netty 解决粘包和拆包问题
- TCP 粘包/拆包的基础知识
- 粘包和拆包的问题说明
- TCP粘包/拆包 原因
- 粘包和拆包的解决策略
- tcp 粘包/拆包 的问题案例
- 大致流程如图:
- 代码展示(jdk1.7)
- TimeServer 服务端启动类
- TimeServerHandler 服务端业务处理类
- TimeClient 客户端启动类
- TimeClientHandler 客户端业务逻辑类
- 启动服务端和客户端后的效果展示
- 服务端 打印显示
- 客户端打印显示
- 结果简单分析
- 使用Netty 解决问题
- 代码展示(jdk1.7)
- TimeServer
- TimeServerHandler
- TimeClient
- TimeClientHandler
- 效果展示
- 服务端效果打印
- 客户端效果打印
- LineBasedFrameDecoder 和StringDecoder/StringEncoder 原理分析
- LineBasedFrameDecoder
- StringDecoder/StringEncoder
- 踩坑记录
TCP 粘包/拆包的基础知识
TCP 是个流协议,意思是没有界限的一串数据。TCP 底层并不了解上层业务数据的具体含义,它会根据TCP缓冲区的实际情况进行包的划分。所以在业务上认为,一个完整的包可能会被TCP 拆分成多个包进行发送,也有可能把多个小的包封装成一个大的数据包发送,这就是所谓的TCP 粘包/拆包问题。
粘包和拆包的问题说明

假设客户端分别发送了两个独立的数据包 Data1 和 Data2 给服务端,由于服务端一次读取到的字节数是不确定的,故可能存在一下5种情况
(1)服务端分两次读取到了两个独立的数据包,分别是Data1 和Data2,没有粘包和拆包
(2)服务端一次接收到两个数据包,Data1 和 Data2 粘合在一起,即 TCP 粘包
(3)服务端分两次读取到了两个数据包,第一次读取到了完整的Data1 包和 Data2 包的部分内容,第二次读取到了Data2包的剩余内容, 即 TCP 拆包
(4)服务端分两次读取到了两个数据包,第一次读取到了Data1 包的部分内容Data_1,第二次读取到了Data1包的剩余内容Data1_2和Data2的全部内容,和第三种情况类似。
(5)如果此时服务端TCP接收滑窗非常小,而数据包Data1和Data2比较大,很有可能发生第五种可能,即服务端分多次才能将Data1和Data2包接收完全,期间发生多次拆包。
TCP粘包/拆包 原因
问题产生的原因有三个
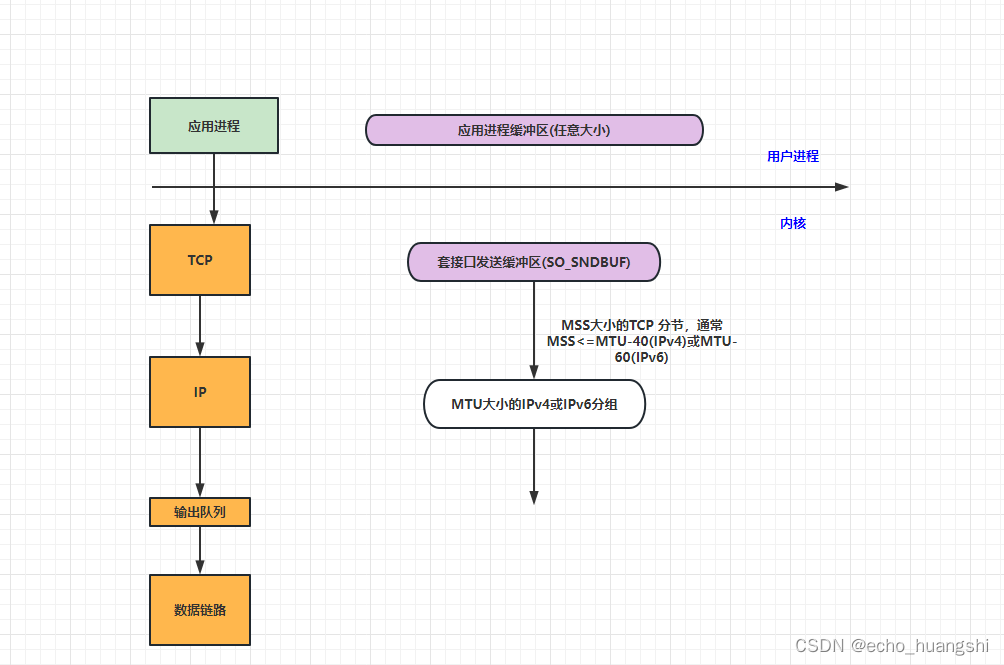
(1) 应用程序 write 写入的字节大小 大于 套接口发送缓冲区大小
(2)进行 MSS 大小的TCP分段
(3)以太网帧的playload 大于MTU 进行了IP分片
粘包和拆包的解决策略
由于底层的TCP 无法理解上层 业务数据,所以在底层是无法保证数据包不被拆分和重组的,这个问题只能通过上层的应用协议栈设计来解决,业界的主流协议的解决方案:
(1)消息定长,例如每个报文的大小固定长度200字节,如果不够,空位补空格
(2)在包尾增加回车换行符进行分割,例如FTP协议
(3)将消息分为消息头和消息体,消息头中包含表示消息总长度的字段,通常设计思路为消息头的第一个字段使用 int32 来表示消息的总长度。
tcp 粘包/拆包 的问题案例
下面我们模拟下 粘包和拆包的现象。
大致流程如图:
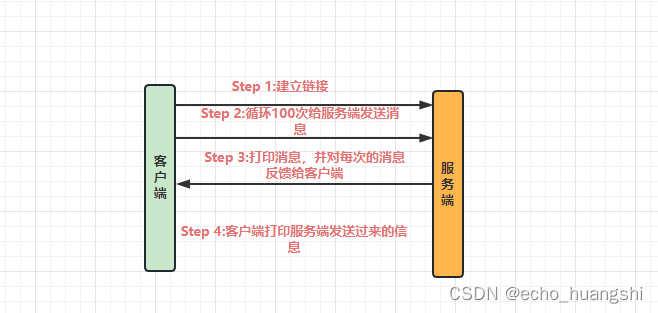
注意这里客户端给服务端发送了100次消息。正常 服务端 那边能收到100次正常的消息。并且客户端那边也能收到服务端发过来的100次正确的消息。 重点在于100次正确的消息。
代码展示(jdk1.7)
TimeServer 服务端启动类
public class TimeServer {
public void bind(int port){
//配置服务端的NIO线程组
// 开启两个线程组,一个用于服务端接受客户端的连接
// 一个用于进行 SocketChannel的网络读写
