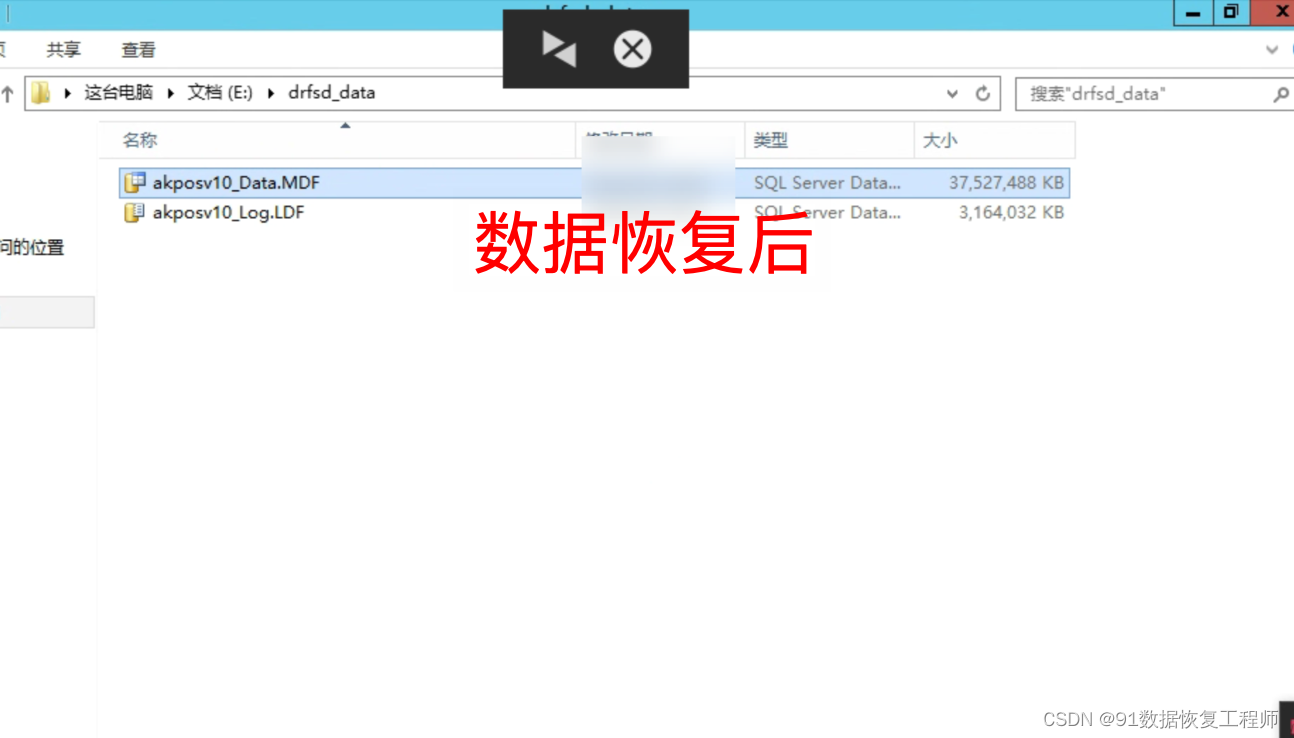
这场比较郁闷,C题短路,连续4次WA,导致罚时太多
A - Arithmetic Progression
Problem Statement
Print an arithmetic sequence with first term
A
A
A, last term
B
B
B, and common difference
D
D
D.
You are only given inputs for which such an arithmetic sequence exists.
Constraints
1
≤
A
≤
B
≤
100
1 \leq A \leq B \leq 100
1≤A≤B≤100
1
≤
D
≤
100
1 \leq D \leq 100
1≤D≤100
There is an arithmetic sequence with first term
A
A
A, last term
B
B
B, and common difference
D
D
D.
All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
A A A B B B D D D
Output
Print the terms of the arithmetic sequence with first term A A A, last term B B B, and common difference D D D, in order, separated by spaces.
Sample Input 1
3 9 2
Sample Output 1
3 5 7 9
The arithmetic sequence with first term 3 3 3, last term 9 9 9, and common difference 2 2 2 is ( 3 , 5 , 7 , 9 ) (3,5,7,9) (3,5,7,9).
