目录
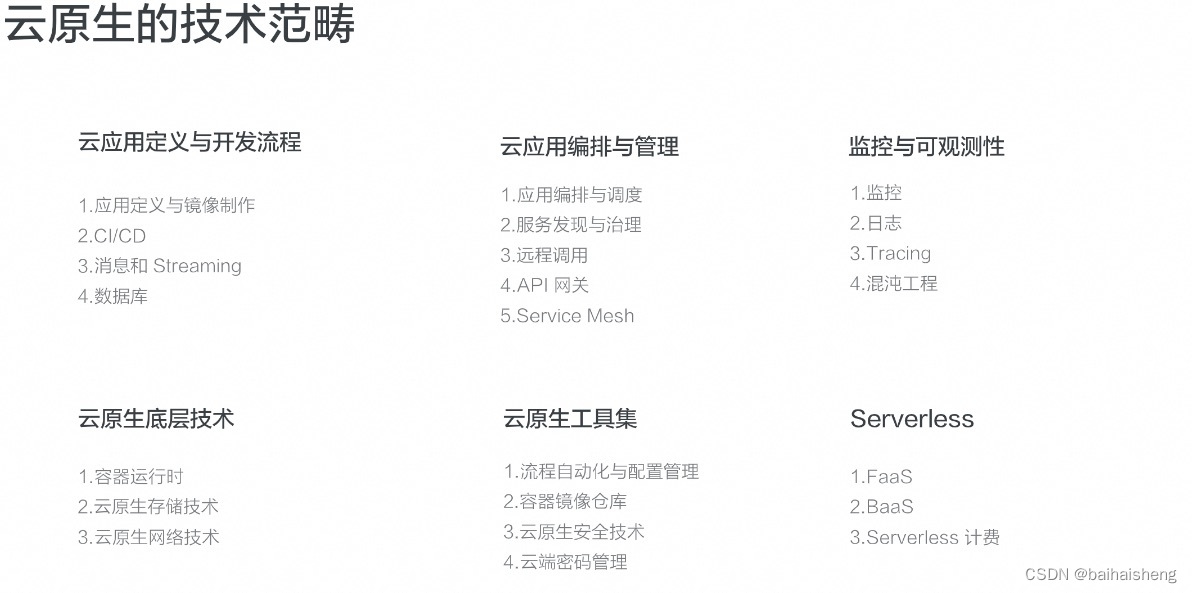
一、涉及到的知识点
1.分部类
2.分部类主要应用在以下两个方面
3.合理使用分部类分割类
4.事件处理程序
5.Math.Ceiling方法
6.Text.Contains()
7.pictureBox.Tag属性
二、实例
1.源码
2.生成效果
在开发一些大型项目或者特殊部署时,可能需要把一个类、结构或接口放在几个文件中来分别进行处理。等到编译时,再自动把它们整合起来,这时就用到了分部类。
分部类相当于将一个会计部门(类、结构或接口)分成两个部门,这两个部门可以单独对公司各部门的账目进行审核,而在繁忙时期,两个部门也可以相互调动人员(这里的人员相当于类中的方法、属性、变量等),或是合成一个整体进行工作
一、涉及到的知识点
1.分部类
分部类是C#4.5中的一个新特性,它的出现使得程序的结构更加合理,代码组织更加紧密。开发人员可以将类、结构或接口的定义拆分到两个或多个源文件中,每个源文件包含类定义的一部分,编译应用程序时,VS会把所有部分组合起来,这样的类被称为分部类。
定义分部类时需要使用partial关键字,分部类的每个部分都必须包含一个partial关键字,并且其声明必须与其他部分位于同一命名空间。使用分部类时,要成为同一类型的各个部分的所有分部类型定义都必须在同一程序集和同一模块(.exe或.dll文件)中进行定义,分部类定义不能跨越多个模块。使用分部类时,各个部分必须具有相同的可访问性,如public、private等。
2.分部类主要应用在以下两个方面
- 当项目比较庞大时,使用分部类可以拆分一个类至几个文件中,这样可以使不同的开发人员同时进行工作,提高了工作效率。
- 使用自动生成的文件源时,无须重新创建源文件即可将代码添加到类中。VS在创建Windows窗体和Web服务包装代码等时都使用此方法。
3.合理使用分部类分割类
C#编码规范中规定,一个类中的代码最好不要超过500行,但是,如果实际开发中,确实需要在一个类中包含超过500行以上的代码时,该怎么办呢?这时可以使用分部类将该类分成几部分,其中每个部分包含一部分实现代码。
例如,本例中,把一个public class Account类,用partial关键字,分割成两个public partial class Account类。
//分部类
//分割类的用法
namespace _124
{
public partial class Account
{
#region 执行两个数的加法运算
/// <summary>
/// 执行两个数的加法运算
/// </summary>
/// <param name="Former">加数</param>
/// <param name="After">被加数</param>
/// <returns>返回相加后的结果</returns>
public static double Addition(double Former, double After)
{
return Former + After;
}
#endregion
#region 执行两个数的减法运算
/// <summary>
/// 执行两个数的减法运算
/// </summary>
/// <param name="Former">减数</param>
/// <param name="After">被减数</param>
/// <returns>返回相减后的结果</returns>
public static double Subtration(double Former, double After)
{
return Former - After;
}
#endregion
#region 执行两个数的乘法运算
/// <summary>
/// 执行两个数的乘法运算
/// </summary>
/// <param name="Former">乘数</param>
/// <param name="After">被乘数</param>
/// <returns>返回相乘后的结果</returns>
public static double Multiplication(double Former, double After)
{
return Former * After;
}
#endregion
#region 执行两个数的除法运算
/// <summary>
/// 执行两个数的除法运算
/// </summary>
/// <param name="Former">除数</param>
/// <param name="After">被除数</param>
/// <returns>返回相除后的结果</returns>
public static double Division(double Former, double After)
{
if (After == 0)
{
MessageBox.Show("被除数不能为0。");
return 0;
}
return Former / After;
}
#endregion
}
public partial class Account
{
/// <summary>
/// 计算一个数的倒数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="num">数据</param>
/// <returns>返回倒数值</returns>
public static double Reciprocal(double num)
{
if (num == 0)
{
MessageBox.Show("分母不能为0。");
return 0;
}
return 1 / num;
}
/// <summary>
/// 计算一个数的开方
/// </summary>
/// <param name="num">数据</param>
/// <returns>返回开方后的值</returns>
public static double SquareRoot(double num)
{
if (num <= 0)
{
MessageBox.Show("负数不能开方。");
return 0;
}
return Math.Sqrt(num);
}
/// <summary>
/// 求一个数的相反数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="num">数据</param>
/// <returns>相反数</returns>
public static double Opposition(double num)
{
return -num;
}
/// <summary>
/// 一个数的百分比
/// </summary>
/// <param name="num">数据</param>
/// <returns>返回百分比</returns>
public static double Percentage(double num)
{
return num / 100;
}
}
}
4.事件处理程序
在C#编程中,事件处理程序是一个方法,它用于响应特定事件的发生。例如,当一个按钮被单击时,可以使用事件处理程序来响应这个事件并执行相应的代码。例如:
this.pictureBox22.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.pictureBox21_Click);在这个例子中,pictureBox22控件的Click事件被添加了一个事件处理程序,即pictureBox21_Click方法。当pictureBox22控件被单击时,pictureBox21_Click方法将被执行。这样就可以在pictureBox22控件被单击时,响应这个事件并执行相应的代码。
这样的设计,可以集中处理功能类似的事件,极大地减少代码量,并且代码更易读、更易维护。
5.Math.Ceiling方法
Math.Ceiling是 C# 中的一个方法,用于将一个浮点数向上取整到最接近的整数。如果浮点数已经是整数,则该方法不会对其做任何修改。
例如,Math.Ceiling(3.14)的结果是4,因为 3.14 最接近的整数是4。Math.Ceiling(5.0)的结果是5,因为 5.0 已经是一个整数。
需要注意的是,如果浮点数是负数,则Math.Ceiling方法会将其向上取整到最接近的负整数。例如,Math.Ceiling(-3.14)的结果是-3,因为-3.14最接近的负整数是-3。
6.Text.Contains()
Text.Contains()是 C# 中的一个方法,用于检查一个字符串是否包含另一个字符串。它返回一个布尔值,表示指定的子字符串是否存在于字符串中。
string str = "Hello World";
bool result = str.Contains("World"); //result 变量的值为 trueText.Contains()方法接受一个字符串参数,用于指定要查找的子字符串。它还接受一个可选的StringComparison枚举值参数,用于指定字符串比较的类型。如果不指定这个参数,则默认使用StringComparison.CurrentCulture,它使用当前文化来比较字符串。
if (!textBox1!.Text.Contains('.', StringComparison.CurrentCulture))
//等价语句