EventLoopGroup bossGroup=new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup=new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap=new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
//NIOServerSocketChannel 对应于 JDK NIO库中的ServerSocketChannel类
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
//设置TCP参数,将它的backlog 设置为1024
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,1024)
//添加服务端初始化类(即绑定I/O 事件的处理类ChildChannelHandler,类似于Reactor
// 模式中的 handler类)
.childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler());
//绑定端口,调用sync 等待绑定操作完成。完成之后Netty 会返回一个ChannelFuture,
//功能类似于JDK 的java.util.concurrent.Future
ChannelFuture future=bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
System.out.println("netty server is start up");
//等待服务端监听端口关闭后才 退出main 函数
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//优雅退出,释放线程池资源
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
/**
* 初始化类
*/
private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>{
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
//添加自定义的业务类
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new TimeServerHandler());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TimeServer().bind(8088);
}
TimeServerHandler 服务端业务处理类
public class TimeServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
//统计次数
private int counter;
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext context, Object msg) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
//由于没有进行编码解码,此时收到的信息为ByteBuf,然后转换为String
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[byteBuf.readableBytes()];
byteBuf.readBytes(req);
String body = new String(req, "UTF-8");
//每次接受消息,统计次数
System.out.println("The time server receive order : " + body+"; the counter is "+ ++counter);
//如果请求消息 是 QUERY TIME ORDER。则返回当前时间给客户端
String currentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(body) ? new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()).toString() : "Bad Order";
currentTime=currentTime+System.getProperty("line.separator");
//将返回信息转换为ByteBuf 然后再发送给客户端
ByteBuf resp = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(currentTime.getBytes());
context.writeAndFlush(resp);
}
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext context){
context.flush();
}
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext context,Throwable cause){
context.close();
}
TimeClient 客户端启动类
public class TimeClient {
public void connect(int port, String host) {
//配置客户端NIO线程组
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
//创建客户端辅助启动类
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
//采用内部类方式 将 ChannelHandler 添加到 ChannelPipeline中
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new TimeClientHandler());
}
});
//发起异步连接操作
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync();
System.out.println("client is connected ,,,");
//等待客户端链路关闭然后 main 函数才退出
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//优雅退出,释放NIO线程组
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 8088;
new TimeClient().connect(port, "127.0.0.1");
}
}
TimeClientHandler 客户端业务逻辑类
public class TimeClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private int counter;
byte[]req;
public TimeClientHandler(){
req=("QUERY TIME ORDER"+System.getProperty("line.separator")).getBytes();
}
/**
* 连接建立时触发
* @param context
*/
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext context){
ByteBuf message=null;
//循环100次,将 QUERY TIME ORDER 这个字符串发送给 服务端
//首先要将字符串转换为ByteBuf才行
for (int i=0;i<100;i++){
System.out.println("6666");
message=Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
message.writeBytes(req);
context.writeAndFlush(message);
}
}
/**
