由于Chrono的官方教程在一些细节方面解释的并不清楚,自己做了一些尝试,做学习总结。
0、Vehicle的driver
driver在上一篇总结中有过介绍,【Chrono Engine学习总结】4-vehicle-4.1-vehicle的基本概念,这里进一步介绍。
对于一个具体的driver系统,控制的状态量即:油门、刹车、转向。这里重点介绍轨迹跟踪用到的driver:ChPathFollowerDriver
driver本质上就是驾驶这个车的东西,本文中的驾驶员、控制器等都可以是指这个driver。当然控制器严格来讲应该是controller。个人认为,上层一些的东西,就叫这个driver,包括转向、速度等多方面的handle,而具体到某个变量例如速度,就叫做controller。
1、闭环驾驶控制器 ChClosedLoopDriver
https://api.projectchrono.org/classchrono_1_1vehicle_1_1_ch_closed_loop_driver.html
顾名思义,这是“闭环”驾驶系统,因此肯定包括控制环节。具体的,一个ChClosedLoopDriver包括:转向控制器ChSteeringController和速度控制器ChSpeedController。
在初始化一个ChClosedLoopDriver时,会自动生成上述两个控制器。
速度控制器ChSpeedController
https://api.projectchrono.org/classchrono_1_1vehicle_1_1_ch_speed_controller.html
速度控制器包括:通过代码设定恒定速度、或通过JSON文件读取速度配置,设置PID参数等。
速度控制器只有一个,即不管是采用何种driver,都是同一个速度控制器。而下面的转向控制器稍微会复杂一些。
转向控制器ChSteeringController
https://api.projectchrono.org/classchrono_1_1vehicle_1_1_ch_steering_controller.html
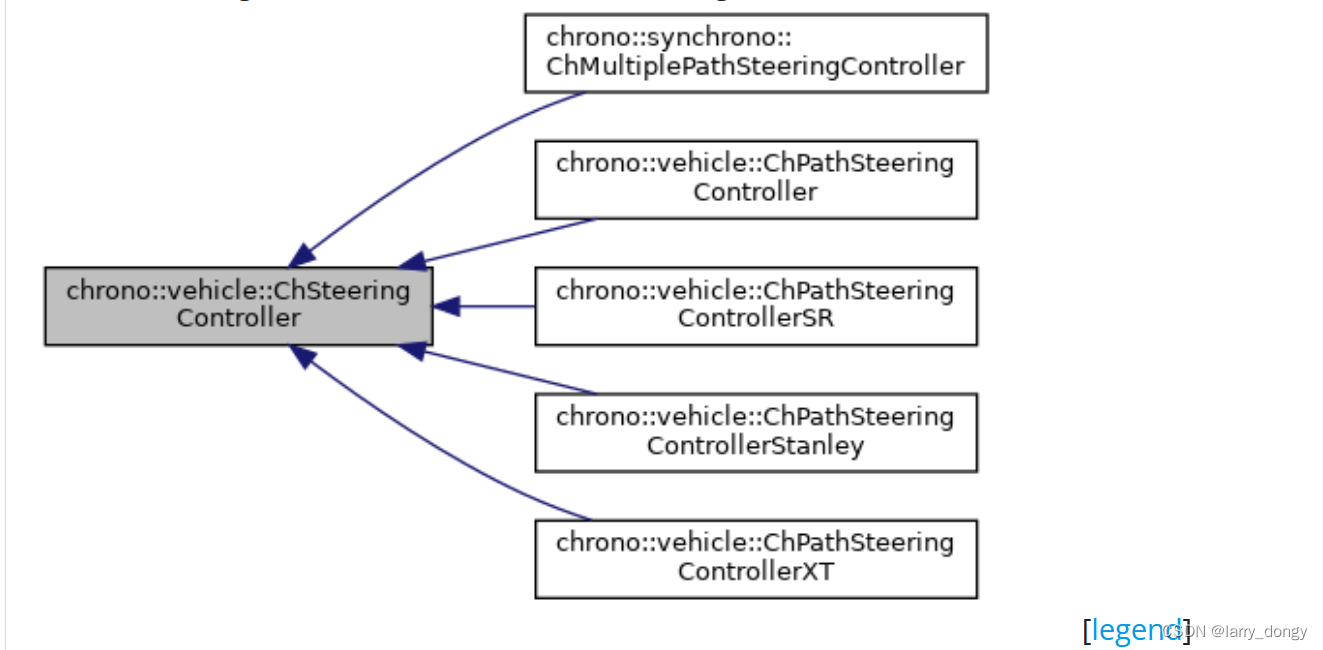 转向控制器是一个基类,不同路径跟踪driver会有不同的转向控制器,例如接下来要重点介绍的
转向控制器是一个基类,不同路径跟踪driver会有不同的转向控制器,例如接下来要重点介绍的ChPathFollowerDriver采用的是ChPathSteeringController控制器。
对于转向控制器,理论上也存在PID参数等,但在这个ChSteeringController基类中没有实现,而是在后面继承的类中进行的实现。
有一个新概念,叫“哨兵点”,和“目标点”:
- Sentinel(哨兵): 通常用来监视或标记某个特定区域、路径或条件的存在。在仿真或游戏环境中,一个哨兵点可能用来指示玩家或系统需要特别注意的地方,或者作为触发某些事件的标记。
- 通过
SetLookAheadDistance函数,给出在仿真时“哨兵点”的位置,即我关注车辆前方多远的具体,在这个点范围内的变化对仿真产生影响。这个距离是以底盘为坐标系的,车辆“前方”。 - Target(目标): 通常指一个要达到或影响的点。在仿真中,这可能是需要导航到的位置,或者是需要与之交互的对象。
进一步解释:在仿真时,vehicle的真实位置,是target真正要到的位置,而为了仿真系统高效的运行,设置一个“安全距离/提前注意”的位置,作为哨兵点,在哨兵点外的轨迹暂时不考虑。类似于碰撞检测,在短时间内不会发生碰撞时,避免复杂的碰撞条件计算。
