目录
四、图像分类问题
4.1 尝试使用全连接神经网络
4.2 引入卷积神经网络
4.3 分类函数Softmax
4.4 交叉熵损失函数
4.5 学习率优化算法
4.6 图像预处理算法
4.6.1 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等
4.6.2 随机填充
4.6.3 随机裁剪
4.6.4 随机缩放
4.6.5 随机翻转
4.6.6 随机打乱真实框排列顺序
四、图像分类问题
图像分类问题是神经网络经常遇到的处理任务,需要将图像按给定的类别进行分类。
本篇通过手写数字识别这个典型的图像分类任务(0~9个数字一共是10个类别),来了解图像分类问题的特点,原理和方法。
我们首先尝试使用典型的全连接神经网络,再引入适合图像处理任务的卷积神经网络。
4.1 尝试使用全连接神经网络
经典的全连接神经网络来包含四层网络:输入层、两个隐含层和输出层,将手写数字识别任务通过全连接神经网络表示:

- 输入层:将数据输入给神经网络。在该任务中,输入层的尺度为28×28的像素值。
- 隐含层:增加网络深度和复杂度,隐含层的节点数是可以调整的,节点数越多,神经网络表示能力越强,参数量也会增加。在该任务中,中间的两个隐含层为10×10的结构,通常隐含层会比输入层的尺寸小,以便对关键信息做抽象,激活函数使用常见的Sigmoid函数。
- 输出层:输出网络计算结果,输出层的节点数是固定的。如果是回归问题,节点数量为需要回归的数字数量。如果是分类问题,则是分类标签的数量。在该任务中,模型的输出是回归一个数字,输出层的尺寸为1。
Python源码 - 激活函数为sigmoid的多层网络参考代码:
import paddle.nn.functional as F
from paddle.nn import Linear
# 定义多层全连接神经网络
class MNIST(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(MNIST, self).__init__()
# 定义两层全连接隐含层,输出维度是10,当前设定隐含节点数为10,可根据任务调整
self.fc1 = Linear(in_features=784, out_features=10)
self.fc2 = Linear(in_features=10, out_features=10)
# 定义一层全连接输出层,输出维度是1
self.fc3 = Linear(in_features=10, out_features=1)
# 定义网络的前向计算,隐含层激活函数为sigmoid,输出层不使用激活函数
def forward(self, inputs):
# inputs = paddle.reshape(inputs, [inputs.shape[0], 784])
outputs1 = self.fc1(inputs)
outputs1 = F.sigmoid(outputs1)
outputs2 = self.fc2(outputs1)
outputs2 = F.sigmoid(outputs2)
outputs_final = self.fc3(outputs2)
return outputs_final然而,全连接神经网络模型并不适合图像分类模型,图像分类任务需要考虑图像数据的空间性,以及如何分类(波士顿房价预测是回归任务,是回归到一个具体数字,手写数字识别实际上是进行分类判断),对于图像识别和分类任务,我们需要引入卷积神经网络,Softmax激活函数以及交叉熵损失函数,整个流程如下图:

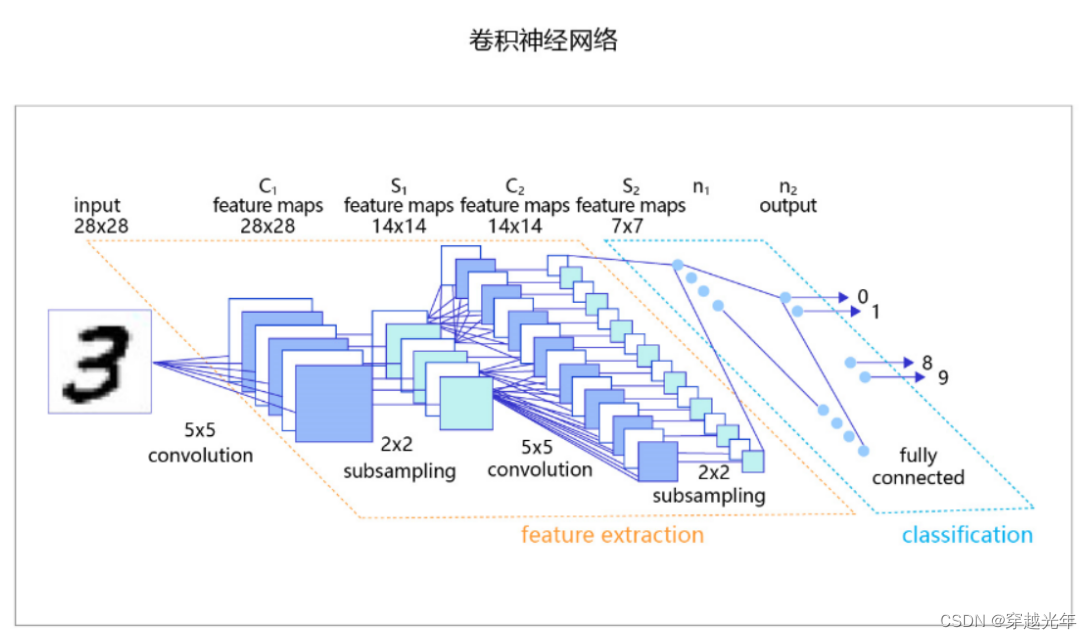
4.2 引入卷积神经网络
图像识别需要考虑数据的空间分布,更适合使用卷积神经网络模型,模型中包含卷积层(convolution)和池化层(subsampling),以及最后一个全连接层(fully connected)
关于卷积神经网络,可以参考这一篇:
PyTorch学习系列教程:卷积神经网络【CNN】 - 知乎
