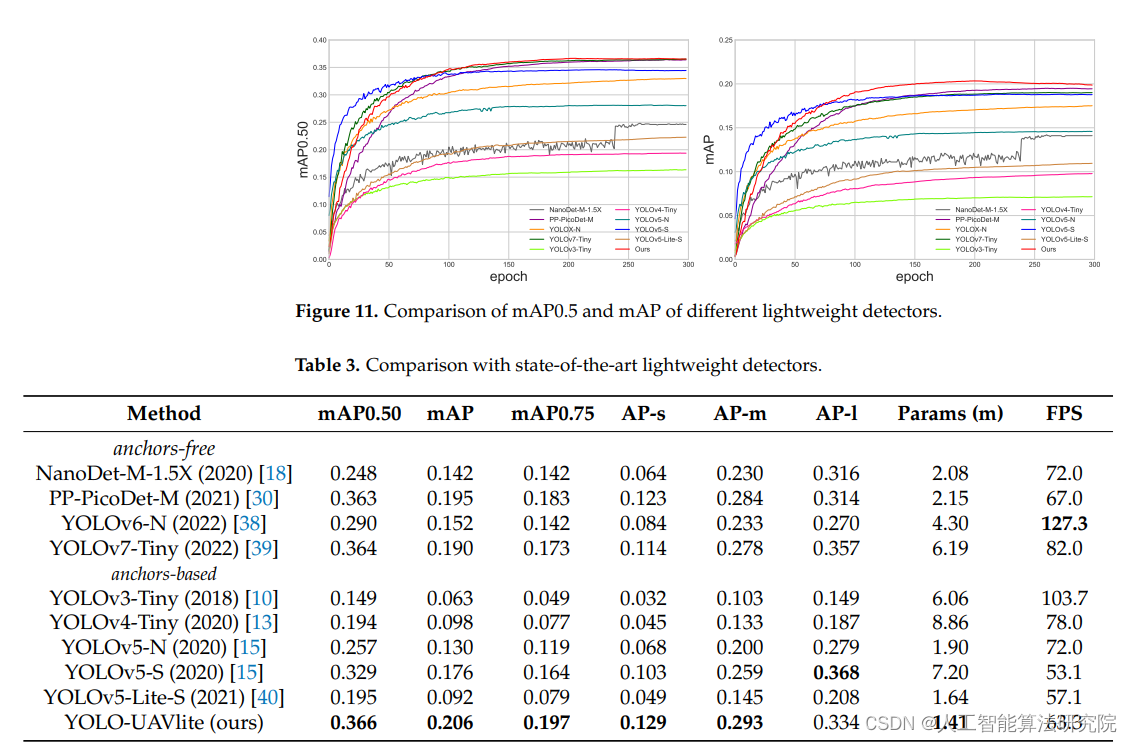
Redis中支持五种数据类型中有序集合Sorted Set的底层数据结构使用的跳跃表,为何不使用其他的如平衡二叉树、b+树等数据结构呢?
1,redis的设计目标、性能需求:
redis是高性能的非关系型(NoSQL)内存键值数据库,它以其快速的操作速度而闻名。
读取速度:Redis能实现极高的读取速度,据官方测试报告,可以达到每秒约110,000次读取操作。
写入速度:与读取相比,写入速度略低,但仍然相当可观,官方数据显示,Redis的写入速度大约是每秒81,000次操作。
类似产品如Memcached等,无法达到如此性能。
2,有序集合都可以借助什么数据结构及其基本原理
有序集合需求:自然有序,查找高速,支持范围查找
2.1,传统数组/链表+排序
数组或链表可以存储数据,可以新增或修改数据后重新排序,
而在集合排序方面,最快的归并排序也需要O(NlongN)的时间复杂度。
时间不够快,但实现、使用方面简单

2.2,跳跃表(链表的优化–链表+多级索引)
跳跃表最早是由William Pugh在1990年提出的,被用来代替平衡树(如AVL树和红黑树)来实现有序集合。跳跃表的查询复杂度为O(log n),与平衡树相当,但由于其实现较为简单,所以在实际使用中比平衡树更加高效。
例:查找90

增加指针,让指针指向远处个节点,
如上图,共四层,最底层(原链表L1)节点是10 - 20 - 30 -… - 120,中间层L2增加节点10 - 30 - 40 - 60 - 80 - 100 - 120,L2上层L3增加节点10 - 40 - 80 - 120 最高层10 - 120
这样形成三个新的链表,但它包含的节点个数只有原来的一部分;
当我们查找数据之时,先沿着这个最高层链表进行查找。当碰到比待查数据大的节点时,再到中间层,最后回到原来的链表中进行查找。
如查找90,共经历6步。
过程类似二分查找,时间复杂度支持平均O(logN),最坏O(N)的节点查找,还可以顺序性操作来批量处理节点。
2.3,平衡二叉树/红黑树

平衡二叉树的查询复杂度为O(logN),但新增、删除需要调整保持平衡,实现相对复杂;
范围查询方面,平衡二叉树支持范围查询,但是这这种数据结构要范围查找要往回找,即回溯到父结点,而B+树的叶子结点的指针的效率则更高
2.4,B+树
B+ Tree是一种经典的多路平衡查找树,它通常被用来实现磁盘上的数据结构。在B+ Tree中,每个节点可以包含多个键值对,而且所有叶子节点都被连接成一个链表。B+ Tree的查询复杂度也是O(log n),但由于其实现较为复杂,所以在实际使用中通常用于数据库系统等需要高效读写的场景中。

3,跳跃表与平衡树的实现

//redis源码中跳跃表结构的实现:
/* ZSETs use a specialized version of Skiplists */
typedef struct zskiplistNode {
sds ele;
double score;//分值
struct zskiplistNode *backward;//后退指针
//层
struct zskiplistLevel {
struct zskiplistNode *forward;//前进指针
unsigned long span;//跨度
} level[];
} zskiplistNode;
如图,一个跳表节点,有level数组,每个元素都有一个指向其他节点的指针,可以通过这些层来加快访问速度
3.1使用java实现跳跃表:
import java.util.Random;
class Node {
int key;
int value;
Node[] next;
public Node(int level, int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = new Node[level + 1];
}
}
public class SkipList {
private static final int MAX_LEVEL = 16; // 最大层数
private int level; // 当前层数
private Node head; // 头节点
private Random random; // 用于生成随机层数
public SkipList() {
this.level = 0;
this.head = new Node(MAX_LEVEL, 0, 0);
this.random = new Random();
}
// 生成随机层数
private int randomLevel() {
int level = 0;
while (level < MAX_LEVEL && random.nextDouble() < 0.5) {
level++;
}
return level;
}
// 插入节点
public void insert(int key, int value) {
Node[] update = new Node[MAX_LEVEL + 1];
Node current = head;
for (int i = level; i >= 0; i--) {
while (current.next[i] != null && current.next[i].key < key) {
current = current.next[i];
}
update[i] = current;
}
int newLevel = randomLevel();
if (newLevel > level) {
for (int i = level + 1; i <= newLevel; i++) {
update[i] = head;
}
level = newLevel;
}
Node newNode = new Node(newLevel, key, value);
for (int i = 0; i <= newLevel; i++) {
newNode.next[i] = update[i].next[i];
update[i].next[i] = newNode;
}
}
// 查找节点
public Node search(int key) {
Node current = head;
for (int i = level; i >= 0; i--) {
while (current.next[i] != null && current.next[i].key < key) {
current = current.next[i];
}
}