* 读取信息
* @param context
* @param obj
* @throws UnsupportedEncodingException
*/
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext context,Object obj) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
//接受到的是ByteBuf,需要将其转为String
ByteBuf buf=(ByteBuf) obj;
byte[]req=new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
String body=new String(req,"UTF-8");
//打印次数
System.out.println("Now is : "+body+" ; the counter is "+ ++counter);
}
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext context,Throwable cause){
//释放资源
System.out.println("Unexpected exception from downstream : "+cause.getMessage());
context.close();
}
}
启动服务端和客户端后的效果展示
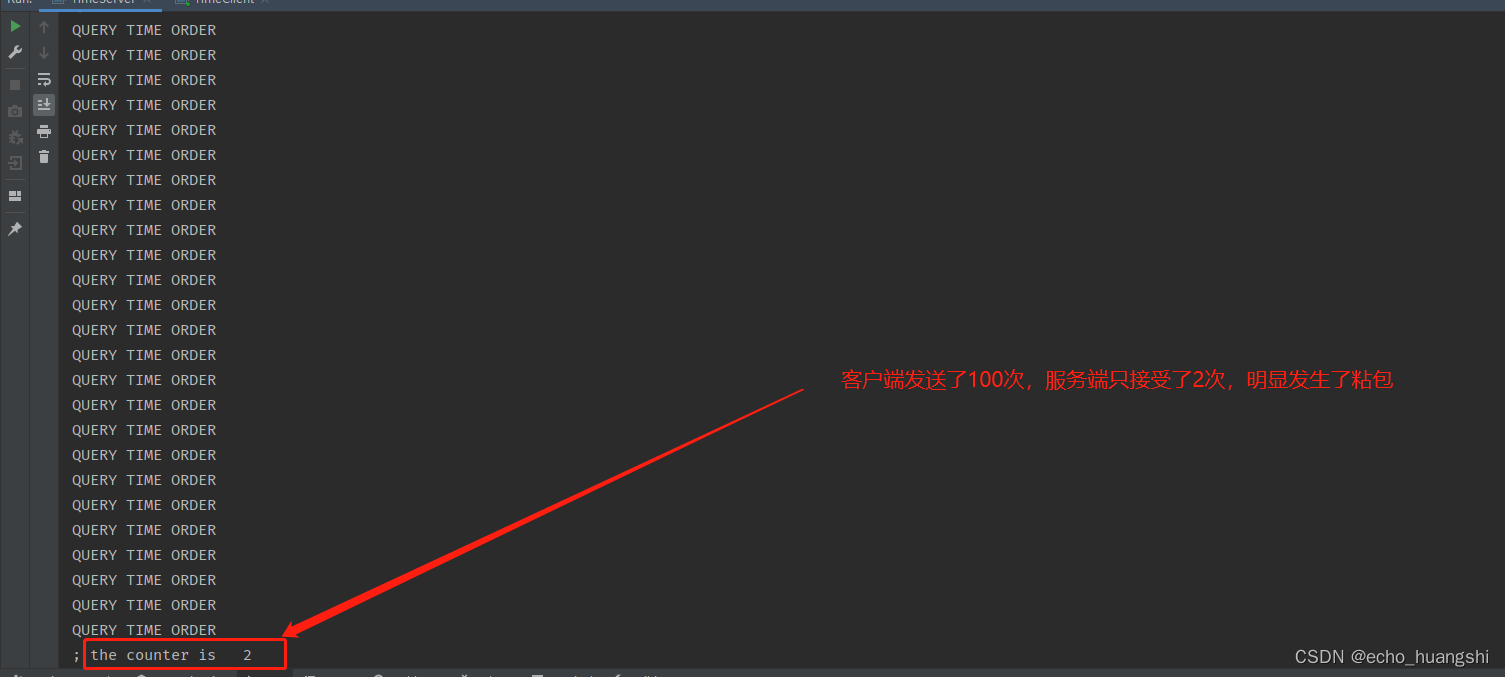
服务端 打印显示
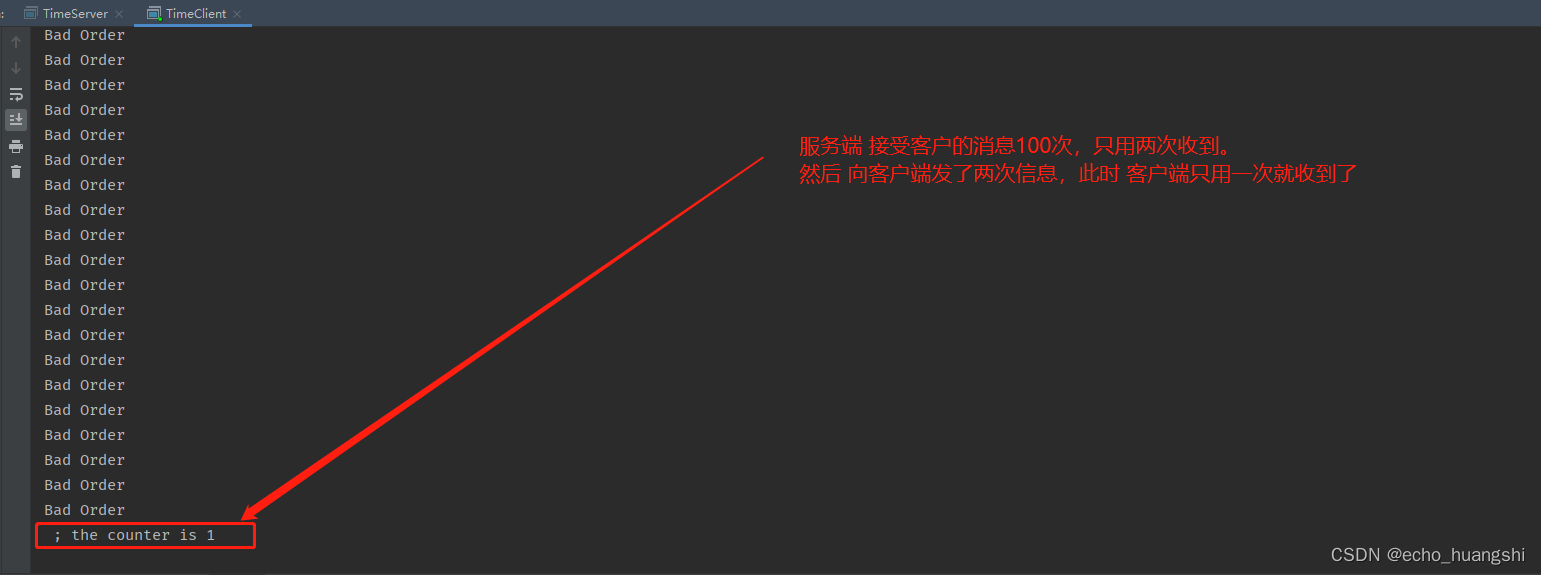
客户端打印显示
结果简单分析
虽然两边信息都发送了,但是 不是我们要的效果,我们要的效果是 客户端发送过来的 每次都是 QUERY TIME ORDER。 但是 服务端 接受到的 是两次 ,每次 平均 50 个 QUERY TIME ORDER
进行拼接得到的字符串。显示对于业务逻辑是 bad order。
使用Netty 解决问题
主要是添加了解码器和编码器。然后 写数据和读数据 不用再和 ByteBuf 进行打交道了。得到的已经是解码后 的String,很方便。
代码展示(jdk1.7)
TimeServer
public class TimeServer {
public void bind(int port){
EventLoopGroup bossGroup=new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup=new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap=new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,1024)
.childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler());
//绑定端口
ChannelFuture future=bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
System.out.println("netty server is start up");
//等待服务端监听端口关闭后才 退出main 函数
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//优雅退出,释放线程池资源
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>{
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
//增加解码器
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder(Charset.forName("GBK")));
//增加编码器