Specify the look-ahead distance. This defines the location of the “sentinel” point (in front of the vehicle, at the given distance from the chassis reference frame).
2、轨迹跟踪控制器 ChPathFollowerDriver
https://api.projectchrono.org/classchrono_1_1vehicle_1_1_ch_path_follower_driver.html
这个控制器包括:速度控制器ChSpeedController和轨迹转向控制器ChPathSteeringController。
正如1.1 所说,速度控制器都是一样的,这里重点介绍轨迹转向控制器。
ChPathSteeringController
https://api.projectchrono.org/classchrono_1_1vehicle_1_1_ch_path_steering_controller.html
这个控制器继承了基类ChSteeringController,包括上面所说的所有功能。除此之外,包括:
- 设置PID参数
void SetGains (double Kp, double Ki, double Kd) - 计算目标点位置:由于需要跟踪轨迹,因此哨兵点给的位置不一定落在目标轨迹上,因此需要通过计算出真正需要抵达的目标点。这个目标点就通过
CalcTargetLocation函数计算哨兵点对应轨迹上的最近点是哪个,用于具体的控制。
轨迹跟踪控制器部分的关键代码如下:
// 控制器创建与设置
ChPathFollowerDriver driver(hmmwv.GetVehicle(), path, "my_path", 5.0); // 目标速度是5.0m/s,轨迹是path
driver.SetColor(ChColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.8f));
driver.GetSteeringController().SetLookAheadDistance(5); // 设置转向控制器的哨兵点距离
driver.GetSteeringController().SetGains(0.8, 0, 0); // 设置转向控制器的PID参数,这里P=0.8
driver.GetSpeedController().SetGains(0.4, 0, 0); // 设置速度控制器的PID
driver.Initialize();
// 循环仿真部分。只需要进行子系统的时间同步,然后动力学仿真一步即可。
driver.Synchronize(time);
driver.Advance(step_size);
到这里已经介绍了,轨迹跟踪的控制器是如何工作的。但还没有介绍上面跟踪的轨迹是怎么来。接下来进行介绍。
3、轨迹
轨迹本质上是一个贝塞尔曲线BezierCurve,即:ChBezierCurve。
https://api.projectchrono.org/classchrono_1_1_ch_bezier_curve.html
通过:
auto path = ChBezierCurve::read(vehicle::GetDataFile(path_file), closed_loop);
从文件读取一个轨迹,closed_loop表示,这个轨迹是否是一个闭环,即首尾相连?
