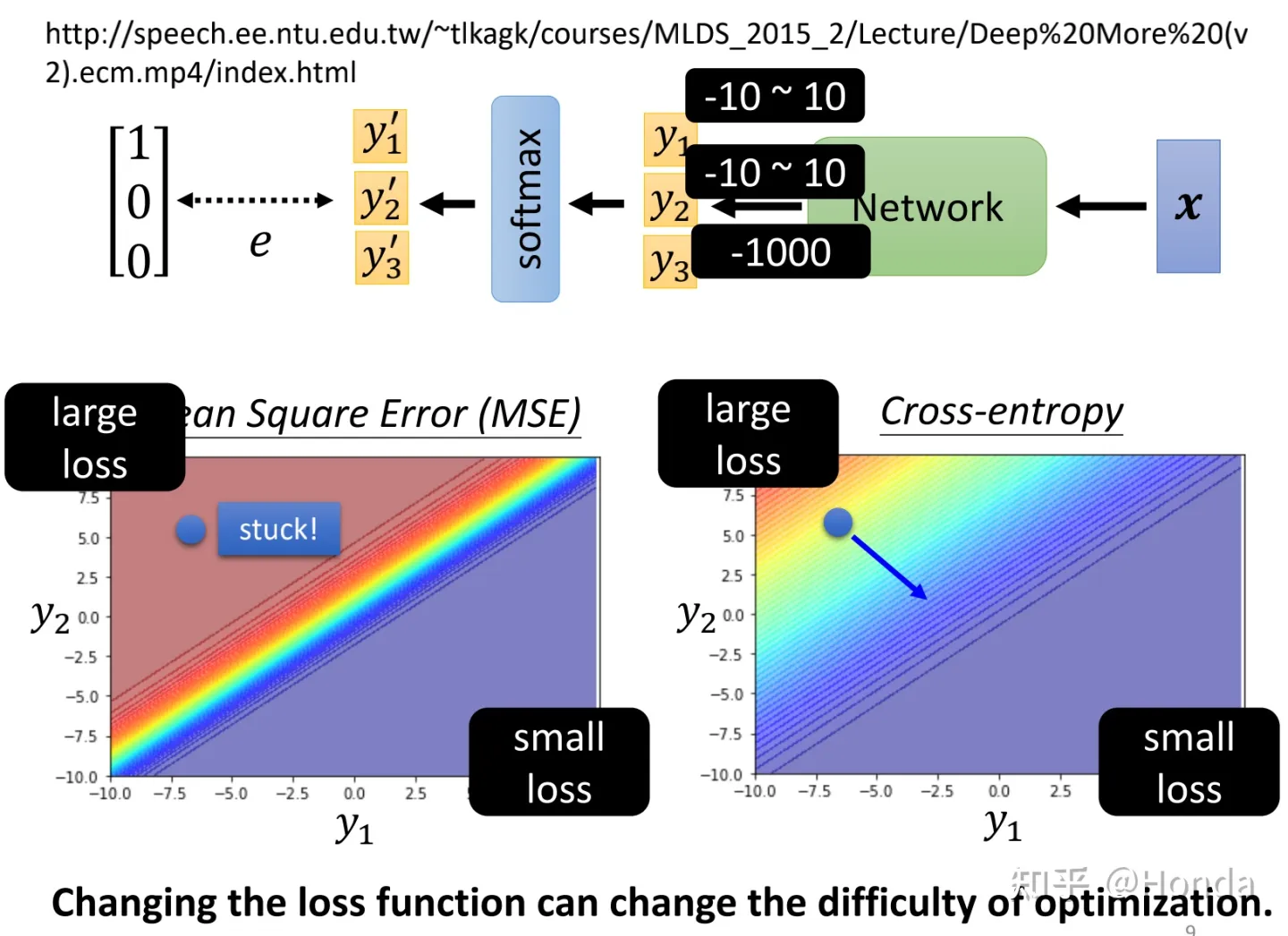
Spring MVC阶段测试
1.新建Maven项目,静态资源文件,如JS、CSS、图片应存放在( C )目录下。
A、src/main/java
B、src/test/java
C、src/main/resources/static
D、src/main/resources/templates
2.新建Maven项目,Web的模板文件应存放在( A )目录下。
A、src/main/java
B、src/test/java
C、src/main/resources/static
D、src/main/resources/templates
3.Spring Booot项目的全局配置文件application.properties存放的目录为( C )。
A、src/main/java
B、src/test/java
C、src/main/resources
D、src/main/resources/static
4.控制器中有一个成员变量,已经在Spring配置文件中声明,要将这个成员变量注入的注解是(C )。
A、@RequestMapping
B、@RequestParam
C、@Autowired
D、@Controller
解析:成员变量:在类体的变量部分中定义的变量,也称为属性。
成员变量:定义在类中,方法体之外。变量在创建对象时实例化。成员变量可被类中的方法、构造方法以及特定类的语句块访问。
public interface IUserService { 成员变量 public boolean insertUser(User user);{ // 其他代码 }}
@Autowired
private IUserService IUserService = null;
5.用于从请求URL中获取参数并映射到方法参数中的注解是( B)。
A、@RequestMapping
B、@RequestParam
C、@PathVariable
D、@RequestBody
解析:
@RequestParam
每个参数都已Key=Value的形式跟在url的后方,@RequestParam可以获取url后面参数中与自己所定义的参数名的值并注入到所注解的参数中。
// url:xxx?name=值&age=值
@GetMapping("test")
public String test2(@RequestParam("name")String name){
return name;
}
6.将一个请求URL指向一个类的方法的注解是( D )。
A、@Autowired
B、@Controller
C、@RequestParam
D、@RequestMapping
解析:
@Controller
public class MainController {
@RequestMapping("/main")
//具体代码
}
7.将前台form表单input控件中的name属性,绑定到控制器类中的方法参数所使用的注解是( A )。
A、@RequestParam
B、@Controller
C、@RequestMapping
D、@Autowired
解析:
public ModelAndView login(@RequestParam("loginName") String loginName, @RequestParam("password") String password, ModelAndView mv)
8.下面关于Model 和ModelAndView说法不正确的是( D )。
A、ModelAndView类用来存储处理完后的结果数据,以及显示该数据的视图。
B、Model类只是用来传输数据
C、ModelAndView类使用addObject方法存储数据
D、Model类使用addObject方法存储数据
解析:C:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.ui;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
public interface Model {
Model addAttribute(String var1, @Nullable Object var2);
Model addAttribute(Object var1);
Model addAllAttributes(Collection<?> var1);
Model addAllAttributes(Map<String, ?> var1);
Model mergeAttributes(Map<String, ?> var1);
boolean containsAttribute(String var1);
@Nullable
Object getAttribute(String var1);
Map<String, Object> asMap();
}
D:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.web.servlet;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
public class ModelAndView {
@Nullable
private Object view;
@Nullable
private ModelMap model;
@Nullable
private HttpStatus status;
private boolean cleared = false;
public ModelAndView() {
}
public ModelAndView(String viewName) {
this.view = viewName;
}
public ModelAndView(View view) {
this.view = view;
}
public ModelAndView(String viewName, @Nullable Map<String, ?> model) {
this.view = viewName;
if (model != null) {
this.getModelMap().addAllAttributes(model);
}
}
public ModelAndView(View view, @Nullable Map<String, ?> model) {
this.view = view;
if (model != null) {
this.getModelMap().addAllAttributes(model);
}
}
public ModelAndView(String viewName, HttpStatus status) {
