- 队列的特点:先进先出(FIFO)
- 队列的时间复杂度:入队和出队
O(1),查找O(n) - 优先队列:
priorityQueue,按优先级出队,实现Heap(Binary,Fibonacci...) - js里没有队列,但是可以用数组模拟

225. 用队列实现栈 (easy)
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
int top() 返回栈顶元素。
boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。注意:
你只能使用队列的基本操作 —— 也就是 push to back、peek/pop from front、size 和 is empty 这些操作。
你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list (列表)或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。示例:
输入:
[“MyStack”, “push”, “push”, “top”, “pop”, “empty”]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 2, 2, false]解释:
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.top(); // 返回 2
myStack.pop(); // 返回 2
myStack.empty(); // 返回 False提示:
1 <= x <= 9
最多调用100 次 push、pop、top 和 empty
每次调用 pop 和 top 都保证栈不为空进阶:你能否仅用一个队列来实现栈。
方法1.使用两个 Queue 实现
- 思路:还是考察栈和队列的熟悉程度,没有什么具体的工程实际意义,可以用两个队列来实现栈的功能,但是一个队列的数据导入另一个队列顺序还是没有改变,所以其中一个队列只是用来做备份的,在代码里queue2就是备份队列,入栈的时候,队列1入队,出栈的时候,如果队列1为空,则交换队列1和队列2,为的是将备份队列的元素全部加入队列1,然后将队列1中除了最后一个元素外全部出队,并且加入备份队列,
- 复杂度分析:push的时间复杂度为
O(1),pop的时间复杂度为O(n)。空间复杂度O(n),其中n是栈内元素的个数,用两个队列来存储
动画过大,点击查看
Js:
var MyStack = function() {
this.queue1 = [];
this.queue2 = [];//备份的队列
};
MyStack.prototype.push = function(x) {
this.queue1.push(x);
};
MyStack.prototype.pop = function() {
// 减少两个队列交换的次数, 只有当queue1为空时,交换两个队列
if(!this.queue1.length) {
[this.queue1, this.queue2] = [this.queue2, this.queue1];
}
while(this.queue1.length > 1) {//当队列1的元素数量大于1的时候不断将元素push进备份队列
this.queue2.push(this.queue1.shift());
}
return this.queue1.shift();//最后将队列1最后一个元素出队
};
MyStack.prototype.top = function() {
const x = this.pop();//查看栈顶,队列出队,然后在push进队列1
this.queue1.push(x);
return x;
};
MyStack.prototype.empty = function() {
return !this.queue1.length && !this.queue2.length;
};
方法2.使用一个 队列 实现
动画过大,点击查看
- 思路:使用一个 队列 实现,入栈的时候直接push进队列就行,出栈的时候将除了最后一个元素外的元素全部加入到队尾。
- 复杂度分析:push的时间复杂度为
O(1),pop的时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
js:
var MyStack = function() {
this.queue = [];
};
MyStack.prototype.push = function(x) {
this.queue.push(x);
};
MyStack.prototype.pop = function() {
let size = this.queue.length;
while(size-- > 1) {//将除了最后一个元素外的元素全部加入到队尾。
this.queue.push(this.queue.shift());
}
return this.queue.shift();
};
MyStack.prototype.top = function() {
const x = this.pop();//先出栈,然后在加入队列
this.queue.push(x);
return x;
};
MyStack.prototype.empty = function() {
return !this.queue.length;
};
933. 最近的请求次数 (easy)
写一个 RecentCounter 类来计算特定时间范围内最近的请求。