Sample Input 2
10 10 1
Sample Output 2
10
The arithmetic sequence with first term 10 10 10, last term 10 10 10, and common difference 1 1 1 is ( 10 ) (10) (10).
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
signed main()
{
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
int A, B, C;
cin >> A >> B >> C;
for (int i = A; i <= B; i += C)
cout << i << " ";
return 0;
}
B - Append
Problem Statement
You have an empty sequence
A
A
A. There are
Q
Q
Q queries given, and you need to process them in the order they are given.
The queries are of the following two types:
1 x: Append
x
x
x to the end of
A
A
A.
2 k: Find the
k
k
k-th value from the end of
A
A
A. It is guaranteed that the length of
A
A
A is at least
k
k
k when this query is given.
Constraints
1
≤
Q
≤
100
1 \leq Q \leq 100
1≤Q≤100
In the first type of query,
x
x
x is an integer satisfying
1
≤
x
≤
1
0
9
1 \leq x \leq 10^9
1≤x≤109.
In the second type of query,
k
k
k is a positive integer not greater than the current length of sequence
A
A
A.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
Q
Q
Q
q
u
e
r
y
1
\mathrm{query}_1
query1
q
u
e
r
y
2
\mathrm{query}_2
query2
⋮
\vdots
⋮
q
u
e
r
y
Q
\mathrm{query}_Q
queryQ
Each query is in one of the following two formats:
1 1 1 x x x
2 2 2 k k k
Output
Print
q
q
q lines, where
q
q
q is the number of queries of the second type.
The
i
i
i-th line should contain the answer to the
i
i
i-th such query.
Sample Input 1
5
1 20
1 30
2 1
1 40
2 3
Sample Output 1
30
20
Initially,
A
A
A is empty.
The first query appends
20
20
20 to the end of
A
A
A, making
A
=
(
20
)
A=(20)
A=(20).
The second query appends
30
30
30 to the end of
A
A
A, making
A
=
(
20
,
30
)
A=(20,30)
A=(20,30).
The answer to the third query is
30
30
30, which is the
1
1
1-st value from the end of
A
=
(
20
,
30
)
A=(20,30)
A=(20,30).
The fourth query appends
40
40
40 to the end of
A
A
A, making
A
=
(
20
,
30
,
40
)
A=(20,30,40)
A=(20,30,40).
The answer to the fifth query is
20
20
20, which is the
3
3
3-rd value from the end of
A
=
(
20
,
30
,
40
)
A=(20,30,40)
A=(20,30,40).
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
signed main()
{
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
int Q;
cin >> Q;
std::vector<int> S;
while (Q --)
{
int Op, X;
cin >> Op >> X;
if (Op == 1)
S.push_back(X);
else
cout << S[S.size() - X] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
C - Divide and Divide
Problem Statement
There is a single integer
N
N
N written on a blackboard.
Takahashi will repeat the following series of operations until all integers not less than
2
2
2 are removed from the blackboard:
Choose one integer
x
x
x not less than
2
2
2 written on the blackboard.
Erase one occurrence of
x
x
x from the blackboard. Then, write two new integers
⌊
x
2
⌋
\left \lfloor \dfrac{x}{2} \right\rfloor
⌊2x⌋ and
⌈
x
2
⌉
\left\lceil \dfrac{x}{2} \right\rceil
⌈2x⌉ on the blackboard.
Takahashi must pay
x
x
x yen to perform this series of operations.
Here,
⌊
a
⌋
\lfloor a \rfloor
⌊a⌋ denotes the largest integer not greater than
a
a
a, and
⌈
a
⌉
\lceil a \rceil
⌈a⌉ denotes the smallest integer not less than
a
a
a.
What is the total amount of money Takahashi will have paid when no more operations can be performed?
It can be proved that the total amount he will pay is constant regardless of the order in which the operations are performed.
Constraints
2 ≤ N ≤ 1 0 17 2 \leq N \leq 10^{17} 2≤N≤1017
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N N N
Output
Print the total amount of money Takahashi will have paid, in yen.
