1191:流感传染
【题目描述】
有一批易感人群住在网格状的宿舍区内,宿舍区为n*n的矩阵,每个格点为一个房间,房间里可能住人,也可能空着。在第一天,有些房间里的人得了流感,以后每天,得流感的人会使其邻居传染上流感,(已经得病的不变),空房间不会传染。请输出第m天得流感的人数。
【输入】
第一行一个数字n,n不超过100,表示有n*n的宿舍房间。
接下来的n行,每行n个字符,’.’表示第一天该房间住着健康的人,’#’表示该房间空着,’@’表示第一天该房间住着得流感的人。
接下来的一行是一个整数m,m不超过100。
【输出】
输出第m天,得流感的人数。
【输入样例】
5 ....# .#.@. .#@.. #.... ..... 4【输出样例】
16
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e2 + 10;
char a[N][N];//房间数组
int dx[] = { 0,0,1,-1 };
int dy[] = { 1,-1,0,0 };
bool vis[N][N];//标记当天生病的
int main()
{
int n; cin >> n;
//存储房间
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
cin >> a[i][j];
}
}
//记录生病的人数
int cnt=0;
int m;
cin >> m;
//开始感染
for (int day = 2; day <= m; day++)
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof vis);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if (a[i][j] == '@'&&!vis[i][j])
{
//遍历所有可能感染的方向
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int bx = i + dx[k], by = j + dy[k];
//超出房间的边界
if (i<1 || i>n || j<1 || j>n)continue;
if (a[bx][by] == '.')
{
a[bx][by] = '@';
//标记当天被感染的
vis[bx][by] = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if (a[i][j] == '@')
cnt++;
}
}
cout << cnt;
return 0;
}
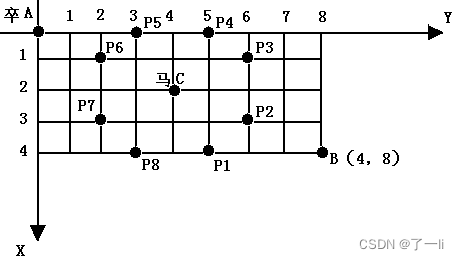
1314:【例3.6】过河卒(Noip2002)
|
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 1e2 + 10;
int a[N][N];
//马可走的八个方向
int dx[] = {1,1,-1,-1,2,2,-2,-2};
int dy[] = {2,-2,2,-2,1,-1,1,-1};
bool vis[N][N];//马运动的轨迹
/*
//边界
a[i][j]=1
//递推关系式
a[i][j]=a[i-1][j]+a[i][j-1]
*/
signed main()
{
int tx, ty;//B点坐标
int cx, cy;//C点坐标
cin >> tx >> ty >> cx >> cy;
vis[cx][cy] = 1;//标记马
//马运动的轨迹
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
int cxx = cx + dx[i], cyy = cy + dy[i];
//如果新生成的坐标越界,则跳过,继续生成下一个坐标
if (cxx<0 || cxx>tx || cyy<0 || cyy>ty)continue;//0也是边界
vis[cxx][cyy] = 1;
}
//边界
a[0][0] = 1;
//处理第一行
for (int j = 1; j <= ty; j++)
{
if (!vis[0][j])
a[0][j] = a[0][j - 1];
else
a[0][j] = 0;
}
//处理第一列
for (int i = 1; i <= tx; i++)
{
if (!vis[i][0])
a[i][0] = a[i - 1][0];
else
a[i][0] = 0;
}
//递推
for (int i = 1; i <= tx; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= ty; j++)
{
if (!vis[i][j])
a[i][j] = a[i - 1][j] + a[i][j - 1];
else
a[i][j] = 0;
}
}
cout << a[tx][ty] << endl;
return 0;
}1194:移动路线
【题目描述】
X桌子上有一个m行n列的方格矩阵,将每个方格用坐标表示,行坐标从下到上依次递增,列坐标从左至右依次递增,左下角方格的坐标为(1,1),则右上角方格的坐标为(m,n)。
小明是个调皮的孩子,一天他捉来一只蚂蚁,不小心把蚂蚁的右脚弄伤了,于是蚂蚁只能向上或向右移动。小明把这只蚂蚁放在左下角的方格中,蚂蚁从
左下角的方格中移动到右上角的方格中,每步移动一个方格。蚂蚁始终在方格矩阵内移动,请计算出不同的移动路线的数目。
对于1行1列的方格矩阵,蚂蚁原地移动,移动路线数为1;对于1行2列(或2行1列)的方格矩阵,蚂蚁只需一次向右(或向上)移动,移动路线数也为1……对于一个2行3列的方格矩阵,如下图所示:
(2,1) (2,2) (2,3) (1,1) (1,2) (1,3) 蚂蚁共有3种移动路线:
路线1:(1,1) → (1,2) → (1,3) → (2,3)
路线2:(1,1) → (1,2) → (2,2) → (2,3)
路线3:(1,1) → (2,1) → (2,2) → (2,3)
【输入】
输入只有一行,包括两个整数m和n(0 < m+n ≤ 20),代表方格矩阵的行数和列数,m、n之间用空格隔开。
【输出】
输出只有一行,为不同的移动路线的数目。
【输入样例】
2 3【输出样例】
3
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 1e2 + 10;
int a[N][N];
signed main()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
//处理边界
a[1][1] = 1;
//处理第一行
for (int j = 2; j <= m; j++)
a[1][j] = a[1][j-1];
//处理其余路线
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
a[i][1] = a[i - 1][1];
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 2; j <= m; j++)