请你实现 RecentCounter 类:
RecentCounter() 初始化计数器,请求数为 0 。
int ping(int t) 在时间 t 添加一个新请求,其中 t 表示以毫秒为单位的某个时间,并返回过去 3000 毫秒内发生的所有请求数(包括新请求)。确切地说,返回在 [t-3000, t] 内发生的请求数。
保证 每次对 ping 的调用都使用比之前更大的 t 值。示例 1:
输入:
[“RecentCounter”, “ping”, “ping”, “ping”, “ping”]
[[], [1], [100], [3001], [3002]]
输出:
[null, 1, 2, 3, 3]解释:
RecentCounter recentCounter = new RecentCounter();
recentCounter.ping(1); // requests = [1],范围是 [-2999,1],返回 1
recentCounter.ping(100); // requests = [1, 100],范围是 [-2900,100],返回 2
recentCounter.ping(3001); // requests = [1, 100, 3001],范围是 [1,3001],返回 3
recentCounter.ping(3002); // requests = [1, 100, 3001, 3002],范围是 [2,3002],返回 3提示:
1 <= t <= 109
保证每次对 ping 调用所使用的 t 值都 严格递增
至多调用 ping 方法 104 次
- 思路:将请求加入队列,如果队头元素请求的时间在
[t-3000,t]之外 就不断出队 - 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(q),q是ping的次数。空间复杂度O(w),w是队列中最多的元素个数
js:
var RecentCounter = function() {
this.queue = []
};
RecentCounter.prototype.ping = function(t) {
this.queue.push(t);//新请求入队
const time = t-3000;//计算3000ms前的时间
while(this.queue[0] < time){//如果队头元素请求的时间在[t-3000,t]之外 就不断出队
this.queue.shift();
}
return this.queue.length;//在[t-3000,t]区间内队列剩余的元素就是符合要求的请求数
};
703. 数据流中的第 K 大元素 (easy)
设计一个找到数据流中第 k 大元素的类(class)。注意是排序后的第 k 大元素,不是第 k 个不同的元素。
请实现 KthLargest 类:
KthLargest(int k, int[] nums) 使用整数 k 和整数流 nums 初始化对象。
int add(int val) 将 val 插入数据流 nums 后,返回当前数据流中第 k 大的元素。示例:
输入:
[“KthLargest”, “add”, “add”, “add”, “add”, “add”]
[[3, [4, 5, 8, 2]], [3], [5], [10], [9], [4]]
输出:
[null, 4, 5, 5, 8, 8]解释:
KthLargest kthLargest = new KthLargest(3, [4, 5, 8, 2]);
kthLargest.add(3); // return 4
kthLargest.add(5); // return 5
kthLargest.add(10); // return 5
kthLargest.add(9); // return 8
kthLargest.add(4); // return 8提示:
1 <= k <= 104
0 <= nums.length <= 104
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
-104 <= val <= 104
最多调用 add 方法 104 次
题目数据保证,在查找第 k 大元素时,数组中至少有 k 个元素
方法1:暴力排序
- 思路:当数据流有新的元素的时候,重新按升序排序数组,倒数第k个元素就是第k大的数
- 复杂度分析:时间复杂度
O(c*zlogz),z为数据流的最长长度,c为加入元素的个数,排序复杂度是O(zlogz),加入c次排序就需要排序c次。
方法2:堆
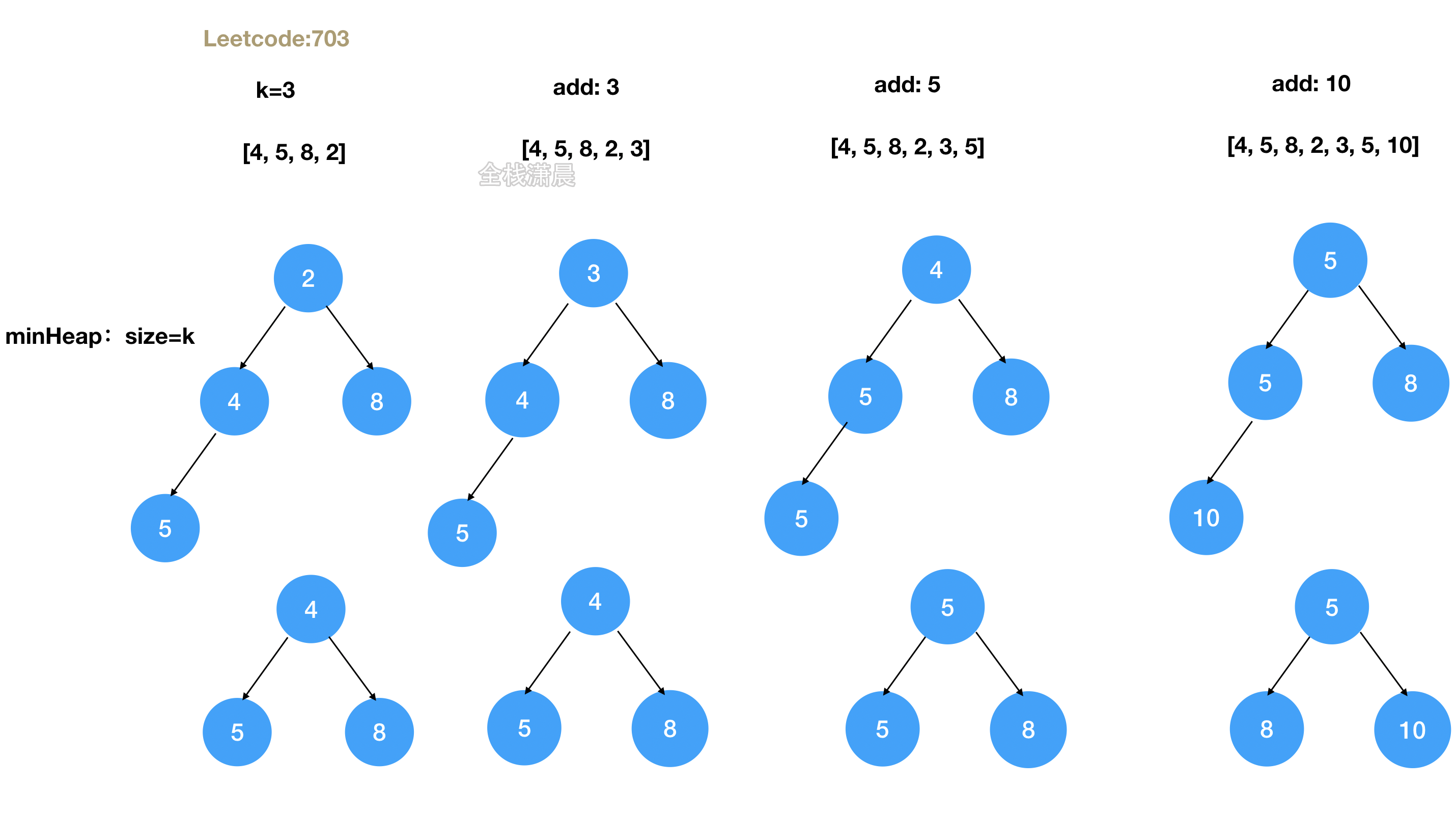
- 思路:用一个size是k的小顶堆来存贮前k个元素,堆顶是最小的元素,在循环数组的过程中,不断加入元素然后调整元素在堆中的位置,如果此时优先队列的大小大于 k,我们需要将优先队列的队头元素弹出,以保证优先队列的大小为 k,最后堆顶就是第K大元素的位置
- 复杂度分析:时间复杂度
O(nlogk),n是初始数组的大小,k是堆的大小,初始堆化和单次插入堆的复杂度都是O(logk),数组的每个数都要插入堆中一次,所以是O(nlogk)。 空间复杂度:O(k), 即堆的大小
js:
var KthLargest = function (k, nums) {
this.k = k;
this.heap = new Heap();
for (const x of nums) {//将数组中的数加入小顶堆
this.add(x);//加入小顶堆
}
};
KthLargest.prototype.add = function (val) {
