提示:如果没有基础的可以看我的博客 ===> MyBatis概述与MyBatis入门程序
MyBatis完成单表的CRUD
- 一、准备工作
- 二、Insert(Create)
- 1.使用 map 的方式插入数据
- (1)编写 SQL 语句
- (2)编写测试代码
- (3)运行结果
- 2.使用 pojo 来传参数
- (1)创建 pojo 实体类
- (2)编写 SQL 语句
- (3)编写测试代码
- (4)运行结果
- 三、delete
- (1)编写 SQL 语句
- (2)编写测试代码
- (3)运行结果
- 四、Update
- (1)编写 SQL 语句
- (2)编写测试代码
- (3)运行结果
- 五、Select(Retrieve)
- 1.查询一个
- (1)编写 SQL 语句
- (2)编写测试代码
- (3)运行结果
- 2.查询所有
- (1)编写 SQL 语句
- (2)编写测试代码
- (3)运行结果
- 六、关于SQL Mapper的namespace
一、准备工作
- 创建module(Maven的普通Java模块):mybatis-crud
- pom.xml
- 打包⽅式 jar
- 依赖:
- mybatis 依赖
- mysql 驱动依赖
- junit依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.gdb</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-crud</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.33</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.14</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.13.2</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> </properties> </project> - mybatis-config.xml 放在类的根路径下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <settings> <setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/> <!-- 日志设置为 MyBatis 提供的标准日志 --> </settings> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <!-- 事务管理设置为 JDBC 默认开启事务,需要手动提交 --> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/自己对应的数据库名"/> <property name="username" value="用户名(一般是root)"/> <property name="password" value="登录密码!"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <mappers> <!--sql映射⽂件创建好之后,需要将该⽂件路径配置到这⾥--> <mapper resource="articleMapper.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration> - articleMapper.xml 放在类的根路径下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="article"> </mapper> - 提供com.gdb.utils.SqlSessionUtil⼯具类