a[i][j] = a[i][j - 1] + a[i - 1][j];
cout << a[n][m];
return 0;
} 1196:踩方格
|
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 1e2 + 10;
int a[N][N];
int l[N], r[N], u[N];//向左 右 上 的方案总数
signed main()
{
int n; cin >> n;
l[1] = r[1] = u[1] = 1;
/*
若i-1步向左,那么第i部只能向上或者向左
若i-1步向右,那么第i部只能向上或者向右
若i-1步向上,那么第i部能向上或者向左或者向右
*/
int ans = 0;//记录方案数
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
l[i] = u[i - 1] + l[i - 1];
r[i] = u[i - 1] + r[i - 1];
u[i] = u[i - 1] + l[i - 1] + r[i - 1];
ans = l[i] + r[i] + u[i];
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}1313:【例3.5】位数问题
【题目描述】
在所有的N�位数中,有多少个数中有偶数个数字33?由于结果可能很大,你只需要输出这个答案对1234512345取余的值。
【输入】
读入一个数N(N≤1000)�(�≤1000)。
【输出】
输出有多少个数中有偶数个数字33。
【输入样例】
2【输出样例】
73
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
/*
1位数 2位数 3位数 4位数
even[1] odd[1] even[2] odd[2] even[3] odd[3] even[4] odd[4]
0 3 9*even[1]+odd[1] 9*odd[1]+even[1] 9*even[2]+odd[2] 9*odd[2]+even[2] 8*even[3]+odd[3] 8*odd[3]+even[3]
1
2
4
5
6
7
8
9
*/
const int N = 1e3 + 10, mod = 12345;
int even[N], odd[N];
signed main() {
even[1] = 9; odd[1] = 1;
int n; cin >> n;
int t = 9;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if (i == n) t = 8;//当走到最高位时,最高位不能为0,方案少一种变为8
odd[i] = (t * odd[i - 1] % mod + even[i - 1] % mod) % mod;
even[i] = (t * even[i - 1] % mod + odd[i - 1] % mod) % mod;
}
cout << even[n] << endl;
return 0;
}1201:菲波那契数列
【题目描述】
菲波那契数列是指这样的数列: 数列的第一个和第二个数都为1,接下来每个数都等于前面2个数之和。
给出一个正整数a,要求菲波那契数列中第a个数是多少。
【输入】
第1行是测试数据的组数n,后面跟着n行输入。每组测试数据占1行,包括一个正整数a(1<=a<=20)。
【输出】
输出有n行,每行输出对应一个输入。输出应是一个正整数,为菲波那契数列中第a个数的大小。
【输入样例】
4 5 2 19 1【输出样例】
5 1 4181 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e2+10;
int fbnq(int x)
{
if (x <= 2)return 1;
return fbnq(x - 1) + fbnq(x - 2);
}
int main()
{
int n; cin >> n;
int x;
while (n--)
{
cin >> x;
cout << fbnq(x) << endl;;
}
return 0;
}1202:Pell数列
【题目描述】
Pell数列a1,a2,a3,...�1,�2,�3,...的定义是这样的,a1=1,a2=2,...,an=2an−1+an−2(n>2)�1=1,�2=2,...,��=2��−1+��−2(�>2)。
给出一个正整数 k�,要求Pell数列的第 k� 项模上 3276732767 是多少。
【输入】
第1行是测试数据的组数 n�,后面跟着 n� 行输入。每组测试数据占 11 行,包括一个正整数k(1≤k<1000000)�(1≤�<1000000)。
【输出】
n� 行,每行输出对应一个输入。输出应是一个非负整数。
【输入样例】
2 1 8【输出样例】
1 408
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+10;
#define int long long
int m = 32767;
int a[N];
int pell(int x)
{
//剪枝(求过的项不需要重复求)
if (a[x])return a[x];
if (x <= 2)return a[x]=x;
return a[x]=(2 * pell(x - 1) % m + pell(x - 2) % m) % m;
}
signed main()
{
int n; cin >> n;
int x;
while (n--)
{
cin >> x;
cout << pell(x) << endl;;
}
return 0;
}1204:爬楼梯
【题目描述】
树老师爬楼梯,他可以每次走1级或者2级,输入楼梯的级数,求不同的走法数。
例如:楼梯一共有3级,他可以每次都走一级,或者第一次走一级,第二次走两级,也可以第一次走两级,第二次走一级,一共3种方法。
【输入】
输入包含若干行,每行包含一个正整数N,代表楼梯级数,1≤N≤30。
【输出】
不同的走法数,每一行输入对应一行输出。
【输入样例】
5 8 10【输出样例】
8 34 89
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e2+10;
#define int long long
int a[N];
int stairs(int x)
{
/*
s(8) a[8]=s(7)+s(6)=34
s(7) a[7]=s(6)+s(5)=21
s(6) a[6]=s(5)+s(4)=13
s(5) a[5]=s(4)+s(3)=8
s(4) a[4]=s(3)+s(2)=5
s(3) a[3]=s(2)+s(1)=3
*/
//剪枝
if (a[x])return a[x];
if (x <= 2)return a[x] = x;
return a[x]=stairs(x - 1) + stairs(x - 2);
}
signed main()
{
int x;
while (cin >> x)
{
cout << stairs(x)<< endl;
}
return 0;
}