3.1 轨迹文件
轨迹文件内包含的就是节点,第一行有两个数字,N和数字3或9,表示共有N个节点点,3或9表示两种不同的节点类型。从第二行开始,就是每个节点的具体坐标。例如,下图是一个200x200米的正方形环形的轨迹。贝塞尔曲线采用3次插值。

上面的是3列,即需要经过这写节点。如果是9列,则分别是:节点、进入控制点、离开控制点。更多关于样条曲线的内容参考之前我在知乎整理的一篇文章:【学习总结】连续时间SLAM(二)——B样条曲线
3.2 轨迹读取与传递给控制器
// 读取轨迹文件
auto path = ChBezierCurve::read(vehicle::GetDataFile(path_file), closed_loop);
// 将轨迹给轨迹跟踪控制器
ChPathFollowerDriver driver(hmmwv.GetVehicle(), path, "my_path", target_speed);
// ...
// 在仿真循环中
DriverInputs driver_inputs = driver.GetInputs(); // 获取沿轨迹运行时的控制量
hmmwv.Synchronize(time, driver_inputs, terrain); // 将控制量同步给悍马车系统
hmmwv.Advance(step_size); // 悍马车仿真一步。
4、完整代码
#include "chrono/utils/ChFilters.h"
#include "chrono_vehicle/ChVehicleModelData.h"
#include "chrono_vehicle/terrain/RigidTerrain.h"
#include "chrono_vehicle/driver/ChPathFollowerDriver.h"
#include "chrono_vehicle/utils/ChVehiclePath.h"
#include "chrono_vehicle/wheeled_vehicle/ChWheeledVehicleVisualSystemIrrlicht.h"
#include "chrono_models/vehicle/hmmwv/HMMWV.h"
#include "chrono_thirdparty/filesystem/path.h"
using namespace chrono;
using namespace chrono::geometry;
using namespace chrono::vehicle;
using namespace chrono::vehicle::hmmwv;
// 设定一些车辆参数
// Contact method type
ChContactMethod contact_method = ChContactMethod::SMC;
// Type of tire model (RIGID, FIALA, PAC89, PAC02, or TMEASY)
TireModelType tire_model = TireModelType::TMEASY;
// Type of engine model (SHAFTS, SIMPLE, SIMPLE_MAP)
EngineModelType engine_model = EngineModelType::SHAFTS;
// Type of transmission model (SHAFTS, SIMPLE_MAP)
TransmissionModelType transmission_model = TransmissionModelType::SHAFTS;
// Drive type (FWD, RWD, or AWD)
DrivelineTypeWV drive_type = DrivelineTypeWV::RWD;
// Steering type (PITMAN_ARM or PITMAN_ARM_SHAFTS)
// Note: Compliant steering requires higher PID gains.
SteeringTypeWV steering_type = SteeringTypeWV::PITMAN_ARM;
// Visualization type for vehicle parts (PRIMITIVES, MESH, or NONE)
VisualizationType chassis_vis_type = VisualizationType::PRIMITIVES;
VisualizationType suspension_vis_type = VisualizationType::PRIMITIVES;
VisualizationType steering_vis_type = VisualizationType::PRIMITIVES;
VisualizationType wheel_vis_type = VisualizationType::MESH;
VisualizationType tire_vis_type = VisualizationType::MESH;
// 车辆跟踪轨迹、速度的设定
// Input file names for the path-follower driver model
std::string path_file("paths/my_path.txt");
// Set to true for a closed-loop path and false for an open-loop
bool closed_loop = false;
// Desired vehicle speed (m/s)
double target_speed = 12;
// 地型设置
// Rigid terrain dimensions
double terrainHeight = 0;
double terrainLength = 300.0; // size in X direction
double terrainWidth = 300.0; // size in Y direction
// 可视化点,跟踪车辆底盘
// Point on chassis tracked by the chase camera
ChVector<> trackPoint(0.0, 0.0, 1.75);
// Simulation step size 仿真参数
double step_size = 2e-3;
double tire_step_size = 1e-3;
double t_end = 100;
// Render FPS
double fps = 60;
// =============================================================================
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
GetLog() << "Copyright (c) 2017 projectchrono.org\nChrono version: " << CHRONO_VERSION << "\n\n";
chrono::SetChronoDataPath("E:/codeGit/chrono/chrono/build/data/"); // change the default data loading path.
