_lock_init(&vp_dev->lock);
/* enable the device */
rc = pci_enable_device(pci_dev);
if (rc)
goto err_enable_device;
if (force_legacy) {
rc = virtio_pci_legacy_probe(vp_dev);
/* Also try modern mode if we can't map BAR0 (no IO space). */
if (rc == -ENODEV || rc == -ENOMEM)
rc = virtio_pci_modern_probe(vp_dev);
if (rc)
goto err_probe;
} else {
rc = virtio_pci_modern_probe(vp_dev);
if (rc == -ENODEV)
rc = virtio_pci_legacy_probe(vp_dev);
if (rc)
goto err_probe;
}
pci_set_master(pci_dev);
rc = register_virtio_device(&vp_dev->vdev);
reg_dev = vp_dev;
if (rc)
goto err_register;
return 0;
err_register:
if (vp_dev->is_legacy)
virtio_pci_legacy_remove(vp_dev);
else
virtio_pci_modern_remove(vp_dev);
err_probe:
pci_disable_device(pci_dev);
err_enable_device:
if (reg_dev)
put_device(&vp_dev->vdev.dev);
else
kfree(vp_dev);
return rc;
}接QEMU源码全解析 —— virtio(18)中的内容,前文书讲到了virtio_pci_probe函数的第5步,
“(5)调用virtio_pci_legacy_probe或者virtio_pci_modern_probe函数来初始化该PCI设备对应的virtio设备。”,继续往下进行。
(6)virtio_pci_probe函数在调用virtio_pci_modern_probe函数之后,接下来会调用register_virtio_device。代码片段如下:
rc = register_virtio_device(&vp_dev->vdev);
reg_dev = vp_dev;
if (rc)
goto err_register;register_virtio_device函数在Linux内核源码/drivers/virtio/virtio.c中,代码如下:
/**
* register_virtio_device - register virtio device
* @dev : virtio device to be registered
*
* On error, the caller must call put_device on &@dev->dev (and not kfree),
* as another code path may have obtained a reference to @dev.
*
* Returns: 0 on suceess, -error on failure
*/
int register_virtio_device(struct virtio_device *dev)
{
int err;
dev->dev.bus = &virtio_bus;
device_initialize(&dev->dev);
/* Assign a unique device index and hence name. */
err = ida_alloc(&virtio_index_ida, GFP_KERNEL);
if (err < 0)
goto out;
dev->index = err;
err = dev_set_name(&dev->dev, "virtio%u", dev->index);
if (err)
goto out_ida_remove;
err = virtio_device_of_init(dev);
if (err)
goto out_ida_remove;
spin_lock_init(&dev->config_lock);
dev->config_enabled = false;
dev->config_change_pending = false;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->vqs);
spin_lock_init(&dev->vqs_list_lock);
/* We always start by resetting the device, in case a previous
* driver messed it up. This also tests that code path a little. */
virtio_reset_device(dev);
/* Acknowledge that we've seen the device. */
virtio_add_status(dev, VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_ACKNOWLEDGE);
/*
* device_add() causes the bus infrastructure to look for a matching
* driver.
*/
err = device_add(&dev->dev);
if (err)
goto out_of_node_put;
return 0;
out_of_node_put:
of_node_put(dev->dev.of_node);
out_ida_remove:
ida_free(&virtio_index_ida, dev->index);
out:
virtio_add_status(dev, VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_FAILED);
return err;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(register_virtio_device);前文已提到,vp_dev->vdev的类型为struct virtio_device,而传给register_virtio_device函数的实参为vp_dev->vdev的地址,即&vp_dev->vdev。从函数名以及参数类型就能看出,register_virtio_device函数的作用是将一个virtio device注册到系统中。具体步骤如下:
(1)设置virtio设备的Bus为virtio_bus。代码片段如下:
dev->dev.bus = &virtio_bus;virtio_bus在系统初始化的时候会注册到系统中。
virtio_bus在Linux内核源码/drivers/virtio/virtio.c中初始化,代码如下:
static struct bus_type virtio_bus = {
.name = "virtio",
.match = virtio_dev_match,
.dev_groups = virtio_dev_groups,
.uevent = virtio_uevent,
.probe = virtio_dev_probe,
.remove = virtio_dev_remove,
};
int register_virtio_driver(struct virtio_driver *driver)
{
/* Catch this early. */
BUG_ON(driver->feature_table_size && !driver->feature_table);
driver->driver.bus = &virtio_bus;
return driver_register(&driver->driver);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(register_virtio_driver);
在系统初始化的时候,通过register_virtio_driver函数注册到系统中。
(2)设置virtio设备的名字为类似"virtio0"、"virtio1"的字符串。代码片段如下:
/* Assign a unique device index and hence name. */
err = ida_alloc(&virtio_index_ida, GFP_KERNEL);
if (err < 0)
goto out;
dev->index = err;
err = dev_set_name(&dev->dev, "virtio%u", dev->index);
if (err)
goto out_ida_remove;dev_set_name函数在Linux内核源码/drivers/base/core.c中,代码如下:
/**
* dev_set_name - set a device name
* @dev: device
* @fmt: format string for the device's name
*/
int dev_set_name(struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list vargs;
int err;
va_start(vargs, fmt);
err = kobject_set_name_vargs(&dev->kobj, fmt, vargs);
va_end(vargs);
return err;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(dev_set_name);(3)然后调用virtio_reset_device函数重置设备。代码片段如下:
/* We always start by resetting the device, in case a previous
* driver messed it up. This also tests that code path a little. */
virtio_reset_device(dev);(4)最后,调用device_add函数,将设备注册到系统中。代码片段如下:
/*
* device_add() causes the bus infrastructure to look for a matching
* driver.