if (!textBox1!.Text.Contains('.'))7.pictureBox.Tag属性
设置pictureBox的Tag属性的字符串内容=该按键的功能,比如,设置按键CE的Tag属性为"CE"。其它按键属性的设置以此类推。
//
// pictureBox22
//
pictureBox22 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.ce,
Location = new Point(91, 72),
Name = "pictureBox22",
Size = new Size(66, 24),
TabIndex = 21,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "CE"
};
//pictureBox22.Click += PictureBox22_Click;
pictureBox22.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox22).BeginInit();设置pictureBox的Tag属性的用途是当触发按钮事件时,把该按钮的Tag属性作为Switch表达式的参数列表,从而响应按钮事件。例如:
private void PictureBox21_Click(object? sender, EventArgs e)
{
ButtonTag = (sender as PictureBox)!.Tag!.ToString()!;//获取当前按钮的标识
switch (ButtonTag)
{
//点击到数字键
case "0": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "1": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "2": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "3": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "4": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "5": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "6": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "7": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "8": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "9": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
//点击到运算符
case "+": OperatorType = ButtonTag; isnum = true; textBox1!.Text = "0"; break;
case "-": OperatorType = ButtonTag; isnum = true; textBox1!.Text = "0"; break;
case "*": OperatorType = ButtonTag; isnum = true; textBox1!.Text = "0"; break;
case "/": OperatorType = ButtonTag; isnum = true; textBox1!.Text = "0"; break;
case "%": AuxiliaryCalculation(ButtonTag); break;
case "1/X": AuxiliaryCalculation(ButtonTag); break;
case "+-": AuxiliaryCalculation(ButtonTag); break;
case "Sqrt": AuxiliaryCalculation(ButtonTag); break;
case ".": DecimalPoint(); break;
case "=": Calculation(ButtonTag); isnum = false; break; //计算结果
//C 则是 "Clear" 的简称,它用于清除计算器中的所有数据,包括存储器和寄存器的内容。
case "C":
{
Value_1 = "";
Value_2 = "";
OperatorType = "";
textBox1!.Text = "0";
break;
}
//CE 是 "Clear Entry" 的缩写,它的主要作用是清除当前正在输入的数字或者运算符。
case "CE": textBox1!.Text = "0"; Value_1 = ""; break;
default: Backspace(); break; /*"Back":*/
}
}二、实例
本实例将使用分部类制作一个计算器,其中主要是用分部类来分别记录计算器的计算方法,如将实现加、减、乘和除的方法放在一个分部类中,而将实现正负、开方、百分比和倒数的方法放在另一个分部类中。
1.源码
// 使用分部类实现多种计算方法
namespace _124
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private Panel? panel1;
private PictureBox? pictureBox5;
private PictureBox? pictureBox4;
private PictureBox? pictureBox3;
private PictureBox? pictureBox2;
private PictureBox? pictureBox1;
private PictureBox? pictureBox10;
private PictureBox? pictureBox9;
private PictureBox? pictureBox8;
private PictureBox? pictureBox7;
private PictureBox? pictureBox6;
private PictureBox? pictureBox20;
private PictureBox? pictureBox19;
private PictureBox? pictureBox18;
private PictureBox? pictureBox17;
private PictureBox? pictureBox16;
private PictureBox? pictureBox15;
private PictureBox? pictureBox14;
private PictureBox? pictureBox13;
private PictureBox? pictureBox12;
private PictureBox? pictureBox11;
private PictureBox? pictureBox23;
private PictureBox? pictureBox22;
private PictureBox? pictureBox21;
private PictureBox? pictureBox24;
private TextBox? textBox1;
public string Value_1 = ""; //操作数1
public string Value_2 = ""; //操作数2
public string OperatorType = ""; //运算符种类
string ButtonTag = ""; //记录当前输入的键值
bool isnum = false; //判断输入的是计算的那个值,他就是一个开关,按下运算符号时翻转,按下等号后,要复原
bool IsNotDecimalPoint = false; //是否包含小数点
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
Load += Form1_Load;
}
private void Form1_Load(object? sender, EventArgs e)
{
//
// pictureBox24
//
pictureBox24 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.Close,
Location = new Point(226, 0),
Name = "pictureBox24",
Size = new Size(11, 11),
TabIndex = 23,
TabStop = false
};
pictureBox24.Click += PictureBox24_Click;
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox24).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox23
//
pictureBox23 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.c,
Location = new Point(161, 72),
Name = "pictureBox23",
Size = new Size(66, 24),