this.heap.offer(val);//加入堆
if (this.heap.size() > this.k) {//大小超过了小顶堆的size,就从小顶堆删除一个最小的元素
this.heap.poll();//删除最小的元素
}
return this.heap.peek();//返回堆顶
};
class Heap {
constructor(comparator = (a, b) => a - b, data = []) {
this.data = data;
this.comparator = comparator;//比较器
this.heapify();//堆化
}
heapify() {
if (this.size() < 2) return;
for (let i = Math.floor(this.size()/2)-1; i >= 0; i--) {
this.bubbleDown(i);//bubbleDown操作
}
}
peek() {
if (this.size() === 0) return null;
return this.data[0];//查看堆顶
}
offer(value) {
this.data.push(value);//加入数组
this.bubbleUp(this.size() - 1);//调整加入的元素在小顶堆中的位置
}
poll() {
if (this.size() === 0) {
return null;
}
const result = this.data[0];
const last = this.data.pop();
if (this.size() !== 0) {
this.data[0] = last;//交换第一个元素和最后一个元素
this.bubbleDown(0);//bubbleDown操作
}
return result;
}
bubbleUp(index) {
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1;//父节点的位置
//如果当前元素比父节点的元素小,就交换当前节点和父节点的位置
if (this.comparator(this.data[index], this.data[parentIndex]) < 0) {
this.swap(index, parentIndex);//交换自己和父节点的位置
index = parentIndex;//不断向上取父节点进行比较
} else {
break;//如果当前元素比父节点的元素大,不需要处理
}
}
}
bubbleDown(index) {
const lastIndex = this.size() - 1;//最后一个节点的位置
while (true) {
const leftIndex = index * 2 + 1;//左节点的位置
const rightIndex = index * 2 + 2;//右节点的位置
let findIndex = index;//bubbleDown节点的位置
//找出左右节点中value小的节点
if (
leftIndex <= lastIndex &&
this.comparator(this.data[leftIndex], this.data[findIndex]) < 0
) {
findIndex = leftIndex;
}
if (
rightIndex <= lastIndex &&
this.comparator(this.data[rightIndex], this.data[findIndex]) < 0
) {
findIndex = rightIndex;
}
if (index !== findIndex) {
this.swap(index, findIndex);//交换当前元素和左右节点中value小的
index = findIndex;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
swap(index1, index2) {//交换堆中两个元素的位置
[this.data[index1], this.data[index2]] = [this.data[index2], this.data[index1]];
}
size() {
return this.data.length;
}
}
347. 前 K 个高频元素 (medium)
给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你返回其中出现频率前 k 高的元素。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2
输出: [1,2]
示例 2:输入: nums = [1], k = 1
输出: [1]提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 105
k 的取值范围是 [1, 数组中不相同的元素的个数]
题目数据保证答案唯一,换句话说,数组中前 k 个高频元素的集合是唯一的进阶:你所设计算法的时间复杂度 必须 优于 O(n log n) ,其中 n 是数组大小。
方法1:优先队列

- 思路:循环数组,加入小顶堆,当堆的size超过k时,出堆,循环完成之后,堆中所有的元素就是前k大的数字
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(nlogk),循环n次,每次堆的操作是O(logk)。空间复杂度O(k),