this.view = viewName;
this.status = status;
}
public ModelAndView(@Nullable String viewName, @Nullable Map<String, ?> model, @Nullable HttpStatus status) {
this.view = viewName;
if (model != null) {
this.getModelMap().addAllAttributes(model);
}
this.status = status;
}
public ModelAndView(String viewName, String modelName, Object modelObject) {
this.view = viewName;
this.addObject(modelName, modelObject);
}
public ModelAndView(View view, String modelName, Object modelObject) {
this.view = view;
this.addObject(modelName, modelObject);
}
public void setViewName(@Nullable String viewName) {
this.view = viewName;
}
@Nullable
public String getViewName() {
return this.view instanceof String ? (String)this.view : null;
}
public void setView(@Nullable View view) {
this.view = view;
}
@Nullable
public View getView() {
return this.view instanceof View ? (View)this.view : null;
}
public boolean hasView() {
return this.view != null;
}
public boolean isReference() {
return this.view instanceof String;
}
@Nullable
protected Map<String, Object> getModelInternal() {
return this.model;
}
public ModelMap getModelMap() {
if (this.model == null) {
this.model = new ModelMap();
}
return this.model;
}
public Map<String, Object> getModel() {
return this.getModelMap();
}
public void setStatus(@Nullable HttpStatus status) {
this.status = status;
}
@Nullable
public HttpStatus getStatus() {
return this.status;
}
public ModelAndView addObject(String attributeName, @Nullable Object attributeValue) {
this.getModelMap().addAttribute(attributeName, attributeValue);
return this;
}
public ModelAndView addObject(Object attributeValue) {
this.getModelMap().addAttribute(attributeValue);
return this;
}
public ModelAndView addAllObjects(@Nullable Map<String, ?> modelMap) {
this.getModelMap().addAllAttributes(modelMap);
return this;
}
public void clear() {
this.view = null;
this.model = null;
this.cleared = true;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.view == null && CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.model);
}
public boolean wasCleared() {
return this.cleared && this.isEmpty();
}
public String toString() {
return "ModelAndView [view=" + this.formatView() + "; model=" + this.model + "]";
}
private String formatView() {
return this.isReference() ? "\"" + this.view + "\"" : "[" + this.view + "]";
}
}
9.在MVC模式中执行数据库操作,访问数据库的功能类属于MVC中哪一个组件( A )。
A、M-模型
B、V-视图
C、C-控制器
D、M-控制器
解析:目前市面上流行的实际分层方式[ S - D(M) - V - C ]:
以前,很多人认为可以直接在Controller层就调用model层来进行数据库的交互。但是这是不严谨的,耦合性太强,违背了MVC的初衷,即解耦。所以随着MVC学习的深入,慢慢地又加入到了业务层Service和数据访问层Dao:
D(Dao)数据访问对象——与数据库建立连接,封装了对数据库的CURD操作
S(Service)业务逻辑模型——做一些业务逻辑地处理,并给Controller返回结果
V(View)视图——是展示给用户的最终页面。视图负责将数据以用户友好的形式展现出来,负责收集展示数据。
C(Controller)控制器——接收用户传递过来的数据,将数据封装到实体类中,调用业务逻辑模型,进行业务逻辑的处理,根据业务逻辑模型返回的结果,进行不同的视图跳转。
10.在MVC模式中负责接收用户请求并将请求转发的组件是( C )。
A、M-模型
B、V-视图
C、C-控制器
D、M-控制器
11.下列关于@RequestMapping注解,正确的说法是( C )。
A、只能作用在方法上
B、只能作用在类上
C、 既可以作用在方法上,也可作用在类上