if (current.next[0] != null && current.next[0].key == key) {
return current.next[0];
}
return null;
}
// 删除节点
public void delete(int key) {
Node[] update = new Node[MAX_LEVEL + 1];
Node current = head;
for (int i = level; i >= 0; i--) {
while (current.next[i] != null && current.next[i].key < key) {
current = current.next[i];
}
update[i] = current;
}
if (current.next[0] != null && current.next[0].key == key) {
for (int i = 0; i <= level; i++) {
if (update[i].next[i] != current.next[i]) {
break;
}
update[i].next[i] = current.next[i];
}
while (level > 0 && head.next[level] == null) {
level--;
}
}
}
// 打印跳跃表
public void printSkipList() {
for (int i = level; i >= 0; i--) {
Node current = head;
System.out.print("Level " + i + ": ");
while (current.next[i] != null) {
System.out.print(current.next[i].key + " ");
current = current.next[i];
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SkipList skipList = new SkipList();
skipList.insert(3, 30);
skipList.insert(1, 10);
skipList.insert(2, 20);
skipList.insert(4, 40);
System.out.println("Skip List after insertion:");
skipList.printSkipList();
int searchKey = 2;
Node searchResult = skipList.search(searchKey);
if (searchResult != null) {
System.out.println("Node with key " + searchKey + " found. Value: " + searchResult.value);
} else {
System.out.println("Node with key " + searchKey + " not found.");
}
int deleteKey = 2;
skipList.delete(deleteKey);
System.out.println("Skip List after deletion of key " + deleteKey + ":");
skipList.printSkipList();
}
}
3.2使用java实现平衡二叉树(AVLTree):
class Node {
int key, height;
Node left, right;
public Node(int key) {
this.key = key;
this.height = 1;
}
}
public class AVLTree {
private Node root;
// 获取节点的高度
private int height(Node node) {
return (node == null) ? 0 : node.height;
}
// 获取树的平衡因子
private int getBalance(Node node) {
return (node == null) ? 0 : height(node.left) - height(node.right);
}
// 更新节点的高度
private void updateHeight(Node node) {
node.height = 1 + Math.max(height(node.left), height(node.right));
}
// 执行右旋转
private Node rightRotate(Node y) {
Node x = y.left;
Node T2 = x.right;
// 执行旋转
x.right = y;
y.left = T2;
// 更新高度
updateHeight(y);
updateHeight(x);
return x;
}
// 执行左旋转
private Node leftRotate(Node x) {
Node y = x.right;
Node T2 = y.left;
// 执行旋转
y.left = x;
x.right = T2;
// 更新高度
updateHeight(x);
updateHeight(y);
return y;
}
// 插入节点
public Node insert(Node node, int key) {
if (node == null) {
return new Node(key);
}
// 执行标准的BST插入
if (key < node.key) {
node.left = insert(node.left, key);
} else if (key > node.key) {
node.right = insert(node.right, key);
} else {
// 相等的键不允许插入
return node;
}
// 更新节点的高度
updateHeight(node);
// 获取平衡因子
int balance = getBalance(node);
// 进行平衡操作
// 左重,需要右旋转
if (balance > 1 && key < node.left.key) {
return rightRotate(node);
}
// 右重,需要左旋转
if (balance < -1 && key > node.right.key) {
return leftRotate(node);
}
// 左右,先左旋转后右旋转
if (balance > 1 && key > node.left.key) {