*/
err = device_add(&dev->dev);
if (err)
goto out_of_node_put;这里,老版本代码中是调用的是device_register函数。device_register函数跟设备驱动相关性较大,在此简单介绍一下其作用。
device_register函数在Linux内核源码/drivers/base/core.c中,代码如下:
/**
* device_register - register a device with the system.
* @dev: pointer to the device structure
*
* This happens in two clean steps - initialize the device
* and add it to the system. The two steps can be called
* separately, but this is the easiest and most common.
* I.e. you should only call the two helpers separately if
* have a clearly defined need to use and refcount the device
* before it is added to the hierarchy.
*
* For more information, see the kerneldoc for device_initialize()
* and device_add().
*
* NOTE: _Never_ directly free @dev after calling this function, even
* if it returned an error! Always use put_device() to give up the
* reference initialized in this function instead.
*/
int device_register(struct device *dev)
{
device_initialize(dev);
return device_add(dev);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(device_register);device_register函数向系统注册一个设备。其分为两个简单的步骤——初始化设备(device_initialize(dev))并将其添加到系统中(device_add(dev))。这两个步骤可以分别调用,但放在一起即使用device_register函数是最简单和最常见的。例如,如果有明确的需求在其添加到层级之前使用和重新计数设备,那么应该分别独立地调用这两个助手(函数)。
从此处的代码就可以知道,老版本的内核代码中确实是直接调用了device_register函数,而新版本内核代码在此处则是在register_virtio_device函数的前边先调用了device_initialize(&dev->dev),而后在这里调用了device_add(&dev->dev)。即采用了分开调用的方式。
device_register函数会调用device_add函数,将设备加到系统中,并且会发送一个uevent消息到用户空间,这个uevent消息中包含了virtio设备的vendor id、device id。 udev接收到此消息之后,会加载virtio设备对应的驱动。然后,device_add函数会调用bus_probe_device函数,最终调用到Bus的probe函数和设备的probe函数,也就是virtio_dev_probe函数和virtballoon_probe函数。
device_add函数也在Linux内核源码/drivers/base/core.c中,就在device_register函数上边,代码如下:
/**
* device_add - add device to device hierarchy.
* @dev: device.
*
* This is part 2 of device_register(), though may be called
* separately _iff_ device_initialize() has been called separately.
*
* This adds @dev to the kobject hierarchy via kobject_add(), adds it
* to the global and sibling lists for the device, then
* adds it to the other relevant subsystems of the driver model.
*
* Do not call this routine or device_register() more than once for
* any device structure. The driver model core is not designed to work
* with devices that get unregistered and then spring back to life.
* (Among other things, it's very hard to guarantee that all references
* to the previous incarnation of @dev have been dropped.) Allocate
* and register a fresh new struct device instead.
*
* NOTE: _Never_ directly free @dev after calling this function, even
* if it returned an error! Always use put_device() to give up your
* reference instead.
*
* Rule of thumb is: if device_add() succeeds, you should call
* device_del() when you want to get rid of it. If device_add() has
* *not* succeeded, use *only* put_device() to drop the reference
* count.