D、以上说法均不正确
解析:
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/user")
public class UserController {
// 注入用户服务类
@Autowired
private IUserService IUserService = null;
//测试thymeleaf
//URL:http://127.0.0.1:3000/user/hello
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello")
public String index(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("name", "cai4");
return "index";
}
//显示数据 URL:http://127.0.0.1:3000/user/list
@RequestMapping(value = "/list")
@ResponseBody
public List<User> list(){
//访问模型层得到数据
List<User> users = IUserService.showUserAll();
return users;
}
}
以下controller方法,可以在下划线处插入并且能够在浏览器端输出“hello,world”字符串的是( A )。
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String say( ){
return " hello,world ";
}
A、@ResponseBody
B、@Autowired
C、ModelAndView
D、Model
13.访问以下controller类代码中的getById方法,假设输入参数id值为2,正确的访问路径是( B )。
@RequestMapping(path="/user/{id}",method=RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody User getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
return userService.getUserById(id);
}
A、/user/id=2
B、/user/2
C、/user?id=2
D、/user/{id}=2
解析:
http://127.0.0.1:3000/user/1
14.实现重定向到“main.html”页面正确的代码是(A )。
A、@RequestMapping("/login")
@ResponseBody
public String login( ){ return "redirect:/ main.html"; }
B、@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login( ){ return "redirect:/ main.html"; }
C、@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login( ){ return "main.html"; }
D、@RequestMapping("/login")
@ResponseBody
public String login( ){ return "main.html"; }
解析:
@ResponseBody注解
在Handler方法上添加该注解之后,方法的返回值将以字符串的形式直接响应给浏览器。
重定向
方式一:使用 "redirect" 关键字(不是指java关键字),注意:类的注解不能使用@RestController,要用@Controller;因为@RestController内含@ResponseBody,解析返回的是json串。不是跳转页面
@RequestMapping(value="/test/test01/{name}" , method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String test(@PathVariable String name) {
return "redirect:/ceng/hello.html";
}
方式二:使用servlet 提供的API,注意:类的注解可以使用@RestController,也可以使用@Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/test/test01/{name}" , method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void test(@PathVariable String name, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
response.sendRedirect("/ceng/hello.html");
}
请求转发
方式一:使用 "forward" 关键字(不是指java关键字),注意:类的注解不能使用@RestController 要用@Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/test/test01/{name}" , method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String test(@PathVariable String name) {
return "forword:/ceng/hello.html";
}
方式二:使用servlet 提供的API,注意:类的注解可以使用@RestController,也可以使用@Controller
方式二:使用servlet 提供的API,注意:类的注解可以使用@RestController,也可以使用@Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/test/test01/{name}" , method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void test(@PathVariable String name, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
request.getRequestDispatcher("/ceng/hello.html").forward(request,response);