TabIndex = 22,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "C"
};
pictureBox23.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox23).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox22
//
pictureBox22 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.ce,
Location = new Point(91, 72),
Name = "pictureBox22",
Size = new Size(66, 24),
TabIndex = 21,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "CE"
};
//pictureBox22.Click += PictureBox22_Click;
pictureBox22.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox22).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox21
//
pictureBox21 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.back,
Location = new Point(12, 72),
Name = "pictureBox21",
Size = new Size(75, 24),
TabIndex = 20,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "Back"
};
pictureBox21.Click += PictureBox21_Click;
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox21).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox20
//
pictureBox20 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.Amound,
Location = new Point(188, 192),
Name = "pictureBox20",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 19,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "="
};
pictureBox20.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox20).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox19
//
pictureBox19 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.Add,
Location = new Point(144, 192),
Name = "pictureBox19",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 18,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "+"
};
pictureBox19.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox19).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox18
//
pictureBox18 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.Dot,
Location = new Point(100, 192),
Name = "pictureBox18",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 17,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "."
};
pictureBox18.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox18).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox17
//
pictureBox17 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.Bear,
Location = new Point(56, 192),
Name = "pictureBox17",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 16,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "+-"
};
pictureBox17.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox17).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox16
//
pictureBox16 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources._0,
Location = new Point(12, 192),
Name = "pictureBox16",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 15,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "0"
};
pictureBox16.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox16).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox15
//
pictureBox15 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.Deno,
Location = new Point(188, 162),
Name = "pictureBox15",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 14,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "1/X"
};
pictureBox15.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox15).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox14
//
pictureBox14 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.Decr,
Location = new Point(144, 162),
Name = "pictureBox14",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 13,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "-"
};
pictureBox14.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox14).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox13
//
pictureBox13 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources._3,
Location = new Point(100, 162),
Name = "pictureBox13",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 12,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "3"
};
pictureBox13.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox13).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox12
//
pictureBox12 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources._2,
Location = new Point(56, 162),