Sample Input 1
3
Sample Output 1
5
Here is an example of how Takahashi performs the operations:
Initially, there is one
3
3
3 written on the blackboard.
He chooses
3
3
3. He pays
3
3
3 yen, erases one
3
3
3 from the blackboard, and writes
⌊
3
2
⌋
=
1
\left \lfloor \dfrac{3}{2} \right\rfloor = 1
⌊23⌋=1 and
⌈
3
2
⌉
=
2
\left\lceil \dfrac{3}{2} \right\rceil = 2
⌈23⌉=2 on the blackboard.
There is one
2
2
2 and one
1
1
1 written on the blackboard.
He chooses
2
2
2. He pays
2
2
2 yen, erases one
2
2
2 from the blackboard, and writes
⌊
2
2
⌋
=
1
\left \lfloor \dfrac{2}{2} \right\rfloor = 1
⌊22⌋=1 and
⌈
2
2
⌉
=
1
\left\lceil \dfrac{2}{2} \right\rceil = 1
⌈22⌉=1 on the blackboard.
There are three
1
1
1s written on the blackboard.
Since all integers not less than
2
2
2 have been removed from the blackboard, the process is finished.
Takahashi has paid a total of
3
+
2
=
5
3 + 2 = 5
3+2=5 yen for the entire process, so print
5
5
5.
Sample Input 2
340
Sample Output 2
2888
Sample Input 3
100000000000000000
Sample Output 3
5655884811924144128
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline __int128 read()
{
char ch = getchar();
__int128 x = 0, cf = 1;
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-') cf = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return x * cf;
}
void write(__int128 x)
{
if(x<0)
putchar('-'),x=-x;
if(x>9)
write(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
return;
}
__int128 Quick_Pow(__int128 a, __int128 b)
{
__int128 Result = 1;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1) Result = Result * a;
a = a * a;
b >>= 1;
}
return Result;
}
signed main()
{
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
__int128 N = read();
__int128 T = 0, T2 = 0;
while (Quick_Pow(2, T + 1) <= 4 * N) T ++;
while (Quick_Pow(2, T2 + 1) <= 2 * N) T2 ++;
__int128 Result = N * T - Quick_Pow(2, T2);
write(Result);
return 0;
}
D - Super Takahashi Bros.
Problem Statement
Takahashi is playing a game.
The game consists of
N
N
N stages numbered
1
,
2
,
…
,
N
1,2,\ldots,N
1,2,…,N. Initially, only stage
1
1
1 can be played.
For each stage
i
i
i (
1
≤
i
≤
N
−
1
1\leq i \leq N-1
1≤i≤N−1 ) that can be played, you can perform one of the following two actions at stage
i
i
i:
Spend
A
i
A_i
Ai seconds to clear stage
i
i
i. This allows you to play stage
i
+
1
i+1
i+1.
Spend
B
i
B_i
Bi seconds to clear stage
i
i
i. This allows you to play stage
X
i
X_i
Xi.
Ignoring the times other than the time spent to clear the stages, how many seconds will it take at the minimum to be able to play stage
N
N
N?
Constraints
2
≤
N
≤
2
×
1
0
5
2 \leq N \leq 2\times 10^5
2≤N≤2×105
1
≤
A
i
,
B
i
≤
1
0
9
1 \leq A_i, B_i \leq 10^9
1≤Ai,Bi≤109
1
≤
X
i
≤
N
1 \leq X_i \leq N
1≤Xi≤N
All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N
N
N
A
1
A_1
A1
B
1
B_1
B1
X
1
X_1
X1
A
2
A_2
A2
B
2
B_2
B2
X
2
X_2
X2
⋮
\vdots
⋮
A
N
−
1
A_{N-1}
AN−1
B
N
−
1
B_{N-1}
BN−1
X
N
−
1
X_{N-1}
XN−1
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
5
100 200 3
50 10 1
100 200 5
150 1 2
Sample Output 1
350
By acting as follows, you will be allowed to play stage
5
5
5 in
350
350
350 seconds.
Spend
100
100
100 seconds to clear stage
1
1
1, which allows you to play stage
2
2
2.