public class MybatisUtils { private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; /** * 类加载时初始化sqlSessionFactory对象 */ static { try { SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml")); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 每调⽤⼀次openSession()可获取⼀个新的会话,该会话⽀持⾃动提交。 */ public static SqlSession openSession() { return sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); } }
二、Insert(Create)
1.使用 map 的方式插入数据
(1)编写 SQL 语句
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="article">
<insert id="insertArticleForMap">
insert into article
values (null, #{user_id}, #{title}, #{summary}, #{read_count}, #{create_time}, #{update_time});
</insert>
</mapper>
- 在 Java 程序中,将数据放到 Map 集合中。
- 在 sql 语句中使用 #{map集合的key} 来完成传值,#{} 等同于 JDBC 中的 ?,#{} 就是占位符。底层实际上调用的是 map 的 get 方法来获取 key 对应的 value。
- 小细节:
- key 的名字一般和数据库表的字段名保持一致,增强可读性。
- 由于底层调用的是 get 方法,所以当 key 值不存在的时候,不会报错,而是返回 null。
(2)编写测试代码
@Test
public void insertMap(){
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//前端传过来的数据
map.put("user_id", 12346);
map.put("title", "springboot 配置文件");
map.put("summary", "外部化配置文件");
map.put("read_count", 12346);
map.put("create_time", "2026-05-16 12:15:27");
map.put("update_time", "2026-05-16 12:15:27");
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();
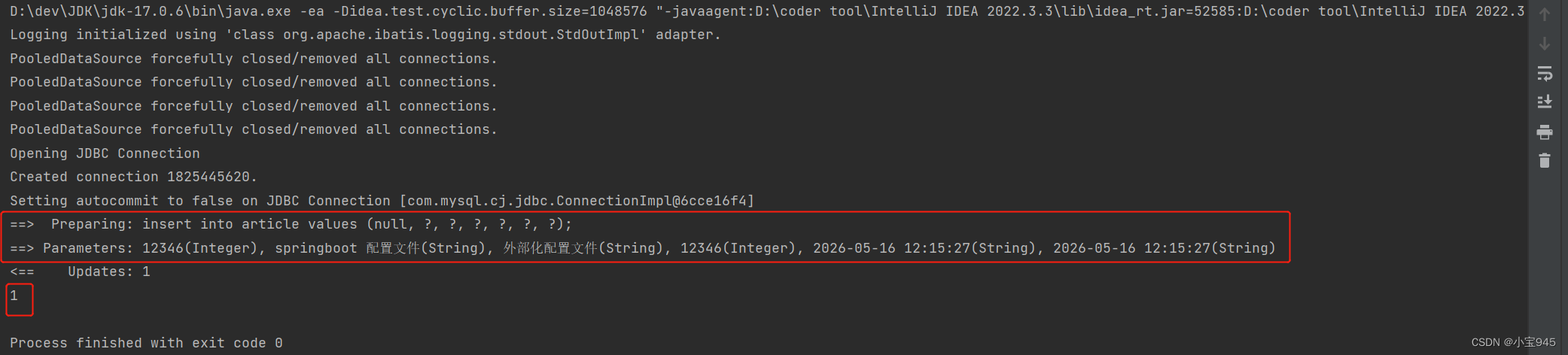
int count = sqlSession.insert("insertArticleForMap", map);
System.out.println(count);
//注意,这里我没有手动提交,是因为我在工具类中获取 sqlSession 的时候,开启了自动提交。
sqlsession.close();
}
(3)运行结果
2.使用 pojo 来传参数
(1)创建 pojo 实体类
public class ArticleDetail {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String summary;
private String title;
private Integer readCount;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