node.left = leftRotate(node.left);
return rightRotate(node);
}
// 右左,先右旋转后左旋转
if (balance < -1 && key < node.right.key) {
node.right = rightRotate(node.right);
return leftRotate(node);
}
// 不需要平衡操作,直接返回节点
return node;
}
// 插入节点的公共接口
public void insert(int key) {
root = insert(root, key);
}
// 打印中序遍历结果
private void inOrderTraversal(Node node) {
if (node != null) {
inOrderTraversal(node.left);
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
inOrderTraversal(node.right);
}
}
// 打印中序遍历结果的公共接口
public void inOrderTraversal() {
inOrderTraversal(root);
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AVLTree avlTree = new AVLTree();
// 插入节点
avlTree.insert(10);
avlTree.insert(20);
avlTree.insert(30);
avlTree.insert(15);
avlTree.insert(5);
// 打印中序遍历结果
System.out.println("Inorder traversal of the AVL tree:");
avlTree.inOrderTraversal();
}
}
3.3java实现B+树:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class BPlusTree {
private BPlusNode root;
private int order;
public BPlusTree(int order) {
this.root = new BPlusLeafNode();
this.order = order;
}
public void insert(int key, String value) {
root = root.insert(key, value);
}
public String search(int key) {
return root.search(key);
}
public void printTree() {
root.print();
}
// B+树节点抽象类
abstract static class BPlusNode {
List<Integer> keys;
BPlusNode() {
this.keys = new ArrayList<>();
}
abstract BPlusNode insert(int key, String value);
abstract String search(int key);
abstract void print();
}
// B+树叶子节点类
static class BPlusLeafNode extends BPlusNode {
List<String> values;
BPlusLeafNode next; // 用于连接叶子节点形成链表
BPlusLeafNode() {
this.values = new ArrayList<>();
this.next = null;
}
@Override
BPlusNode insert(int key, String value) {
int index = 0;
while (index < keys.size() && keys.get(index) < key) {
index++;
}
keys.add(index, key);
values.add(index, value);
// 检查是否需要分裂
if (keys.size() > order) {
int splitIndex = keys.size() / 2;
BPlusLeafNode newLeaf = new BPlusLeafNode();
// 将一半的键和值移至新节点
newLeaf.keys.addAll(keys.subList(splitIndex, keys.size()));
newLeaf.values.addAll(values.subList(splitIndex, values.size()));
keys.subList(splitIndex, keys.size()).clear();
values.subList(splitIndex, values.size()).clear();
// 调整叶子节点链表
newLeaf.next = next;
next = newLeaf;
return newLeaf;
}
return this;
}
@Override
String search(int key) {
int index = 0;
while (index < keys.size() && keys.get(index) <= key) {
if (keys.get(index) == key) {
return values.get(index);
}
index++;
}
return null;
}
@Override
void print() {
System.out.print("Leaf Node: ");
for (int i = 0; i < keys.size(); i++) {
System.out.print("(" + keys.get(i) + ", " + values.get(i) + ") ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// B+树内部节点类
static class BPlusInternalNode extends BPlusNode {
List<BPlusNode> children;
BPlusInternalNode() {
this.children = new ArrayList<>();
}
@Override
BPlusNode insert(int key, String value) {
int index = 0;