Spend
50
50
50 seconds to clear stage
2
2
2, which allows you to play stage
3
3
3.
Spend
200
200
200 seconds to clear stage
3
3
3, which allows you to play stage
5
5
5.
Sample Input 2
10
1000 10 9
1000 10 10
1000 10 2
1000 10 3
1000 10 4
1000 10 5
1000 10 6
1000 10 7
1000 10 8
Sample Output 2
90
Sample Input 3
6
1000000000 1000000000 1
1000000000 1000000000 1
1000000000 1000000000 1
1000000000 1000000000 1
1000000000 1000000000 1
Sample Output 3
5000000000
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int SIZE = 8e5 + 10;
int N;
int A[SIZE], B[SIZE], X[SIZE];
int h[SIZE], w[SIZE], e[SIZE], ne[SIZE], idx;
bool st[SIZE];
int dist[SIZE];
inline void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = c, h[a] = idx ++;
}
inline int Dijkstra(int start, int finish)
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> heap;
heap.push({0, start});
st[start] = 1;
while (heap.size())
{
auto t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int u = t.second, dis = t.first;
for (int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i])
if (dist[e[i]] > w[i] + dis)
dist[e[i]] = w[i] + dis, heap.push({dist[e[i]], e[i]});
}
if (dist[finish] == 0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
return dist[finish];
}
signed main()
{
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
cin >> N;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i ++)
{
cin >> A[i] >> B[i] >> X[i];
add(i, i + 1, A[i]), add(i, X[i], B[i]);
}
cout << Dijkstra(1, N) << endl;
return 0;
}
E - Mancala 2
Problem Statement
There are
N
N
N boxes numbered
0
0
0 to
N
−
1
N-1
N−1. Initially, box
i
i
i contains
A
i
A_i
Ai balls.
Takahashi will perform the following operations for
i
=
1
,
2
,
…
,
M
i=1,2,\ldots,M
i=1,2,…,M in order:
Set a variable
C
C
C to
0
0
0.
Take out all the balls from box
B
i
B_i
Bi and hold them in hand.
While holding at least one ball in hand, repeat the following process:
Increase the value of
C
C
C by
1
1
1.
Put one ball from hand into box
(
B
i
+
C
)
m
o
d
N
(B_i+C) \bmod N
(Bi+C)modN.
Determine the number of balls in each box after completing all operations.
Constraints
1
≤
N
≤
2
×
1
0
5
1 \leq N \leq 2\times 10^5
1≤N≤2×105
1
≤
M
≤
2
×
1
0
5
1 \leq M \leq 2\times 10^5
1≤M≤2×105
0
≤
A
i
≤
1
0
9
0 \leq A_i \leq 10^9
0≤Ai≤109
KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '&' at position 12: 0 \leq B_i &̲lt; N
All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N
N
N
M
M
M
A
0
A_0
A0
A
1
A_1
A1
…
\ldots
…
A
N
−
1
A_{N-1}
AN−1
B
1
B_1
B1
B
2
B_2
B2
…
\ldots
…
B
M
B_M
BM
Output
Let X i X_i Xi be the number of balls in box i i i after completing all operations. Print X 0 , X 1 , … , X N − 1 X_0,X_1,\ldots,X_{N-1} X0,X1,…,XN−1 in this order, separated by spaces.
