文章目录
- 题目描述
- 递归解法
- 非递归解法
题目描述
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回 它的 中序 遍历 。
示例 1:
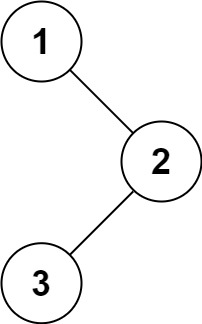
输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,3,2]
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]
提示:
树中节点数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
递归解法
class Solution {
//使用递归的方法
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root,result);
return result;
}
public void inorder(TreeNode root,List<Integer> result){
if (root==null){
return;
}
if (root.left!=null){
inorder(root.left,result);
}
result.add(root.val);
if(root.right!=null){
inorder(root.right,result);
}
}
}
非递归解法
class Solution {
//使用非递归的方法
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root,result);
return result;
}
public void inorder(TreeNode root,List<Integer> result){
if (root==null){
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur=root;//负责遍历
//cur一直往左孩子的方向走,并且把指向的节点压入栈中
//如果cur当前指向的节点为空,就开始从栈中弹出一个节点并且遍历(弹出的这个节点相当于cur上一次指向的节点),遍历完这个节点之后就开始往右孩子的方向走
while (cur!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
if (cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}else {
//cur为空则表示上个节点没有左孩子,弹出刚才的节点并且遍历
cur = stack.pop();
result.add(cur.val);
//开始往当前节点的右孩子方向走
cur = cur.right;
//然后结束本轮循环,进入下一轮循环。如果cur为空则表示也没有右孩子,就继续从栈顶弹出元素遍历,如果不为空则压入栈并且开始找左孩子。
}
}
}
}