while (index < keys.size() && keys.get(index) < key) {
index++;
}
BPlusNode child = children.get(index);
BPlusNode newChild = child.insert(key, value);
if (newChild != child) {
keys.add(index, newChild.keys.get(0));
children.add(index + 1, newChild);
if (keys.size() > order) {
int splitIndex = keys.size() / 2;
BPlusInternalNode newInternal = new BPlusInternalNode();
// 将一半的键和子节点移至新节点
newInternal.keys.addAll(keys.subList(splitIndex, keys.size()));
newInternal.children.addAll(children.subList(splitIndex + 1, children.size()));
keys.subList(splitIndex, keys.size()).clear();
children.subList(splitIndex + 1, children.size()).clear();
return newInternal;
}
}
return this;
}
@Override
String search(int key) {
int index = 0;
while (index < keys.size() && keys.get(index) <= key) {
index++;
}
return children.get(index).search(key);
}
@Override
void print() {
System.out.print("Internal Node: ");
for (int i = 0; i < keys.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(keys.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
for (BPlusNode child : children) {
child.print();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BPlusTree bPlusTree = new BPlusTree(3);
bPlusTree.insert(10, "Value10");
bPlusTree.insert(20, "Value20");
bPlusTree.insert(5, "Value5");
bPlusTree.insert(6, "Value6");
bPlusTree.insert(12, "Value12");
bPlusTree.insert(30, "Value30");
System.out.println("B+ Tree after insertion:");
bPlusTree.printTree();
int searchKey = 12;
String searchResult = bPlusTree.search(searchKey);
if (searchResult != null) {
System.out.println("Value for key " + searchKey + ": " + searchResult);
} else {
System.out.println("Key " + searchKey + " not found.");
}
}
}
4,Redis的作者 @antirez 的原话与总结
There are a few reasons:
1、They are not very memory intensive. It’s up to you basically. Changing parameters about the probability of a node to have a given number of levels will make then less memory intensive than btrees.
2、A sorted set is often target of many ZRANGE or ZREVRANGE operations, that is, traversing the skip list as a linked list. With this operation the cache locality of skip lists is at least as good as with other kind of balanced trees.
3、They are simpler to implement, debug, and so forth. For instance thanks to the skip list simplicity I received a patch (already in Redis master) with augmented skip lists implementing ZRANK in O(log(N)). It required little changes to the code.
主要是从内存占用、对范围查找的支持、实现难易程度这三方面总结的原因,
简单翻译一下:
1、它们不是非常内存密集型的。基本上由你决定。改变关于节点具有给定级别数的概率的参数将使其比 btree 占用更少的内存。
2、Zset 经常需要执行 ZRANGE 或 ZREVRANGE 的命令,即作为链表遍历跳表。通过此操作,跳表的缓存局部性至少与其他类型的平衡树一样好。
3、它们更易于实现、调试等。例如,由于跳表的简单性,我收到了一个补丁(已经在Redis master中),其中扩展了跳表,在 O(log(N) 中实现了 ZRANK。它只需要对代码进行少量修改。
跳跃表的优势:
1,时间复杂度方面:大部分情况下,跳跃表的效率和平衡树媲美;
2,算法实现方面:跳跃表的实现比平衡树、b+树更为简单;
3,范围查找方面,跳表比平衡树操作要简单,平衡树需要回溯到父结点,条表可以做到 O(logn) 的时间复杂度定位区间的起点,然后在原始链表中顺序往后遍历;
4,对于小数据集的性能: 在某些场景下,跳表在小数据集上的性能可能优于B+树。跳表的查询操作在某些情况下可能更迅速。