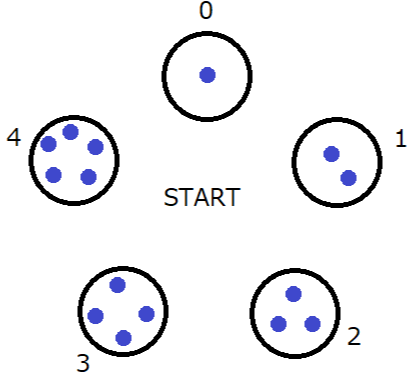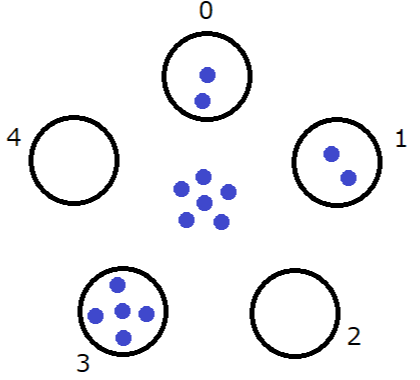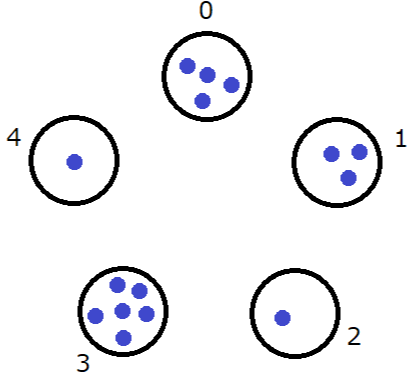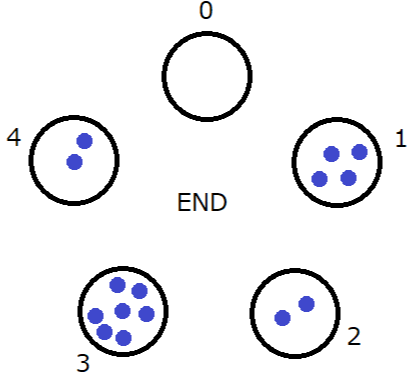
Sample Input 1
5 3
1 2 3 4 5
2 4 0
Sample Output 1
0 4 2 7 2
The operations proceed as follows:
Sample Input 2
3 10
1000000000 1000000000 1000000000
0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
Sample Output 2
104320141 45436840 2850243019
Sample Input 3
1 4
1
0 0 0 0
Sample Output 3
1
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int SIZE = 2e5 + 10;
int N, M;
int A[SIZE], B[SIZE];
struct Segment
{
struct Node
{
int l, r;
LL Sum, Max, Min, Lazy;
}Tree[SIZE << 2];
void Pushup(int u)
{
Tree[u].Sum = Tree[u << 1].Sum + Tree[u << 1 | 1].Sum;
Tree[u].Max = max(Tree[u << 1].Max, Tree[u << 1 | 1].Max);
Tree[u].Min = min(Tree[u << 1].Min, Tree[u << 1 | 1].Min);
}
void Pushdown(int u)
{
if (Tree[u].Lazy)
{
Tree[u << 1].Max += Tree[u].Lazy;
Tree[u << 1].Min += Tree[u].Lazy;
Tree[u << 1].Sum += (LL)(Tree[u << 1].r - Tree[u << 1].l + 1) * Tree[u].Lazy;
Tree[u << 1].Lazy += Tree[u].Lazy;
Tree[u << 1 | 1].Max += Tree[u].Lazy;
Tree[u << 1 | 1].Min += Tree[u].Lazy;
Tree[u << 1 | 1].Sum += (LL)(Tree[u << 1 | 1].r - Tree[u << 1 | 1].l + 1) * Tree[u].Lazy;
Tree[u << 1 | 1].Lazy += Tree[u].Lazy;
Tree[u].Lazy = 0;
}
}
void Build(int u, int l, int r)
{
Tree[u] = {l, r};
if (l == r) return;
int mid = l + r >> 1;
Build(u << 1, l, mid), Build(u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r);
}
void Modify(int u, int l, int r, int d)
{
if (Tree[u].l >= l && Tree[u].r <= r)
{
Tree[u].Sum += (LL)(Tree[u].r - Tree[u].l + 1) * d;
Tree[u].Max += d, Tree[u].Min += d;
Tree[u].Lazy += d;
return;
}
Pushdown(u);
int mid = Tree[u].l + Tree[u].r >> 1;
if (mid >= l) Modify(u << 1, l, r, d);
if (mid < r) Modify(u << 1 | 1, l, r, d);
Pushup(u);
}
int Query(int u, int l, int r, int k)
{
if (Tree[u].l >= l && Tree[u].r <= r)
{
if (k == 1) return Tree[u].Sum;
else if (k == 2) return Tree[u].Max;
else return Tree[u].Min;
}
Pushdown(u);
long long mid = Tree[u].l + Tree[u].r >> 1, Result;
if (k == 1) Result = 0;
else if (k == 2) Result = -1e18;
else Result = 1e18;
if (mid >= l) Result = Query(u << 1, l, r, k);
if (mid < r)
{
if (k == 1) Result += Query(u << 1 | 1, l, r, k);
else if (k == 2) Result = max(Result, Query(u << 1 | 1, l, r, k));
else Result = min(Result, Query(u << 1 | 1, l, r, k));
}
return Result;
}
int Sum(int l, int r) { return Query(1, l, r, 1); }
int Max(int l, int r) { return Query(1, l, r, 2); }
int Min(int l, int r) { return Query(1, l, r, 3); }
}Tool;
signed main()
{