*/
int device_add(struct device *dev)
{
struct subsys_private *sp;
struct device *parent;
struct kobject *kobj;
struct class_interface *class_intf;
int error = -EINVAL;
struct kobject *glue_dir = NULL;
dev = get_device(dev);
if (!dev)
goto done;
if (!dev->p) {
error = device_private_init(dev);
if (error)
goto done;
}
/*
* for statically allocated devices, which should all be converted
* some day, we need to initialize the name. We prevent reading back
* the name, and force the use of dev_name()
*/
if (dev->init_name) {
error = dev_set_name(dev, "%s", dev->init_name);
dev->init_name = NULL;
}
if (dev_name(dev))
error = 0;
/* subsystems can specify simple device enumeration */
else if (dev->bus && dev->bus->dev_name)
error = dev_set_name(dev, "%s%u", dev->bus->dev_name, dev->id);
else
error = -EINVAL;
if (error)
goto name_error;
pr_debug("device: '%s': %s\n", dev_name(dev), __func__);
parent = get_device(dev->parent);
kobj = get_device_parent(dev, parent);
if (IS_ERR(kobj)) {
error = PTR_ERR(kobj);
goto parent_error;
}
if (kobj)
dev->kobj.parent = kobj;
/* use parent numa_node */
if (parent && (dev_to_node(dev) == NUMA_NO_NODE))
set_dev_node(dev, dev_to_node(parent));
/* first, register with generic layer. */
/* we require the name to be set before, and pass NULL */
error = kobject_add(&dev->kobj, dev->kobj.parent, NULL);
if (error) {
glue_dir = kobj;
goto Error;
}
/* notify platform of device entry */
device_platform_notify(dev);
error = device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_uevent);
if (error)
goto attrError;
error = device_add_class_symlinks(dev);
if (error)
goto SymlinkError;
error = device_add_attrs(dev);
if (error)
goto AttrsError;
error = bus_add_device(dev);
if (error)
goto BusError;
error = dpm_sysfs_add(dev);
if (error)
goto DPMError;
device_pm_add(dev);
if (MAJOR(dev->devt)) {
error = device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_dev);
if (error)
goto DevAttrError;
error = device_create_sys_dev_entry(dev);
if (error)
goto SysEntryError;
devtmpfs_create_node(dev);
}
/* Notify clients of device addition. This call must come
* after dpm_sysfs_add() and before kobject_uevent().
*/
bus_notify(dev, BUS_NOTIFY_ADD_DEVICE);
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
/*
* Check if any of the other devices (consumers) have been waiting for
* this device (supplier) to be added so that they can create a device
* link to it.
*
* This needs to happen after device_pm_add() because device_link_add()
* requires the supplier be registered before it's called.
*
* But this also needs to happen before bus_probe_device() to make sure
* waiting consumers can link to it before the driver is bound to the
* device and the driver sync_state callback is called for this device.
*/
if (dev->fwnode && !dev->fwnode->dev) {
dev->fwnode->dev = dev;
fw_devlink_link_device(dev);
}
bus_probe_device(dev);
/*
* If all driver registration is done and a newly added device doesn't
* match with any driver, don't block its consumers from probing in
* case the consumer device is able to operate without this supplier.
*/
if (dev->fwnode && fw_devlink_drv_reg_done && !dev->can_match)
fw_devlink_unblock_consumers(dev);
if (parent)
klist_add_tail(&dev->p->knode_parent,
&parent->p->klist_children);
sp = class_to_subsys(dev->class);
if (sp) {
mutex_lock(&sp->mutex);
/* tie the class to the device */
klist_add_tail(&dev->p->knode_class, &sp->klist_devices);
/* notify any interfaces that the device is here */
list_for_each_entry(class_intf, &sp->interfaces, node)
if (class_intf->add_dev)
class_intf->add_dev(dev);
mutex_unlock(&sp->mutex);
subsys_put(sp);
}
done:
put_device(dev);
return error;
SysEntryError:
if (MAJOR(dev->devt))
device_remove_file(dev, &dev_attr_dev);
DevAttrError:
device_pm_remove(dev);
dpm_sysfs_remove(dev);
DPMError:
dev->driver = NULL;
bus_remove_device(dev);
BusError:
device_remove_attrs(dev);
AttrsError:
device_remove_class_symlinks(dev);
SymlinkError:
device_remove_file(dev, &dev_attr_uevent);
attrError:
device_platform_notify_remove(dev);
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_REMOVE);
glue_dir = get_glue_dir(dev);
kobject_del(&dev->kobj);
Error:
cleanup_glue_dir(dev, glue_dir);
parent_error:
put_device(parent);
name_error:
kfree(dev->p);
dev->p = NULL;
goto done;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(device_add);其中的代码片段:
/* Notify clients of device addition. This call must come
* after dpm_sysfs_add() and before kobject_uevent().
*/
bus_notify(dev, BUS_NOTIFY_ADD_DEVICE);
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);和
bus_probe_device(dev);就是上边所讲到的:
device_register函数会调用device_add函数,将设备加到系统中,并且会发送一个uevent消息到用户空间,这个uevent消息中包含了virtio设备的vendor id、device id。 udev接收到此消息之后,会加载virtio设备对应的驱动。
然后,device_add函数会调用bus_probe_device函数,最终调用到Bus的probe函数和设备的probe函数,也就是virtio_dev_probe函数和virtballoon_probe函数。
欲知后事如何,且看下回分解。

![代码随想录算法训练营第二十三天 | 669. 修剪二叉搜索树,108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树,538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树 [二叉树篇]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/a395825fe2b745fc91499c43d1cb8fda.png)