关于卷积核和输入,输出通道,可以参考这一篇:
如何理解卷积神经网络中的通道(channel)_卷积通道数_叹久01的博客-CSDN博客
Python源码 - 卷积神经网络参考代码:
# 定义 SimpleNet 网络结构
import paddle
from paddle.nn import Conv2D, MaxPool2D, Linear
import paddle.nn.functional as F
# 多层卷积神经网络实现
class MNIST(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(MNIST, self).__init__()
# 定义卷积层,输出特征通道out_channels设置为20,卷积核的大小kernel_size为5,卷积步长stride=1,padding=2
self.conv1 = Conv2D(in_channels=1, out_channels=20, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2)
# 定义池化层,池化核的大小kernel_size为2,池化步长为2
self.max_pool1 = MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# 定义卷积层,输出特征通道out_channels设置为20,卷积核的大小kernel_size为5,卷积步长stride=1,padding=2
self.conv2 = Conv2D(in_channels=20, out_channels=20, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2)
# 定义池化层,池化核的大小kernel_size为2,池化步长为2
self.max_pool2 = MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# 定义一层全连接层,输出维度是1
self.fc = Linear(in_features=980, out_features=1)
# 定义网络前向计算过程,卷积后紧接着使用池化层,最后使用全连接层计算最终输出
# 卷积层激活函数使用Relu,全连接层不使用激活函数
def forward(self, inputs):
x = self.conv1(inputs)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.max_pool1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.max_pool2(x)
x = paddle.reshape(x, [x.shape[0], -1])
x = self.fc(x)
return x4.3 分类函数Softmax
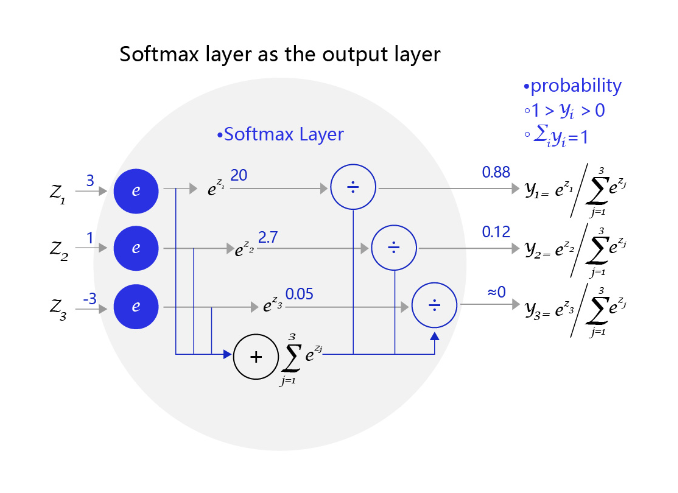
为了进行分类判别,要通过引入Softmax函数到输出层,使得输出层的输出为不同类别概率的集合,并且所有概率之和为1,比如[0.1, 0.2, 0.7]

比如,一个三个标签的分类模型(三分类)使用的Softmax输出层,从中可见原始输出的三个数字3、1、-3,经过Softmax层后转变成加和为1的三个概率值0.88、0.12、0。
4.4 交叉熵损失函数
分类网络模型需要使用交叉熵损失函数不断训练更新模型参数,最终使得交叉熵趋于收敛,从而完成模型训练。
正确解标签对应的输出越大,交叉熵的值越接近0;当输出为1时,交叉熵误差为0。反之,如果正确解标签对应的输出越小,则交叉熵的值越大。

要想搞清楚交叉熵,推荐大家读一下这篇文章:损失函数:交叉熵详解 - 知乎
里面又牵涉到极大似然估计理论,推荐阅读这篇文章:极大似然估计思想的最简单解释_class_brick的博客-CSDN博客
4.5 学习率优化算法