}
15.自定义拦截器要实现( C )接口。
A、Interceptor
B、AbstractInterceptor
C、HandlerInterceptor
D、Validator
解析:
public class Interceptor1 implements HandlerInterceptor{}
16.以下关于拦截器方法说法错误的是( D)。
A、preHandle方法在调用Controller方法前会调用此方法。
B、postHandle方法在调用Controller方法后、页面渲染之前调用此方法
C、afterCompletion方法在页面渲染之后调用
D、postHandle方法在页面渲染之后调用
解析:
preHandle
调用时间:Controller方法处理之前
执行顺序:链式Intercepter情况下,Intercepter按照声明的顺序一个接一个执行
若返回false,则中断执行,注意:不会进入afterCompletion
postHandle
调用前提:preHandle返回true
调用时间:Controller方法处理完之后,DispatcherServlet进行视图的渲染之前,也就是说在这个方法中你可以对ModelAndView进行操作
执行顺序:链式Intercepter情况下,Intercepter按照声明的顺序倒着执行。
备注:postHandle虽然post打头,但post、get方法都能处理
afterCompletion
调用前提:preHandle返回true
调用时间:DispatcherServlet进行视图的渲染之后
多用于清理资源
17.以下代码清单为控制器类实现,启动Spring Boot应用后,在浏览器中输入请求URL:http://localhost:8080/user1/1,运行结果如图所示。
请补充完整代码。(注意:输入答案时区分大小写,标点符号为英文状态下输入。)
@GetMapping("(1) ")
//响应为JSON数据集
(2)
public User get((3) Integer id) {
return userService.getUser(id);
}
1、/user1/{id}
2、@ResponseBody
3、@PathVariable("id")
{id}的注解是@PathVariable("id")
而如果是?id=1则使用@RequestParam(value = "id")
18.以下代码清单实现单文件上传,运行结果如图所示,请补充完整代码。(注意:输入答案时区分大小写,标点符号为英文状态下输入。)
URL地址栏输入 http://localhost:8080/upload/page

图1 文件上传页面

图2 选择文件
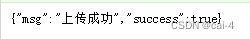
图3 文件上传结果
1)上传文件JSP /WEB-INF/jsp/file/upload.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<html>
<body>
<form method="(1) "
action="/upload /multipart" enctype="(2) ">
<input type="file" name="photo" value="请选择上传的文件" />
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
2)文件上传控制器
package com.springmvc.chapter0320191007.controller;
(3)
public class FileController {
(4)
public (5) Map<String, Object> upload((6) ("photo") (7) photo)
{
String path = "d:/uploaded/";//保存路径
String filename = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS").format(new Date());
//获取上传文件的后缀suffix
String suffix = photo.getOriginalFilename().substring(photo.getOriginalFilename().lastIndexOf("."));
try {
//Spring提供了文件操作类FileCopyUtils
FileCopyUtils.copy(photo.getInputStream(), new FileOutputStream(path + filename + suffix));
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
return (8) (false, "上传失败");
}
return (9) (true, "上传成功");
}
// 处理上传文件结果
private Map<String, Object> dealResultMap(boolean success, String msg) {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<String, Object>();
result.put("success", success);
result.put("msg", msg);
return (10) ;
}
}
1、post
2、multipart/form-data
3、@Controller
4、@PostMapping("/upload/page")
5、@ResponseBody
6、@RequestParam
7、MultipartFile[]
8、dealResultMap
9、dealResultMap
10、result
以下代码清单为拦截器的使用,请补充完整代码。(注意:输入答案时区分大小写,标点符号为英文状态下输入。)
// 自定义简单拦截器Interceptor1
public class Interceptor1 implements (1) {
@Override
public boolean (2) (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("处理器前方法");
// 返回true,不会拦截后续的处理
return true;
}
@Override
public void (3) (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,
ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("处理器后方法");