Name = "pictureBox12",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 11,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "2"
};
pictureBox12.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox12).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox11
//
pictureBox11 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources._1,
Location = new Point(12, 162),
Name = "pictureBox11",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 10,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "1"
};
pictureBox11.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox11).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox10
//
pictureBox10 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.Hund,
Location = new Point(188, 132),
Name = "pictureBox10",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 9,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "%"
};
pictureBox10.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox10).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox9
//
pictureBox9 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.Ride,
Location = new Point(144, 132),
Name = "pictureBox9",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 8,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "*"
};
pictureBox9.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox9).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox8
//
pictureBox8 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources._6,
Location = new Point(100, 132),
Name = "pictureBox8",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 7,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "6"
};
pictureBox8.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox8).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox7
//
pictureBox7 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources._5,
Location = new Point(56, 132),
Name = "pictureBox7",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 6,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "5"
};
pictureBox7.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox7).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox6
//
pictureBox6 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources._4,
Location = new Point(12, 132),
Name = "pictureBox6",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 5,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "4"
};
pictureBox6.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox6).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox5
//
pictureBox5 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.sqrt,
Location = new Point(188, 102),
Name = "pictureBox5",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 4,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "Sqrt"
};
pictureBox5.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox5).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox4
//
pictureBox4 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.Remove,
Location = new Point(144, 102),
Name = "pictureBox4",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 3,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "/"
};
pictureBox4.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox4).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox3
//
pictureBox3 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources._9,
Location = new Point(100, 102),
Name = "pictureBox3",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 2,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "9"
};
pictureBox3.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox3).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox2
//
pictureBox2 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources._8,
Location = new Point(56, 102),
Name = "pictureBox2",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 1,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "8"
};
pictureBox2.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox2).BeginInit();
//
// pictureBox1
//
pictureBox1 = new PictureBox
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources._7,
Location = new Point(12, 102),