js:
class Heap {
constructor(comparator = (a, b) => a - b, data = []) {
this.data = data;
this.comparator = comparator;//比较器
this.heapify();//堆化
}
heapify() {
if (this.size() < 2) return;
for (let i = Math.floor(this.size()/2)-1; i >= 0; i--) {
this.bubbleDown(i);//bubbleDown操作
}
}
peek() {
if (this.size() === 0) return null;
return this.data[0];//查看堆顶
}
offer(value) {
this.data.push(value);//加入数组
this.bubbleUp(this.size() - 1);//调整加入的元素在小顶堆中的位置
}
poll() {
if (this.size() === 0) {
return null;
}
const result = this.data[0];
const last = this.data.pop();
if (this.size() !== 0) {
this.data[0] = last;//交换第一个元素和最后一个元素
this.bubbleDown(0);//bubbleDown操作
}
return result;
}
bubbleUp(index) {
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1;//父节点的位置
//如果当前元素比父节点的元素小,就交换当前节点和父节点的位置
if (this.comparator(this.data[index], this.data[parentIndex]) < 0) {
this.swap(index, parentIndex);//交换自己和父节点的位置
index = parentIndex;//不断向上取父节点进行比较
} else {
break;//如果当前元素比父节点的元素大,不需要处理
}
}
}
bubbleDown(index) {
const lastIndex = this.size() - 1;//最后一个节点的位置
while (true) {
const leftIndex = index * 2 + 1;//左节点的位置
const rightIndex = index * 2 + 2;//右节点的位置
let findIndex = index;//bubbleDown节点的位置
//找出左右节点中value小的节点
if (
leftIndex <= lastIndex &&
this.comparator(this.data[leftIndex], this.data[findIndex]) < 0
) {
findIndex = leftIndex;
}
if (
rightIndex <= lastIndex &&
this.comparator(this.data[rightIndex], this.data[findIndex]) < 0
) {
findIndex = rightIndex;
}
if (index !== findIndex) {
this.swap(index, findIndex);//交换当前元素和左右节点中value小的
index = findIndex;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
swap(index1, index2) {//交换堆中两个元素的位置
[this.data[index1], this.data[index2]] = [this.data[index2], this.data[index1]];
}
size() {
return this.data.length;
}
}
var topKFrequent = function (nums, k) {
const map = new Map();
for (const num of nums) {//统计频次
map.set(num, (map.get(num) || 0) + 1);
}
//创建小顶堆
const priorityQueue = new Heap((a, b) => a[1] - b[1]);
//entry 是一个长度为2的数组,0位置存储key,1位置存储value
for (const entry of map.entries()) {
priorityQueue.offer(entry);//加入堆
if (priorityQueue.size() > k) {//堆的size超过k时,出堆
priorityQueue.poll();
}
}
const ret = [];
for (let i = priorityQueue.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {//取出前k大的数
ret[i] = priorityQueue.poll()[0];
}
return ret;
};
23. 合并K个升序链表 (hard)
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:输入:lists = []
输出:[]
示例 3:输入:lists = [[]]
输出:[]提示:
k == lists.length