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder(Charset.forName("GBK")));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new TimeServerHandler());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TimeServer().bind(8080);
}
}
TimeServerHandler
public class TimeServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private int counter;
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext context, Object msg) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
//String body = (String)msg;
//此时得到的数据就已经是解码后的,直接用,不用像之前还需要 从 ByteBuf 成String
System.out.println("The time server receive order : " + msg + "; the counter is " + ++counter);
String currentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(msg.toString()) ?
new SimpleDateFormat("YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis())).toString() : "Bad Order";
currentTime = currentTime + System.getProperty("line.separator");
//ByteBuf resp = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(currentTime.getBytes());
//此时输出 也是直接输出String, 不用像之前还需要转成ByteBuf
context.writeAndFlush(currentTime);
}
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext context) {
context.flush();
}
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext context, Throwable cause) {
context.close();
}
TimeClient
public class TimeClient {
public void connect(int port, String host) {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.option(ChannelOption.AUTO_READ, true)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
//增加解码器
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder(Charset.forName("GBK")));
//增加编码器
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder(Charset.forName("GBK")));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new TimeClientHandler());
}
});
//发起异步连接操作
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync();
System.out.println("client is connected ,,,");
//等待客户端链路关闭然后 main 函数才退出
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//优雅退出,释放NIO线程组
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 8080;
new TimeClient().connect(port, "127.0.0.1");
}
TimeClientHandler
public class TimeClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private int counter;
byte[]req;
String tempReq;
public TimeClientHandler(){
tempReq="QUERY TIME ORDER"+System.getProperty("line.separator");
System.out.println(tempReq);
req=tempReq.getBytes();
}
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext context){
// ByteBuf message=null;
for (int i=0;i<100;i++){
/* System.out.println("i"+i);
message=Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
message.writeBytes(req);*/
//由于加了编码器和解码器,此时直接输出String 即可
context.writeAndFlush(tempReq);
}
}
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext context,Object obj) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
//String body=(String)obj;
//此时输出 也是直接输出String, 不用像之前还需要转成ByteBuf
System.out.println("Now is : "+obj+" ; the counter is "+ ++counter);
}
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext context,Throwable cause){
//释放资源
System.out.println("Unexpected exception from downstream : "+cause.getMessage());
context.close();
}
}
效果展示
服务端效果打印

客户端效果打印

LineBasedFrameDecoder 和StringDecoder/StringEncoder 原理分析
LineBasedFrameDecoder
LineBasedFrameDecoder 的工作原理是它依次遍历 ByteBuf中可读字节,判断看是否有 “\n” 或者
“\r\n”,如果有,就以此位置为结束位置,从可读索引到结束位置区间的字节就组成了一行。它是以换行符为结束标志的解码器,支持携带结束符或者不携带结束符两种解码方式,同时支持配置单行的最大长度。如果连续读取到最大长度后仍然没有发现换行符,就会抛出异常,同时忽略掉之前读到的异常码流。
StringDecoder/StringEncoder
将接受到的对象转换为字符串,然后继续调用后面的handler。
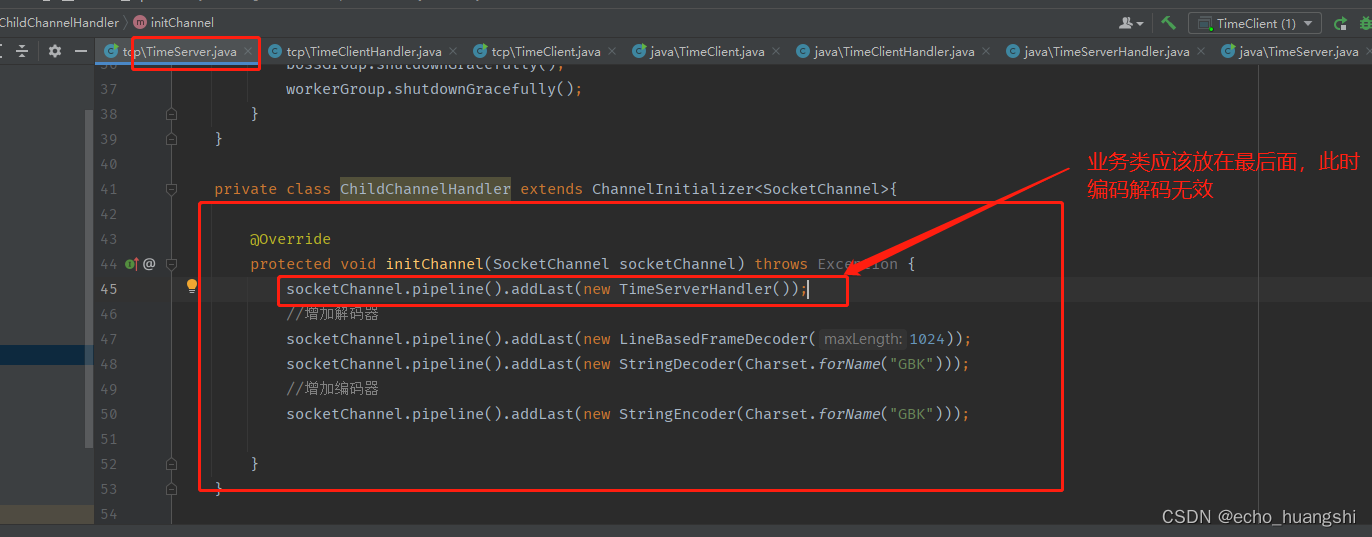
踩坑记录
第一次写没有采用编码的粘包问题的时候 是正常的。但是加了 编码解码器后,没有信息输出了。当时以为是哪里写错了,反复排查,发现是 解码器和编码器 写到了 handler 后面了。导致解码编码没有生效。
如图所示,如果大家还遇到了其他的问题,欢迎讨论。