chrono::vehicle::SetDataPath("E:/codeGit/chrono/chrono/build/data/vehicle/"); // change the vehicle data path
// ----------------------
// Create the Bezier path
// ----------------------
// From data file
auto path = ChBezierCurve::read(vehicle::GetDataFile(path_file), closed_loop);
// Bezier曲线文件:x行 y列,y=3/9. 3:节点坐标;9:节点,incoming控制点,outcoming控制点
// read是一个静态公有成员函数。即使没有创建类的对象,也可以调用这些函数。
// 计算初始车头朝向
auto point0 = path->getPoint(0);
auto point1 = path->getPoint(1);
ChVector<> initLoc = point0;
initLoc.z() = 0.5;
ChQuaternion<> initRot = Q_from_AngZ(std::atan2(point1.y() - point0.y(), point1.x() - point0.x()));
// ------------------------------
// Create the vehicle and terrain
// ------------------------------
// Create the HMMWV vehicle, set parameters, and initialize
HMMWV_Full hmmwv;
hmmwv.SetCollisionSystemType(ChCollisionSystem::Type::BULLET);
hmmwv.SetContactMethod(contact_method);
hmmwv.SetChassisFixed(false);
hmmwv.SetInitPosition(ChCoordsys<>(initLoc, initRot));
hmmwv.SetEngineType(engine_model);
hmmwv.SetTransmissionType(transmission_model);
hmmwv.SetDriveType(drive_type);
hmmwv.SetSteeringType(steering_type);
hmmwv.SetTireType(tire_model);
hmmwv.SetTireStepSize(tire_step_size);
hmmwv.Initialize();
hmmwv.SetChassisVisualizationType(chassis_vis_type);
hmmwv.SetSuspensionVisualizationType(suspension_vis_type);
hmmwv.SetSteeringVisualizationType(steering_vis_type);
hmmwv.SetWheelVisualizationType(wheel_vis_type);
hmmwv.SetTireVisualizationType(tire_vis_type);
// 创建地形。
// Create the terrain
RigidTerrain terrain(hmmwv.GetSystem());
ChContactMaterialData minfo;
minfo.mu = 0.8f;
minfo.cr = 0.01f;
minfo.Y = 2e7f;
auto patch_mat = minfo.CreateMaterial(contact_method);
auto patch = terrain.AddPatch(patch_mat, CSYSNORM, terrainLength, terrainWidth); // thinkness默认1.0
patch->SetColor(ChColor(1, 0.5, 0.5));
patch->SetTexture(vehicle::GetDataFile("terrain/textures/tile4.jpg"), 200, 200);
terrain.Initialize();
// ------------------------
// Create the driver system
// ------------------------
ChPathFollowerDriver driver(hmmwv.GetVehicle(), path, "my_path", target_speed); // ChDriver->ChClosedLoopDriver->ChPathFollowerDriver
driver.SetColor(ChColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.8f));
driver.GetSteeringController().SetLookAheadDistance(5);
driver.GetSteeringController().SetGains(0.8, 0, 0); // SetGains (double Kp, double Ki, double Kd)
driver.GetSpeedController().SetGains(0.4, 0, 0);
driver.Initialize();
// 创建车辆可视化内容
// ---------------------------------------
// Create the vehicle Irrlicht application
// ---------------------------------------
auto vis = chrono_types::make_shared<ChWheeledVehicleVisualSystemIrrlicht>();
vis->SetLogLevel(irr::ELL_NONE);
vis->AttachVehicle(&hmmwv.GetVehicle());
vis->SetWindowTitle("Steering PID Controller Demo");
vis->SetHUDLocation(500, 20); // HUD: 平视显示系统
vis->SetChaseCamera(trackPoint, 6.0, 0.5);
vis->Initialize();
vis->AddSkyBox();
vis->AddLogo();
vis->AddLight(ChVector<>(-150, -150, 200), 300, ChColor(0.7f, 0.7f, 0.7f));
vis->AddLight(ChVector<>(-150, +150, 200), 300, ChColor(0.7f, 0.7f, 0.7f));
vis->AddLight(ChVector<>(+150, -150, 200), 300, ChColor(0.7f, 0.7f, 0.7f));
vis->AddLight(ChVector<>(+150, +150, 200), 300, ChColor(0.7f, 0.7f, 0.7f));
// 可视化哨兵点和目标点
auto ballS = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeSphere>(0.1); // sentinel 哨兵
auto ballT = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeSphere>(0.1);
ballS->SetColor(ChColor(1, 0, 0));
ballT->SetColor(ChColor(0, 1, 0));
int iballS = vis->AddVisualModel(ballS, ChFrame<>());
int iballT = vis->AddVisualModel(ballT, ChFrame<>());
// 记录地盘和驾驶员位置的加速度参数?