0 <= k <= 10^4
0 <= lists[i].length <= 500
-10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4
lists[i] 按 升序 排列
lists[i].length 的总和不超过 10^4
方法1.分治
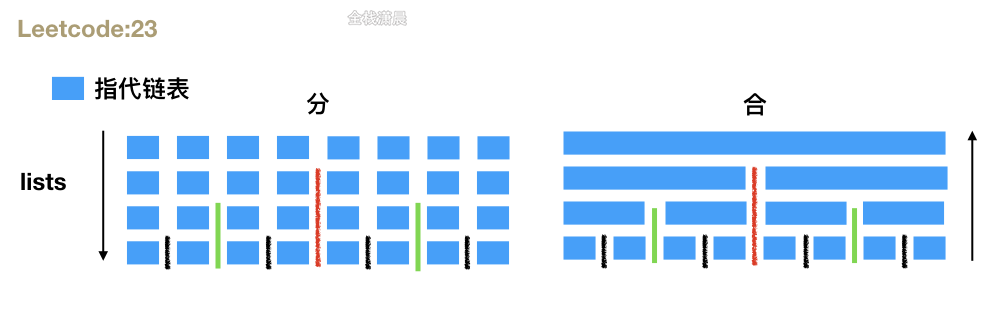
- 思路:自底而上归并,第一次归并2个链表,第二次归并4个链表…,每次归并不断合并两个有序链表,直到合并完所有分治后的链表
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n * logk),n是每个链表节点数,k个链表个数,每次归并,链表数量较少一半,复杂度是O(logk),将两个链表合并成一个顺序链表复杂度是O(2n),所以时间复杂度是O(n * logk)。空间复杂度是O(logk),即递归的空格复杂度
js:
//自顶而下归并 先分在合
var mergeKLists = function (lists) {
// 当是空数组的情况下
if (!lists.length) {
return null;
}
// 合并两个排序链表
const merge = (head1, head2) => {
let dummy = new ListNode(0);
let cur = dummy;
// 新链表,新的值小就先接谁
while (head1 && head2) {
if (head1.val < head2.val) {
cur.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
} else {
cur.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
// 如果后面还有剩余的就把剩余的接上
cur.next = head1 == null ? head2 : head1;
return dummy.next;
};
const mergeLists = (lists, start, end) => {
if (start + 1 == end) {
return lists[start];
}
// 输入的k个排序链表,可以分成两部分,前k/2个链表和后k/2个链表
// 如果将这前k/2个链表和后k/2个链表分别合并成两个排序的链表,再将两个排序的链表合并,那么所有链表都合并了
let mid = (start + end) >> 1;
let head1 = mergeLists(lists, start, mid);
let head2 = mergeLists(lists, mid, end);
return merge(head1, head2);
};
return mergeLists(lists, 0, lists.length);
};
//自底而上合并
var mergeKLists = function (lists) {
if (lists.length <= 1) return lists[0] || null;//当归并的节点只有一个时 返回这个节点
const newLists = [];
//自底而上归并,第一次归并大小为2的链表,第二次归并大小4的链表...
for (let i = 0; i < lists.length; i += 2) {
newLists.push(merge(lists[i], lists[i + 1] || null));
}
return mergeKLists(newLists);
};
const merge = (list_1, list_2) => {//合并两个有序链表
const dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
let p = dummyNode;
while (list_1 && list_2) {
if (list_1.val < list_2.val) {//先将小的节点加入
p.next = list_1;
list_1 = list_1.next;
} else {
p.next = list_2;
list_2 = list_2.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
p.next = list_1 ? list_1 : list_2;//遍历完成还有节点剩余
return dummyNode.next;
};
方法2.优先队列
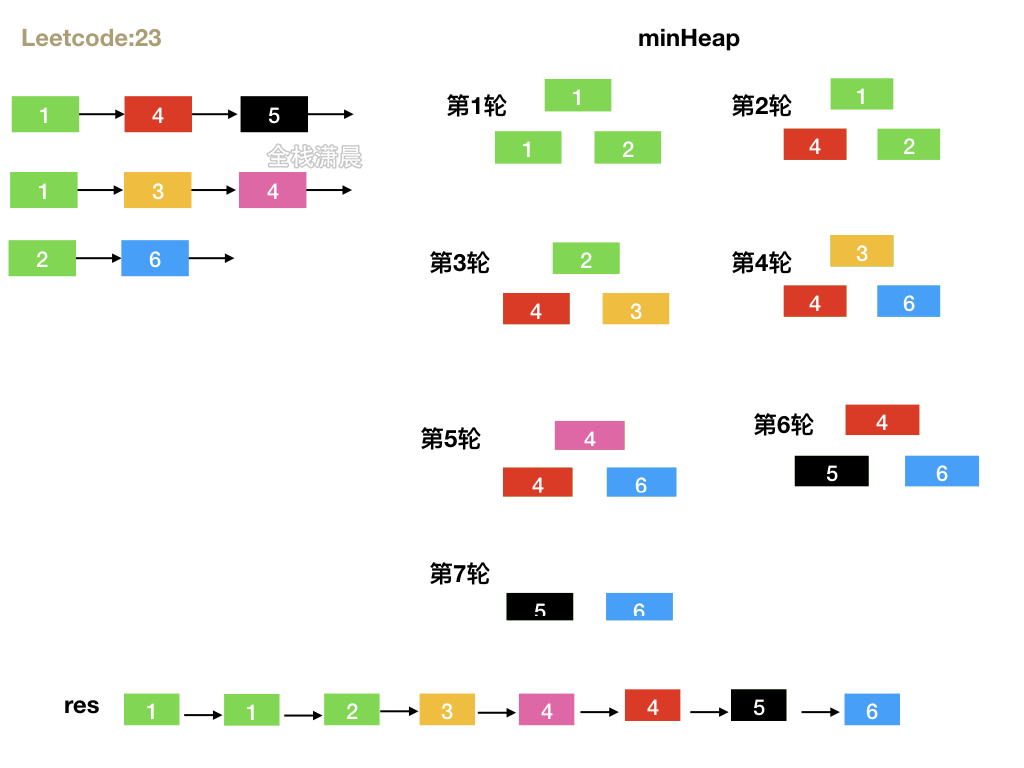
- 思路:新建小顶堆,小顶堆的大小是k,不断从每个链表的头节点开始不断加入小顶堆中,然后取出堆顶值,也就是最小值,然后继续往小顶堆中插入这个最小值在链表的next节点
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(kn * logk),优先队列的大小是k,每次插入和删除是O(logk),总共k * n的节点个数,每个节点插入删除一次,所以总的复杂度是O(kn*logk)。空间复杂度是O(k),即优先队列的大小
js:
class Heap {
constructor(comparator = (a, b) => a - b, data = []) {
this.data = data;
this.comparator = comparator;//比较器
this.heapify();//堆化
}
heapify() {