Name = "pictureBox1",
Size = new Size(40, 24),
TabIndex = 0,
TabStop = false,
Tag = "7"
};
pictureBox1.Click += new EventHandler(PictureBox21_Click);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox1).BeginInit();
//
// textBox1
//
textBox1 = new TextBox
{
Location = new Point(12, 33),
Name = "textBox1",
Size = new Size(215, 23),
TabIndex = 24
};
//
// panel1
//
panel1 = new Panel
{
BackgroundImage = Properties.Resources.bg,
Dock = DockStyle.Fill,
Location = new Point(0, 0),
Name = "panel1",
Size = new Size(240, 230),
TabIndex = 0
};
panel1.Controls.Add(textBox1);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox24);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox23);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox22);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox21);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox20);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox19);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox18);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox17);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox16);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox15);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox14);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox13);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox12);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox11);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox10);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox9);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox8);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox7);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox6);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox5);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox4);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox3);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox2);
panel1.Controls.Add(pictureBox1);
panel1.SuspendLayout();
//
// Form1
//
AutoScaleDimensions = new SizeF(7F, 17F);
AutoScaleMode = AutoScaleMode.Font;
ClientSize = new Size(240, 230);
Controls.Add(panel1);
FormBorderStyle = FormBorderStyle.None;//隐藏窗体的边框
Name = "Form1";
Text = "Form1";
panel1.ResumeLayout(false);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox24).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox23).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox22).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox21).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox20).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox19).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox18).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox17).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox16).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox15).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox14).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox13).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox12).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox11).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox10).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox9).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox8).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox7).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox6).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox5).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox4).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox3).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox2).EndInit();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)pictureBox1).EndInit();
}
/// <summary>
/// Backspace
/// 根据键值触发相应的功能
/// </summary>
private void PictureBox21_Click(object? sender, EventArgs e)
{
ButtonTag = (sender as PictureBox)!.Tag!.ToString()!;//获取当前按钮的标识
switch (ButtonTag)
{
//点击到数字键