学习率是优化器的一个参数,调整学习率看似是一件非常麻烦的事情,需要不断的调整步长,观察训练时间和Loss的变化。经过研究员的不断的实验,当前已经形成了四种比较成熟的优化算法:SGD、Momentum、AdaGrad和Adam,效果如 图所示。
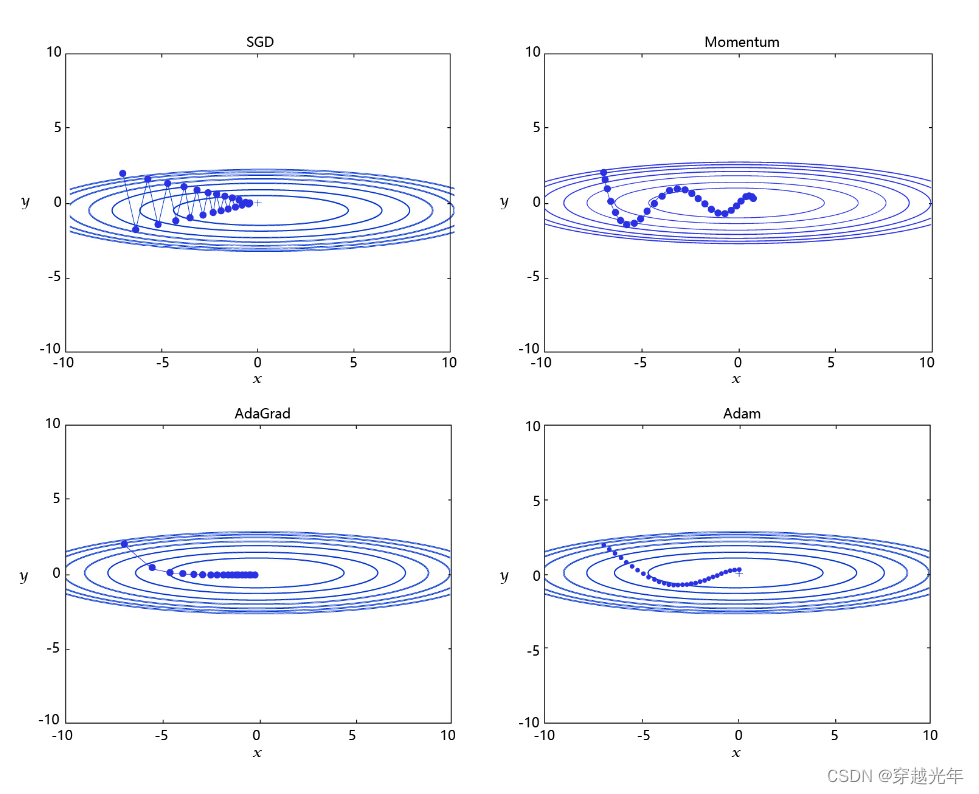
图3: 不同学习率算法效果示意图
- SGD: 随机梯度下降算法,每次训练少量数据,抽样偏差导致的参数收敛过程中震荡。
- Momentum: 引入物理“动量”的概念,累积速度,减少震荡,使参数更新的方向更稳定。
- AdaGrad: 根据不同参数距离最优解的远近,动态调整学习率。学习率逐渐下降,依据各参数变化大小调整学习率。
- Adam: 由于动量和自适应学习率两个优化思路是正交的,因此可以将两个思路结合起来,这就是当前广泛应用的算法。
4.6 图像预处理算法
在计算机视觉中,通常会对图像做一些随机的变化,产生相似但又不完全相同的样本。主要作用是扩大训练数据集,抑制过拟合,提升模型的泛化能力,常用的方法主要有以下几种:
- 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色
- 随机填充
- 随机裁剪
- 随机缩放
- 随机翻转
- 随机打乱真实框排列顺序
下面是分别使用numpy 实现这些数据增强方法。
4.6.1 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等
import numpy as np
import cv2
from PIL import Image, ImageEnhance
import random
# 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等
def random_distort(img):
# 随机改变亮度
def random_brightness(img, lower=0.5, upper=1.5):
e = np.random.uniform(lower, upper)
return ImageEnhance.Brightness(img).enhance(e)
# 随机改变对比度
def random_contrast(img, lower=0.5, upper=1.5):
e = np.random.uniform(lower, upper)
return ImageEnhance.Contrast(img).enhance(e)
# 随机改变颜色
def random_color(img, lower=0.5, upper=1.5):
e = np.random.uniform(lower, upper)
return ImageEnhance.Color(img).enhance(e)
ops = [random_brightness, random_contrast, random_color]
np.random.shuffle(ops)
img = Image.fromarray(img)
img = ops[0](img)
img = ops[1](img)
img = ops[2](img)
img = np.asarray(img)
return img
# 定义可视化函数,用于对比原图和图像增强的效果
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def visualize(srcimg, img_enhance):
# 图像可视化
plt.figure(num=2, figsize=(6,12))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.title('Src Image', color='#0000FF')
plt.axis('off') # 不显示坐标轴
plt.imshow(srcimg) # 显示原图片
# 对原图做 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等 数据增强
srcimg_gtbox = records[0]['gt_bbox']