if (this.size() < 2) return;
for (let i = Math.floor(this.size()/2)-1; i >= 0; i--) {
this.bubbleDown(i);//bubbleDown操作
}
}
peek() {
if (this.size() === 0) return null;
return this.data[0];//查看堆顶
}
offer(value) {
this.data.push(value);//加入数组
this.bubbleUp(this.size() - 1);//调整加入的元素在小顶堆中的位置
}
poll() {
if (this.size() === 0) {
return null;
}
const result = this.data[0];
const last = this.data.pop();
if (this.size() !== 0) {
this.data[0] = last;//交换第一个元素和最后一个元素
this.bubbleDown(0);//bubbleDown操作
}
return result;
}
bubbleUp(index) {
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1;//父节点的位置
//如果当前元素比父节点的元素小,就交换当前节点和父节点的位置
if (this.comparator(this.data[index], this.data[parentIndex]) < 0) {
this.swap(index, parentIndex);//交换自己和父节点的位置
index = parentIndex;//不断向上取父节点进行比较
} else {
break;//如果当前元素比父节点的元素大,不需要处理
}
}
}
bubbleDown(index) {
const lastIndex = this.size() - 1;//最后一个节点的位置
while (true) {
const leftIndex = index * 2 + 1;//左节点的位置
const rightIndex = index * 2 + 2;//右节点的位置
let findIndex = index;//bubbleDown节点的位置
//找出左右节点中value小的节点
if (
leftIndex <= lastIndex &&
this.comparator(this.data[leftIndex], this.data[findIndex]) < 0
) {
findIndex = leftIndex;
}
if (
rightIndex <= lastIndex &&
this.comparator(this.data[rightIndex], this.data[findIndex]) < 0
) {
findIndex = rightIndex;
}
if (index !== findIndex) {
this.swap(index, findIndex);//交换当前元素和左右节点中value小的
index = findIndex;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
swap(index1, index2) {//交换堆中两个元素的位置
[this.data[index1], this.data[index2]] = [this.data[index2], this.data[index1]];
}
size() {
return this.data.length;
}
}
var mergeKLists = function(lists) {
const res = new ListNode(0);
let p = res;
const h = new Heap(comparator = (a, b) => a.val - b.val);
lists.forEach(l => {//插入每个链表的第一个节点
if(l) h.offer(l);
})
while(h.size()) {//
const n = h.poll();//取出最小值
p.next = n;//最小值加入p的next后
p = p.next;//移动p节点
if(n.next) h.offer(n.next);//插入最小节点的后一个节点
}
return res.next;
};
692. 前K个高频单词(medium)
给定一个单词列表 words 和一个整数 k ,返回前 k 个出现次数最多的单词。
返回的答案应该按单词出现频率由高到低排序。如果不同的单词有相同出现频率, 按字典顺序 排序。
示例 1:
输入: words = [“i”, “love”, “leetcode”, “i”, “love”, “coding”], k = 2
输出: [“i”, “love”]
解析: “i” 和 “love” 为出现次数最多的两个单词,均为2次。
注意,按字母顺序 “i” 在 “love” 之前。
示例 2:输入: [“the”, “day”, “is”, “sunny”, “the”, “the”, “the”, “sunny”, “is”, “is”], k = 4
输出: [“the”, “is”, “sunny”, “day”]
解析: “the”, “is”, “sunny” 和 “day” 是出现次数最多的四个单词,
出现次数依次为 4, 3, 2 和 1 次。注意:
1 <= words.length <= 500
1 <= words[i] <= 10