//全参构造、无参构造、toString、set和get方法
}
(2)编写 SQL 语句
<insert id="insertArticleForPojo">
insert into article
values (null, #{userId}, #{title}, #{summary}, #{readCount}, #{createTime}, #{updateTime});
</insert>
- 如果采⽤ POJO 传参,#{} ⾥写的是 get ⽅法的⽅法名去掉 get 之后将剩下的单词⾸字⺟变⼩写(例
如:getAge 对应的是 #{age},getUserName 对应的是 #{userName}),如果这样的 get ⽅法不存在会报
错。
(3)编写测试代码
@org.junit.Test
public void insertPojo(){
//前端传过来的数据
Article article = new Article(null, 12346, "springboot 配置文件", "外部化配置文件", 12346, LocalDateTime.now(), LocalDateTime.now());
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();
int count = sqlSession.insert("insertArticleForPojo", article);
System.out.println(count);
//注意,这里我没有手动提交,是因为我在工具类中获取 sqlSession 的时候,开启了自动提交。
sqlSession.close();
}
(4)运行结果

三、delete
(1)编写 SQL 语句
<delete id="deleteArticleForId">
delete from article where id = #{id};
</delete>
- 注意:当占位符只有⼀个的时候,${} ⾥⾯的内容可以随便写。但是一般要见名知意。
(2)编写测试代码
@Test
public void deleteForId(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();
int count = sqlSession.delete("deleteArticleForId", 6);
System.out.println("删除的记录条数为 ===> " + count);
sqlSession.close();
}
(3)运行结果

四、Update
(1)编写 SQL 语句
<update id="updateArticleForId">
update article
set user_id = #{userId},
title = #{title},
summary = #{summary}
where id = #{id}
</update>
(2)编写测试代码
@Test
public void updateArticleForId() {
Article article = new Article(8, 13, "aaaa", "bbbb", null, null, null);
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();
int count = sqlSession.update("updateArticleForId", article);
System.out.println("修改的记录条数 ===> " + count);
sqlSession.close();
}
(3)运行结果

五、Select(Retrieve)
- select 语句和其他语句不同的是:查询会有一个结果集。注意 mybatis 是怎么处理结果集的。
- 在 标签中添加 resultType 属性,用来指定查询结果转换成的类型。