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin >> N >> M;
Tool.Build(1, 1, N);
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i ++)
cin >> A[i], Tool.Modify(1, i, i, A[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= M; i ++)
cin >> B[i], B[i] ++;
for (int i = 1; i <= M; i ++)
{
int X = Tool.Sum(B[i], B[i]), Turn = X / N, Rest = X % N;
Tool.Modify(1, 1, N, Turn);
if (Rest && B[i] + Rest > N)
{
if (B[i] + 1 <= N) Tool.Modify(1, B[i] + 1, N, 1);
Tool.Modify(1, 1, Rest - N + B[i], 1);
}
else if (Rest) Tool.Modify(1, B[i] + 1, B[i] + Rest, 1);
Tool.Modify(1, B[i], B[i], -X);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i ++)
cout << Tool.Sum(i, i) << " ";
return 0;
}
F - S = 1
Problem Statement
You are given integers
X
X
X and
Y
Y
Y, which satisfy at least one of
X
≠
0
X \neq 0
X=0 and
Y
≠
0
Y \neq 0
Y=0.
Find a pair of integers
(
A
,
B
)
(A, B)
(A,B) that satisfies all of the following conditions. If no such pair exists, report so.
−
1
0
18
≤
A
,
B
≤
1
0
18
-10^{18} \leq A, B \leq 10^{18}
−1018≤A,B≤1018
The area of the triangle with vertices at points
(
0
,
0
)
,
(
X
,
Y
)
,
(
A
,
B
)
(0, 0), (X, Y), (A, B)
(0,0),(X,Y),(A,B) on the
x
y
xy
xy-plane is
1
1
1.
Constraints
−
1
0
17
≤
X
,
Y
≤
1
0
17
-10^{17} \leq X, Y \leq 10^{17}
−1017≤X,Y≤1017
(
X
,
Y
)
≠
(
0
,
0
)
(X, Y) \neq (0, 0)
(X,Y)=(0,0)
X
X
X and
Y
Y
Y are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
X X X Y Y Y
Output
If there is a pair of integers ( A , B ) (A, B) (A,B) that satisfies the conditions, print it in the following format:
A A A B B B
Otherwise, print -1.
Sample Input 1
3 5
Sample Output 1
1 1
The area of the triangle with vertices at points ( 0 , 0 ) , ( 3 , 5 ) , ( 1 , 1 ) (0, 0), (3, 5), (1, 1) (0,0),(3,5),(1,1) is 1 1 1. Thus, ( A , B ) = ( 1 , 1 ) (A, B) = (1, 1) (A,B)=(1,1) satisfies the conditions.
Sample Input 2
-2 0
Sample Output 2
0 1
Sample Input 3
8752654402832944 -6857065241301125
Sample Output 3
-1
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
int Exgcd(int a, int b, int &x, int &y)
{
if (!b)
{
x = 1, y = 0;
return a;
}
int d = Exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y -= a / b * x;
return d;
}
signed main()
{
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
int X, Y;
cin >> X >> Y;
if (((2 % __gcd(X, Y) + abs(__gcd(X, Y))) % __gcd(X, Y)) != 0)
cout << -1 << endl;
else
{
int A, B;
int d = Exgcd(Y, X, A, B);
cout << A * (2 / abs(d)) << " " << (-B) * (2 / abs(d)) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
G - Leaf Color
G题还没研究,等后面研究下。
视频题解
Atcoder Beginner Contest 340(A ~ F)
最后祝大家早日