// GC: gravity center,质心/底盘的加速度; driver:驾驶员位置的加速度
utils::ChRunningAverage fwd_acc_GC_filter(filter_window_size); // fwd: forward,
utils::ChRunningAverage lat_acc_GC_filter(filter_window_size); // lat: latitute
utils::ChRunningAverage fwd_acc_driver_filter(filter_window_size);
utils::ChRunningAverage lat_acc_driver_filter(filter_window_size);
// ---------------
// Simulation loop
// ---------------
// Driver location in vehicle local frame
ChVector<> driver_pos = hmmwv.GetChassis()->GetLocalDriverCoordsys().pos;
// Number of simulation steps between miscellaneous events
double render_step_size = 1 / fps;
int render_steps = (int)std::ceil(render_step_size / step_size);
// Initialize simulation frame counter and simulation time
int sim_frame = 0;
int render_frame = 0;
hmmwv.GetVehicle().EnableRealtime(true);
while (vis->Run()) {
// Extract system state
double time = hmmwv.GetSystem()->GetChTime();
ChVector<> acc_CG = hmmwv.GetVehicle().GetChassisBody()->GetPos_dtdt(); // 获取车体地盘质心的加速度
ChVector<> acc_driver = hmmwv.GetVehicle().GetPointAcceleration(driver_pos); // 获取驾驶员所在位置点的加速度
double fwd_acc_CG = fwd_acc_GC_filter.Add(acc_CG.x()); // 这是一步滤波,获取窗口范围内的平均加速度
double lat_acc_CG = lat_acc_GC_filter.Add(acc_CG.y());
double fwd_acc_driver = fwd_acc_driver_filter.Add(acc_driver.x());
double lat_acc_driver = lat_acc_driver_filter.Add(acc_driver.y());
// End simulation
if (time >= t_end)
vis->Quit();
// Driver inputs
DriverInputs driver_inputs = driver.GetInputs();
// Update sentinel and target location markers for the path-follower controller.
vis->UpdateVisualModel(iballS, ChFrame<>(driver.GetSteeringController().GetSentinelLocation()));
vis->UpdateVisualModel(iballT, ChFrame<>(driver.GetSteeringController().GetTargetLocation()));
vis->BeginScene();
vis->Render();
vis->EndScene();
// Update modules (process inputs from other modules)
driver.Synchronize(time);
terrain.Synchronize(time);
hmmwv.Synchronize(time, driver_inputs, terrain);
vis->Synchronize(time, driver_inputs);
// Advance simulation for one timestep for all modules
driver.Advance(step_size);
terrain.Advance(step_size);
hmmwv.Advance(step_size);
vis->Advance(step_size);
// Increment simulation frame number
sim_frame++;
}
return 0;
}
搞清楚之前的可视化、地型、vehicle后,这部分控制的内容好像并不复杂。





![[NSSCTF]-Web:[SWPUCTF 2021 新生赛]easyrce解析](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f60f09ccf9fa4e83a5cff43d0fb2aad5.png)