words[i] 由小写英文字母组成。
k 的取值范围是 [1, 不同 words[i] 的数量]
方法1:排序
js:
var topKFrequent = function (words, k) {
const map = {};
words.forEach(v => map[v] = (map[v] || 0) + 1);
const keys = Object.keys(map).sort((a, b) => map[b] - map[a] || a.localeCompare(b))
return keys.slice(0, k);
};
方法2:堆
js:
class Heap {
constructor(comparator = (a, b) => a - b, data = []) {
this.data = data;
this.comparator = comparator;//比较器
this.heapify();//堆化
}
heapify() {
if (this.size() < 2) return;
for (let i = Math.floor(this.size()/2)-1; i >= 0; i--) {
this.bubbleDown(i);//bubbleDown操作
}
}
peek() {
if (this.size() === 0) return null;
return this.data[0];//查看堆顶
}
offer(value) {
this.data.push(value);//加入数组
this.bubbleUp(this.size() - 1);//调整加入的元素在小顶堆中的位置
}
poll() {
if (this.size() === 0) {
return null;
}
const result = this.data[0];
const last = this.data.pop();
if (this.size() !== 0) {
this.data[0] = last;//交换第一个元素和最后一个元素
this.bubbleDown(0);//bubbleDown操作
}
return result;
}
bubbleUp(index) {
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1;//父节点的位置
//如果当前元素比父节点的元素小,就交换当前节点和父节点的位置
if (this.comparator(this.data[index], this.data[parentIndex]) < 0) {
this.swap(index, parentIndex);//交换自己和父节点的位置
index = parentIndex;//不断向上取父节点进行比较
} else {
break;//如果当前元素比父节点的元素大,不需要处理
}
}
}
bubbleDown(index) {
const lastIndex = this.size() - 1;//最后一个节点的位置
while (true) {
const leftIndex = index * 2 + 1;//左节点的位置
const rightIndex = index * 2 + 2;//右节点的位置
let findIndex = index;//bubbleDown节点的位置
//找出左右节点中value小的节点
if (
leftIndex <= lastIndex &&
this.comparator(this.data[leftIndex], this.data[findIndex]) < 0
) {
findIndex = leftIndex;
}
if (
rightIndex <= lastIndex &&
this.comparator(this.data[rightIndex], this.data[findIndex]) < 0
) {
findIndex = rightIndex;
}
if (index !== findIndex) {
this.swap(index, findIndex);//交换当前元素和左右节点中value小的
index = findIndex;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
swap(index1, index2) {//交换堆中两个元素的位置
[this.data[index1], this.data[index2]] = [this.data[index2], this.data[index1]];
}
size() {
return this.data.length;
}
}
var topKFrequent = function (nums, k) {
const map = new Map();
for (const num of nums) {//统计频次
map.set(num, (map.get(num) || 0) + 1);
}
//创建小顶堆
const priorityQueue = new Heap((a, b) => {
return a[1] === b[1] ? b[0].localeCompare(a[0]) : a[1] - b[1]
});
//entry 是一个长度为2的数组,0位置存储key,1位置存储value
for (const entry of map.entries()) {
priorityQueue.offer(entry);//加入堆
if (priorityQueue.size() > k) {//堆的size超过k时,出堆