srcimg_label = records[0]['gt_class']
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.title('Enhance Image', color='#0000FF')
plt.axis('off') # 不显示坐标轴
plt.imshow(img_enhance)
image_path = records[0]['im_file']
print("read image from file {}".format(image_path))
srcimg = Image.open(image_path)
# 将PIL读取的图像转换成array类型
srcimg = np.array(srcimg)
# 对原图做 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等 数据增强
img_enhance = random_distort(srcimg)
visualize(srcimg, img_enhance)
4.6.2 随机填充
# 随机填充
def random_expand(img,
gtboxes,
max_ratio=4.,
fill=None,
keep_ratio=True,
thresh=0.5):
if random.random() > thresh:
return img, gtboxes
if max_ratio < 1.0:
return img, gtboxes
h, w, c = img.shape
ratio_x = random.uniform(1, max_ratio)
if keep_ratio:
ratio_y = ratio_x
else:
ratio_y = random.uniform(1, max_ratio)
oh = int(h * ratio_y)
ow = int(w * ratio_x)
off_x = random.randint(0, ow - w)
off_y = random.randint(0, oh - h)
out_img = np.zeros((oh, ow, c))
if fill and len(fill) == c:
for i in range(c):
out_img[:, :, i] = fill[i] * 255.0
out_img[off_y:off_y + h, off_x:off_x + w, :] = img
gtboxes[:, 0] = ((gtboxes[:, 0] * w) + off_x) / float(ow)
gtboxes[:, 1] = ((gtboxes[:, 1] * h) + off_y) / float(oh)
gtboxes[:, 2] = gtboxes[:, 2] / ratio_x
gtboxes[:, 3] = gtboxes[:, 3] / ratio_y
return out_img.astype('uint8'), gtboxes
# 对原图做 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等 数据增强
srcimg_gtbox = records[0]['gt_bbox']
img_enhance, new_gtbox = random_expand(srcimg, srcimg_gtbox)
visualize(srcimg, img_enhance)
4.6.3 随机裁剪
随机裁剪之前需要先定义两个函数,multi_box_iou_xywh和box_crop这两个函数将被保存在box_utils.py文件中。
import numpy as np
def multi_box_iou_xywh(box1, box2):
"""
In this case, box1 or box2 can contain multi boxes.