- 一般使用全限定类名。
1.查询一个
(1)编写 SQL 语句
<select id="selectArticleForId" resultType="com.gdb.pojo.Article">
select id,
user_id as userId,
title,
summary,
read_count as readCount,
create_time as createTime,
update_time as updateTime
from article
where id = #{id};
</select>
- 注意底层调用的是 set 方法,如果返回的结果名和属性名不同的话,结果为 null。
- 可以通过采用 as 关键字起别名。
(2)编写测试代码
@Test
public void selectArticleForID() {
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();
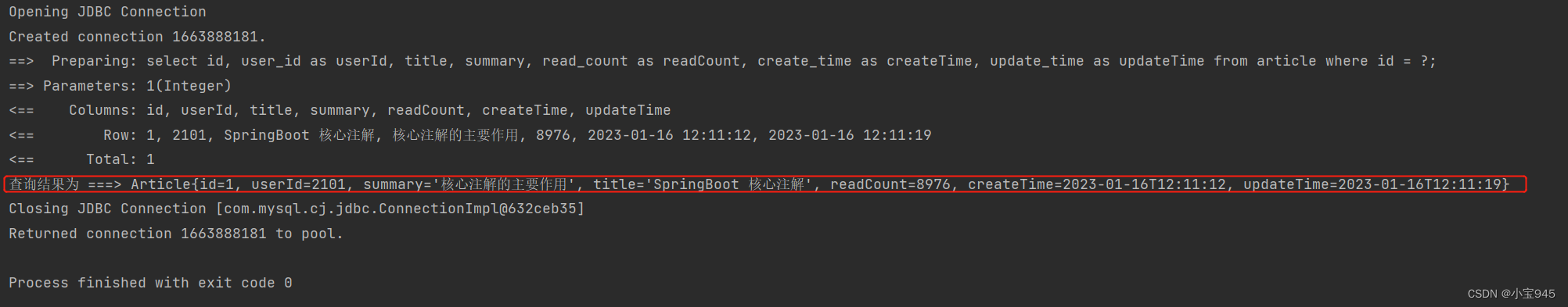
Article article = sqlSession.selectOne("selectArticleForId", 1);
System.out.println("查询结果为 ===> " + article);
sqlSession.close();
}
(3)运行结果
2.查询所有
(1)编写 SQL 语句
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.gdb.pojo.Article"> -- 注意这里指定的是查询结果 List 中存储的元素
select id,
user_id as userId,
title,
summary,
read_count as readCount,
create_time as createTime,
update_time as updateTime
from article
</select>
(2)编写测试代码
@Test
public void selectAll() {
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();
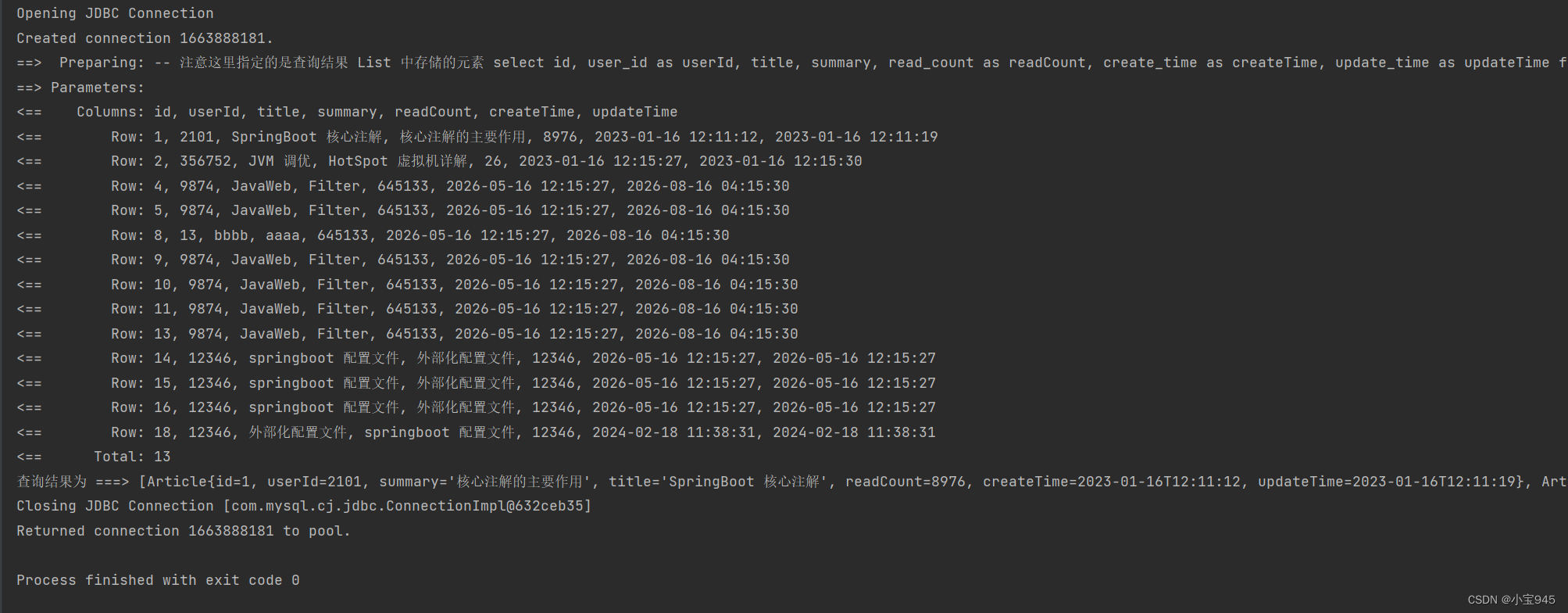
List<Article> articles = sqlSession.selectList("selectAll");
System.out.println("查询结果为 ===> " + articles);
sqlSession.close();
}
(3)运行结果
六、关于SQL Mapper的namespace
- 在 SQL Mapper 配置⽂件中 标签的 namespace 属性可以翻译为命名空间,这个命名空间主要是
为了防⽌ sqlId 冲突的。 - 所以在 Java 程序中实际的写法是 namespace + id。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="article">
<delete id="deleteArticleForId">
delete from article where id = #{id};
</delete>
</mapper>
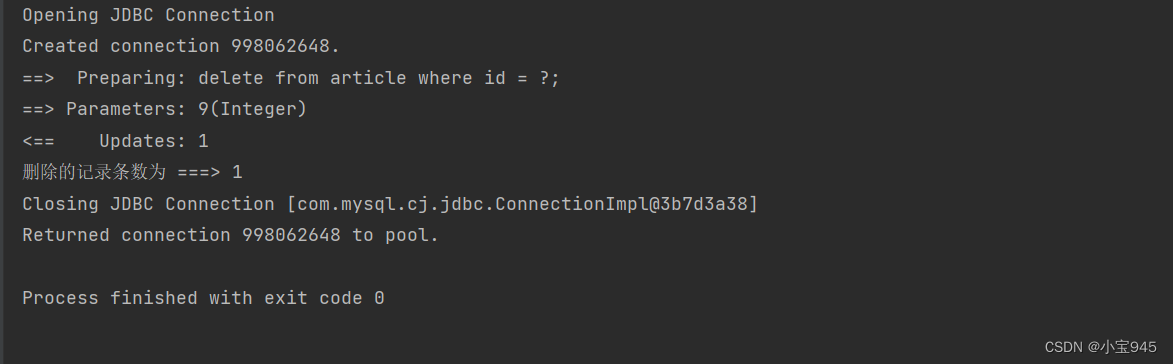
@Test
public void deleteForId() {
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();
int count = sqlSession.delete("article.deleteArticleForId", 9);
System.out.println("删除的记录条数为 ===> " + count);
sqlSession.close();
}