priorityQueue.poll();
}
}
const ret = [];
for (let i = priorityQueue.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {//取出前k大的数
ret[i] = priorityQueue.poll()[0];
}
return ret;
};
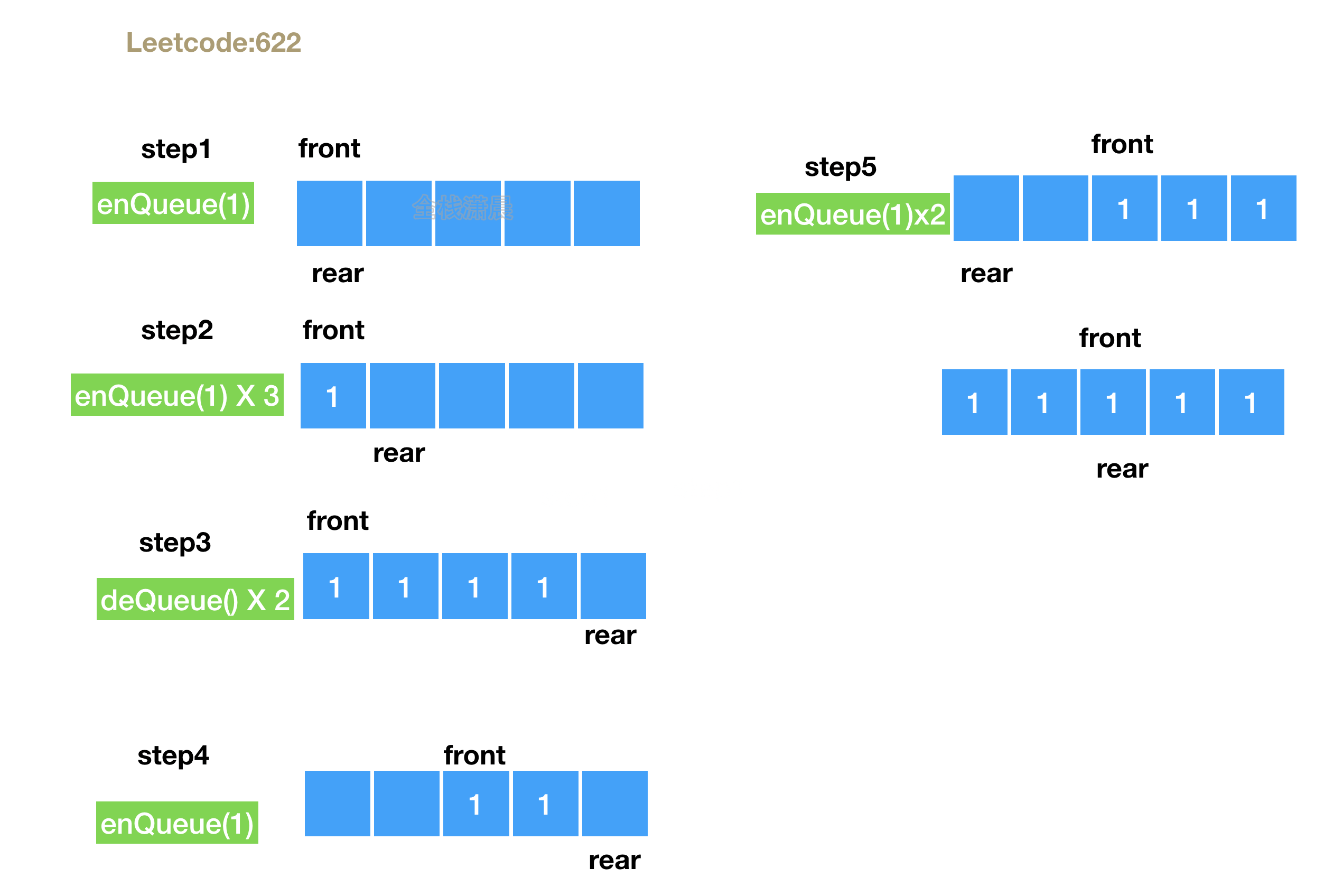
622. 设计循环队列 (medium)
设计你的循环队列实现。 循环队列是一种线性数据结构,其操作表现基于 FIFO(先进先出)原则并且队尾被连接在队首之后以形成一个循环。它也被称为“环形缓冲器”。
循环队列的一个好处是我们可以利用这个队列之前用过的空间。在一个普通队列里,一旦一个队列满了,我们就不能插入下一个元素,即使在队列前面仍有空间。但是使用循环队列,我们能使用这些空间去存储新的值。
你的实现应该支持如下操作:
MyCircularQueue(k): 构造器,设置队列长度为 k 。
Front: 从队首获取元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
Rear: 获取队尾元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
enQueue(value): 向循环队列插入一个元素。如果成功插入则返回真。
deQueue(): 从循环队列中删除一个元素。如果成功删除则返回真。
isEmpty(): 检查循环队列是否为空。
isFull(): 检查循环队列是否已满。示例:
MyCircularQueue circularQueue = new MyCircularQueue(3); // 设置长度为 3
circularQueue.enQueue(1); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(2); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(3); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 false,队列已满
circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 3
circularQueue.isFull(); // 返回 true
circularQueue.deQueue(); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 true
circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 4提示:
所有的值都在 0 至 1000 的范围内;
操作数将在 1 至 1000 的范围内;
请不要使用内置的队列库。
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(1),空间复杂度O(k)
js:
var MyCircularQueue = function(k) {
this.front = 0
this.rear = 0
this.max = k
this.list = Array(k)
};
MyCircularQueue.prototype.enQueue = function(value) {
if(this.isFull()) {
return false
} else {
this.list[this.rear] = value
this.rear = (this.rear + 1) % this.max
return true
}
};
MyCircularQueue.prototype.deQueue = function() {
let v = this.list[this.front]
this.list[this.front] = undefined
if(v !== undefined ) {
this.front = (this.front + 1) % this.max
return true
} else {
return false
}
};
MyCircularQueue.prototype.Front = function() {
if(this.list[this.front] === undefined) {
return -1
} else {
return this.list[this.front]
}
};
MyCircularQueue.prototype.Rear = function() {
let rear = this.rear - 1
if(this.list[rear < 0 ? this.max - 1 : rear] === undefined) {
return -1
} else {
return this.list[rear < 0 ? this.max - 1 : rear]
}
};
MyCircularQueue.prototype.isEmpty = function() {
return this.front === this.rear && !this.list[this.front]
};
MyCircularQueue.prototype.isFull = function() {
return (this.front === this.rear) && !!this.list[this.front]
};
视频讲解:传送门