case "0": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "1": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "2": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "3": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "4": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "5": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "6": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "7": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "8": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
case "9": ReadNumber(ButtonTag); break;
//点击到运算符
case "+": OperatorType = ButtonTag; isnum = true; textBox1!.Text = "0"; break;
case "-": OperatorType = ButtonTag; isnum = true; textBox1!.Text = "0"; break;
case "*": OperatorType = ButtonTag; isnum = true; textBox1!.Text = "0"; break;
case "/": OperatorType = ButtonTag; isnum = true; textBox1!.Text = "0"; break;
case "%": AuxiliaryCalculation(ButtonTag); break;
case "1/X": AuxiliaryCalculation(ButtonTag); break;
case "+-": AuxiliaryCalculation(ButtonTag); break;
case "Sqrt": AuxiliaryCalculation(ButtonTag); break;
case ".": DecimalPoint(); break;
case "=": Calculation(ButtonTag); isnum = false; break; //计算结果
//C 则是 "Clear" 的简称,它用于清除计算器中的所有数据,包括存储器和寄存器的内容。
case "C":
{
Value_1 = "";
Value_2 = "";
OperatorType = "";
textBox1!.Text = "0";
break;
}
//CE 是 "Clear Entry" 的缩写,它的主要作用是清除当前正在输入的数字或者运算符。
case "CE": textBox1!.Text = "0"; Value_1 = ""; break;
default: Backspace(); break; /*"Back":*/
}
}
/// <summary>
/// X,关闭窗体
/// </summary>
private void PictureBox24_Click(object? sender, EventArgs e)
{
Close();
}
/// <summary>
/// 记录当前输入的数字键的值
/// </summary>
/// <param name="num">键值</param>
public void ReadNumber(string num)
{
if (IsNotDecimalPoint)
{
if (textBox1!.Text == "0")
textBox1.Text = "0.";
else
textBox1.Text += ".";
IsNotDecimalPoint = false;
}
if (textBox1!.Text == "0")
textBox1.Text = "";
if (isnum) //如果是计算之前的值
{
textBox1.Text += num; //累加输入值
Value_2 = textBox1.Text; //显示在文本框中
}
else //计算之后的值
{
textBox1.Text += num; //累加输入值
Value_1 = textBox1.Text; //等待连续计算
}
}
/// <summary>
/// +-*/%计算
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n"></param>
public void Calculation(string n)
{
ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNull(n);
double tem_v = 0; //记录计算后的结果
if (Value_1.Length <= 0 || Value_2.Length <= 0)//判断是否有计算的两个值
return;
if (OperatorType.Length > 0) //如果可以计算
{
switch (OperatorType)
{
case "+": tem_v = Account.Addition(Convert.ToDouble(Value_1), Convert.ToDouble(Value_2)); break;
case "-": tem_v = Account.Subtration(Convert.ToDouble(Value_1), Convert.ToDouble(Value_2)); break;
case "*": tem_v = Account.Multiplication(Convert.ToDouble(Value_1), Convert.ToDouble(Value_2)); break;
case "/": tem_v = Account.Division(Convert.ToDouble(Value_1), Convert.ToDouble(Value_2)); break;
}
}
if (tem_v == Math.Ceiling(tem_v)) //如果计算结果为整数对结果进行取整
{
textBox1!.Text = Convert.ToInt64(tem_v).ToString();
}
else
{
textBox1!.Text = tem_v.ToString(); //以双精度进行显示
}
Value_1 = textBox1.Text; //等待连续计算
Value_2 = "";
}
/// <summary>
/// 辅助计算
/// </summary>
/// <param name="str"></param>
public void AuxiliaryCalculation(string str)
{
double tem_v = 0; //记录计算结果
switch (str)
{
case "%": tem_v = Account.Percentage(Convert.ToDouble(textBox1!.Text)); break;
case "1/X": tem_v = Account.Reciprocal(Convert.ToDouble(textBox1!.Text)); break;
case "+-": tem_v = Account.Opposition(Convert.ToDouble(textBox1!.Text)); break;
case "Sqrt": tem_v = Account.SquareRoot(Convert.ToDouble(textBox1!.Text)); break;
}
if (tem_v == Math.Ceiling(tem_v)) //如果计算结果为整数对结果进行取整
{
textBox1!.Text = Convert.ToInt64(tem_v).ToString();
}
else
{
textBox1!.Text = tem_v.ToString(); //以双精度进行显示
}
Value_1 = textBox1.Text; //等待连续计算
Value_2 = "";
}
/// <summary>
/// 删除输入的值
/// </summary>
public void Backspace()
{
var BackspaceStr = textBox1!.Text; //记录当前文本框中的值
if (BackspaceStr != "0") //如果值不为零
{
string ToAbs = Math.Abs(Convert.ToDouble(BackspaceStr)).ToString();//获取该值的绝对值
if ((BackspaceStr.Length == 1) || (ToAbs.Length == 1))//如果当前文本框中只有一个数值
{
textBox1.Text = "0"; //将文本框清零
}
else { textBox1.Text = BackspaceStr[..^1]; }//删除指定的值
Value_1 = textBox1.Text; //显示删除后的结果
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 非小数点则为真
/// </summary>
public void DecimalPoint()
{
if (!textBox1!.Text.Contains('.'))
IsNotDecimalPoint = true;
else
IsNotDecimalPoint = false;
}
}
}
2.生成效果