}
@Override
public void (4) (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("处理器完成方法");
}
}
//注册拦截器
@Configuration
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages="com.springmvc.chapter0320191007")
public class App1 implements WebMvcConfigurer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
SpringApplication.run(App1.class, args);
}
@Override
public void (5) (InterceptorRegistry registry) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
InterceptorRegistration ir=registry.addInterceptor((6) );
// 拦截interceptor路径下所有请求
ir.addPathPatterns("(7) ");
}
}
1、HandlerInterceptor
2、preHandle
3、postHandle
4、afterCompletion
5、addInterceptors
6、new Interceptor1()
7、/**
20.程序实现如下功能。在浏览器中输入URL测试应用
http://localhost:8080/
显示用户登录页面,如图1所示,登录成功后跳转到图2所示页面。请补充完整代码。(注意:输入答案时区分大小写,标点符号为英文状态下输入。)
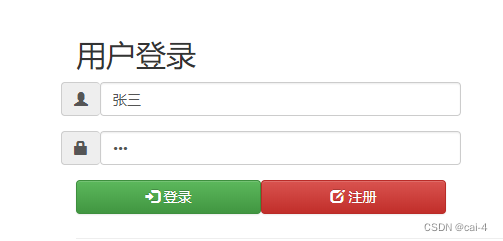
图1 用户登录页面

图2 登录成功后跳转的页面
1) 静态页面index.html 核心代码:
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
。。。。。
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function(){
$("#loginbtn").click(function(){
var loginName = $("#loginName");
var password = $("#password");
var msg = "";
if(loginName.val() == ""){
msg = "登录名不能为空!";
loginName.focus();
}else if(password.val() == ""){
msg = "密码不能为空!";
password.focus();
}
if(msg != ""){
alert(msg);
}else{
$("#loginform").submit();
}
})
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
用户登录
<form action="login" method="post" id="loginform">
<input th="text" name="loginName" id="loginName" />
<input th="password" name="password" id="password" />
<button th="button" id="loginbtn"> 登录</button>
<button th="button" id="registerbtn"> 注册</button>
</body>
</html>
2) 通过控制类访问index.html
package nuc.edu.cn.chapter03.controller;
/***Import***/
(1)
public class IndexController {
//Spring MVC会自动生成视图,并且绑定数据模型
public String index(Model model) {
System.out.println("IndexController index方法被调用。。。。");
return "index";
}
}
3)处理请求的控制类LoginController
package nuc.edu.cn.chapter03.controller;
/***Import***/
(2)
public class LoginController {
@PostMapping("(3) ")
public ModelAndView login(
(4) String loginName,
(5) String password,
ModelAndView mv) {
System.out.println("LoginController login方法被调用。。。");
System.out.println("LoginController 登录名 :"+loginName+
" 密码:"+password);
mv.setViewName("redirect:/main");
return mv;
}
}
4)处理请求的控制类 MainController
package nuc.edu.cn.chapter03.controller;
/***Import***/
@Controller
public class MainController {
@RequestMapping(" (6) ")
public String main() {
System.out.println("MainController main方法被调用。。。");
//根据Thymeleaf默认模板,将返回resources/templates/main.html
return "main";
}
}
5)静态页面main.html 核心代码:
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
。。。。
</head>
<body>
<a th:href=" #">测试表达式访问数据</a><br/>
<a th:href=" #">测试条件判断</a><br/>
<a th:href=" #">测试循环</a><br/>
</body>
</html>
1、@Controller
2、@Controller
3、/main
4、@RequestParam("loginName")
5、@RequestParam("password")
6、/main