Only two cases can be processed in this method:
1, box1 and box2 have the same shape, box1.shape == box2.shape
2, either box1 or box2 contains only one box, len(box1) == 1 or len(box2) == 1
If the shape of box1 and box2 does not match, and both of them contain multi boxes, it will be wrong.
"""
assert box1.shape[-1] == 4, "Box1 shape[-1] should be 4."
assert box2.shape[-1] == 4, "Box2 shape[-1] should be 4."
b1_x1, b1_x2 = box1[:, 0] - box1[:, 2] / 2, box1[:, 0] + box1[:, 2] / 2
b1_y1, b1_y2 = box1[:, 1] - box1[:, 3] / 2, box1[:, 1] + box1[:, 3] / 2
b2_x1, b2_x2 = box2[:, 0] - box2[:, 2] / 2, box2[:, 0] + box2[:, 2] / 2
b2_y1, b2_y2 = box2[:, 1] - box2[:, 3] / 2, box2[:, 1] + box2[:, 3] / 2
inter_x1 = np.maximum(b1_x1, b2_x1)
inter_x2 = np.minimum(b1_x2, b2_x2)
inter_y1 = np.maximum(b1_y1, b2_y1)
inter_y2 = np.minimum(b1_y2, b2_y2)
inter_w = inter_x2 - inter_x1
inter_h = inter_y2 - inter_y1
inter_w = np.clip(inter_w, a_min=0., a_max=None)
inter_h = np.clip(inter_h, a_min=0., a_max=None)
inter_area = inter_w * inter_h
b1_area = (b1_x2 - b1_x1) * (b1_y2 - b1_y1)
b2_area = (b2_x2 - b2_x1) * (b2_y2 - b2_y1)
return inter_area / (b1_area + b2_area - inter_area)
def box_crop(boxes, labels, crop, img_shape):
x, y, w, h = map(float, crop)
im_w, im_h = map(float, img_shape)
boxes = boxes.copy()
boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 2] = (boxes[:, 0] - boxes[:, 2] / 2) * im_w, (
boxes[:, 0] + boxes[:, 2] / 2) * im_w
boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 3] = (boxes[:, 1] - boxes[:, 3] / 2) * im_h, (
boxes[:, 1] + boxes[:, 3] / 2) * im_h
crop_box = np.array([x, y, x + w, y + h])
centers = (boxes[:, :2] + boxes[:, 2:]) / 2.0
mask = np.logical_and(crop_box[:2] <= centers, centers <= crop_box[2:]).all(
axis=1)
boxes[:, :2] = np.maximum(boxes[:, :2], crop_box[:2])
boxes[:, 2:] = np.minimum(boxes[:, 2:], crop_box[2:])
boxes[:, :2] -= crop_box[:2]
boxes[:, 2:] -= crop_box[:2]
mask = np.logical_and(mask, (boxes[:, :2] < boxes[:, 2:]).all(axis=1))
boxes = boxes * np.expand_dims(mask.astype('float32'), axis=1)
labels = labels * mask.astype('float32')
boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 2] = (boxes[:, 0] + boxes[:, 2]) / 2 / w, (
boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]) / w
boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 3] = (boxes[:, 1] + boxes[:, 3]) / 2 / h, (
boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]) / h
return boxes, labels, mask.sum()
# 随机裁剪
def random_crop(img,
boxes,
labels,
scales=[0.3, 1.0],
max_ratio=2.0,
constraints=None,
max_trial=50):
if len(boxes) == 0:
return img, boxes
if not constraints:
constraints = [(0.1, 1.0), (0.3, 1.0), (0.5, 1.0), (0.7, 1.0),
(0.9, 1.0), (0.0, 1.0)]
img = Image.fromarray(img)
w, h = img.size
crops = [(0, 0, w, h)]
for min_iou, max_iou in constraints:
for _ in range(max_trial):
scale = random.uniform(scales[0], scales[1])
aspect_ratio = random.uniform(max(1 / max_ratio, scale * scale), \
min(max_ratio, 1 / scale / scale))
crop_h = int(h * scale / np.sqrt(aspect_ratio))
crop_w = int(w * scale * np.sqrt(aspect_ratio))
crop_x = random.randrange(w - crop_w)
crop_y = random.randrange(h - crop_h)
crop_box = np.array([[(crop_x + crop_w / 2.0) / w,
(crop_y + crop_h / 2.0) / h,
crop_w / float(w), crop_h / float(h)]])
iou = multi_box_iou_xywh(crop_box, boxes)
if min_iou <= iou.min() and max_iou >= iou.max():
crops.append((crop_x, crop_y, crop_w, crop_h))
break
while crops:
crop = crops.pop(np.random.randint(0, len(crops)))
crop_boxes, crop_labels, box_num = box_crop(boxes, labels, crop, (w, h))
if box_num < 1:
continue
img = img.crop((crop[0], crop[1], crop[0] + crop[2],
crop[1] + crop[3])).resize(img.size, Image.LANCZOS)
img = np.asarray(img)
return img, crop_boxes, crop_labels
img = np.asarray(img)
return img, boxes, labels
# 对原图做 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等 数据增强
srcimg_gtbox = records[0]['gt_bbox']
srcimg_label = records[0]['gt_class']
img_enhance, new_labels, mask = random_crop(srcimg, srcimg_gtbox, srcimg_label)
visualize(srcimg, img_enhance)
4.6.4 随机缩放
# 随机缩放
def random_interp(img, size, interp=None):
interp_method = [
cv2.INTER_NEAREST,
cv2.INTER_LINEAR,
cv2.INTER_AREA,
cv2.INTER_CUBIC,
cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4,
]
if not interp or interp not in interp_method:
interp = interp_method[random.randint(0, len(interp_method) - 1)]
h, w, _ = img.shape
im_scale_x = size / float(w)
im_scale_y = size / float(h)
img = cv2.resize(
img, None, None, fx=im_scale_x, fy=im_scale_y, interpolation=interp)
return img
# 对原图做 随机缩放
img_enhance = random_interp(srcimg, 640)
visualize(srcimg, img_enhance)4.6.5 随机翻转
# 随机翻转
def random_flip(img, gtboxes, thresh=0.5):
if random.random() > thresh:
img = img[:, ::-1, :]
gtboxes[:, 0] = 1.0 - gtboxes[:, 0]
return img, gtboxes
# 对原图做 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等 数据增强
img_enhance, box_enhance = random_flip(srcimg, srcimg_gtbox)
visualize(srcimg, img_enhance)4.6.6 随机打乱真实框排列顺序
# 随机打乱真实框排列顺序
def shuffle_gtbox(gtbox, gtlabel):
gt = np.concatenate(
[gtbox, gtlabel[:, np.newaxis]], axis=1)
idx = np.arange(gt.shape[0])
np.random.shuffle(idx)
gt = gt[idx, :]
return gt[:, :4], gt[:, 4]